화학물질 중독과 약물 중독, Chemical poisoning and drug poisoning
화학물질 중독과 약물 중독의 개요와 예방
-
미국은 약물 중독, 가정용 화학 물질 중독을 예방하기 위해 약물 및 가정용 화학 물질 컨테이너, 소아 중독 예방 기준(Child poisoning prevent proof)정책을 법으로 정한 이후 미 소아청년들에게 약물 중독 사고와 화학물질 중독사고의 발생률이 상당히 감소됐다.
-
미 제약회사나 화학물질 제조회사는 특히 가정용 화학물질 중독과 약물중독을 예방하기 위해 약물이나 화학물질을 담는 용기의 뚜껑을 영유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들과 심지어는 성인들도 쉽게 열 수 없게 하는 법을 제정했다. 또 약물이나 가정용 화학 물질을 싼 포장을 쉽게 뜯을 수 없게 만든다. 정말로 조그마한 노력과 돈으로 이 나라의 소아청소년들의 건강과 안녕, 행복을 위해, 미 전 국민 건강 증진을 위해 노력하는 위대한 나라가 바로 미국인 것 같다.
-
미국에서는 소아청소년들이 약물이나 가정용 화학물질을 먹고 마시고 피부에 묻혀 생기는 소아청소년 중독사고 발생률이 이 법이 제정된 후 상당히 많이 줄어들었다.
-
동네나 지역사회의 소아청소년 약물 및 화학물질 중독 예방 교육 프로그램이나 세미나를 통해,
-
인터넷, 소셜 의학 TV, 라디오 등 대중 메디아 교육 프로그램을 통해,
-
범국민 소아청소년 중독 예방교육, 약물, 화학물질 중독 예방 교육 프로그램을 통해,
-
각 초중고교 학생 중독 예방교육 프로그램을 통해,
-
학교 약물, 화학물질 중독 예방 교육 프로그램을 통해,
-
소아청소년 중독 예방교육을 위해
-
미소아청소년과 학회 및 의학계에서 발간한 약물, 화학물질 중독 예방 팸플릿 등을 통해,
-
제약회사 및 화학물질의 제조회사에서 직접 만든 약물 중독, 화학물질 중독 예방 교육용 팸플릿을 통해,
-
그 외 다른 대중 메디아를 통한 부모 소아청소년 중독 예방교육 등을 꾸준히 계속 실시한 덕택으로 미 소아청소년 중독 사고가 많이 많이 줄어들었다.
-
그러나 아직도 약물이나 가정용 화학물질 소아청소년 중독사고가 여러 가지 이유로 계속 생기고 있는 실정이다.

사진 1-33 약물, 술, 화학 약품, 청소용 화학 물, 살충 제 등을 마시시고 중독되지 않게 잘 보관 한다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
영유들이 약물이나 화학물질에 중독되지 않게 항상 주의 한다.
화학물질 중독과 약물 중독의 원인
-
아무리 예방을 잘 해도 화학물질 중독 사고나 약물 중독 사고가 소아청소년들에게 비교적 흔히 생길 수 있다.
-
미국에서는 연간 백만 명의 소아청소년들이 약물이나 화학물질에 중독되고 연간 약 3천 명이 죽고 그 중 500명은 5세 이하 영유들이다(출처; Pediatric Emergencies. Dermer J. Pascoe, M.D, and Etc. p.299).
-
특히 한 살 이전 영아들이나 한두 살 된 타들러 유아들은 손에 잡히는 것은 무엇이든지 입에 넣고 빨고 먹고 노는 경향이 있고, 그들은 사리판단을 제대로 할 수 없기 때문에 약물 중독사고 등이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다.
-
영유아들에게 화학물질이나 약물, 또는 독극물 중독 사고가 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
소아청소년 화확 물질 중독 사고의 50%는 부엌에서, 20%는 화장실에서, 10%는 침실에서, 나머지는 집 안팎에서 생긴다.
-
화학물질이나 약물이 피부에 접촉될 때 피부 화상, 피부염, 및 전신 중독이 생길 수 있고,
-
화학물질이나 약물을 기도 속으로 흡인하거나 경구로 섭취해 위장 관을 통해 전신으로 흡수되어 전신 약물 중독 및 화학 물질 중독이 생길 수 있다.
-
치료용 주사 약물을 주사로 맞거나 경구용 약물을 섭취한 후 소아청소년 약물 중독사고가 생길 수 있다.
