1형 당뇨병-2, Type 1 Diabetes mellitus-2
1형 당뇨병 환아의 전반적 건강관리 General health maintenance in type 1 diabetes
1. 1형 당뇨병 합병증을 예방한다.
-
1형 당뇨병을 오랫동안 앓을 때 여러 가지 합병증이 생길 수 있다.
- 급성 합병증,
- 만성 합병증이 생기지 않게 당뇨병을 최상으로 치료하는 것은 아주 중요하다.
- 저혈당증이 생기지 않게 치료하고,
- 고혈당증이 생기지 않게 예방하고,
- 탈수가 되지 않게 치료하고
- 당뇨병성 케톤 산혈증이 생기지 않게 예방하고 생기면 적절히 곧 치료한다.
- 심장 혈관 계통이나 신경계통이 손상되지 않게 예방한다.
- 특히 당뇨병성 심장병,
- 당뇨병성 신장병,
- 당뇨병성 눈병이 생기지 않게 예방해야 한다.
-
이런 급성 만성 합병증이 생기지 않게 예방하기 위해서는 가능한 혈당 농도와 HbA1c 농도를 정상 농도로 유지한다.
-
그렇게 할 수 없으면 그에 가깝게 유지하고, 규칙적으로 육체적 운동을 하고,
-
스트레스를 많이 받지 않게 스트레스 관리를 잘하고
-
균형 잡힌 음식물을 섭취한다.
-
고혈압이 생기지 않게 예방하고
-
이때 생긴 고혈압을 적절히 치료하고
-
담배를 피우지 말고
-
고 지질혈증이 생기지 않게 예방하는 것은 당뇨병을 치료할 때 더 특별히 관심을 가져야 한다.
-
다음에 구체적으로 더 알아보자.
2. 고혈압을 예방한다.
-
혈압을 규칙적으로 측정해 혈압이 정상적인지 비정상적으로 높은지 알아본다.
-
고혈압이 발생되지 않게 건강관리를 잘 한다.
-
1형 당뇨병으로 혈압이 정상 이상으로 높아지면 눈병, 심장병, 신장병 등 당뇨병성 합병증이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다.
-
그래서 고혈압으로 인한 합병증이 생기지 않게 특별히 예방해야 한다.
-
고혈압이 생기면 바로 적절히 치료하고 엑스트라 식염 섭취를 하지 않도록 조심한다.
3. 콜레스테롤, 트라이글리세라이드(TG), 좋은 콜레스테롤(HDL)과 나쁜 콜레스테롤(LD)에 관심을 갖는다.
-
당뇨병과 고혈압, 고 지질혈증으로 전신에 있는 크고 작은 혈관과 심장 혈관이 손상될 수 있다.
-
관상동맥 병과 심장마비가 생기게 하는 주요인 중 하나가 당뇨병이다.
-
균형 잡힌 음식물을 섭취하고 적절한 육체적 운동, 적절한 인슐린으로 당뇨병을 적절히 잘 치료하면 전신에 있는 혈관의 손상과 심장관상 동맥 손상이 생기지 않게 또는 덜 생기게 예방할 수 있다.
4. 흡연해서는 안 된다.
-
당뇨병이 있는 사람들이 흡연하면 혈관 손상과 심장 손상이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있고 다른 종류의 당뇨병성 합병증이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있고 더 심하게 생길 수 있다.
-
담배를 피었으면 금연하고 금연하기가 어려우면 의사의 도움을 받아 금연한다.
5. 눈 건강에 특히 유의해야 한다.
-
당뇨병이 오랫동안 지속되면 백내장이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있고
-
안저 망막혈관 손상이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다.
-
당뇨병은 성인 실명의 주원인이 된다.
-
이런 당뇨병성 눈 손상이 생기지 않게 예방하고,
-
생기면 조기에 적절히 치료한다.
-
그래서 안과에서 규칙적으로 눈 검진을 받아야 한다.
-
정상적으로 혈압을 재고 고혈압이 있으면 고혈압을 적절히 치료하고 혈당 농도를 정상치로 유지해서 눈 건강을 최상으로 유지한다.
-
눈에 어떤 이상이 생기면 의사의 검진을 곧 받아야 한다.
6. 신장 손상을 예방한다.
-
당뇨병으로 신장 내 작은 혈관이 손상될 수 있다.
-
당뇨병성 고혈압으로 신장의 혈관이 손상되기 쉽다.
-
성인 신장 부전증의 원인이 당뇨병으로 생길 수 있다.
-
신장에 어떤 이상이 생기나 매년 뇨단백, 크레아티닌(Creatinine), 혈중 요소질소(BUN) 등을 검사한다.
-
고혈당과 고혈압을 잘 치료해서 혈당과 혈압을 정상치로 유지하면 신장이 덜 손상 되거나 신장손상이 되는 시기를 지연시킬 수 있다.
7. 1형 당뇨병이나 다른 병을 앓을 때의 건강관리 룰
-
인슐린 주사치료를 임의대로 중지해서는 절대로 안 된다. 그러나 소변 당(요당) 검사나 혈당 검사 등의 결과에 따라 인슐린 주사 용량을 변경해서 치료할 필요가 생길 수 있다.
-
혈당 검사를 더 자주해야할 때도 있다.
-
소변 케톤 검사를 의사의 지시에 따라 한다.
-
건강에 어떤 이상이 있으면 체온을 잰다.
-
음료수를 충분히 섭취한다.
-
너무 아파서 먹지도 못하고 음료수를 마실 수 없고 기동할 수 없으면 응급으로 의사에게 연락해서 조언을 얻고 응급 치료를 받는다.
-
그렇지 않으면 병원 응급실로 직접 간다.
-
체온, 혈당치, 소변검사 결과를 의사에게 보고한다.
8. 1형 당뇨병 환아는 다음과 같이 발 건강관리를 특별히 잘 해야 한다.
1). “발 건강을 위해 해야 할 것“
-
발을 따뜻한 물과 순한 비누로 매일 씻는다. 그 후 물기를 잘 닦는다.
-
발에 절상, 찰과상, 물집, 티눈 등이 있는지 평소 잘 살펴본다.
-
특히 발가락 사이에 어떤 손상이 있는지 체크한다.
-
필요에 따라 의사의 발 진찰을 받는다.
-
발이 건성이면 순한 피부용 크림이나 로션을 발에 바른다.
-
그러나 발가락 사이나 찰과상이나 열상에는 바르지 않는다.
-
발에 잘 맞고 깨끗하고 바래지 않는 양말을 신고 튼튼한 신발을 신는다.
-
엘라스틱 밴드를 매지 않고 댓님도 매지 않는다.
-
발가락 맨 끝의 모양으로 발톱을 깎은 후 의사, 간호사 또는 족의에게 보여 올바르게 깎았는지 확인한다.
2). “발 건강을 위해 해서는 안 될 것“
-
발을 물속에 오랫동안 담그라고 의사가 지시하지 않는 한 발을 물에 오랫동안 담가서는 안 된다.
-
엡솜 염, 보릭 산, 옥도정기, 알코올, 과산화수소액 등 강한 화학 물질액이나 상품용 티눈 치료약액, 또는 티눈 플라스터 등을 의사의 지시 없이 사용해서는 안 된다.
-
의사의 처방 없이 약국 진열대에 있는 코티손 연고를 사용해서는 안 된다.
-
발 이외 신체 다른 부분에 바르는 코티손 연고를 발에 발라도 안 된다.
-
밖에서 맨발로 걸어서도 안 된다.
-
어느 종류든지 불편하고 잘 맞지 않는 신발은 신지 말고 새 신발을 신을 때에는 점진적으로 신는 시간을 증가시키다.
- 티눈, 바로 주위의 피부층을 파고 들어가는 발톱 병(지조내생), 다른 발 문제 등을 의사의 지시 없이 집에서 치료해서는 안 된다.출처 및 참조문헌,소아 1형 당뇨병 참조문헌과 웹사이트 참조.
- 그 외
1형 당뇨병과 인슐린 주사 치료 Type 1 diabetes and insulin treatment
-
2형 당뇨병은 경구용 당뇨병 치료약(경구용 혈당 강하제)으로 어느 정도 치료될 수 있지만 1 형 당뇨병은 경구용 혈당 강하제로 치료되지 않는다.
-
1형 당뇨병을 치료할 수 있는 경구용 당뇨병 치료약은 아직 개발되어 있지 않다.
-
경구용 인슐린도 아직 개발되지 않다.
-
인슐린 비강 분무제가 있으나 소아 당뇨병 치료에는 널리 사용치 않는다.
-
인슐린을 경구로 섭취하면 인슐린이 위 속에서 파괴되어 인슐린 치료 효과가 없어진다.
-
1형 당뇨병은 인슐린 정맥주사나 피하주사로 치료한다.
-
요즘은 인슐린을 기도 속으로 흡입해 당뇨병을 치료하기도 한다.
-
인슐린 펌프로 치료하기도 한다.
-
인슐린을 주사로 투여한 후 인슐린의 치료 효과가 나타나기 시작하는 때(몇 분 또는 몇 시간), 최고 치료 효과가 나타나는 때, 치료효력 지속시간 등에 따라 인슐린이 다음과 같이 크게 3가지 형으로 분류될 수 있다.
- 인슐린 치료효력이 속히 나타나지만 짧은 기간 동안 치료 효력이 지속되는 속성형 인슐린
- 인슐린의 치료효력이 속성형 인슐린의 치료효력보다 훨씬 더 늦게 나타나지만 인슐린 치료효력의 지속기간이 더 길은 장기형 인슐린
- 인슐린 치료효과가 속성형 인슐린의 치료효력보다 더 늦게 나타나고 장기형 인슐린의 치료효력보다 더 속히 나타나지만, 치료효력 지속시간이 속성형 인슐린과 장기형 인슐린의 중간 정도 나타나는 중간형 인슐린 형에 있다.
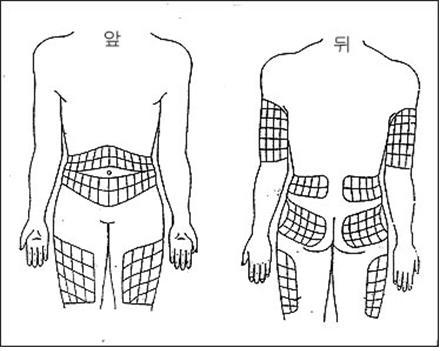
그림 1-57. ▦로 표시된 신체 부위에 인슐린주사를 놓을 수 있다. ▦로 표시된 부위에 있는 한 지점에 인슐린 주사를 준다. 그리고 그 부위에 있는 또 다른 지점으로 옮겨가면서 인슐린 주사를 준다. 그리고 또 다른 부위로 옮겨서 인슐린 주사를 준다. 인슐린 주사는 피하에 놓는다. 피부층 바로 아래에 지방층이 있다. 인슐린 주사를 놓을 때 주사바늘과 피부층 표면과의 각도는 약 80~90% 되게 한다. 야윈 사람은 피부층을 한 손으로 집고 그 지점 피부에 주사를 놓는다.Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. indianaspolis, Indiana와 소아가정간호백과
