화상(열상), Thermal burns
2005년 미국 응급 의료 외상 통계
출처: NEJM September 2008 p.1037. |
화상의 종류
1. 열화상(열성 화상)
타는 불 화염이나 뜨거운 다리미 열 등으로 생기는 열화상(보통 흔히 말하는 화상)을 열상 또는 열성화상이라고 한다.
2. 열탕 화상
끓는 물이나 뜨거운 물이나 물 이 외 뜨거운 액체 또는 증기 등으로 생기는 열탕 화상,
3. 전기 열상(전기 감전 화상/전기 화상),
전기 감전으로 생기는 전기 열상(전기 감전 화상, 전기 화상),
4. 화학 화상 (화학 물질 화상),
화학물질에 노출되어 생기는 화학 화상 (화학 물질 화상),
5. 방사능 화상
방사능에 노출되어 생기는 방사능 화상 등 여러 종류의 화상(열상)이 있다.
태어나서부터 사춘기가 될 때까지 소아청소년(0~18세)들의 사망의 주원인은 안전사고이다.
|
화상은 소아청소년들의 안전사고 중 상당한 비중을 차지한다. 일상생활 중 소아청소년 자녀들, 특히 영유아들에게 화상 사고가 나지 않게 잘 예방해야 한다. 소아청소년 자녀가 열 화상을 갑자기 입었을 때 소아청소년과, 응급의료 센터에서 응급치료를 받기 전에 부모가 1차 화상 응급처치를 사고 난 현장에서, 대개의 경우, 집에서 적절히 해야 한다. 이런 저런 이유로, 부모는 적어도 반 의사가 되어야 한다. |
화상의 원인
-
화상의 원인은 소아청소년 자녀의 나이에 따라 조금 다를 수 있다.
-
소아청소년들이 타는 불에서 나는 화염에 노출되거나 타는 불에 직접 접촉되거나 끓는 물이나 뜨거운 다리미 등에 직접 접촉돼 열화상을 입을 수 있다.
-
소아청소년들이 X선, 자외선, 열기, 핵방열, 전자자석 방열, 고압전기, 화학물질, 기계적 마찰로 열화상을 입을 수 있다.
-
생후 6개월~2세까지 영유아들은 불에서 나오는 화염으로 화상을 입는 경우보다 뜨거운 물이나 다리미 등에 직접 접촉할 때 화상을 입는 경우가 더 많다.
-
2세 이후 유아들 학령기 아이들은 뜨거운 물로 열탕화상을 입는 것 보다 불로 열화상을 입는 경우가 더 많다. 특히 성냥을 가지고 놀다가 불이 나서 열화상을 입는다든지 뜨거운 스토브 등을 만져 열화상을 입는 경우가 흔하다.
-
2세 이후 유아들이나 학령기 아이들 또는 사춘기 아이들은 고압전기 감전으로 전기 화상을 입을 수 있고 화염 물질로 화상을 입거나 화학물질에 접촉되어 화학 화상을 입을 수 있다.
-
뜨거운 목욕탕 물로 열탕 화상을 입거나
-
영유아들이 놀다가 낸 화재로 열화상을 입을 수 있다.
-
소아청소년들이 화상을 입지 않도록 집안 바깥을 두루 살펴 각종의 화상 안전사고를 예방해야 한다.
화상의 너비와 깊이에 따른 화상 분류
-
화상을 입은 피부의 너비에 따라 화상을 1~100% 화상으로 나눈다.
-
화상을 입은 피부 층의 깊이와 피하 조직의 깊이 따라 화상을 1~4도 화상으로 분류한다(연기를 흡입했을 때, [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병과 안전사고 예방–화상/열상 사고 예방 참조).
-
화상의 증상 징후는 화상의 원인, 화상의 종류, 화상의 깊이, 화상의 표면적, 화상을 입은 신체의 부위, 화상을 입은 소아청소년의 나이에 따라 다르다.
1. 1도 화상 The first degree burn
-
피부의 표피층이 햇볕, 뜨거운 물, 또는 불 등으로 된 열화상 또는 열탕 화상을 1도 화상이라고 한다.
-
1도 화상을 입은 부위가 화끈거리며 피부의 색이 붉고 피부가 살짝 부을 수 있다.
-
물집은 잡히지 않는다.
- 1도 화상을 적절히 치료하면 1도 화상을 입은 후 5~10일 지나면 덴 피부의 표피가 살짝 벗겨지거나 조금도 벗겨지지 않으면서 잘 낫는 것이다.
2. 2도 화상 The second degree burn
-
타는 불 또는 뜨거운 물이나 다리미 등으로 피부 층의 표피층과 진피층이 데었을 때, 또는 표피층이 다 데고 진피층의 일부만 된 화상을 2도 화상이라고 한다.
-
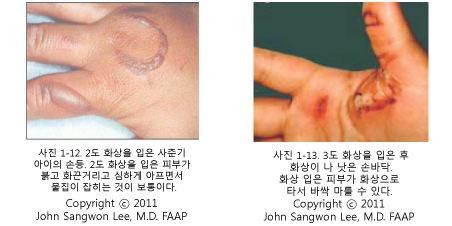
2도 화상을 입은 피부가 붉고 화끈거리고 심하게 아프면서 물집이 잡히는 것이 보통이다 (사진 16. 사진 17 참조).
-
2도 화상은 표재성 2도 화상과 심층성 2도 화상으로 분류된다.
-
피부 층의 표피 층만 화상을 입으면 표재성 2도 화상이라 한다.
-
맑은 체액이 고인 물집이 잡히고 진물이 난다.
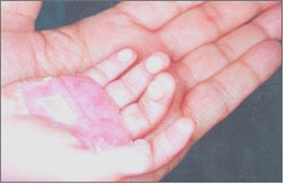 |
▴ 사진 1-11. 2도 화상을 입은 영아 아의 손바닥. 2도 화상을 입은 피부가 붉고 화끈 거리고 심하게 아프면서 물집이 잡혔다가 나아가는 것을 볼 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP |
-
표피층과 표피층의 바로 밑에 있는 진피층까지 입은 화상을 심층성 2도 화상이라고 한다.
-
심층성 2도 화상을 입은 화상 상처에 있는 모세혈관과 말초 신경도 손상될 수 있다.
-
출혈성 포진, 백색 포진 또는 적색 포진이 진피층에 생길 수 있다.
-
적절히 치료하면 보통 3주 걸려 치유된다.
- 화상으로 손상된 피부 층, 피하 층의 모세혈관에서 혈장과 체액이 흘러나오고 화상 입은 피부에 물집이 생길 수 있다. 나중에 심한 흉터가 생길 수 있고 그 흉터가 수축될 수 있다.
- 2도 화상 피부 상처가 박테리아에 감염되면 화상이 곪을 수 있다. 이런 이유로 화상을 입은 피부 상처가 박테리아에 감염되지 않게 적절히 잘 치료해야 한다.
- 경구용, 주사용, 또는 국소용 항생제로 화상 상처가 박테리아에 감염되지 않게 예방치료를 한다.
- 경미한 2도 화상의 대부분은 잘 치료되면 1~2주 내에 잘 낫는다.
- 2도 화상 상처가 박테리아에 감염되지 않고 화상 상처가 곪지 않으면 2도 화상을 입은 피부 상처에 흉터가 거의 생기지 않는다.
- 화상 상처가 박테리아에 감염되어 화상 상처가 곪으면 본래 화상 상처의 너비가 더 커질 수 있고 화상 상처의 깊이도 더 깊어질 수 있다. 그리고 흉터가 더 크게 생길 수 있다.
- 화상으로 생긴 물집이 다 나은 후 얼마동안 화상 입었던 피부색은 붉을 수 있다. 그러나 그 후 몇 개월이 지나면 본래의 피부색으로 되돌아가는 것이 보통이다.
3. 3도 화상 The third degree burn
-
피부의 표피층과 진피 층, 전체 피부층 바로 밑에 있는 피하 조직 까지 덴 화상을 3도 화상이라고 한다.