-
자살 기도를 하기 위해 사용한 화학물질이나 약물로 사망하지 않고 중독만 되기도 한다.
-
오늘 날 일부의 사춘기 아이들이 마약, 습관성 약물, 또는 화학물질 등을 섭취 해 그들에게 중독사고가 생기기도 한다.
-
요즘 사춘기가 시작되기 전 후기 학령기 아이들에게도 이런 종류의 중독 사고가 생기기도 한다.
-
가정에서 부모 자녀 사이에서 생기는 스트레스, 소아청소년들이 스스로 겪는 스트레스, 부모의 이혼, 별거, 사별 등으로 스트레스를 받는 소아청소년들에게 화학물질 중독이나 약물중독 사고가 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과–제2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방–약물 중독 사고 예방 참조.
-
화학물질 중독 예방, 휘발유·등유 중독 예방, 살충제·제초제 등 농약 중독사고 예방, 납 중독 예방 참조)
중독을 더 흔히 일으킬 수 있는 화학물질과 약물
-
어떤 종류의 약물이든 화학물질이든 중독될 수 있다. 보다 더 흔히 중독될 수 있는 약물과 화학물질은 다음과 같다.
-
아세트아미노펜(상품명–타이레놀 등), 수면제, 철분제 등 약물,
-
화장품이나 비누나 비누가루 등 청소용 화학물질 등
-
니스, 왁스, 석유, 휘발유, 페인트 등
-
좀약, 쥐약, 농약, 살충제, 제초제, 비료 등의 화학물질 등
- 음식물을 담는 부엌 용기로 쓰는 풀라스틱 그릇이나 음식물을 포장할 때 쓰는 포장 용 플라스틱에서 묻는 화학 물질로 화학 물질 중독이 생길 수 있고 각종 그릇 딹기 용 화학 물질로 화학 물질 중독이 생길 수 있다.
-
-
호기심이 많은 영유아들은 예쁜 용기에 담겨 있는 약물이나 각종 가정용 화학물질 등을 보고 갖고 놀고 마시고 먹고 피부에 바르고 묻힐 수 있다. 그 것이 눈에도 들어갈 수 있다. 그래서 각종 화학물질 중독사고가 생길 수 있다.
-
소아청소년들에게 화학물질이나 약물, 또는 독극물로 인한 중독사고가 생기지 않게 극히 조심해야 한다.
-
화학물질이나 약물 등을 특히 영유아들의 손에 닿지 않는 장소에 잘 보관해야 한다.
-
필요에 따라 안전 캐비닛 속에 넣고 아무나 열지 못하게 자물쇠로 잠그고 특히, 영유아들이 도저히 꺼낼 수 없게 보관해야 한다.
-
화학물질이나 약물 등을 원래 담았던 용기에서 다른 용기로 옮겨 담지 말아야 한다. 다른 용기에 옮겨 담은 화학물질이나 약물을 현재 담겨 있는 용기의 약물이나 화학물질로 잘못 알고 그 내용물을 잘못 사용하거나 잘못 섭취해서 약물중독 등이 생길 수 있다. 그 때문에, 화학물질이나 약물 등을 원래 담았던 용기에서 다른 용기로 옮겨 담지 말아야 한다.

사진 33.영유들의 손에 닿지 않는 곳에 가정용 화학물질이나 약물,독극물질을 잘 보관해야 한다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
화학물질 중독과 약물 중독의 치료
- 화학물질이나 약물, 또는 독극물을 조금이라도 빨거나 마시거나 먹거나, 또 피부에 묻거나 기도내로 흡인했다고 의심하거나 피부에 독극물이나 화학물질이 접촉된 것을 목격했을 때는 그 종류나 양에 관계없이 현장에서 화학물질 중독과 약물 중독 최초 응급처치를 즉시 시작해야 한다.
-
약물이나 화학물질, 독극물에 중독되거나 중독될 것 같아서 걱정되어 환아를 병원 응급실로 데리고 가기 전에 가능한 한 독극물 중독 치료센터(Poisoning Control Center)의 전화 상담 처치 도움을 받는다.
-
미 독극물 중독 응급 치료센터는 연간 5백만 명 이상의 독극물이나 약물 중독 문제를 도왔다고 한다 (출처: Robert M. Reece, M.D. Manual Emergency Pediatrics, 4th Ed. p.205).
-
상황에 따라, 의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과, 응급 의료 센터의 전화 지시에 따라 현장에서 바로 부모가 일차 최초 응급처치를 시작 한다.