표 1-13. 과거에는 인슐린 약 효과가 나타나기 시작하는 시간에 따라 3가지 형의 인슐린으로 분류했었다.
| 인슐린 주사후 치료 효력이 나타나는 시간 | 속성형 인슐린 (Short Acting) |
중간형 인슐린 (Intermediate Acting) |
장기형 인슐린 (Long Acting) |
|||
| 레귤라 (Regular) |
세미렌테 (Semi- Lente) |
엔피에치 (NHP) |
렌테 (Lente) |
초 렌테 (Ultra- Lente) |
피제트아이 (PZI) |
|
| 인슐린 주사 후 치료효력이 나타나는 시간 | 30분 | 1~3시간 | 1~3시간 | 1~3시간 | 4~6시간 | 4~6시간 |
| 인슐린 주사 후 치료효력이 최대로 나타나는 시간 | 2~4시간 | 2~8시간 | 6~12시간 | 6~12시간 | – | 12~24시간 |
| 인슐린 주사 후 치료 효력이 지속되는 기간 | 5~7시간 | 12~16시간 | 12~16시간 | 12~16시간 | 24~28시간 | 36시간 이상 |
최근(2009년)에는 인슐린을
- 속성작용 인슐린(Rapid acting insulin),
- 단기작용 인슐린(Short acting insulin),
- 중등도 기간작용 인슐린(Intermediate acting insulin),
- 장기작용 인슐린(장시간형 인슐린/Long acting insulin),
- 혼합 인슐린(Premixed insulin)으로 표 1-14와 같이 분류한다.
| 인슐린의 형과 종류 | 인슐린치료 효력이 시작되는 시간 | 인슐린 치료 효력이 최고로 나타나는 시간 | 인슐린치료효력 지속시간 |
| 신속 작용 인슐린/ Rapid acting insulin) Lispro (Humalog), Aspart (NovoLog), Glulisine (Apidra) | 5~15분 | 30~90분 | 5시간 |
| 단기 작용 인슐린/ Short acting insulin) Regular U100, Regular U500(Concentrated), Buffered regular (Velosulin) | 30~60분 | 2~3시간 | 5~8시간 |
| 중간 기간 작용 인슐린/ Intermediate acting insulin) Isophane Insulin (NPH, Humulin, N/Novolin N) | 2~4시간 | 4~10시간 | 10~16시간 |
| 지속작용 인슐린/ Long acting insulin Glargine (Lantus) | 2~4시간 | 절정시간이 없음 | 20~24시간 |
| 지속작용 인슐린/ Long acting insulin) Detemir (Levemir) | 천천히 | 6~8시간 | 6~24시간 (용량에 따라 다름) |
| 혼합 인슐린(복합형 인슐린/혼합형 인슐린/Premixed insulin) | |||
| 70% NPH /30% Regular (Humulin 70/30) | 30~60분 | 이중 최고 약효 | 10~16시간 |
| 50% NPH /50% Regular (Humulin 50/50) | 30~60분 | 이중 최고 약효 | 10~16시간 |
| 75% NPL/25% lispro (Humalog Mix 75/25) | 5~15분 | 이중 최고 약효 | 10~16시간 |
| 70% NPA/30% aspart (NovoLog Mix 70/30) | 5~15분 | 이중 최고 약효 | 10~16시간 |
출처 및 참조문헌
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman, p.399
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition, p.1038
-
Others
인슐린의 성분의 근원에 따라 인슐린을 다음과 같이 분류할 수 있다
-
인슐린은 사람 재조합 DNA(Recombinant DNA)기술로 만든 사람 재조합 DNA 인슐린,
-
돼지 췌장에서 만든 돼지 인슐린
-
소 췌장에서 만든 소 인슐린 등이 있고
-
돼지 인슐린과 소 인슐린을 혼합해서 만든 돼지 소 혼합형 인슐린 등이 있다.
-
그 외 20종 이상의 인슐린이 더 있다.
-
그 여러 종류의 인슐린 중 한 종류나 한 종류 이상의 인슐린을 의사의 처방에 따라 선택해 치료에 쓴다.
-
그러나 2006년부터 미국에서는 소 인슐린과 돼지 인슐린은 더 이상 제조되지 않는다.
-
소 인슐린이나 돼지 인슐린을 쓸 때 인슐린 알레르기가 생길 수 있지만 사람 재조합 DNA 인슐린은 인슐린 알레르기가 잘 생기지 않는다.
-
여러 종류의 인슐린들 중 어떤 종류의 인슐린을 선택해서 치료할 것인가는 1형 당뇨병 환아의 연령, 1형 당뇨병의 중증도, 치료효력 등에 따라 의사가 처방하는 것이 보통이다.
인슐린 치료 용량
-
인슐린 치료 용량은 환아의 나이, 체중, 혈당 농도에 따라 결정한다.
-
당뇨병성 산혈증, 케톤증이나 당뇨병성 혼수 등의 유무에 따라 인슐린 치료 용량이 다를 수 있다.
-
하루 24시간 동안 필요로 하는 인슐린 총량은 일반적으로 체중 매 kg당 0.5~1유니트(Units)정도이다.
-
그렇지만 앞서 설명한 대로 체중 혈당 농도 치에 기준을 두고 계산한 인슐린 치료 용량으로 당뇨병을 치료해서는 절대로 안 된다.
-
그날그날 육체적 활동량, 정신적 활동량, 또는 그날그날 섭취하는 음식물의 종류와 음식물의 양 등에 따라 인슐린 치료 용량이 다를 수 있기 때문이다.
-
예를 들면, 환아의 체중이 10kg이면 그 환아의 하루 인슐린 총량은 5~10유니트가 적절한 치료 용량이 될 수 있다. 그 5~10 유니트의 인슐린 치료 용량을 인슐린의 종류에 따라 한 번에 전부 주사로 주든지, 2 등분해서 그 1회분을 아침에 1회, 저녁에 1회, 1일 2회 주사로 주어 1형 당뇨병을 치료할 수 있다.
-
그러나 인슐린의 치료 용량은 반드시 의사의 처방에 따라 결정해야 한다.
-
인슐린을 비강 점막에 분무해서 치료하는 연구를 하고 있지만 아직 소아 1형 당료병 치료에 임상적으로 쓰이고 있는 단계에 도달하지 않았다.
-
인슐린 펌프치료는 요즘 선택적으로 널리 쓰고 있다.
인슐린 주사를 놓는 방법
-
학령기 아이나 사춘기 아이 중 당뇨병 환아 본인이 직접 인슐린 피하주사로 놓을 수 있으면 환아 본인이 자기의 당뇨병을 치료할 수 있다.
-
본인 자신이 주사를 놓아 치료할 수 없는 어린아이의 경우는 그의 부모가 인슐린 피하주사로 자녀의 당뇨병을 치료한다.
-
큰 혈관이 없고 지방 조직이 많은 상박부위, 복부부위, 허벅다리 부위에 인슐린을 피하주사로 놓는다.
-
관절이나 관절의 부근 부위, 배꼽이나 배꼽 주위에는 인슐린 피하주사를 놓지 않는다(그림 1-57 참조).
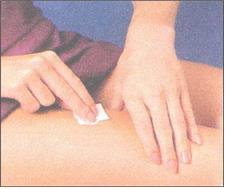
그림 1-58. 인슐린 피하주사를 놓기 바로 전 70% 소독용 알코올 스펀지로 주사 놓을 피부를 깨끗이 소독한다.
Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. indianaspolis, Indiana 및 소아가정간호백과
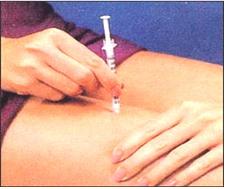
그림 1-59. 인슐린 피하주사를 놓을 피부를 한 손으로 살짝 잡아당기고 주사 바늘이 피부 표면에 80~90도로 피하 주사한다.
Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianapolis, Indiana 및 소아가정간호백과
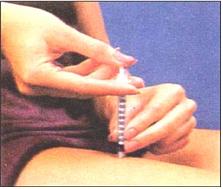
그림 1-60. 약 2~5초 내 피하주사기 내 인슐린을 피하 에 주입한다.
Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. indianaspolis, Indiana 및 소아가정간호백과
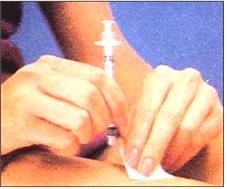
그림 1-61. 인슐린 피하주사를 놓은 후 주사바늘을 수직으로 뺀다. 주사를 놓은 피부에 70% 알코올 스펀지를 놓고 손가락으로 30초 동안 꼭 누른다.
Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. indianaspolis, Indiana 및 소아가정간호백과
인슐린을 피하에 주입할 때 다음과 같은 펌프, 제트, 펜, 주사기로 줄 수 있다.
-
인슐린 펌프용(Insulin Pumps),
-
인슐린 제트 인젝터(Jet Injectors),
-
인슐린 펜(Insulin Pens)과
-
인슐린 주사기(Insulin Syringes) 등이 있다.
소변 당(뇨 당/소변 포도당) 검사 Urine glucose test (Urine test for sugar)
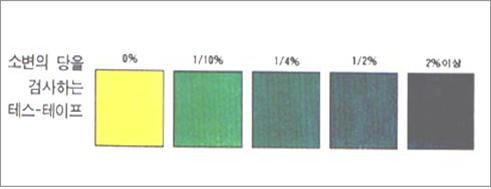
그림 1-68. 소변에 혈당이 나오면 테스–테이프 색이 초록색으로 변한다. Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianaspolis, Indiana