-
3도 화상을 입으면 피부 층과 피부층 아래에 있는 피하 조직에 있는 모세혈관, 지방조직, 말초신경도 화상을 입는다.
-
3도 화상 상처가 흰색, 갈색, 또는 흙색으로 변할 수 있다.
-
화상 입은 피부가 화상으로 타서 바싹 마를 수 있다.
-
3도 화상이 박테리아에 감염되면 화상 상처가 곪을 수 있다.
-
곪은 화상 상처를 적절히 잘 치료하지 않으면 오랫동안 잘 낫지 않고 크고 선명한 흉터가 더 크게 생길 수 있고 화상 입었던 피부층이 정상적으로 재생되지 않을 수 있다.
-
3도 화상으로 손상된 피부층과 피하 조직은 피부 이식으로 치료 할 수 있다.
4. 4도 화상 The fourth degree burn
-
피부층과 전체 피부층 바로 밑에 있는 피하 조직 과 그 부위에 있는 근육, 근육을 둘러싼 근육막, 뼈 모두가 데었을 때의 화상을 4도 화상이라고 한다.
화상 치료 Burn treatments
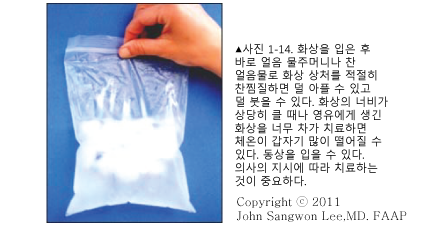
-
화상의 원인, 화상의 종류, 화상 입은 피부층과 피하 조직의 깊이와 너비의 크기(면적), 나이, 화상, 열화상을 입은 신체 부위, 화상을 입었을 때 건강상태 등에 따라 치료가 다르다.
-
1~2도 화상을 경미하게 입었을 때는 의사의 지시에 따라 부모 자신이 1차 응급처치를 집에서 적절히 할 수 있다. 그렇지 않으면 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 치료를 받든지 화상 특수 전문의의 치료를 화상 치료센터에서 받아야 한다.
-
화상을 입었을 때 가능한 한 화상을 더 이상 입지 않도록 화상을 입었던 현장에서 안전한 장소로 환아를 옮겨 놓는다.
-
화상을 입게 한 뜨거운 물이나 물체, 또 타는 불에 더 이상 노출되지 않게 환아를 안전한 장소로 옮긴다.
-
숨을 제대로 쉬지 못하거나 숨이 멈췄거나 심장 박동이 정지되었으면 기본 심폐 소생술처치 내지 진보 심폐 소생술을 한다.
다음과 같이 기본 심폐 소생술 처치를 한다.
- 우선 숨을 쉬게 기도를 확보 한다. 목 기도 부위를 압박하거나 쪼이는 것은 목에서 풀어주고 기도 속을 막는 구토물을 제거한다. 공기가 기도를 통해 잘 유통되게 하는 처치를 우선 해 숨을 쉬게 처치한다. 이 처치를 기도확보와 호흡유지 치료(Airway and breathing establishment=A)라 한다.
- 심장혈관순환계의 기능을 복구(Cardiovascular function/circulation=C)하고
- 화상의 정도를 평가 진단(Diagnosis=D)한다.
- 필요에 따라 약물 치료(Drug treatments=D)를 한다.
- 인간 생명유지를 하기 위해 기본 심폐 소생술을 ABCDD라고도 한다고 이미 전술 했다.
|
ABCDD를 요약하면 ① 기도확보와 호흡유지(Airway and Breathing establishment)를 한다–A. ② 심장혈관순환계 기능 복구(Cardiovascular function/circulation)를 한다–B. ③ 진단(Diagnosis)하고–D ④ 필요에 따라 약물치료(Drug treatments)를 한다–D. |
- 기본 심폐 소생술을 이론적으로 ①~④ 응급처치로 나누어 생각할 수 있지만 응급 의료 상황에 따라 임상에서는 ①~④ 응급처치를 동시해야 한다.
- 최근, 성인 심폐소생술(ABCDD)을 BACDD 순서로 하라고 권장 한다.
- 화상으로 아프면 화상 상처를 찬물(섭씨 15~25도)에 30분 정도 담그거나 찬물 찜질대로 찬찜질 치료를 하면 덜 아프고 화상 상처의 깊이, 너비가 작아지고 흉터가 적게 생기고 사망률도 준다(출처; NEJM September 2008 p.1037). 이런 치료를 할 때 동상을 입지 않게 주의해야 한다.
- 2도 이상 화상을 입은 자녀를 목격한 부모, 주위 사람들은 몹시 당황한다. 그렇지만 화상을 입은 자녀를 진정시키고 가능한 한 화상 상처의 깊이와 너비가 얼마 정도인지 대략 알아본다.
옷에 붙은 불 열기로 열화상을 입을 때
- 불로 타는 옷을 입은 쪽 몸통을 바닥에 대고 눕게 해서 불을 끄든지,
- 젖은 코트나 담요로 불붙은 옷을 덮어 불을 끄든지,
- 물을 끼얹어 불을 끄든지.
- 타는 옷 불을 끄는 동시 옷을 손으로 벗기든지 가위로 잘라 벗긴다.
- 상황에 따라 가장 빠르고 적절한 다른 방법으로 타는 옷을 벗긴다.
- 화상을 심하게 입었을 때는 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과의 지시에 따라 화상 응급치료를 사고 현장에서 시작한다.
- 화상을 경미하게 입었을 때는 부모나 주위에 있는 사람이 집에서 1차 화상 응급처치를 하고, 단골 소아청소년과 또는 병원 응급실에서 치료해 줄 것인가를 빨리 결정한다.
- 부모가 아주 경미한 화상을 1차 화상 상처 응급 치료법을 확실히 모르면 단골 소아청소년과의 지시에 따라 치료한다.
화상을 입은 후 단골 소아청소년과나 병원 응급실로 환아를 데리고 가기 바로 전 다음과 같이 1차 화상상처 응급치료를 할 수 있다.

- 너비가 작은 2도 화상이나 2도 이하 화상을 입었을 때는 열화상 상처를 얼음물 주머니나 찬 물수건으로 찬찜질을 해 줄 수 있다. 찬 물수건은 어름 덩어리를 넣은 찬물에 적신 수건을 쓰던지 얼음 덩어리를 싸서 만든 찬 수건을 의미한다.
- 손발의 일부에 화상을 입었을 때는 화상 입은 손발 상처를 찬 얼음물 속에 2~5분 동안
담그면 통증이 훨씬 덜해 질 수 있고 덜 부을 수 있다. 화상 입은 즉시 냉장고 얼음 어는 냉동 칸에 손을 몇 동안 잠시 넣어 통증을 가시게 할 수 있다
- 찬 얼음 덩어리 물속에 신체의 일부를 담글 때 담근 화상 상처 부위가 동상에 걸리지 않게 주의한다. 체온이 정상 이하로 떨어지지 않게 주의해야 한다. 이런 가정 화상 응급처치를 최초로 시작하면서 병원 응급실이나, 단골 소아청소년과의 전화 지시 치료를 받고 그들의 지시에 따라 적절한 병원 응급치료실 등으로 데리고 가서 추적 치료를 받는다.
- 화상을 입은 신체 부위, 특히 손가락이나 팔목에 낀 반지나 팔찌는 빼놓는다. 화상 입은 피부 상처나 그 주위의 신체 부위를 덮은 옷은 걷든지 벗긴다.
- 화상 상처로 생긴 경미한 통증은 타이레놀(Tylenol)이나 모트린(Motrin/부르펜)등 해열 진통제로 진통시키고 얼음물 주머니 찬찜질을 해서 진통시켜 준다.
- 화상의 정도에 따라 이 정도로 1차 가정 화상 응급처치를 한 후 병원 응급실로 환아를 데리고 갈 것인가 또는 단골 소아청소년과로 데리고 갈 것인가를 결정한다. 단골 소아청소년과 의사와 전화 상담해 적절한 추적 치료를 받는다.