-
필요에 따라 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단을 이용해 병원 응급실이나 독극물 응급치료센터, 또는 적절한 병원으로 환아를 이송한다.
-
병원 응급실에 도착하기 전이나, 의사나 구급대가 현장에 도착할 때까지 화학물질이나 약물, 또는 독극물에 중독됐다고 의심할 때는 그 물질을 담은 용기에 쓰여 있는 주의 사항과 치료방법에 따라 현장에서 바로 응급 치료를 할 수 있다.
-
그러나 최근 미 소아청소년과 학회에서는 독극물 등을 담은 용기에 쓰여 있는 주의사항과 그 물질에 중독됐을 때의 응급처치방법이 때로는 적절치 않을 수 있기 때문에 화학물질이나 약물, 또는 독극물이 들어 있는 용기의 주의사항이나 치료 방법에 따라 치료하기 전에 꼭 의사의 지시를 받으라고 권장한다.
-
화학 물질 중독 증상 징후가 있는 환아나 중독이 될 수 있을 까 걱정되는 환아를 병원 응급실로 데리고 갈 때 구급차를 이용할 것인지, 다른 교통수단을 이용해 급히 데리고 갈 것인가는 그때 상황에 따라 결정해야 한다.
-
화학물질이나 약물, 또는 독극물 등이 담겨있던 용기와 포장박스에 있는 설명서, 용기에 남아있는 화학물질이나 약물을 병원 응급실로 갈 때 가지고 가면 진단 치료하는데 도움이 된다.
-
화학물질, 약물, 독극물의 종류에 따라 화학물질, 약물, 독극물을 빨거나 마시거나 먹은 후 중독 증상 징후가 바로 나타날 수도 있고, 바로 나타나지 않을 수 있다.
-
피부 계통나 호흡기 계통, 또는 소화기 계통 등을 통해 핏속으로 서서히 흡수되면서 중독 증상 징후가 서서히 늦게 나타날 수도 있다.

▴ 사진 1-34. 이페칵 시럽(Ipecac syrup)을 의사의 처방에 따라 집에 보관했다가 위 속으로 삼킨 독극물이나 약물을 응급으로 토하게 할 때 쓸 수 있는 약물이다. 무슨 이유로든, 화학물질이나 약물을 과량으로 섭취했을 때 중독되지 않게 이페칵 시럽으로 구토시켜 응급치료를 해도 된다고 과거에는 미 소아청소년과학회는 권장했었다. 그러나 요즘엔, 미소아청소년과 학회는 이페칵 시럽을 가정에 의사의 처방 없이 보관하지 말라고 권장한다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
Robert M. Reece, M.D. Manual Emergency Pediatrics, 4th Ed. p.207에 있는 Toxidromes 정보는 어떤 약물이나 화학물질에 중독되었는지 알아보는데 중요한 자료로 쓸 수 있다. 그러나 비의료인에게는 이해하기 어려운 점도 있다.
-
약물이나 화학물질 또는 독극물 등을 마신 후나 그런 것이 피부나 점막에 접촉된 후에 아무런 중독 증상 징후가 바로 나타나지 않더라도 독극물 치료센터나 병원 응급실 또는 단골 소아청소년과의 지시에 따라 현장에서 1차 응급처치를 당장 시작하던지 병원 응급실로 바로 데리고 간다.
-
강한 산성 물질, 알칼리성 물질, 또는 가솔린이나 등유를 먹었을 때는 구토시키는 응급치료를 하지 않는 것이 보통이다. 그러나 예외가 있을 수 있다. 가능한 한 구토시키는 응급처치를 해 약물이나 화학물질 등 중독 치료를 시작하기 전에 의사의 지시에 따라 치료 하는 것이 치료 원칙이다.
-
강한 산성 물질, 알칼리성 물질, 또는 가솔린이나 등유 등을 제외한 거의 모든 약물이나 독극물, 또는 화학물질을 경구로 섭취했을 때는 될 수 있는 한 빨리 구토시킨다. 이때도 가능한 한 역시 의사의 지시에 따라 응급처치를 시작한다.
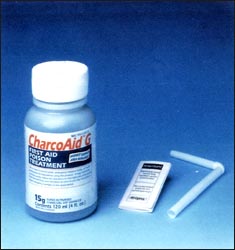
사진 1-35. 활성탄말 현탁액(활성탄 현탁액)은 위속 화학물질, 독극물이나 약물 등 유해 물질을 흡수하는 작용이 있어 해독 치료에 쓰인다.