그림 1-69. a-소변 당, b-소변 케톤
소변에 당이 나와 있는지 케톤체가 나와 있는지 알기 위해 테스–테이프 등으로 검사한다.
Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianapolis, Indiana
1. 소변 당(뇨 당/소변 포도당) 검사 개요
-
대개의 경우, 혈당의 농도가 180mg/dl이거나 그 이상이면 핏속에 있는 혈당(글루코스/Glucose)이 신장 사구체를 통과해서 소변으로 분비될 수 있다.
-
소변 화학검사에서 소변에 당이 나오지 않으면 혈당의 농도가 180mg/dl 이든지, 혈당농도가 정상치이든지, 정상치 이하일 것이라고 추정할 수 있다.
-
혈당의 농도가 정상 이하일 때는 정상치 보다 어느 정도 더 낮은지 혈당 농도 검사를 하지 않고서 확실히 알 수 없다.
-
소변에 당이 섞여 나오면 혈당의 농도가 180mg/dl 정도이든지, 또는 180mg/dl 이상일 것이라고 추정할 수 있다.
-
그러나 정확한 혈당 농도 치는 혈당을 측정하지 않고서는 확실히 알 수 없다.
-
소변에 당과 케톤이 동시 나오면 혈당 농도가 정상 이상으로 높고 핏속에 케톤체가 있고 당뇨병이 잘 치료되지 않았거나 현재 당뇨병 합병증이 생겨있다는 것을 의미한다.
-
1형 당뇨병이 있는 환아의 소변에 당이 나오는지, 안 나오는지, 당만 나오는지, 당과 케톤이 동시 나오는지, 또 당이나 케톤이 소변에 얼마나 나오는지 등을 알아보는 것은 1형 당뇨병을 치료할 때 상당히 중요한 정보가 된다.
-
그러나 소변에 나온 당을 검사한 결과로 핏속 혈당 농도나 케톤 농도가 얼마나 높은지 정확히 알 수 없다.
-
소변 당 검사를 하기위해 받았던 소변에서 검출된 당은 언제 신장 사구체에서 걸러진 혈당인지 확실히 알 수 없다.
-
따라서 혈당의 농도를 검사해서 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 방법이 소변 당을 검사해서 소변에 있는 당의 양에 따라 당뇨병을 치료하는 방법보다 훨씬 더 효과적이다.
-
당뇨병이 있는 환아 자신이나 환아의 부모는 혈당 농도를 검사하는 방법과 소변화학검사로 소변 당을 검사해서 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 방법을 동시 배워야 한다.