- 필요에 따라 의료구급대의 도움을 받아 단골 소아청소년과나 종합 병원 응급 의료센터로 이송한다.
- 병원에서는 화상 상처로 생긴 심한 통증은 데메롤(Demerol)이나 모르핀(Morphine) 등 강력한 진통제로 진통치료 한다,
- 일반적으로 화상의 원인과 깊이, 화상 너비, 덴 신체 부위, 나이, 전반적 건강상태에 따라 부모가 1차 가정 화상 응급치료를 할 수 있는 능력에 따라 가정 화상 응급치료를 집에서 계속 할 것인가 아니면 종합 병원 응급실에서 치료받을 것인가, 단골 소아청소년과나 종합 병원 외래에서 치료 받을 것인가, 또는 종합병원 화상 센터 입원 치료를 받을 것인 가를 결정한다.
- 화상의 표면적의 너비가 10% 이상이고, 2도나 그 이상의 화상을 입었을 때는 가능한 한 종합 병원 입원 치료를 받는 것이 보통이다.
- 손, 얼굴, 외음부에 생긴 2~3도 화상은 화상의 너비가 작더라도 더 세심한 화상 치료가 요하고 다음과 같은 이유로 가능한 한 종합 병원에서 입원치료를 받는다.

화상을 종합 병원 입원치료를 받아야 하는 이유
-
이상 열거한 신체 부위에 생긴 2~3도 화상을 적절히 치료하지 않으면 화상 입은 신체 부위의 기능장애가 생길 우려가 있을 수 있고,
-
적절히 잘 치료되지 않은 화상 상처는 차후 흉터가 더 심하게 더 크게 생기기 쉽고
-
성형수술을 받아야 하는 차후 문제가 생기기 쉽다.
-
화상 상처로 생긴 흉터를 차후에 치료하는 데 진료비가 더 많이 들 수 있고
-
흉터로 생긴 정신적 고통과 부담은 화상을 입은 당시 바로 적절히 치료할 때 드는 진료 비 보다 훨씬 더 많이 들 수 있다.
-
화상을 입은 환아의 나이가 어리면 어릴수록 화상 상처에 박테리아 감염이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다.
-
화상 상처가 깊고 크지 않아도 될 수 있는 한 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 지시에 따라 치료 받는다.
-
깊고 큰 심한 화상을 입은 환아는 잘 먹지도 못하고 구토 및, 또는 설사를 할 수 있고 때로는 심하게 탈수 될 수 있다.
-
2도나 그 이상 화상을 심하게 크게 입었을 때는 혈액 내 혈청과 전해질 등이 화상 상처의 모세혈관을 통해 화상 상처로 흘러나와 심하게 탈수가 될 수 있고 때로는 전체의 혈 양이 감소될 수 있고 혈압이 떨어지고 쇼크에 빠질 수 있다.
-
화재 열기로 피부에 열화상을 입었을 때는 상기도, 하기도, 또는 전체 기도의 점막층에 열화상이 생길 수 있고 폐도 열화상을 입을 수 있고 붓고 손상될 수 있다.
-
2도 화상이나 그 이상의 화상을 입은 부위를 가능한 한 무균 거즈로 덮고 찬찜질을 하면서 단골 소아청소년과나 종합 병원 응급실로 가서 치료받는다. 춥지 않게 담요나 포대기로 환아를 잘 싸 보온한다.
-
얼음 덩어리를 화상 상처에 직접 대지도 말고 버터, 기름, 어떤 종류의 연고도 의사의 지시 없이는 화상 상처에 바르지 않는다.
다음과 같은 증상 징후가 있으면 기도 열화상을 의심한다.
-
화재가 난 장소에서 뜨거운 연기나 독성 가스 등을 흡인했을 때
-
화재가 난 장소에서 얼굴이나 목 부위에 화상을 입었을 때
-
화재가 난 장소에서 있었고 목이 쉬었을 때
-
화재가 난 장소에서 구출된 후 호흡곤란이 있을 때
-
기도 점막층이 화상을 입었을 가능성이 상당히 많고 기도 점막층이 부을 수 있고, 숨쉬기가 곤란한 증상 징후가 생기는 것이 보통이다.
기도에 열화상이 생겼다 추정하면 다음과 같이 처치한다.
-
의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 지시에 따라 현장에서 응급처치를 시작해야 한다.
-
호흡곤란이 생기거나 혼수상태에 있을 때는
-
목을 뒤로, 옆으로 살짝 젖혀 기도를 열어 숨을 잘 쉬게 해 주고
-
필요에 따라 기본 심폐 소생술 치료를 시작한다.
-
척추 뼈가 골절 됐다고 의심하면 환아를 함부로 움직여서는 안 된다(ABCD 치료방법 참조)
-
다시 설명하면, 숨을 잘 쉬지 못할 때는 환아의 나이에 따라, 입과 코에 처치자의 입을 대고, 또는 입에만 처치자의 입을 대고 인공호흡을 해 주고, 심장이 잘 뛰지 않거나 약하게 뛸 때는 판단에 따라 심장 마사지도 하면서 인간생명유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 하면서 병원 응급실로 데리고 가야한다.
-
이때도 가능한 한 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 전화 응급치료 지시에 따라 어떤 종류의 응급처치를 계속 해야 하는지 알아야 한다.
-
숨을 잘못 쉬거나 여러 가지 이유로 호흡곤란이 심할 때는 종합 병원에서는 필요에 따라 기관 내관 삽입 호흡 치료를 하든지 기관 절개수술 호흡 치료를 하고 새로 만든 인공 기도를 통해 인공호흡치료를 할 수 있다.
-
화재가 난 현장에 있던 환아의 피부에 열화상이 생길 때는 상·하 기도의 점막층에도 열화상이 동시 생길 수 있는 것이 보통이다.
-
열화상 이 외 골절이나 다른 종류의 외상을 동시 입을 수 있고 뜨거운 열기로 인해 생명에 위험한 화상성 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
-
화재가 난 현장에서 금방 구출된 환아가 처음 보기엔 화상을 조금도 입지 않은 것 같더라도 기도 점막층에 열화상이 있는지, 골절 또는 그외 외상이 있는지 진찰 진단을 받고 그에 해당한 치료를 받는다.
1도 화상은 다음과 같이 치료 한다.
-
화상 상처를 찬물주머니나 얼음물주머니로 찬찜질을 하거나 얼음 덩어리 물에 잠시 담그거나 경구용 타이레놀로 진통시킬 수 있다.
-
화상 상처가 더 빨리 낫게 해 주기 위해 의사가 처방 하지 않은 연고나 로션을 화상에 발라 줄 필요 없다.
-
1도 화상을 입은 상처를 2~3일 동안 마른 붕대로 감아치료하든지 무균 거즈로 덮어 치료해 준다.
-
1도 화상을 입은 피부 상처는 7~10일 정도 지나면 표피가 얇게 벗겨지거나 벗겨지지 않은 상태로 잘 낫다.
2도 화상은 다음과 같이 처치한다.

- 1도 화상을 입었을 때와 같이 화상을 입은 상처를 어름덩어리 찬물에 담그든지, 얼음물이나 얼음물 주머니로 찬찜질을 하면 통증이 감소되고 덜 부을 수 있다. 그래도 계속 아프면 경구용 타이레놀 등으로 진통시킨다.
-
2도 화상으로 생긴 물집은 가능한 한 터뜨리지 말고 그대로 놓고 관찰 치료한다.
-
물집이 터지고 데인 피부가 벗겨졌을 때도 벗겨진 피부는 그대로 놓고 관찰치료 한다.
-
세균이 화상 상처에 감염되면 벗겨진 화상 상처에 세균이 감염되어 피부 감염병이 낫지 않고 오래 갈 수 있다. 이때는 살균 가위로 벗겨진 피부를 잘라낸다.