빨대를 이용해서 경구로 섭취할 수 있고 비위관을 통해 위 속애 주입해서 위내 유해 물질을 제거할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
집에 보관했던 이페칵 시럽을 경구로 섭취하면 15분 내 위 속 내용물을 토하는 것이 보통이다. 그러나 역시 의사와 상의한 후 이페칵 시럽으로 치료한다(사진 34 참조).
-
필요에 따라, 병원 응급실에서는 구위 튜브(구위관/Orogastric tube)를 경구나 비위관(Nasogastric tube)를 비강을 통과해 위 속에 넣고 그 구위 튜브를 통해 위 속에 있는 독극물이나 약물, 또는 화학물질을 뽑아 제거해 치료하기도 한다.
-
먹거나 마신 위 속 약물이나 독극물, 또는 화학물질을 현장에서 빨리 구토하게 해 위 속의 약물이나 독극물, 또는 화학물질에 중독되지 않도록 응급히 치료해야 한다고 설명했다.
-
약물이나 독극물, 또는 화학물질을 구토해 치료하는 방법에 대해 다음에 구체적으로 더 설명한다.
-
가능한 한 의사에게 전화 문의 한 후 의사의 지시에 따라 다음과 같이 치료할 수 있다.
- 위(胃) 내 약물이나 화학물질 등 유해 물질을 활성탄말 현탁액(활성탄 현탁액)으로 응급 치료를 할 수 있다.

사진 1-35. 활성탄 현탁액을 숟가락이나 빨대로 먹여 약물, 화학물질, 독극물 등 위내 유해성 물질에 중독되지 않게 응급치료를 할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 사진 1-36. 활성탄 현탁액을 숟가락으로나 빨대로 먹여 위내 약물, 화학물질, 독극물 등 유해성 물질에 중독되지 않게 치료할 수 있다. Use with Permission.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 약물, 독극물, 또는 화학물질 등을 먹고 의식을 잃고 혼수상태에 빠져 있을 때,
-
황산 등 강한 산성 물질,양잿물 등 강한 알칼리성 물질을 먹었을 때,
-
등유나 휘발유 등을 마셨을 때는 의사의 지시 없이 함부로 구토시켜 치료해서는 안 된다.
-
병원에서는 중독을 일으킨 약물, 독극물, 또는 화학물질 등의 종류와 양, 중독의 증상 징후와 중증도, 섭취한 후 경과된 시간 등에 따라 기본 생명 유지 심폐소생술 치료, 적절한 해독제 등으로 치료한다. 표 14 해독제 치료 참조.
-
이페칵 시럽으로 구토를 시키든지, 비위관이나 구위관으로 위 속에 남아있는 내용물을 제거해서 치료해 주기도 한다.
|
활성 탄말에 잘 흡수되는 혼합물질과 약물
|
|
표 활성 탄말에 잘 흡수되지 않는 혼합물과 약물
|
표 13 활성 탄 현탁액에 잘 흡수되는 혼합물과 약물 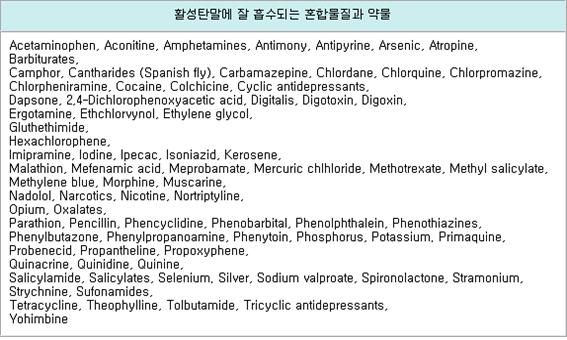
활성탄 현탁액 치료
표 14. 다음과 같은 위내 약물 또는 화학물질 등 유해성 물질로 중독상태에 있거나 중독 상태에 빠지기 직전 응급치료 할 때 위 내용물을 비우는 치료(위세척 치료), 이페칵 경구 섭취 치료 금기, 활성탄 현탁액 경구 치료 금기
| 위 내 중독물질 비우는 치료(위세척 치료) 금기 | 이페칵(Ipecac) 시럽 치료 금기 | 활성탄말 치료 금기 |
|
|
|
출처 및 참조문헌 Robert M. Reece, M.D. Manual Emergency Pediatrics, 4th Ed. p.210
-
활성탄 현탁액(부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호–활성탄 현탁액 상비약 참조)을 먹이든지, 비위관이나 구위관을 통해 약물이나 독극물 등 유해성 물질을 흡인해서 뽑아낸 후 위 속에 활성탄 현탁액을 넣어 유해성 물질 중독을 예방하고 치료할 수 있다.