그림 1-70. 소변이 테스–테이프에 충분히 묻도록 5mm 정도 테스–테이프를 소변 속에 넣었다가 바로 꺼낸다. 피검물 용기 속 소변에 이물질이 들어가지 않도록 주의한다.
Used with permission from EliLillyandCo. Indianaspolis, Indiana
2. 소변에서 당(글루코스/포도당)과 케톤을 검사하는 소변 화학검사 시약
-
클리니 테스트(Clini test),
-
테스 테이프(Tes tape),
-
클리니스틱스(Clinistix),
-
디아스틱스(Diastix),
-
케토 디아스틱스(Keto Diastix),
-
케토스틱스(Ketostix),
-
아세테스트(Acetest)
-
멀티스틱스(Multistix 10 SG) 등이 있다.
-
소변 화학검사 시약으로 소변 당 검사 하는 방법은 시약의 종류에 따라 조금씩 다르다.
-
시약으로 소변 당을 검사하기 전에 소변 화학 검사 시약 사용법을 잘 읽은 후 사용해야 한다.
-
1형 당뇨병을 치료할 때 소변 당이나 소변 케톤을 검사할 수 있다.
-
아침식사 30분전, 점심 저녁식사 30분 전과 밤에 잠자러 들어가기 바로 전에 한 번 검사한다.
-
1일 4회 소변 화학 검사 시약으로 다음과 같이 소변 당 검사를 할 수 있다.
① 소변 당과 케톤을 검사할 소변을 깨끗한 종이컵이나 플라스틱 컵에 받는다.
이 때 1회 소변 볼 때 소변을 다음과 같이 3개의 컵에 받는다.
- 첫 번째의 컵에 맨 처음 본 소변을 조금 받는다.
- 두 번째 컵에 그 다음 본 소변을 조금 받는다.
- 두 번째 컵에 소변을 받은 후 첫 번째 받은 소변은 버려도 된다.
② 그 다음 물 한 컵을 마신다.
③ 그 후 30분 정도 기다렸다가 세 번째 컵에 소변을 받는다.
④ 세 번째 컵에 받은 소변으로 소변 당과 소변 케톤을 검사한다.
- 소변 화학검사 시약으로 소변을 검사한 후 두 번째 받은 소변과 세 번째 받은 소변을 전부 버린다.
- 소변 화학 검사에 어떤 특이한 이상이 있으면 버리지 말고 의사에게 문의한 후 필요치 않다면 그 소변도 버린다.
⑤ 이렇게 복잡하게 소변을 받아서 소변 당을 검사할 시간이 없든지, 또는 여러 가지 이유로 위 ①~④에서 설명한 대로 세 컵에 소변을 따로따로 받아 소변 당 검사를 할 수 없는 때도 있다. 때로는 처음 본 소변으로 소변 당 검사를 해야 할 때도 많이 있다.
⑥ 소변 당 검사 결과에 따라 하루에 필요로 하는 총 칼로리 양, 인슐린 치료 용량, 그 날 육체적 활동량의 정도 등을 조절하여 1형 당뇨병을 치료할 수 있지만 혈당 농도를 검사해서 그 결과에 따라 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 것이 훨씬 더 효과적이다.
3. 소변 화학검사 테스–테이프로 소변 당을 검사하는 방법
-
소변에 당이나 케톤이 나와 있는지 검사할 수 있는 여러 종류의 소변 화학검사 시약이 있다. 그 중 테스–테이프 시약으로 소변에서 당을 검사하는 방법에 대해서 설명한다.
-
테스–테이프가 들어 있는 갑 뚜껑을 열고 테스–테이프를 1½인치(약 3cm) 정도 잡아당겨 뺀다.
-
테스–테이프 갑에서 일정량의 테스–테이프를 꺼내고 뚜껑을 꼭 닫는다.
-
그리고 팽팽하게 잡아당겨 1회 소변 당 검사용 피검물에 쓸 수 있는 테스–테이프 1회분을 떼 낸다.
-
테스–테이프에 소변이 충분히 묻도록 ¼인치(약 0.5cm) 정도를 소변 속에 넣었다가 바로 꺼낸다. 소변을 받은 용기에 이물질이 들어가지 않도록 주의한다.
-
테스–테이프를 소변 속에 넣었다가 꺼낸 후 1분 동안 들고 있다가 테스–테이프에 있는 색의 변화를 살핀다.
-
당이 없으면 노란색으로 변화된다.
-
소변에 당이 있으면 초록색으로 변한다.
-
그 초록색과 테스–테이프 갑에 있는 차트 색과 비교해서 0.5% 이상이면 1분 후 초록색을 다시 확인해 본다.
4. 테스 테이프 소변 화학검사 시약 등을 보관하는 방법
-
소변에 나와 있는 당을 검사할 수 있는 소변 화학검사 시약에는 여러 종류가 있고,
-
그 종류에 따라 소변의 당과 케톤을 검사하는 방법이 조금씩 다를 수 있다.
-
소변에 나온 당의 양을 +, ++, +++, ++++ 등으로 표시하기도하고,
-
또 0%, 1/10%, 1/4%, 1/2%, 2%와 그 이상으로 표시하기도 한다.
-
소변에 나온 당의 양을 플러스(+)로 표시할 때는 소변에 나온 당의 양이 정확히 얼마나 나오는지 확실히 알 수 없다.
-
테스–테이프로 검사해서 나온 소변의 당의 양을 0%, 1/10%, 1/4%, 1/2%, 2% 와 그 이상으로 표시한다.
-
소변의 당을 검사할 수 있는 테스–테이프 시약이나 다른 종류의 소변 화학검사 시약 속에는 소변 당의 양을 측정할 수 있는 극소량의 효소가 들어 있다.
-
이 시약의 효소의 효능을 잘 유지해야 소변 당 검사 결과가 잘 나올 수 있다.
-
테스–테이프 시약이 직사광선, 습기, 열 등에 노출되지 않도록 시약을 서늘하고 건조한 곳에 잘 보관해야 한다.
-
부엌이나 화장실, 또는 목욕실에 테스–테이프 시약을 보관해서는 안 된다.
1) 소변 당 검사 Urine test for urine
-
일반적으로 소변에 있는 당이나 케톤을 통상적으로 검사해 당뇨병을 치료하는 기준은 두지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
그러나 때로는 소변 당(포도당) 검사를 의사의 지시에 따라 할 수 있고 당뇨병을 치료할 때 많은 좋은 정보를 얻을 수 있다.
2) 소변 케톤 검사 Urine ketones test
-
적절하게 잘 치료되지 않은 당뇨병이 있을 때는 케톤체가 몸속에서 생성되고 케톤체가 소변으로 나온다.
-
당뇨병성 산혈증이 있을 때 혈중 케톤체가 소변으로 나올 수 있다.
-
특히 인플루엔자 등 전신 감염병을 잃든지 신체 어디가 아플 때는 소변 케톤을 검사해보는 것이 좋다.
-
구토를 하든지 구기가 있든지 혈당 농도가 250mg% 이상이면 소변 케톤체를 검사한다.
-
1형 당뇨병을 가진 환아가 필요할 때마다 스스로 검사할 수 있게 소변 케톤 검사 시약 테이프를 항시 보관했다가 필요할 때 마다 사용한다.
-
소아 1형 당뇨병 참조문헌과 웹사이트 참조.
혈당을 집에서 측정하는 방법 How to measure the blood glucose at home
-
말초 정맥혈이나 말초 동맥혈을 주사로 뽑거나 또는 란셋 등으로 피부층에서 피를 뽑아 혈당 농도를 검사하는 방법도 있고,
-
또 피를 뽑지 않고 혈당측정 기구를 피부에 대어 혈당 농도가 얼마인지를 알아내는 방법도 있다. 특히 USA Medical Supplies에서 피를 뽑지 않고 당뇨병 환자의 혈당치를 알아낼 수 있는 기구 등 당뇨병 치료와 진단에 필요한 의료기구 일체를 구입할 수 있다.
-
소변에 당이 비정상적으로 많이 나오면 혈당 농도가 정상 이상으로 높다고 볼 수 있다.
-
그렇지만 혈당 농도가 어느 정도 높은지 혈당 검사를 하지 않고서는 정확히 알 수 없다.
-
오래 전부터 소아 1형 당뇨병을 치료할 때 가정에서 써왔던 혈당 농도 검사 방법에 대해서 자세히 설명한다.
-
일반적으로 소변에 당이 나오지 않을 때는 혈당 농도가 적어도 180mg/dl 이하 일 가능성이 높다. 그렇지만 혈당 농도가 180mg/dl 보다 얼마나 더 낮은지 확실히 알 수 없다.
-
소변 당을 검사하기 바로 전 그 당시의 혈당 농도가 얼마나 낮은지 더 높은지 정확히 알 수 없다.
-
당뇨병이 있는 환아의 소변에 당이 조금도 안 나올 때는 혈당 농도가 생명을 위협할 수 있을 정도 아주 낮을 수 있다.
-
소변에 나온 당은 그 소변을 검사할 당시 신장의 사구체에서 걸러 나온 혈당이 있을 뿐만 아니라 그 검사용 소변을 받기 훨씬 이전 신장의 사구체에서 걸러져 나왔던 당도 포함되어 있다.
-
다시 설명하면, 검사할 당시 받은 소변에 있는 당은 검사용 소변을 받기 전 맨 마지막으로 사구체에서 분비된 소변과 바로 전번에 본 소변을 받을 당시부터 사구체에서 나온 소변이라고 할 수 있다.
-
금방 받은 검사용 소변으로 소변 화학검사를 하면 소변에 당이 나와 있다는 것을 알 수 있지만 신장의 사구체에서 언제쯤 걸러 나온 당인지 확실히 알 수 없다.
-
그러므로 당뇨병이 있는 아이의 소변을 검사해서 소변에 있는 당의 양에 기준을 두고 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 것보다 혈당 농도를 직접 검사해서 혈당치에 따라 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 것이 더 효과적 치료이다.
-
1형 당뇨병이 있는 환아의 소변을 검사해서 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 것보다 혈당 농도를 검사해서 혈당치에 따라 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 것이 더 효과적이다.
-
그래서 요즘 주로 혈당을 검사해서 1형 당뇨병을 치료한다.