-
15%나 그 이상 2도 화상이 있을 때, 또는 2%나 그 이상의 3도 화상이 얼굴, 손발, 외음부에 생겼을 때는 입원 치료를 받는 것이 보통이다.
-
박테리아 감염으로 화상 상처가 곪거나 감염병을 일으킨 박테리아가 전신으로 퍼져 패혈증을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
마펜나이드 아세테이트(Mafenide Acetate), 설파마이론(Sulfamylon), 실버 설파다이아진(Silver Sulfadiazine), 또는 실버덴(Silvadene)연고 중 한 종류를 의사의 처방에 따라 2도 이상 화상 상처에 발라 치료할 수 있다.
-
심한 화상을 입은 소아청소년들 중 일부에게 화상성 위궤양이 생길 수 있으므로 그에 대한 예방적 치료를 한다.
-
심한 화상을 입은 환아 자신은 물론이고 그의 부모 형제자매들에게도 정신적 정서적인 문제가 생길 수 있다. 그에 대한 심리 치료를 적절히 받아야 한다.
-
소아가 소아 학대로 화상을 입을 수 있으므로 소아 신체 학대로 생긴 화상인지 항시 유의해야 한다.
-
전기 화상을 입고 있는 환아를 맨손으로 만지지 말고 전기가 통하지 않는 나무 등으로 감전을 일으킨 전기 자원에서 환아를 떼어 놓는다. 전기 화상은 화상의 정도를 막론하고 의사의 치료를 받아야 한다.
-
가능한 한 심한 화상은 종합 병원 화상 치료 센터에서 화상 전문의 치료를 받는 것이 이상적이다.
-
심한 화상은 소아청소년과 전문의, 외과 전문의, 그 외 화상 전문의 등이 함께 치료하는 것이 일반적이다.
-
화상 상처에 잘 달라붙지 않는 무균 텔파(Telfa) 거즈나 다른 종류의 멸균 거즈로 화상 상처를 덮어 치료할 수 있다.
-
화상 상처 부위와 크기 등에 따라 다르지만 의사의 지시에 따라 1~2일마다 새 무균 거즈로 화상 상처를 덮어주고 의사의 처방에 따라 적절한 경구용 항생제나 혈관용 항생제로 화상 상처가 곪지 않게 예방 치료 한다.
-
필요에 따라 파상풍 백신 예방접종을 받는다.
-
심한 화상은 항생제, 산소호흡, 기본 심폐 소생술, 또는 진보 심폐 소생술, 진통제, 수혈, 전해질용액 정맥주사, 파상풍 예방접종 등으로 치료한다.
-
화상 상처가 다 나은 후에 적절한 시기에 화상으로 생긴 흉터를 성형 수술로 치료한다.
-
3도나 그 이상 화상, 80% 이상 화상으로 손상된 피부는 비타민 D를 정상적으로 만들 수 없다. 따라서 일생동안 비타민 D를 섭취해야 한다, 참조문헌– 37.
-
화재가 나지 않게 예방하고 뜨거운 물이나 물체에 데지 않게 예방해서 화상을 입지 않도록 하는 것이 무엇보다 중요하다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방 참조).
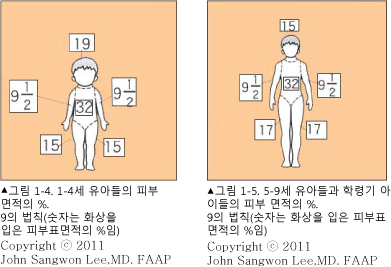
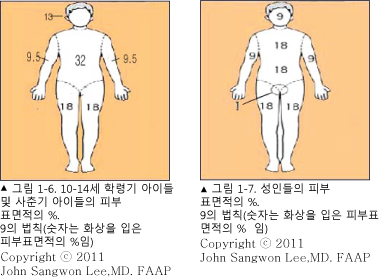
9 법(구의 법/9의 법/9 법칙) Rule of nines
-
화상의 정도를 화상의 깊이와 화상을 입은 피부의 표면적의 너비에 따라 분류할 수 있다.
-
화상의 정도를 “몇 도“의 “몇 % 화상“을 입었다는 식으로 표시하는 것이 보통이다.
-
화상의 정도에 따라 치료와 예후는 다르다.
-
화상을 입은 피부 표면적의 너비를 Lund-Browder charter for children으로 계산할 수 있다.
-
소아청소년들의 신체 각 부위의 피부 표면적의 너비는 그림 23~26에 보는 것 같이 나이에 따라 다르다.
-
한 사람의 피부 전체 피부면적의 크기를 100%로 정하고, 신체 각 부위의 피부 면적의 크기는 신체의 전체 피부 면적에 비례해서 몇 가지 유형으로 비율을 정한다.
-
신체의 전체 피부 면적이 100%라고 정하고 그 중 10%가 되는 피부 면적이 화상을 입었을 때는 10% 화상을 입었다고 한다.
-
임상에서 화상을 입은 피부 면적의 크기를 더 정확하게 알아보기 위해서는 쓰는 방법이 있다.
-
그 방법을 9 법칙 또는 9법이라고 한다.
-
성인들과 12~14세 연령층 초기 사춘기 아이들과 그 이상 먹은 사춘기 아이들의 머리와 목의 피부 표면적은 9%,
-
한쪽 위팔에서 그쪽 손까지의 피부 표면적은 9%,
-
몸통의 앞쪽 피부 표면적은 18%,
-
몸통의 뒤쪽 피부 표면적은 18%,
-
한쪽 허벅다리에서 그쪽 발까지의 피부 표면적은 18%,
-
성인의 외음부(외부 생식기)의 피부 표면적을 1%로 정한다.
-
피부 전체 표면적을 100%로 정한다.
-
화상을 입은 피부 표면적의 크기를 1~100%로 정한다.
표 8. 화상 피부 면적의 크기를 나이에 따라 9법으로 계산하는 법.
| 신체 부위
나이 |
머리 | 오른쪽 위팔에서 손까지 | 몸통의 앞과 뒤 | 왼쪽 위팔에서 손까지 | 오른쪽 허벅다리에서 발까지 | 왼쪽 허벅다리에서 발까지 | 외음부 | 전체 피부 표면적(단위=%) |
| 1~4세 | 19 | 9.5 | 32 | 9.5 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 100 |
| 5~6세 | 15 | 9.5 | 32 | 9.5 | 17 | 17 | 9 | 100 |
| 10~12세 | 13 | 9.5 | 32 | 9.5 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 100 |
| 12~18세와 그 이후 | 9 | 9 | 36 | 9 | 18 | 18 | 1 | 100 |
화상을 입은 피부 표면적의 크기를 1~100%로 정한다.
|
다음은 “화상 상처는 어떻게 치료하나”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 화상 상처는 어떻게 치료하나
Q.
얼마 전 다리미에 살짝 스치듯이 데었는데 까맣게 피부껍질이 탔더라구요
그래서 물로 차갑게 해주고 아이가 만질까봐 연고 바르고 붕대로 감아 보호해주었는데 잠깐 붕대를 교체하는 와중에 아이가 껍질을 벗겨 속살이 드러나고야 말았답니다.
그러자 2차 감염이 되었는지 노랗게 곯았거든요. 계속 연고를 발라 이젠 염증은 없는데 상처가 꽤 커요. 계속 연고(마데카솔)를 발라주면 흉이 없어질는지요. 팔뚝인데 여자아이라 너무 흉할 것 같아서요. 몹시 자책감이 드네요. 제가 혹시 붕대를 감아놔서 흉이 더 커진 건 아닐까요? 흉이 되도록 없도록 하는 방법을 알려주시면 감사하겠어요.
그럼 더운 날씨에 수고하시고 건강하세요… 끝까지 읽어주셔서 감사합니다…
A.
영란님
안녕하십니까. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이와 성별, 과거 현재 가족의 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견, 적절한 임상검사 등의 결과를 종합해서 진단 치료하는 것이 이상적이지만 주신 정보를 참작해서 답변을 드립니다.