-
활성탄 현탁액을 위 속에 넣으면 활성탄 현탁액에 위장관 속에 남아 있는 독극물이나 약물 또는 화학물질 등 유해성 물질이 흡수되어 중독이 예방될 수도 있고 치료될 수 있다.
-
약물중독, 화학물질 중독 치료는 부록 참조.
-
약물중독이나 화학물질 중독 또는 약물 중독 치료는 어디까지나 의사가 책임지고 적절히 치료하는 것이 원칙이다.
표 16. 미 독극물 중독 예방 및 응급치료센터
|
|
다음은 “아기가 혈압약을 먹고 약물 중독 사고가 생겼어요 ”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A 아기가 혈압약을 먹고 약물 중독 사고가 생겼어요
Q.
안녕하세요?
이제 돌 지난 여자 아기 엄마입니다.
3주 전 우리아기가 캑캑하면서 뭘 뱉길래 보니 할머니 가방에서 혈압약을 꺼내 입안에 넣었던 거였어요.
한 알을 내가 꺼냈고 한 알은 부서져서 혓바닥에 있길래 손으로 꺼내 가제 수건으로 혀를 닦았습니다. 보아하니 넘긴 것 같지는 않아서 병원에 가지 않고 그냥 있었는데 이후로도 아기에게 다른 이상은 없었습니다.
요는 할머니가 그때 병원에 가지 않은 것이 걱정이 되서 지금 병이 날 지경입니다.
의사선생님의 소견을 듣고 싶습니다.
3주 동안 아무 일이 없는데 안심해도 될까요?
혹 그때 한 두알 먹었다면 나중에라도 무슨 증세가 나타날 수 있나요?
할머니가 너무 걱정하셔서 ….
꼭 답변 주세요.
A.
정아님
안녕하십니까. 좋은 질문을 해 주셔서 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등을 종합해서 병을 진단 치료하는 것이 이상적이지만 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
혈압 약을 먹은 후 3주 이후에는 먹었던 혈압 약의 대부분은 신체 밖으로 배설되거나 신진대사에 의해서 신체 내에서 더 이상 발견될 수 없습니다. 따라서 안심하셔도 됩니다. 할머님께서도 이 글을 읽으시라고 하셔요.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호 백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방–안전사고, 약물 중독 사고. 약물 독극물 중독사고 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 특히 여성용 손가방 소아 중독에 관한 정보를 읽어 보시시 바랍니다.
소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단 치료를 받고 상담하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요.감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Chemical poisoning and drug poisoning
화학물질 중독과 약물 중독
Overview and prevention of chemical and drug poisoning
- In order to prevent drug poisoning and household chemical poisoning, the United States has established drug and household chemical containers, and child poisoning prevent-proof policies in law to prevent drug addiction and household chemical addiction.
- The incidence rate has been significantly reduced.
- S. pharmaceutical companies and chemical manufacturers have made it difficult for infants, school-age children, adolescents, and even adults to open the lids of drugs or chemicals, especially to prevent household chemical poisoning and drug poisoning.
- The legislation was enacted. It also makes it difficult to open cheap packaging for drugs or household chemicals.
- Americans seem to be a great country that strives for the health, well-being, and happiness of children and adolescents in this country with a really small effort and money, and to promote the health of the entire United States.
- In the United States, the incidence of child and adolescent poisoning accidents caused by eating and drinking drugs or household chemicals and being buried on the skin has decreased considerably since the legislation was enacted.
- Through education programs or seminars on the prevention of drug and chemical poisoning to children and adolescents in the neighborhood or community,
- Through public media education programs such as the Internet, social medicine TV, and radio,
- Through education programs for the prevention of poisoning to children and adolescents, drug and chemical substance poisoning prevention education programs,
- Through each elementary, middle, and high school student poisoning prevention education program,
- Through the school drug and chemical poisoning prevention education program, For poisoning prevention education for children and adolescents
- Through the drug and chemical poisoning prevention pamphlets published by the Society for Children and Adolescents and the medical community,
- Through a pamphlet for the prevention of drug addiction and chemical addiction, made by pharmaceutical companies and chemical manufacturers,
- The number of accidents of addiction to children and adolescents in the United States has decreased a lot of thanks to the continued education of parental child and adolescent poisoning prevention education through other public media.
