후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증 Acquired hypothyroidism
- 태어날 때는 갑상선의 크기나 기능이 정상이지만 출생 이후 여러 가지 원인으로 생긴 갑상선 기능 저하증을 후천성 갑상선 기능저하증이라고 한다.
- 아이들에게 생기는 후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증을 연소성 갑상선 기능 저하증이라고도 한다.
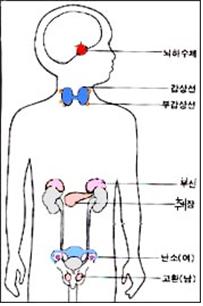
그림1-37. 내분비선.
뇌하수체, 갑상선, 부갑상선, 췌장,부신, 난소, 고환 등을 통틀어 내분비선이라 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 원인
- 어떤 아이는 비정상적으로 아주 작은 갑상선을 갖고 태어날 수 있다. 생후 첫 몇 달 동안 또는 그 후 몇 년 동안은 작았던 갑상선에서 분비되는 갑상선 호르몬 양으로 정상적으로 성장 발육 될 수 있고 갑상선 기능 저하증이 나타나지 않을 수 있다.
- 그렇지만 점점 더 성장 발육해 전보다 체중과 신장이 더 많이 증가되기 때문에 태어날 때부터 정상 크기보다 훨씬 작은 갑상선에서 필요로 하는 만큼 갑상선 호르몬 양이 충분히 분비될 수 없다.
- 때문에 갑상선 기능 저하증의 증상 징후가 점차로 더 뚜렷이 나타나기 시작한다.
- 이런 종류의 갑상선 기능 저하증은 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 일종이다.
- 그렇지만 후천성으로 생긴 갑상선 기능 저하증으로 오진할 수도 있다.
다음과 같은 때는 후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증이 생길 수 있다.
-
- 갑상선 암·갑상선 기능 항진증을 치료하기 위해 갑상선의 일부나 전부를 수술 제거 치료를 하거나 방사능 요도치료로 갑상선 기능 제거 치료를 받았을 때,
- 항 갑상선제로 치료 받을 때,
- 뇌하수체 장애,
- 만성 갑상선염이 있을 때,
- 림프구성 갑상선염,
- 갑상선 호르몬 합성 이상,
- 이소성 갑상선 수술제거
- 설 갑상선이나 설하 갑상선 등을 수술 제거 치료 받았을 때,
- 당뇨병이 있을 때 병발증으로,
- 갑상선 주위 암 등을 방사능으로 치료 받았을 때,
- 장기간 옥도치료를 받을 때,
- 그 외 다른 여러 가지 원인으로 후천성으로 갑상선 기능이 저하될 수 있고
- 그로 인해 후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증(後天性 甲狀腺 機能 低下症)이 생길 수 있다.
- 이상 설명한 후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 여러 원인들 중 만성 갑상선염이 가장 흔한 원인이다.
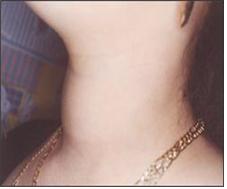
그림 1-38. 갑상선 비대.
갑상선 기능 항진증이 있고 갑상선이 비대해졌다. 15세 사춘기 여아의 목의 중앙 앞부분이 갑상선 비대로 두드러지게 나와 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 증상 징후
- 갑상선 기증 저하의 정도, 원인, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 성장 지연·점액수종·변비·과도수면, 골격 성장장애, 두통, 시력장애, 성조숙증·젖 분비 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
- 학습장애, 지능장애, 과도 활동 장애 및, 또는 주의력 결핍 장애, 행동문제, 수면문제 등이 생길 수 있다.
후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 진단 치료
- 병력·증상 징후 ·진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면
-
- 갑상선 호르몬-티록신(T4),
- 유리 티록신(T4),
- 트리요오드타이오닌(T3),
- 유리 트리요오드타이오닌(T3),
- 갑상선 자극 호르몬(TSH)
- 농도·혈중 갑상선 글로불린(Tg) 농도,
- 혈중 갑상선 호르몬 결합 글로불린(TBG) 농도 등을 검사하고
- 피, 갑상선 방사핵종 스캔,
- 갑상선 초음파 검사 등으로 진단한다.