그림 1-71. 혈당을 집에서 측정하는데 쓰는 혈당 측정기.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

그림 1-72. 혈당을 측정할 피를 뽑는데 쓰는 바늘.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

그림 1-73. 혈당을 측정하기 위해 손가락 끝 피부층을 바늘로 찌른다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.. FAAP

그림 1-74. 혈당을 측정하는데 쓰는 원터치 테스트 스트립.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
당뇨병 환아와 그 부모는 집에서 혈당을 검사하는 방법을 배워야 한다.
-
앞서 설명한 바와 같이 혈당의 농도를 측정해서 혈당치에 따라 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 것이 이상적이기 때문이다.
다음과 같은 경우, 혈당 농도를 측정하지 않고 소변 당을 검사해서 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는데 도움을 얻기도 한다.
-
사춘기 이전 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들 중 어떤 아이는 혈당 측정을 하기 위해 혈당 검사용 피를 채취하는 것을 아주 싫어해서 도저히 혈당을 측정 할 수 없다.
-
이 경우, 가끔 혈당을 검사하는 대신 소변 당을 검사해서 1형 당뇨병을 치료하는 데 도움을 얻을 수 있다.
-
다른 특별한 경우, 학교 또는 다른 특별한 장소에서 혈당을 검사하는 대신 소변 당을 검사할 수 있다.
-
혈당 농도가 비정상적으로 극히 높을 때, 감염병을 앓을 때, 또 그 밖에 다른 경우, 혈당을 측정하고 소변에서 당을 동시 검사해서 1형 당뇨병을 치료할 수 있다.
-
소변검사를 해서 소변에 당과 케톤이 나오는지 알아보고 핏속 혈당과 케톤을 검사하여 그 결과에 따라 1형 당뇨병을 치료할 때도 있다.
-
혈당의 농도가 정상 이하로 낮으면 저혈당이라 한다. 저혈당으로 생긴 증상을 저혈당증이라 한다. 혈당이 아주 낮아 심한 저혈당증이 생겼을 때 글루카곤 주사를 놓아 저혈당증을 치료할 수 있다. 당뇨병 있는 환아는 글루카곤 주사약을 저혈당증 응급치료용으로 쓸 수 있게 항상 가지고 다니든지 집이나 학교 등에 항상 보관했다가 필요할 때 써야 한다.
글루카곤 주사약 Glucagon
-
글루카곤은 췌장의 랑게르한스섬의 알파세포에서 분비되는 호르몬이다.
-
간에서 글리코겐을 글루코스(혈당)로 변화시키고 아민노산 등을 글루코스로 변화시키는 작용을 하는 호르몬이다.
-
당뇨병이 있는 환아들이나 성인들에게 저혈당이 생길 때 글루카곤 주사로 응급 치료하면 혈당이 높아질 수 있다.
-
그래서 저혈당을 치료할 때 쓸 수 있게 글루카곤을 비치해야 한다.

그림 1-75. 글루카곤 주사약.
1형 당뇨병이 있는 환아에게 저혈당증이 심하게 생길 때 혈당 농도를 응급으로 높이기 위해 쓸 수 있는 저혈당 응급치료용 약물이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
|
비강내 글루카곤 분말 주입으로 1형 당뇨병 소아청소년에게 생긴 저혈당을 치료할 수 있다. Intranasal glucagon reverses hypoglycemia in children and adolescents 1형 당뇨병이 있는 소아청소년 아이들의 저혈당증을 응급 치료를 할 때 근육용 글루카곤을 응급으로 근육주사를 주어 치료했다. 그러나 최근 미 예일 의과대학 연구팀에 의하면 1형 당뇨병 소아청소년 환자에게 생긴 저혈당증을 글루카곤 분말을 비강 내 주입해 치료한 결과 주입 후 20분내 혈당이 증가돼서 저혈당증이 치료됐다고 한다. 1형 당뇨병이 있는 성인에게 글루카곤 분말을 비강내 주입치료 한 결과 혈당이 증가되어 저혈당증이 치료됐다고 한다. 지금까지 근육주사 글루카곤 키트를 당뇨병 환자 자신이 지참하고 있다가 저혈당이 생기면 글루카곤을 본인이 근육주사로 맞아 저혈당증을 치료하던 것을 글루카곤 비강 분말을 비강내에 본인이 주입해 치료할 수 있는 의술이 생겼다. 소스: SARA FREEMAN, Pediatric News Digital Network September 16, 2015 부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다 www.koreapediatrics.com http://blog.naver.com/drsangwonlee http://doctorleeflowerphoto.com https://www.flickr.com/drleesangwon/
|
잘 치료되지 않은 1형 당뇨병과 고혈당증 Undercontrolled type 1 diabetes and higher blood glucose
-
적절한 인슐린 주사, 적절한 육체적 운동, 균형 잡힌 음식물 섭취, 육체적 안정, 정신적 안정 등으로 1형 당뇨병을 적절히 치료해도 혈당이 이상적으로 잘 조절되지 않는 때가 있다.
-
이런 당뇨병을 잘 치료되지 않은 1형 당뇨병(Undercontrolled type 1 diabetes mellitus)이라고 한다.
-
혈당 농도가 정상 이상으로 상당히 높으면 고혈당(과혈당)이라 하고 그때 생기는 증상은 고혈당증 또는 과(고)혈당증이라 한다.
-
고혈당의 정도에 따라 고혈당에 의해 여러 가지의 증상 징후가 생긴다.
-
1형 당뇨병이 있는 환아들의 부모들은 고혈당증의 원인, 고혈당증의 증상 징후와 그 예방과 치료에 대해 잘 알아야 한다.
-
1형 당뇨병이 있는 환아에게 고혈당증이 생기면
-
보통 때보다 소변을 더 자주 많이 보고,
-
갈증이 더 심해지고,
-
기운이 더 없고,
-
시력이 나빠지며,
-
소변에 당이 더 많이 나온다.
-
-
고혈당증이 있을 때는 적절한 음식물 섭취, 적절한 육체적 운동, 인슐린 치료 등으로 고혈당을 적절히 잘 조절해서 속히 치료해야 한다.
-
고혈당증을 빨리 적절히 치료하지 않고 오랫동안 방치하면 신경, 심장, 혈관, 신장 사구체, 시신경 등 신체의 각계통의 각종 기관과 조직이 계속 손상될 수 있다.
Type 1 Diabetes mellitus-2 1형 당뇨병-2,
General health maintenance in type 1 diabetes
1. Prevent complications of type 1 diabetes.
• A number of complications can arise when you have type 1 diabetes for a long time.
o acute complications,
o It is very important to treat diabetes in the best way so that chronic complications do not arise.
o Treating so that hypoglycemia does not occur,
o Prevent hyperglycemia from occurring,
o Treat to prevent dehydration
o Prevent the occurrence of diabetic ketoacidemia and, if it does, treat it as soon as possible.
o Prevent damage to the cardiovascular system or nervous system.
o especially diabetic heart disease,
o diabetic kidney disease,
o Diabetic eye disease should be prevented from occurring.
• To prevent such acute chronic complications from occurring, keep the blood glucose and HbA1c levels at normal levels as much as possible.
• If you can’t do that, stay close to it, do physical exercise regularly,
• Take good care of stress management so you don’t get a lot of stress
• Eat a balanced diet.
• Prevent high blood pressure from occurring
• Properly treat high blood pressure,
• do not smoke
• Preventing hyperlipidemia from developing should be of particular concern when treating diabetes.
• Let’s learn more about it next time.
2. Prevent high blood pressure.
• Measure your blood pressure regularly to see if your blood pressure is normal or abnormally high.
• Take good care of your health so that high blood pressure does not occur.
• If your blood pressure rises above normal with type 1 diabetes, diabetic complications, such as eye disease, heart disease, and kidney disease, are more likely to occur
• Therefore, special prevention is required to prevent complications from high blood pressure.
• If you develop high blood pressure, treat it appropriately and be careful not to consume extra salt.
3. I am interested in cholesterol, triglycerides (TG), good cholesterol (HDL) and bad cholesterol (LD).
• Diabetes, high blood pressure and hyperlipidemia can damage large and small blood vessels and cardiovascular vessels throughout the body.
• Diabetes is one of the main causes of coronary artery disease and heart attack. • Eating a well-balanced diet, adequate physical exercise, and adequate treatment of diabetes with adequate insulin can prevent or reduce damage to blood vessels throughout the body and coronary arteries.
4. Do not smoke.
• Smoking in people with diabetes may lead to blood vessel damage and heart damage more easily, and other types of diabetic complications more easily and more severely.
• If you have smoked, quit smoking. If it is difficult to quit, quit smoking with the help of a doctor.
5. Pay special attention to eye health.
• Long-lasting diabetes can make cataracts easier to develop
• Fundus retinal vessel damage may be more prone to occur. • Diabetes is a major cause of blindness in adults.
• Prevents diabetic eye damage from occurring,
• If it occurs, treat it early and appropriately.
• So, you should get regular eye exams at your ophthalmologist.
• Check your blood pressure normal and, if you have high blood pressure, treat it properly and keep your blood sugar level at a normal level to keep your eye health at its best.
• If you have any abnormalities in your eyes, you should see a doctor immediately.
6. Prevents kidney damage.
• Diabetes can damage small blood vessels in the kidneys.
• Diabetic hypertension is susceptible to damage to blood vessels in the kidneys.
• Diabetes may be the cause of kidney failure in adults. • Any abnormality in the kidneys, urine protein, creatinine (Creatinine), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), etc. are checked every year.
• Treating high blood sugar and high blood pressure well to keep blood sugar and blood pressure at normal levels can lead to less kidney damage or delay the period of kidney damage.
7. Health care rules when suffering from type 1 diabetes or other diseases
• Insulin injection therapy should never be stopped at will. However, depending on the results of a urine glucose (urinary glucose) test or blood glucose test, it may be necessary to change the insulin injection dose and treat it.
• Sometimes you need to test your blood sugar more often.
• Urine ketone testing as directed by your doctor.
• If you have any health problems, take your temperature.
• Drink plenty of water.
• If you are too sick to eat, drink, or maneuver, call your doctor in an emergency for advice and seek emergency treatment.
• Otherwise, go directly to the hospital emergency room.
• Report your body temperature, blood sugar level, and urine test results to your doctor.
8. Children with type 1 diabetes should take special care of their feet as follows. One).
- “What to do for foot health”
• Wash your feet daily with warm water and mild soap. After that, dry it well.
• Check your feet for cuts, abrasions, blisters, and corns.
• Check for any damage, especially between your toes.
• See a doctor’s foot as needed.
• If your feet are dry, apply a mild skin cream or lotion to your feet.
• However, do not apply between toes, abrasions or lacerations.
• Wear clean, fade-resistant socks that fit your feet and wear sturdy shoes.
• Don’t wear an elastic band and don’t wear it.
• After shaving the toenail in the shape of the tip of the toe, show it to a doctor, nurse, or family doctor to make sure it is cut correctly.
2). “What not to do for foot health”
• Do not immerse your feet in water for a long time unless your doctor tells you to immerse them in the water for a long time.
• Do not use strong chemical liquids such as Epsom salt, boric acid, jade tablets, alcohol, hydrogen peroxide liquid, commercial corn treatment liquid, or corn plaster without the instructions of a doctor.
• Do not use cortisone ointment from pharmacy shelves without a doctor’s prescription.
• Do not apply cortisone ointment applied to any part of the body other than the feet.
• Do not walk barefoot outside.
• Avoid wearing shoes of any type that are uncomfortable and do not fit well, and gradually increase the amount of time you wear when wearing new shoes.
• Corns, toenail disease that digs into the immediate skin layer (internal endogenous), and other foot problems should not be treated at home without a doctor’s instructions. Sources and references, see references and websites for pediatric type 1 diabetes.
• etc
Type 1 diabetes and insulin treatment
• Type 2 diabetes can be treated to some extent with oral diabetes medications (oral hypoglycemic drugs), but type 1 diabetes is not treated with oral hypoglycemic drugs.
• No oral diabetes medications have been developed to treat type 1 diabetes.
• Oral insulin is not yet developed. • Insulin nasal spray, but not widely used to treat childhood diabetes.
• Taking insulin orally destroys the insulin in the stomach, making the insulin treatment ineffective.
• Type 1 diabetes is treated with an intravenous or subcutaneous injection of insulin.
• These days, insulin is inhaled into the airways to treat diabetes.
• Sometimes treated with an insulin pump.
• After insulin is administered as an injection, insulin can be classified into three types as follows, depending on the time when the therapeutic effect of insulin begins to appear (a few minutes or hours), the time when the best treatment effect appears, and the duration of the treatment effect. I can.
1. Insulin treatment effect appears quickly, but the treatment effect lasts for a short period of time.
2. Long-term insulin whose therapeutic efficacy is much later than that of rapid insulin, but the duration of insulin therapeutic efficacy is longer.
3. Insulin treatment effect appears later than the therapeutic effect of fast-type insulin and appears more quickly than that of long-term insulin, but the duration of treatment is in the intermediate type of insulin, which is intermediate between fast-type insulin and long-term insulin.