- However, poisoning accidents to children and adolescents with drugs or household chemicals continue to occur for various reasons.

Picture 1-33
Drink drugs, alcohol, chemicals, cleaning chemicals, pesticides, etc. and store them well to prevent poisoning.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Always be careful not to poison the infants to drugs or chemicals.
Causes of chemical and drug poisoning
- No matter how well prevented, accidents of chemical or drug poisoning can be relatively common among children and adolescents.
- In the United States, one million children and adolescents per year are poisoned to drugs or chemicals, and about 3,000 die annually, of which 500 are infants and children under the age of five (source; Pediatric Emergencies. Dermer J. Pascoe, MD, and Etc. p.299).
- In particular, infants one-year-old or one or two years old toddler children tend to eat and play with whatever they hold in their mouths, and they can’t make good judgments, so drug poisoning accidents can occur more easily.
- Infants and toddlers are more likely to be poisoned by chemicals, drugs, or poisons.
- 50% of childhood and adolescent chemical poisoning accidents occur in the kitchen,
- 20% in the bathroom,
- 10% in the bedroom,
- and the rest both inside and outside the home.
- Skin burns, dermatitis, and systemic poisoning can occur when chemicals or drugs come into contact with the skin, chemicals or drugs are aspirated into the airways or ingested orally and absorbed into the body through the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in systemic drug poisoning and chemical poisoning.
- Drug poisoning accidents may occur in children and adolescents after receiving therapeutic injection drugs by injection or taking oral drugs.
- Chemicals or drugs used for suicidal attempts can lead to poisoning without death.
- Today, some adolescent children take drugs, addictive drugs, or chemicals, causing addiction to them.
- These days, even in late school-age children before puberty begins, this kind of poisoning accident also occurs. The stress that occurs between parents and children at home, the stress that children and adolescents experience on their own, and children and adolescents who are stressed by parents’ divorce, separation, and bereavement are more likely to develop chemical poisoning or drug poisoning accidents.
- Parents should also be at least the half-doctor-see Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing-Volume 2 Prevention of Child and Adolescent Disease Safety Accidents-Prevention of Drug Addiction Accidents.
- Chemical substance poisoning prevention, gasoline/kerosene poisoning prevention, pesticide poisoning accident prevention such as pesticides and herbicides, lead poisoning prevention)
- Chemicals and drugs that can cause poisoning more often
- Any kind of drug or chemical can be poison.
Drugs and chemicals that can be more commonly poisoned include:
- Drugs such as acetaminophen (brand name-Tylenol, etc.), sleeping pills, iron
- Cosmetics, cleaning chemicals such as soap or soap powder, etc.
- Varnish, wax, petroleum, gasoline, paint, etc.
- Chemicals such as mothballs, rodenticides, pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, etc.
- Chemicals from plastic bowls used as kitchen containers for food or plastic packaging used for food packaging can cause chemical poisoning, and chemical poisoning may occur with chemicals used for washing various dishes.
- Curious infants and toddlers can see drugs and various household chemicals in pretty containers, play with them, drink, eat, and apply them to their skin.
- It can get into your eyes as well.
- So, various chemical poisoning accidents can occur.
- Children and adolescents must be extremely careful not to cause poisoning accidents caused by chemicals, drugs, or poisons. Chemicals and drugs should be kept well, especially in a place out of reach of infants and toddlers.
- If necessary, it should be placed in a safety cabinet and locked with a lock so that no one can open it, especially so that infants and toddlers cannot retrieve it.
- Do not transfer chemicals or drugs from the original container to another container.
- Chemicals or drugs transferred to another container may be mistaken for drugs or chemicals in the current container, and drug poisoning may occur due to incorrect use or ingestion of the contents.
- For this reason, do not transfer chemical substances or drugs from the original container to another container.

Photo 33.
Make sure to keep household chemicals, drugs, and poisons out of reach of infants. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Treatment of chemical and drug poisoning
- If you suspect that you have sucked, drank, or eaten any chemicals, drugs, or poisons, or if you suspect that they have been sucked into the skin or aspirated into the airways, Substance addiction and drug addiction first aid should be initiated immediately.
- If you are concerned about being addicted to drugs, chemicals or poisons, or because you are concerned about being addicted, seek help from the Poisoning Control Center before taking your child to the hospital emergency room.
- The U.S. Toxic Poisoning Emergency Treatment Center is said to have helped more than 5 million people per year with poison or drug addiction problems (Source: Robert M. Reece, M.D.