잘 치료 하신 것 같습니다.
화상을 입으면 화상 상처를 치료하는 동시에 화상을 입은 상처에 박테리아가 감염되지 않게 예방하고 박테리아에 감염되면 화상 상처 감염병을 치료하고 가능한 한 흉터가 적게 생기게 치료 하고 파상풍을 예방하고 앞으로 화상을 더 이상 입지 않도록 예방을 해 주는 것이 화상 기본치료입니다.
자녀가 화상을 입으면 부모는 죄책감을 갖는 것이 보통입니다. 이번 기회를 이용 해 앞으로 안전사고 예방을 더 잘 하시기 부탁드립니다.
동국제약 마데카솔 연고의 성분이 무엇인지 확실히 몰라서 그 약에 관해서 답변을 드릴 수 없어 죄송합니다.
그러나 흉터를 적게 할 수 있는 방법은 있지만 흉터가 조금도 생기지 않게 하는 치료 방법은 없습니다.
소아청소년과에서 흉터에 관해서 문의하시기를 바랍니다.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방–안전사고 예방 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
다음은 “화상, 열상으로 생긴 흉터”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강 상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 화상, 열상으로 생긴 흉터에 관해
Q.
1. 지난 1월 아기가 다리미에 2도 화상을 입었어요.
발 측면이구요 화상전문병원에서 2주간 치료받았습니다. (연고는 안 바르고 붕대로 감고 소독만 해주었음, 항생제복용) 지금은 그 부위가 약1cm정도 굳은살 박힌 것처럼 보여요. (실제로 만져보면 부드러움. 원래 화상/열상 후 흉터가 이렇게 생기나요?) 어떻게 관리해 줘야할까요? zinc oxide 10%가 들어간 연고를 몇 번 발라줬는데 괜찮나요? (이걸 판매하는 분말로는 화상, 베인 곳, 튼 곳, 기저귀발진에도 사용한다고 하던데 이 용도로 사용해도 되나요? 혹은 바셀린, 라놀린크림을 사용하는 건 괜찮은가요? ) 2. 밥 투정이 심하고 가리는 음식물이 많습니다. 조리법을 달리하고 다른 걸 첨가해도 한번 싫은 건 절대로 안 먹습니다. 지금 17개월인데요… 영양 보조제 추천해 주실래요? 감사합니다. *^^*
A.
미애님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
Q.
2도 화상
Å. 동양인들이나 아프리카 흑인들에게 생긴 2~3도 화상을 적절히 치료 받고 나은 후에도 화상 상처로 상흔이 다소 남을 수 있습니다.
화상 상처가 다 아묾은 후 생긴 상흔은 도포용 약을 발아 치료하거나 경구용 또는 주사용 약물로 치료해도 완전히 없어지지 않습니다. 필요에 따라 성형수술 치료를 받아야 거의 없어 질수 있습니다.
Q.
음식물을 잘 먹지 않는 아이
A.
소아청소년들을 수 10년 동안 진료 하다보면 저 애는 “잠을 잘 자지 않는다.” “잘 자라지 않는다.” “밥을 잘 먹지 않는다.” “하루 종일 아무 것도 먹지 않는다.” 등등의 자녀들 성장 발육 육아의 문제에 관한 질문을 자주 받습니다.
다 중요한 질문이고 또 그냥 넘어가서는 안 될 부모들의 자녀 사랑 관심 사항들입니다.
영유아가 “밥을 잘 먹지 않는다” 는 자녀를 소아청소년과에 데리고 왔을 때 그 소아청소년들을 머리끝서부터 발 끝 까지 자세히 진찰 하고 체중과 키를 잽니다. 그 자녀는 그 동안 자라왔던 체중 백분위선을 따라 또 신장의 백분위선을 따라 정상적으로 잘 크고 있는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
그런도 “아무 것도 먹지 않는다”고 호소하는 부모들이 있습니다.
체중과 신장을 재고 체중 치와 신장 치를 그 자녀의 성장차트에 그려보십시오. 자녀가 자녀의 체중 백분위선과 신장 백분위선을 따라 잘 자라는 지 알아보십시오 (참고로, 여기서 말하는 백분위와 백퍼센트는 다른 말입니다).
하루 종일 먹는 주식과 간식의 이름과 양을 전부 적어 보시고 자녀는 하루 종일 총 몇 칼로리가 필요하고 몇 칼로리를 섭취하는지 계산해 보십시오.
미국에서는 소아청소년과 의사들은 정기 건강 검진을 받으러 온 소아청소년들의 체중과 신장을 재고 그들이 체중 배분위선과 신장 백분위선을 따라 정상적으로 자라는지 의사와 부모가 다 같이 알아보는 것이 기본입니다. 참고하시기 바랍니다.
그래도 걱정되시면 다시 연락해 주시든지 아기 자녀의 단골 소아청소년과에서 상담하시기 바랍니다.
성인들과 같이 17개월 된 유아들도 자신들이 더 좋아 먹는 음식물이 따로 있고 싫어하는 음식물이 따로 있습니다.
그 자녀가 좋아하는 음식물을 될 수 있는 대로 요리 해 주는 것이 좋으나 여기에서도 상식이 통해야합니다.
아무리 부모에게 좋은 음식물이라도 각 자녀에게는 싫은 음식물이 있습니다.
탄수화물, 단백질, 지방, 비타민, 광물질(미네랄) 등 각종 영양분이 골고루 든 균형 잡힌 음식물을 섭취하면 됩니다.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제3권 소아청소년들의 성장 발육 육아–해당 연령의 성장 발육, 생후 1개월~6세 영유아들의 발육 이정표. 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요–이유식. 제14권 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병–음식물을 잘 먹지 않는 아이 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
그리고 질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
표 미국 연간 안전사고 사망의 원인, 사망자 수, 및 사망 원인 순서
|
가장 많은 사망의 원인에서 가정 적은 사망의 원인의 순 |
사망의 원인 (한글) |
사망의 원인 (영어) |
연간 사망자 수 |
1년간 |
|
첫 번째 사망의 원인 |
차 충돌 사망 |
Car crash |
~44,000 명 |
1년 간 |
|
두 번째 사망의 원인 |
낙상 사고 사망
|
Falling |
~15,000 |
1년 간 |
|
세 번째 사망의 원인 |
중독 사망(약물 또는 화학물질 중독)
|
Poisoning |
~9,500 |
1년 간 |
|
네 번째 사망의 원인 |
화제 및 화상
|
Fire |
~3,700 |
1년 간 |
|
다섯 번째 사망의 원인 |
익사사망 |
Drowning |
~3,500 |
1년 간 |
|
여섯 번째 사망의 원인 |
질식 사망 ~3,200 |
Choking |
~3,200 |
1년 간 |
|
일곱 번째 사망의 원인 |
수술 치료 합병증 사망 |
Complications with medical procedure |
~3,000 |
1년 간 |
|
여덟 번째 사망의 원인 |
소총 또는 단총 등 화기 사망 |
Firearm discharge |
~1,150 |
1년 간 |
|
아홉 번째 사망의 원인 |
차에 치어 사망
|
Getting hit by a car |
~1,100 |
1년 간 |
|
열 번째 사망의 원인 |
감전사
|
Electrocution |
~500 |
1년 간 |
소스-1981, CDC
Thermal burns 화상
- US emergency medical trauma statistics for 2005 11,000,000 people received emergency treatment for acute skin injuries.
- Among them, more than 500,000 people received burn treatment
- 7 million 300,000 people received cure treatment
- 2 million people have been treated for cuts and cuts
- Every year, 4,700,000 people were treated by animal bites. Source: NEJM September 2008 p.1037.
Type of burn
1. Heat burn
Thermal burns (commonly referred to as burns) caused by burning fire flames or hot iron heat are called thermal burns.
2. Hot water burn
Hot water burns caused by boiling water, hot water, or other hot liquid or steam, etc.