Figure 1-57. Insulin injections can be placed on the body part marked ▦. Insulin injection is given at a point in the area marked ▦. Then, as you move to another point in the area, give an insulin injection. Then, move it to another site and give it an insulin injection. Insulin injections are placed subcutaneously. There is a layer of fat just below the skin layer. When administering insulin injection, the angle between the needle and the surface of the skin layer should be about 80 to 90%. A lean person picks up a layer of skin with one hand and injects an injection into the skin at that point. Indianapolis, Indiana and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia
표 1-13. 과거에는 인슐린 약 효과가 나타나기 시작하는 시간에 따라 3가지 형의 인슐린으로 분류했었다.
| Time when treatment effect appears after insulin injection | Short-Acting | Intermediate Acting | Long-Acting | |||
| Regular | Semi- Lente | NHP | Lente | Ultra- Lente | PZI | |
| The time when the treatment effect appears after insulin injection | 30 minutes | 1~3 hours | 1~3 hours | 1~3 hours | 4~6 hours | 4~6 hours |
| The time at which the treatment effect is maximized after insulin injection | 2~4 hours | 2~8 hours | 6~12 hours | 6~12 hours | – | 12~24 hours |
| How long treatment lasts after insulin injection | 5~7 hours | 12~16 hours | 12~16 hours | 12~16 hours | 24~28 hours | 36 hours and more 이상 |
2009 insulin
Rapid-acting insulin,
• Short-acting insulin,
• intermediate-acting insulin,
• long-acting insulin (Long acting insulin),
• It is classified as premixed insulin as shown in Table 1-14.
Type and type of insulin
| Type and type of insulin | The time when insulin treatment begins to take effect | The time at which insulin treatment is at its peak | Insulin treatment effect the duration |
| Rapid-acting insulin) Lispro (Humalog), Aspart (NovoLog), Glulisine (Apidra) | 5~15 minutes | 30~90 minutes | 5 hours |
| Short-acting insulin) Regular U100, Regular U500(Concentrated), Buffered regular (Velosulin) | 30~60 minutes | 2~3 hours | 5~8 hours |
| Intermediate-acting insulin) Isophane Insulin (NPH, Humulin, N/Novolin N) | 2~4 hours | 4~10 hours | 10~16 hours |
| Long-acting insulin Glargine (Lantus) | 2~4 hours | No peak time | 20~24 hours |
| Long acting insulin) Detemir (Levemir) | 천천히 | 6~8 hours | 6~24시간 (용량에 따라 다름) |
| Mixed insulin (complex insulin/mixed insulin /Premixed insulin) | |||
| 70% NPH /30% Regular (Humulin 70/30) | 30~60 minutes | The best medicinal effect of all | 10~16 hours |
| 50% NPH /50% Regular (Humulin 50/50) | 30~60 minutes | The best medicinal effect of all | 10~16 hours |
| 75% NPL/25% lispro (Humalog Mix 75/25) | 5~15 minutes | The best medicinal effect of all | 10~16 hours |
| 70% NPA/30% aspart (NovoLog Mix 70/30) | 5~15 minutes | The best medicinal effect of all | 10~16 hours |
Sources and references
• Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman, p.399
• The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition, p.1038
Others Insulin can be classified as follows depending on the source of the ingredients of insulin.
• Insulin is human recombinant DNA insulin made with human recombinant DNA (Recombinant DNA) technology,
• Porcine insulin made from porcine pancreas
• bovine insulin made from the bovine pancreas,
• There is a mixture of pig and cow insulin, which is made by mixing pig insulin and bovine insulin.
• There are more than 20 other types of insulin.
• Choose one or more than one type of insulin according to your doctor’s prescription and use it for treatment.
• However, since 2006, bovine insulin and porcine insulin are no longer manufactured in the United States.
• Insulin allergy can occur when using bovine or pig insulin, but human recombinant DNA insulin is less prone to insulin allergy.
• It is common for a doctor to prescribe which type of insulin to choose from among several types of insulin, depending on the age of the child with type 1 diabetes, the severity of type 1 diabetes, and the efficacy of the treatment.
Insulin therapeutic dose
• The insulin treatment dose is determined by the child’s age, weight, and blood sugar level.
• Depending on the presence or absence of diabetic acidemia, ketosis or diabetic coma, the insulin treatment dose may vary.
• The total amount of insulin required for 24 hours a day is generally 0.5 to 1 unit per kilogram of body weight.
• Nevertheless, diabetes should never be treated with an insulin therapeutic dose calculated based on body weight and blood sugar levels as previously described.
• This is because the dose of insulin treatment may vary depending on the amount of physical activity, mental activity, or the type of food and amount of food consumed that day.
• For example, if the patient’s weight is 10kg, the total amount of insulin per day for the patient is 5-10 units, which may be an appropriate therapeutic dose. Depending on the type of insulin, the 5 to 10 units of insulin treatment dose is given as an injection at a time, or divided into two, and the dose is given as an injection once in the morning, once in the evening, and twice a day.
Diabetes can be cured.
• However, the therapeutic dose of insulin must be determined according to the doctor’s prescription.
• Insulin is being sprayed onto the nasal mucosa to treat treatment, but it has not yet reached the stage of clinical use in the treatment of type 1 diabetes in children.
• Insulin pump therapy is widely used selectively these days.
How to give an insulin injection
• If you are a school-age or adolescent child with diabetes, you can directly administer insulin by subcutaneous injection, so that the child can treat his or her diabetes.
• In the case of a young child who cannot be treated by injecting himself or herself, his parents treat their child’s diabetes with an insulin subcutaneous injection.
• Insulin is injected by subcutaneous injection into the upper arm, abdomen, and thigh areas that do not have large blood vessels and have a lot of adipose tissue.
• Do not place an insulin subcutaneous injection in the joint or near the joint, or around the navel or navel (see Figure 1-57).