- Manual Emergency Pediatrics, 4th Ed. p.205).
- Depending on the situation, parents start the first aid on the spot immediately following the telephone instructions from the medical paramedics, regular pediatrics, and emergency medical centers.
- If necessary, use an ambulance or other suitable means of transportation to transport the child to a hospital emergency room or poison emergency treatment center, or to an appropriate hospital.
- If you suspect that your child has been poisoned by a chemical, drug, or poison before arriving at the hospital emergency room or until your doctor or paramedic arrives at the site, follow the precautions and treatment methods written on the container containing the substance.
- You can do it.
- However, in the recent American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents, the precautions written on containers containing poisons and first aid measures in case of poisoning may sometimes be inappropriate.
- Therefore, precautions for containers containing chemicals, drugs, or poisons. It is recommended to seek the instructions of a doctor before treatment according to the method or treatment method.
- Whether to use an ambulance or other means of transportation to take a child with signs of chemical poisoning or a child who is worried about possible poisoning to the hospital emergency room should be taken according to the situation at that time.
- It is helpful for diagnosis and treatment if you take the chemicals, drugs, or poisons in the container and the instructions in the packaging box, and the chemicals or drugs that remain in the container when you go to the hospital emergency room.
- Depending on the type of chemical, drug, or poison, symptoms of poisoning may or may not appear immediately after sucking, drinking, or eating the chemical, drug, or poison.
- Symptoms, signs of poisoning may appear slowly as it is gradually absorbed into the blood through the skin, respiratory system, or digestive system.

▴ Photo 1-34.
Ipecac syrup is a drug that can be used for emergency vomiting of poison or drugs swallowed in the stomach after keeping it at home according to the doctor’s prescription.
For whatever reason, in the past, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents recommended that emergency treatment by vomiting with Ipecac syrup is allowed to avoid poisoning when excessive intake of chemicals or drugs.
However, these days, the Academy of Young Children and Adolescents recommends against storing ipecac syrup at home without a doctor’s prescription. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- Robert M. Reece, M.D. Manual Emergency Pediatrics, 4th Ed.
- The Toxidromes information on p.207 can be used as an important resource in determining which drugs or chemicals you are addicted to.
- However, it is difficult to understand for non-medical people.
- After drinking drugs, chemicals, or poisons, or after they come into contact with the skin or mucous membrane
- Even if no signs or symptoms of poisoning appear immediately, first aid is initiated at the site or taken directly to the hospital emergency room according to the instructions of a poison treatment center, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrics department.
- It is common to avoid vomiting emergency treatment when strongly acidic, alkaline, or gasoline, or kerosene is ingested.
- However, there may be exceptions.
- The principle of treatment is to take first aid to vomit as much as possible and follow the instructions of a doctor before starting treatment for poisonings such as drugs or chemicals.
- When a strong acid, alkaline substance, or almost any drug, poison, or chemical substance, except gasoline or kerosene, is taken orally, vomiting is possible as soon as possible.
- At this time, as much as possible, start first aid according to the doctor’s instructions.

Photo 1-35. The activated charcoal suspension (activated carbon suspension) is used for detoxification because it absorbs harmful substances such as gastric chemicals, poisons, and drugs.
It can be taken orally with a straw and can be put into the stomach through a nasogastric tube to remove harmful substances from the stomach. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- If your child takes Ipecac syrup at home orally, it is common to vomit the contents of your stomach within 15 minutes.
- However, after consulting a doctor, it is also treated with ipecac syrup (see photo 34).
- If necessary, in the hospital emergency room, an oral or nasogastric tube is inserted into the stomach through the nasal cavity, and poisons, drugs, or chemicals in the stomach are sucked through the oral tube.
- It may be removed and treated.
- He explained that drugs poisons, or chemicals in the stomach that have been eaten or drank should be treated in an emergency so as not to be poisoned to drugs, poisons, or chemicals in the stomach by making them vomit quickly on site.
- The following will explain more specifically how to treat drugs, poisons, or chemicals by vomiting.
- If possible, call your doctor and follow your child’s doctor’s instructions to treat: Toxic substances such as drugs or chemicals in the stomach can be treated as an activated charcoal suspension.