3. Electric thermal burn (electric shock burn/electric burn),
Electric lacerations caused by electric shock (electric shock burns, electric burns),
4. Chemical burns (chemical substance burns), Chemical burns caused by exposure to chemicals,
5. Radioactive burn
There are several types of burns (heat burns), such as radiation burns caused by exposure to radiation.
- From birth to puberty, the main cause of death among children and adolescents (ages 0-18) is safety accidents.
- Burns account for a significant proportion of safety accidents among children and adolescents.
- During daily life, children adolescents, especially infants, should be prevented from getting burn accidents.
- When a child of a child or adolescent suddenly suffers a thermal burn, before receiving emergency treatment at the Pediatric clinic or an emergency medical center, parents should take appropriate first aid treatment at the site of the accident, usually at home.
- For this and that reason, parents should at least be half-doctor.
Cause of burn
- The cause of the burn may vary slightly depending on the age of the child and adolescent child.
- Children and adolescents can get thermal burns by being exposed to flames from burning fires, direct contact with burning fires, or direct contact with boiling water or hot irons.
- Children and adolescents may suffer thermal burns from X-rays, ultraviolet rays, heat, nuclear radiation, electromagnetic radiation, high voltage electricity, chemicals, and mechanical friction.
- Infants and toddlers from 6 months to 2 years of age are more likely to get burned when they come into direct contact with hot water or irons than when they are burned by a flame from a fire.
- Infants after 2 years of age school-age children are more likely to suffer from heat burns from fire than from hot water burns.
- In particular, it is common to get thermal burns from a fire while playing with matches or to get thermal burns by touching a hot stove.
- Infants after 2 years of age, school-age children, or adolescent children may suffer from electric burns due to high voltage electric shock, burns with flame substances, or chemical burns due to contact with chemical substances.
- Hot bath water burns Infants and toddlers can get thermal burns from fires while playing.
- To prevent children and adolescents from getting burned, they should look inside and outside the house to prevent various burns accidents.
Classify images according to image width and depth
- The burn is divided into 1 to 100% burns according to the width of the burned skin.
- Burns are classified into 1 to 4-degree burns according to the depth of the burned skin layer and the depth of the subcutaneous tissue.
And safety accident prevention-burn/heat injury prevention).
- Symptoms of a burn differ depending on the cause of the burn,
- the type of the burn, the depth of the burn,
- the surface area of the burn,
- the part of the body that has been burned,
- and the age of the burned child and adolescent.
1. The first-degree burn
- Thermal or hot water burns in which the epidermal layer of the skin is caused by sunlight, hot water, or fire is called a first-degree burn.
- The first-degree burned area is hot, the color of the skin is red, and the skin may be slightly swollen.
- No blisters are caught.
- If first-degree burns are properly treated, 5 to 10 days after the first-degree burn has passed, the epidermis of the dented skin heals well without peeling off slightly or at all.
2. The second-degree burn
- A burn in which the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin layer are burned by burning fire, hot water, or iron, or when the epidermal layer is completely burned and only part of the dermis layer is called a second-degree burn.
- It is common for the skin with a second-degree burn to become red, hot, and severely painful, resulting in blisters (refer to Photograph 16. Photo 17 ).
- Second-degree images are classified into superficial second-degree images and deep second-degree images.
- When only the epidermal layer of the skin layer is burned, it is called a superficial second-degree burn.
- Blisters with clear body fluids are caught and oozes.

Photo 1-11. Infants with second-degree burns of palm.
- Second-degree burned skin is red and hot Blisters with pain and severe pain
- You can see it is getting better.
- Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP·
- Burns inflicted to the epidermal layer and the dermal layer immediately below the epidermal layer are called deep second-degree burns.


- The capillaries and peripheral nerves in the burn wound with a deep second-degree burn can also be damaged.
- Hemorrhagic blisters, white blisters, or red blisters may develop in the dermal layer.
- If properly treated, it usually takes 3 weeks to heal.
- Plasma and body fluids flow out of the capillaries of the skin layer damaged by burns or the subcutaneous layer, and blisters may form on the burned skin.
- Later, severe scars may develop and the scars may contract.
- Second-degree burns If the skin wound is infected with bacteria, the burn can be infected.
- For this reason, burned skin wounds must be properly treated to prevent bacterial infection.
- Preventive treatment to prevent infection of the burn wound with bacteria with oral, injection, or topical antibiotics.
- Most of the minor second-degree burns heal well within 1-2 weeks if they are treated well.
- If the second-degree burn wound is not infected with bacteria and the burn wound is not infected, scars rarely appear on the second-degree burned skin wound.
- If the burn wound is infected with bacteria and the burn wound infections, the original burn wound may become wider and the depth of the burn wound may be deeper.
- And the scar can be larger.
- After the blisters from the burn have healed, the skin color that has been burned for some time may be red.
- However, after a few months, it usually returns to its original skin color.
3. The third-degree burn
- A burn that extends to the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin and to the subcutaneous tissue directly under the entire skin layer is called a third-degree burn.
- When third-degree burns, capillaries in the skin layer and subcutaneous tissue below the skin layer, adipose tissue, and peripheral nerves are also burned.
- Third-degree burn wounds may turn white, brown, or earthy.
- Burned skin can burn and dry out.
- If third-degree burns are infected with bacteria, the burn wound may be infected.
- If infected burn wounds are not treated properly, they may not heal well for a long time, and large, clear scars may appear larger, and the burned skin layer may not regenerate normally.
- Skin layers and subcutaneous tissue damaged by third-degree burns can be treated with skin grafts.
4. The fourth-degree burn
- A burn when the skin layer and the subcutaneous tissue directly under the entire skin layer, the muscles in the area, the muscle membrane surrounding the muscle, and all of the bones are burned is called a fourth-degree burn.
Burn treatments
- The treatment differs depending on the cause of the burn, the type of the burn, the size (area) of the depth and width of the skin layer and subcutaneous tissue injured, the age, the burn, the part of the body affected by the heat burn, and the health condition when the burn has occurred.
- In the case of minor burns of the 1st to 2nd degree, the parents themselves can properly perform first aid at home according to the doctor’s instructions.
- Otherwise, you should seek treatment from a regular pediatrician or a burn specialist at a burn treatment center.
- In the event of a burn, move the child from the burned site to a safe place to avoid further burns as much as possible.
- Move the child to a safe place so that it is no longer exposed to hot water or objects that have caused burns, or to a burning fire.
- If your child is unable to breathe properly, have stopped breathing, or your heart rate has stopped, basic CPR or advanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed.
Basic CPR treatments are performed as follows.
- First of all, secure the airways to breathe.
- Squeezing the throat airway releases it from the throat and removes vomit that clogs the airway.
- The treatment that allows air to flow well through the airways is given priority, and treatment is given to breathing.
- This treatment is called airway and breathing establishment (A).
- Restoring the function of the cardiovascular circulatory system (Cardiovascular function/circulation=C)
- and The degree of burn is evaluated and diagnosed (Diagnosis=D).
- Do drug treatments (Drug treatments=D) as needed.
- It has already been mentioned that basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation is also known as ABCDD maintains human life.
To summarize ABCDD
- ① Perform Airway and Breathing Establishment-A.
- ② Recover cardiovascular function/circulation-B.
- ③ Diagnosis-D
- ④ Drug treatments as needed-D.
- Basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation can theoretically be considered divided into first-aid measures, but depending on the emergency medical situation, first-aid measures must be simultaneously performed in the clinic.
Recently, it is recommended to perform adult cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ABCDD) in the order of BACDD.
- If your child is sick with a burn, immerse the burn in cold water (15-25 degrees Celsius) for about 30 minutes or treat it with a cold compress to make it less painful, reduce the depth and width of the burn wound, reduce scarring, and cause death rate (Source: NEJM September 2008 p.1037).
- Be careful not to get frostbite when doing these treatments.
- Parents and people around who have witnessed a child who has suffered a burn of 2 degrees or more are very embarrassed.