Figure 1-58. Immediately before administering the insulin subcutaneous injection, clean the skin to be injected with a 70% rubbing alcohol sponge. Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianapolis, Indiana and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia

Figure 1-59. Pull the skin to place the insulin subcutaneous injection with one hand, and inject the injection needle subcutaneously at 80 to 90 degrees on the skin surface. Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianapolis, Indiana and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia

Figure 1-60. Inject insulin in the hypodermic syringe subcutaneously within about 2 to 5 seconds. Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianapolis, Indiana and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia

Figure 1-61. After placing the insulin subcutaneous injection, pull the injection needle vertically. Place a 70% alcohol sponge on the injected skin and press firmly with your finger for 30 seconds. Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. indianaspolis, Indiana and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia When insulin is injected subcutaneously, it can be given with pumps, jets, pens, and syringes such as:
• Insulin Pumps,
• Insulin Jet Injectors,
• Insulin Pens and
• Insulin Syringes. Urine glucose test (Urine test for sugar)

Figure 1-68. When blood sugar is released in the urine, the color of the test-tape turns green. Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianaspolis, Indiana

Figure 1-69. a-urine sugar, b-urine ketone To see if there is sugar in the urine or a ketone body, it is tested with a test-tape or the like. Used with permission from Eli Lilly and Co. Indianapolis, Indiana
1.Urine glucose (urinary glucose/urine glucose) test overview
• In most cases, when the blood sugar level is 180 mg/dl or higher, blood sugar (glucose/Glucose) in the blood can pass through the renal glomerulus and be excreted into the urine.
• If the urine chemistry test shows no sugar in the urine, it can be estimated that the blood sugar level is 180mg/dl, the blood sugar level is normal, or below the normal level.
• When the blood sugar level is below normal, it is not clear to what extent it is lower than the normal level without performing a blood sugar level test.
• If the urine contains sugar, it can be estimated that the blood sugar level is around 180mg/dl, or more than 180mg/dl.
• However, the exact blood sugar level cannot be determined without measuring blood sugar.
• If sugar and ketones are present in the urine at the same time, it means that the blood sugar level is higher than normal, and there is a ketone body in the blood, and diabetes is not well treated or there is a diabetes complication.
• Whether or not a child with type 1 diabetes has sugar in the urine, whether it is sugar only, whether sugar and ketones are present at the same time, and how much sugar or ketones are in the urine is very important information when treating type 1 diabetes. Becomes.
• However, it is not possible to know exactly how high the blood sugar or ketone levels in the blood are from the results of testing the glucose in the urine.
• It is unclear when the glucose detected in the urine you were given for a urine glucose test was the blood sugar that was filtered out of the renal glomerulus.
• Therefore, testing your blood sugar level to treat type 1 diabetes is much more effective than testing your urine sugar and treating diabetes based on the amount of sugar in your urine.
• The child with diabetes, or the child’s parent, should learn how to test blood sugar levels and how to treat type 1 diabetes by testing urine sugar with a urine chemistry test.