- By feeding the activated charcoal suspension with a spoon or straw, you can provide emergency treatment to avoid being poisoned to harmful substances in the stomach such as drugs, chemicals, and poisons. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-36. Activated carbon suspension can be fed with a spoon or straw to prevent addiction to harmful substances such as drugs, chemicals, and poisons in the stomach. Use with permission Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- When you lose consciousness after eating drugs, poisons, or chemicals, and are in a coma,
- When you eat strong acidic substances such as sulfuric acid or strong alkaline substances such as lye, If you drink kerosene or gasoline, you should not treat it by vomiting without a doctor’s instructions. In hospitals, basic life-sustaining cardiopulmonary resuscitation treatment, appropriate antidote, etc. are treated according to the type and amount of drugs, poisons, or chemicals that caused addiction, symptoms, and severity of addiction, and the time elapsed after ingestion.
Chemical Compounds and drugs to be absorbed by Activated Charcoal
See Table 14 Antidote Treatment.
Vomiting can be done with ipecac syrup, or by removing the contents of the stomach with a nasogastric tube or an oral gastric tube.
| 위 내 중독물질 비우는 치료(위세척 치료) 금기Contraindications Ipecac Syrup treatment for Treatment of emptying toxic substances in the stomach (gastric lavage treatment) | 이페칵(Ipecac) 시럽 치료 금기
Contraindications Ipecac Syrup treatment |
활성탄말 치료 금기 Contraindications Activated charcoal treatment |
|
|
|
출처 및 참조문헌 Robert M. Reece, M.D. Manual Emergency Pediatrics, 4th Ed. p.210
- By feeding on activated charcoal suspensions (parents should also become anti-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing)-Vol. 21, nursing at home school for children and adolescents-by inhaling harmful substances such as drugs or poisons through a nasogastric tube or an oral gastrointestinal tube.
- After extracting, you can prevent and treat toxic substance poisoning by putting activated charcoal suspension in your stomach.
- When an activated charcoal suspension is placed in the stomach, poisoning can be prevented or treated by absorbing harmful substances such as poisons, drugs or chemicals remaining in the gastrointestinal tract in the activated charcoal suspension.
- See Appendix for drug poisons and chemical poisons, treatment.
- Drug poisons, chemical substance poisons,, or drug poisons, treatment is the principle that the doctor is responsible for the treatment appropriately.
- Table 16. US Poisoning Prevention and Emergency Treatment Center Starting January 1, 2002, you can get free advice on poisoning prevention and emergency treatment across the country by calling 1-800-222-1222 in the United States.
- According to the US Consumer Safety and Prevention Committee’s announcement, you can use this phone to get help 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
- After the phone was opened, until recently, 44,000 cases of toxic poisoning-related health problems have been treated as counseling.
- I believe that Korean Americans living outside the United States can also use the phone to get help with the prevention and treatment of poisoning.
- However, inquiries outside the Americas must pay a phone call fee and can only make calls in English.
- In Korea, you can call 00365-1-800-222-1222 (as of July 2010).
The following is an example of an Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer about “My baby took a blood pressure medication and had a drug addiction accident”.
Q&A
- My baby took a blood pressure medication and had a drug addiction accident Q. Hello? This is the mother of the baby girl who has passed her stone.
- She found out what my baby spit out three weeks ago, her grandmother took her blood pressure pills out of her bag and put it in her mouth.
- She took out one, and one was broken and on her tongue, so she took it out with her hand and wiped her tongue with a gauze towel.
- She doesn’t seem to have passed it over, so she just stayed without going to the hospital, but the baby hasn’t had any other abnormalities since.
- She was worried that her grandmother then she didn’t go to the hospital, so she’s getting sick now.
- I would like to hear from the doctor.
- Can I rest assured that nothing has happened in three weeks?
- If she ate one or two at that time, what symptoms could appear later? Her grandmother was so worried.
- Please answer me.
- Jung Ah Hello.
- Thanks for asking a good question.
- It is ideal to diagnose and treat the disease by synthesizing the child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, but I will provide an answer based on the information provided.
- After 3 weeks of taking the blood pressure medication, most of the blood pressure medication taken is excreted from the body or can no longer be found in the body by metabolism.
- So you can rest assured.
- My grandmother told me to read this article too.
- [Parents should also be at least the half-doctor-Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing]-Vol. 2 Prevention of child and adolescent disease safety accidents-Safety accidents, drug addiction accidents.
- Please refer to drug poisoning accidents, etc. In particular, please read the information on poisoning to children’s handbags for women.
- Please consult with the Pediatric and Adolescent clinic after receiving medical examination and treatment.
- If you have more questions, please contact us again, thank you.
- Lee Sang-won., MD
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”