- Nevertheless, calm down the burned child and get a rough idea of the depth and width of the burn wound as much as possible.
- When you get a thermal burn from the heat on your clothes
- Either extinguish the fire by lying on the side of the body wearing the burning clothes on the floor,
- Extinguish the fire by covering it with a wet coat or blanket,
- Either pour water to turn off the fire.
- At the same time as turning off the fire,
- remove the clothes by hand or cut them off with scissors.
- Depending on the situation, take off your burning clothes in the fastest and most appropriate way.
- When a burn is severely injured, emergency burn treatment is initiated at the accident site according to the instructions of the medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, and regular pediatric clinic.
- In the case of minor burns, a parent or a nearby person will provide first aid for burns at home, and a regular pediatric clinic or hospital emergency room will quickly decide whether to treat them.
- If parents are unsure of the emergency treatment for a very minor burn, treat it according to the instructions of a regular pediatric clinic.
- Immediately before taking the child to a regular pediatric and adolescent department or hospital emergency room after a burn injury, first-line burn injury emergency treatment can be performed as follows.
- In the event of a 2 degree burn with a small width or a burn less than 2 degrees, a cold compress can be applied to the thermal wound with an ice water bag or a cold wet towel.
- A cold wet towel means a cold towel made by using a towel soaked in cold water with a block of ice or wrapped in a block of ice.
- When part of the limbs are burned, the burned limbs and limbs are in cold ice water for 2 to 5 minutes.
- Soaking can make the pain much less and less swelling.
- As soon as you get burned, you can freeze the ice in the refrigerator by putting your hand in the freezer compartment for a few moments to relieve the pain.
- When immersing a part of the body in cold ice water, be careful not to get frostbite on the soaked burn wound.
- Be careful not to drop your body temperature below normal.
- When first starting such home burn emergency treatment, they receive treatment by phone orders from the hospital emergency room or regular pediatrics department, and according to their instructions, they are taken to the appropriate hospital emergency treatment room, etc., for follow-up treatment.
- Exclude parts of the body that have been burned, especially rings or bracelets worn on fingers or wrists.
- Walking or removing clothing that covers the burned skin wound or body area around it Slight pain caused by burn wounds can be relieved with antipyretic analgesics such as Tylenol or Motrin, and a cold pack of ice water to relieve pain. Depending on the severity of the burn, it is decided whether to take the child to the hospital emergency room or to the regular pediatric and adolescents clinic after performing the first home burn emergency treatment to this extent.
- Call a regular pediatrician and receive appropriate follow-up treatment.
- If necessary, with the help of a medical paramedic, they are transferred to a regular pediatrics department or an emergency medical center in a general hospital. In hospitals, severe pain caused by burn wounds is treated with powerful pain relievers such as Demerol or Morphine.
- In general, depending on the cause and depth of the burn, the width of the burn, the body part, the age, and the overall health condition, whether the parents will continue to provide emergency home burn emergency treatment at home, depending on their ability to provide primary home burn emergency treatment, or at a general hospital. Decide whether to receive treatment in the emergency room, at a regular pediatrics department, or outpatient at a general hospital, or inpatient treatment at a burn center at a general hospital.
- When the width of the surface area of the burn is more than 10% and a burn of 2 degrees or more is injured, it is common to receive treatment in a general hospital as much as possible. Even if the width of the burn is small, more detailed burn treatment is required for the second to third-degree burns on the hand, face, and vulva. Reasons why burns should be treated in a general hospital when you get a thermal burn from the heat on the fire
- Either extinguish the fire by lying on the side of the body wearing the burning clothes on the floor,

- Extinguish the fire by covering it with a wet coat or blanket,
- Either pour water to turn off the fire.
- At the same time as turning off the fire, remove the clothes by hand or cut them off with scissors.
- Depending on the situation, take off your burning clothes in the fastest and most appropriate way.
- When a burn is severely injured, emergency burn treatment is initiated at the accident site according to the instructions of the medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, and regular pediatrics department.
- In the case of minor burns, a parent or a nearby person will provide first aid for burns at home, and a regular pediatrics department or hospital emergency room will quickly decide whether to treat them.
- If parents are unsure of the emergency treatment for a very minor burn, treat it according to the instructions of a regular pediatrician.
- Immediately before taking the child to a regular pediatric clinic or hospital emergency room after a burn injury, first-line burn injury emergency treatment can be performed as follows.
- In the event of a 2 degree burn with a small width or a burn less than 2 degrees, a cold compress can be applied to the thermal wound with an ice water bag or a cold wet towel.
- A cold wet towel means a cold towel made by using a towel soaked in cold water with a block of ice or wrapped in a block of ice.
- When part of the limbs are burned, the burned limbs and limbs are in cold ice water for 2 to 5 minutes.
Soaking can make the pain much less and less swelling. - As soon as your child gets burned, you can get the ice in the refrigerator and you can put the ice bars into water. You can have your child’s burn body parts in the cold water for a few moments to relieve the pain.
- When immersing a part of the body in cold ice water, be careful not to get frostbite on the soaked burn wound.
- Be careful not to drop your body temperature below normal.
- When first starting such home burn emergency treatment, they receive treatment by phone orders from the hospital emergency room or regular pediatrician, and according to their instructions, they are taken to the appropriate hospital emergency treatment room, etc., for follow-up treatment.
- Exclude parts of the body that have been burned, especially rings or bracelets worn on fingers or wrists.
- Removing clothing that covers the burned skin wound or body area around it
- Slight pain caused by burn wounds can be relieved with antipyretic analgesics such as Tylenol or Motrin, and a cold pack of ice water to relieve pain.
- Depending on the severity of the burn, it is decided whether to take the child to the hospital emergency room or to the regular pediatric after performing the first home burn emergency treatment to this extent.
- Call a regular pediatrician and receive appropriate follow-up treatment.
- If necessary, with the help of a medical paramedic, they are transferred to a regular pediatric or an emergency medical center in a general hospital.
- In hospitals, severe pain caused by burn wounds is treated with powerful pain relievers such as Demerol or Morphine.
- In general, depending on the cause and depth of the burn, the width of the burn, the body part, the age, and the overall health condition, whether the parents will continue to provide emergency home burn emergency treatment at home, depending on their ability to provide primary home burn emergency treatment, or at a general hospital.
- Decide whether to receive treatment in the emergency room, at a regular pediatrics department or outpatient at a general hospital, or inpatient treatment at a burn center at a general hospital.
- When the width of the surface area of the burn is more than 10% and a burn of 2 degrees or more is injured, it is common to receive treatment in a general hospital as much as possible.
- Even if the width of the burn is small, more detailed burn treatment is required for the second to third-degree burns on the hand, face, and vulva.
- Reasons why burns should be treated in a general hospital If the 2-3 degree burns on the above-listed body parts are not properly treated, there may be a risk of dysfunction of the burned body parts.
- Burn wounds that are not properly healed are more prone to later scarring, more severe and larger.
- It is easy to have problems after having to undergo plastic surgery. It can cost more to treat scars caused by burn wounds in the future.
- The mental pain and burden of scarring can be far more expensive than the cost of treating a burn right at the time of an injury.
- The younger the burned child is, the more likely it is to develop a bacterial infection in the burn wound.
- As long as the burn wound does not need to be deep and large, it is treated according to the instructions of a regular pediatrician.
- A patient with a deep, large, and severe burn may not eat well, may vomit and have diarrhea, and may sometimes become severely dehydrated.
- When a burn of 2 degrees or more is severely burned, serum and electrolytes in the blood flow through the capillaries of the burn wound to the burn wound, leading to severe dehydration, sometimes reducing the total blood volume, reducing blood pressure, and causing shock.
- Thermal burns to the skin due to the heat of a fire may cause thermal burns in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, lower respiratory tract, or the entire airway, and may cause thermal burns in the lungs, as well as swelling and damage.