- 또 신피그래피 검사 등으로 갑상선의 유무와 기능 등을 알아보고 확진한다.
- 필요에 따라 방사능 옥도섭취 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
- 그 중 T4, T3, 혈중 갑상선 호르몬 결합 글로불린(TBG/Thyroxine binding globulin) 검사,
- 갑상선 자극 호르몬(TSH) 농도,
- 방사핵종 스캔검사 등 검사로 확진할 때가 많다.
- 이 병의 원인에 따라 치료할 수 있다.
- 소디움-L-티록신(Thyroxine) 갑상선 호르몬으로 치료한다.
Acquired hypothyroidism 후천성 갑상선 기능 저하증
• At birth, the size or function of the thyroid gland is normal, but hypothyroidism caused by various causes after birth is called acquired hypothyroidism.
• Acquired hypothyroidism in children is also called juvenile hypothyroidism.

Figure 1-37. Endocrine glands. The pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal gland, ovary, and testes are all called endocrine glands. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Causes of acquired hypothyroidism
• Some children may be born with an unusually small thyroid gland. The amount of thyroid hormone secreted by the thyroid gland, which was small during the first few months or years after birth, can lead to normal growth and development, and hypothyroidism may not appear.
• However, as it grows and develops, gaining more weight and height than before, the thyroid gland, which is much smaller than its normal size from birth, cannot produce enough thyroid hormones as needed.
• Because of this, the symptoms of hypothyroidism begin to become more and more pronounced.
• This type of hypothyroidism is a type of congenital hypothyroidism.
• However, it may be misdiagnosed as an acquired hypothyroidism.
Acquired hypothyroidism can occur when:
o When a part or all of the thyroid gland is surgically removed to treat thyroid cancer or hyperthyroidism, or when a thyroid gland function is removed through radioactive urethral therapy, o When being treated with antithyroid drugs,
o pituitary gland disorders,
o When you have chronic thyroiditis,
o lymphocytic thyroiditis,
o abnormal thyroid hormone synthesis,
o Ectopic thyroid surgery removal
o When the gland or sublingual thyroid has been surgically removed,
o As a complication when you have diabetes,
o When cancer around the thyroid gland has been treated with radiation,
o When receiving iodine treatment for long-term,
o Thyroid function may decrease due to acquired factors due to various other causes,
o As a result, acquired hypothyroidism may occur.
o Among the various causes of acquired hypothyroidism described above, chronic thyroiditis is the most common cause.

Figure 1-38. Hypertrophy of the thyroid gland. I have hyperthyroidism and my thyroid gland is enlarged. The central anterior part of the neck of a 15-year-old adolescent girl is prominent with an enlarged thyroid gland. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Symptoms, signs of acquired hypothyroidism
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on the degree of hypothyroidism, the cause, and the presence or absence of complications.
• Symptoms such as growth retardation, myxedema, constipation, excessive sleep, skeletal growth disorders, headache, vision problems, precocious puberty, and lactation may occur.
• Learning difficulties, intelligence disorders, hyperactivity disorders and/or attention deficit disorders, behavioral problems, and sleep problems may occur.
Diagnosis, treatment of acquired hypothyroidism
• If you suspect this disease by combining medical history, symptoms, and medical findings,
• o thyroid hormone-thyroxine (T4),
o free thyroxine (T4),
o Triiodothyonine (T3), o Free triiodothyonine (T3),
o Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
o Concentration•The concentration of thyroid globulin (Tg) in the blood,
o Blood thyroid hormone-binding globulin (TBG) concentration, etc.
o Blood, thyroid radionuclide scan,
o It is diagnosed by ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
• In addition, the presence and function of the thyroid gland are checked and confirmed through a scinography test.
• If necessary, it can be diagnosed with a radioactive oxido intake test.
• Among them, T4, T3, blood thyroid hormone binding globulin (TBG/Thyroxine binding globulin) test,
• thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration,
• It is often confirmed by tests such as radionuclide scanning.
• Depending on the cause of the disease, it can be treated.
• Treated with sodium-L-thyroxine thyroid hormone
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drle epediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”