Figure 1-70. Put the test tape in the urine about 5mm so that the urine is sufficiently adhered to the test tape and take it out immediately. Be careful not to let foreign substances enter the urine in the specimen container. Used with permission from EliLillyandCo. Indianaspolis, Indiana
2. A urine chemistry test reagent that tests for sugar (glucose/glucose) and ketones in the urine.
• Clini test,
• Tes tape,
• Clinistix,
• Diastix,
• Keto Diastix,
• Ketostics,
• Acetest
• Multistix 10 SG.
• The urine sugar test method with a urine chemistry test reagent differs slightly depending on the type of reagent.
• Before testing urine sugar with a reagent, read the Urine Chemistry Test Reagent Instructions carefully before using it.
• When treating type 1 diabetes, urine sugar or urine ketones may be tested. • Check once 30 minutes before breakfast, 30 minutes before lunch and dinner, and just before going to bed at night.
• As a urine chemistry test reagent 4 times a day, you can perform a urine sugar test as follows.
① Urine Receive urine to be tested for sugar and ketones in a clean paper cup or plastic cup. At this time, when you urinate once, you receive urine in 3 cups as follows.
• Get some of the first urine you see in the first cup.
• In the second cup, take a small amount of the urine you see next.
• After receiving the urine in the second cup, you may discard the first urine received.
② Then, drink a cup of water.
③ After that, wait for about 30 minutes and urinate in the third cup.
④ Test urine sugar and urine ketone with the urine received in the third cup.
• After testing your urine with a urine chemistry reagent, discard the second and third urine.
• If you have any unusual abnormalities in your urine chemistry test, do not throw it away. Ask your doctor and discard the urine if you don’t need it.
⑤ There are times when there is no time to test urine sugar after receiving such complicated urine, or for various reasons, urine sugar test cannot be performed by receiving urine separately in three cups as described in ①~④ above. Sometimes, you may need to do a urine sugar test with the first urine you see.
⑥ You can treat type 1 diabetes by adjusting the total amount of calories you need per day, the amount of insulin treatment, and the degree of physical activity that day, depending on the results of the urine sugar test. Treatment is much more effective.
3. Urine chemistry test How to test urine sugar with test-tape
• There are several types of urine chemistry reagents that can test your urine for sugar or ketones. Among them, a method of testing sugar in urine with a test-tape reagent will be described.
• Open the cap containing the test tape and pull out the test tape by 1½ inch (about 3cm).
• Take out a certain amount of test tape from the test tape box and close the lid tightly.
• Then, pull out the test tape, which can be used for the test object per urine, by pulling it tightly.
• Put ¼ inch (about 0.5 cm) in the urine to get enough urine on the test tape and take it out immediately. Be careful not to let foreign objects get into the container where you received your urine.
• Put the test tape in the urine, take it out, hold it for 1 minute, and watch the color change on the test tape.
• If there is no sugar, it turns yellow.
• If there is sugar in the urine, it turns green.
• If it is more than 0.5% compared to the green color and the color of the chart on the test-tape box, check the green color again after 1 minute.
4. How to store test tape urine chemistry test reagents,
etc.
• There are several types of urine chemistry reagents that can test for sugar in the urine,
• Depending on the type, the method of testing for sugar and ketones in urine may be slightly different.
• The amount of sugar in urine is expressed as +, ++, +++, ++++, etc.
• It can also be expressed as 0%, 1/10%, 1/4%, 1/2%, 2% and more.
• When you mark the amount of sugar in your urine as a plus (+), you are not sure exactly how much sugar is in your urine.
• Indicate the amount of sugar in urine produced by test-tape as 0%, 1/10%, 1/4%, 1/2%, 2% and more.
• Test-tape reagents, which can test urine sugar, or other types of urine chemistry reagents, contain trace amounts of enzymes that can measure the amount of sugar in the urine.
• Maintaining the efficacy of this reagent’s enzymes will lead to a good urine sugar test result.
• Reagents should be stored in a cool, dry place so that test-tape reagents are not exposed to direct sunlight, moisture, or heat.
• Do not store test-tape reagents in the kitchen, bathroom, or bathroom.
1) Urine test for urine
• In general, there is no standard for treating diabetes by routinely testing for sugars or ketones in the urine.
• Sometimes, however, a urine sugar (glucose) test can be done as directed by your doctor and a lot of good information can be obtained when treating diabetes.
2) Urine ketones test
• When diabetes is not properly treated well, ketone bodies are produced in the body and ketone bodies are released in the urine.
• When you have diabetic acidemia, ketone bodies in the blood can come out of the urine.
• It is a good idea to test for urine ketones, especially when you lose a systemic infectious disease such as influenza or when you are sick anywhere in your body.
• If your blood sugar level is 250mg% or higher, whether you are vomiting or having goji, test for a urine ketone body.
• Always keep a urine ketone test reagent tape so that children with type 1 diabetes can test themselves whenever they need it, and use it whenever necessary.
• See children’s type 1 diabetes references and websites.
How to measure the blood glucose at home
• There is also a method of testing blood sugar levels by drawing peripheral venous blood or peripheral arterial blood by injection or by drawing blood from the skin layer with a lancet, etc.
• There is also a method to find out what the blood sugar level is by placing a blood sugar measuring device on the skin without drawing blood. In particular, you can purchase all medical equipment necessary for diabetic treatment and diagnosis, such as a device that can find out the blood sugar level of a diabetic patient without drawing blood from USA Medical Supplies.
• If the urine contains an abnormally large amount of sugar, it can be considered that the blood sugar level is higher than normal.
• However, it is not possible to know exactly how high your blood sugar level is without performing a blood sugar test.
• Explains in detail the blood sugar level test method used at home when treating type 1 diabetes in children for a long time.
• In general, when there is no sugar in the urine, the blood sugar level is likely to be at least 180mg/dl or less. However, it is not clear how much lower blood sugar levels are than 180mg/dl.
• It is not known exactly how low or higher blood sugar levels were at that time just before the urine sugar was tested.
• When a child with diabetes has no sugar in the urine, blood sugar levels can be very low, potentially life-threatening.
• The sugar in the urine contains not only the blood sugar that was filtered out of the glomerulus of the kidney when the urine was tested but also the sugar that was filtered out of the glomerulus of the kidney long before the urine for the test was received.
• In other words, the sugar in the urine received at the time of the test is the urine released from the glomerulus last before receiving the urine for the test and the urine from the glomerulus from the time the urine was seen the previous time.
• A urine chemistry test with the urine you just received will tell you there is sugar in your urine, but you are not sure when the sugar has been filtered out of the kidney’s glomerulus.
• Therefore, rather than testing the urine of a diabetic child and treating type 1 diabetes based on the amount of sugar in the urine, it is more effective to test the blood sugar level and treat type 1 diabetes based on the blood sugar level.
• It is more effective to treat type 1 diabetes based on blood sugar levels by testing blood sugar levels than to treat type 1 diabetes by testing the urine of a child with type 1 diabetes.
• So these days, type 1 diabetes is treated mainly by testing blood sugar.

Figure 1-71. A blood glucose meter used to measure blood sugar at home. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-72. A needle used to draw blood to measure blood sugar. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-73. To measure blood sugar, the skin layer of the fingertip is pierced with a needle. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.. FAAP

Figure 1-74. One-touch test strip used to measure blood sugar. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Children with diabetes and their parents should learn how to test their blood sugar at home.
• This is because it is ideal to treat type 1 diabetes according to the blood sugar level by measuring the blood sugar level as described above. In the following cases, a urine sugar test without measuring the blood sugar level may help to treat type 1 diabetes.
• Some pre-adolescent infants, school-age children, or adolescents do not like to take blood for blood sugar testing to measure blood sugar, so they can’t measure their blood sugar.
• In this case, instead of checking your blood sugar from time to time, you can test your urine sugar to help treat type 1 diabetes.
• In other special cases, urine sugar may be tested instead of testing blood sugar at a school or other special location.
• Type 1 diabetes can be treated when blood sugar levels are abnormally extremely high, when you have an infectious disease, or in other cases, by measuring your blood sugar and simultaneously testing the sugar in your urine.\
• In some cases, type 1 diabetes can be treated by performing a urine test to see if sugar and ketones are present in the urine, and to test for blood sugar and ketones in the blood.
• When the blood sugar level is below normal, it is called hypoglycemia. Symptoms caused by hypoglycemia are called hypoglycemia. If your blood sugar is very low and you have severe hypoglycemia, glucagon injections can be used to treat hypoglycemia. Children with diabetes should always carry glucagon injections with them so that they can be used for emergency treatment of hypoglycemia, or keep them at home or at school and use them when necessary.
Glucagon Injection
• Glucagon is a hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the islet of Langerhans in the pancreas.
• It is a hormone that changes glycogen into glucose (blood sugar) in the liver and amino acid into glucose.
• When children or adults with diabetes develop hypoglycemia, emergency treatment with glucagon injections can raise blood sugar.
• So you should have glucagon available to treat hypoglycemia.

Figure 1-75. Glucagon injection. It is a hypoglycemic emergency treatment drug that can be used to raise blood sugar levels in an emergency when hypoglycemia occurs severely in children with type 1 diabetes. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Intranasal glucagon powder injection can treat hypoglycemia in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes.
Intranasal glucagon reverses hypoglycemia in children and adolescents When providing emergency treatment for hypoglycemia in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes, muscle glucagon was administered as an emergency intramuscular injection. However, according to a recent research team at Yale Medical University, hypoglycemia in children with type 1 diabetes was treated by injecting glucagon powder intranasally.
As a result, the blood sugar increased within 20 minutes after the injection, and the hypoglycemia was cured. It is reported that hypoglycemia was cured by increasing blood sugar as a result of intranasal injection of glucagon powder to adults with type 1 diabetes.
Until now, a diabetic patient himself brought an intramuscular injection glucagon kit, and when hypoglycemia occurs, he was given an intramuscular injection of glucagon to treat hypoglycemia, and a medical technique was developed that can be treated by injecting glucagon nasal powder into the nasal cavity.
Source: SARA FREEMAN, Pediatric News Digital Network September 16, 2015 Parents should also visit www.koreapediatrics.com http://blog.naver.com/drsangwonlee http://doctorleeflowerphoto.com http://flickr.drleesangwon https://www.flickr.com/drleesangwon/
Under controlled type 1 diabetes and higher blood glucose
• Proper insulin injection, adequate physical exercise, balanced diet, physical stability, mental stability, etc. Sometimes, even with adequate treatment of type 1 diabetes, blood sugar is not optimally controlled.
• This type of diabetes is called undercontrolled type 1 diabetes mellitus.
• When the blood sugar level is significantly higher than normal, it is called hyperglycemia (hyperglycemia), and the symptom that occurs is called hyperglycemia or hyperglycemia.
• Depending on the level of hyperglycemia, various symptomatic signs are caused by high blood sugar.
• Parents of children with type 1 diabetes should be familiar with the causes of hyperglycemia, the symptoms of hyperglycemia, and its prevention and treatment.
• If a child with type 1 diabetes develops hyperglycemia
o urinating more often than usual,
o The thirst becomes more intense, o There is no energy,
o poor eyesight,
o There is more sugar in the urine.
• When you have hyperglycemia, you should promptly treat high blood sugar with proper dietary intake, proper physical exercise, and insulin treatment. ‘
• If hyperglycemia is not treated quickly and properly and left unattended for a long time, various organs and tissues of the body’s various systems, such as nerves, heart, blood vessels, kidney glomeruli, and optic nerves, may continue to be damaged.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drle epediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”