- Cover the area with second-degree burns or higher burns as much as possible with sterile gauze and apply cold compresses to your regular pediatrics department or the emergency room of a general hospital for treatment.
- Wrap the baby well with a blanket or swaddle to keep it warm.
- Do not apply ice cubes directly to burn wounds, and do not apply butter, oil, or any kind of ointment to burn wounds without instructions from a doctor.
- Suspect airway thermal burns if you have any of the following symptoms:
- When hot smoke or toxic gas is inhaled in a place where there is a fire
- When you get a burn on your face or neck in a place where there is a fire when your child was in a place where there was a fire and your throat was sore
- When you have difficulty breathing after being rescued from a fire It is very likely that the airway mucosa is burned, the airway mucosa may be swollen, and symptoms of difficulty breathing are common.
- If it is assumed that there is a thermal burn in the airway, treat it as follows.
- First aid must be initiated at the site according to the instructions of a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrician.
- When your child has trouble breathing or is in a coma
- Tilt your neck slightly to the back and side to open the airway to help you breathe well.
- Begin basic CPR treatment as needed.
- If you suspect that the vertebral bone has been fractured, you should not move the child carelessly (refer to ABCD treatment method).
- In other words, if your child cannot breathe well, give artificial respiration with the patient’s mouth to the mouth and nose, or only the mouth of the patient, and when the heart is not beating well or beating weakly, depending on the judgment, the heart You should take them to the hospital emergency room while doing massage and basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation to maintain human life.
- Even at this time, you should know what kind of first aid your child needs to continue, as much as possible by following the emergency room or phone emergency treatment instructions from your regular pediatrician.
- If your chiold breathes incorrectly or has severe breathing difficulties for various reasons, in general hospitals, if necessary, endotracheal breathing therapy or tracheostomy breathing therapy can be performed, and artificial ventilation can be performed through a newly created artificial airway.
- When a thermal burn occurs on the skin of a patient at the site of a fire, it is common for a thermal burn to occur simultaneously in the mucous membrane layers of the upper and lower airways.
- In addition to thermal burns, fractures and other types of trauma can occur at the same time, and the heat can lead to life-threatening burn pneumonia.
- Even if the child, who was rescued from the scene of the fire, seems to have not suffered any burns at first glance, he or she is examined for thermal burns, fractures, or other trauma on the mucous membrane of the airways, and receive appropriate treatment.
- First-degree burns are treated as follows.
- Burn wounds can be treated with a cold or ice pack, briefly soaked in ice cubes, or oral Tylenol to relieve pain.
- Your child doesn’t need to apply an ointment or lotion to your burn that isn’t prescribed by his doctor to make the burn heal faster.
- Treat the wound with a first-degree burn by wrapping it with a dry bandage for 2-3 days or by covering it with sterile gauze.
- Skin wounds with first-degree burns heal well after 7 to 10 days with the epidermis peeling off thinly or not peeling off.
Second-degree burns are treated as follows.
- If your child immerses a burned wound in cold water, such as a first-degree burn, or apply a cold compress with an ice or ice water bag, the pain can be reduced and swelling can be reduced.
- If your child still gets pain, you can use oral Tylenol to relieve pain.
- Blisters caused by second-degree burns should be left undisturbed and treated with observation as much as possible.
- Even when blisters burst and then skin peels off, leave the peeled skin as it is and conduct observational treatment.
- When bacteria become infected with a burn wound, the peeled burn wound can become infected with the bacteria, which can lead to skin infections that do not heal and last a long time. In this case, cut off the peeled skin with sterilizing scissors.
- When there is a 15% or more second-degree burn, or a 2% or a more third-degree burn on the face, limbs, or vulva, it is common to receive hospitalization treatment.
- Bacterial infection can infect a burn wound or spread the bacteria that caused the infectious disease throughout the body, causing sepsis.
- One of Sulfamylon, Silver Sulfadiazine, or Silverden Ointment can be applied to burn wounds of 2 degrees or higher according to the doctor’s prescription.
- Some children and adolescents who have suffered severe burns may develop a burned gastric ulcer, so preventive treatment is required.
- Mental and emotional problems may arise not only for the child with severe burns but also for his parents, siblings.
- Your child should receive appropriate psychological treatment for it.
- Since children can be burned due to pediatric abuse, it should always be noted if the burn is caused by pediatric physical abuse.
- Do not touch the child with electric burns with bare hands, and keep the child away from the electric source that caused the electric shock by a tree that does not conduct electricity.
- Electrical burns, regardless of the severity of the burn, should be treated by a doctor. Ideally, burns as severe as possible should be treated by a burn specialist at a general hospital burn treatment center.
- Severe burns are generally treated by a pediatrician, surgeon, or another burn specialist.
- Burn wounds can be covered and treated with sterile Telfa gauze or other types of sterile gauze that do not adhere well to burn wounds.
- Although it depends on the area and size of the burn wound, cover the burn wound with new sterile gauze every 1-2 days according to the doctor’s instructions, and prevent the burn wound from infections with appropriate oral antibiotics or vascular antibiotics according to the doctor’s prescription.
- Get vaccinated against tetanus vaccine as needed.
- Severe burns are treated with antibiotics, oxygen respiration, basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or advanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation, pain relievers, blood transfusions, intravenous electrolyte solutions, and tetanus vaccination.
- After the burn wound is healed, the scar caused by the burn is treated with plastic surgery at an appropriate time.
- Vitamin D cannot be made normally for skin damaged by 3 degree or more burns or 80% or more burns.
- Therefore, you must consume vitamin D throughout your life, Refer to 37.
- It is of utmost importance to prevent fires and prevent burns by preventing them from being burned by hot water or objects ([Parents should also be at least a half-doctor-Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing)-Volume 2 Prevention of Child and Adolescent Disease Safety Accidents)
9 Law /Rule of nines


- The degree of a burn can be classified according to the depth of the burn and the width of the surface area of the burned skin.
- It is common to indicate the degree of burns in the form of “some percent burns” of “several degrees”.
- Treatment and prognosis are different depending on the severity of the burn.
- The width of the surface area of the burned skin can be calculated with the Lund-Browder charter for children.
- The width of the skin surface area of each part of the body of children and adolescents varies according to age, as shown in Figures 23-26.
- The size of the total skin area of a person’s skin is set at 100%, and the size of the skin area of each part of the body is proportional to the total skin area of the body, and the ratio is set in several types.
- When the total skin area of the body is set to be 100%, and 10% of the skin area is burned, 10% is said to have been burned.
- In clinical practice, there is a method to use to more accurately determine the size of the burned skin area.
The method is referred to as the 9 law.
- The skin surface area of the head and neck of adults and early adolescent children aged 12-14 years old and adolescent children who ate more than 9%
- The skin surface area from one upper arm to the hand is 9%,
- 18% of the skin surface area in front of the torso,
- 18% of the skin surface area behind the torso,
- The skin surface area from one thigh to that foot is 18%,
- The skin surface area of an adult’s vulva (external genital organs) is set at 1%.
- The entire skin surface area is set at 100%. Set the size of the surface area of the burned skin from 1 to 100%.·
표 8. 화상 피부 면적의 크기를 나이에 따라 9법으로 계산하는 법.Table 8. How to calculate the size of the burned skin area according to the age in the 9 raws.
| 신체 부위
나이 Body parts /age |
머리Head | 오른쪽 위팔에서 손까지
From the upper right arm to the hand |
몸통의 앞과 뒤Front and back of the torso | 왼쪽 위팔에서 손까지From the left upper arm to the hand | 오른쪽 허벅다리에서 발까지From the right thigh to the foot | 왼쪽 허벅다리에서 발까지From the left thigh to the foot | 외음부Total skin surface area of the vulva | 전체 피부 표면적(단위=%)
Total skin surface area of the vulva (unit=%) |
| 1~4years old | 19 | 9.5 | 32 | 9.5 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 100 |
| 5~6years old | 15 | 9.5 | 32 | 9.5 | 17 | 17 | 9 | 100 |
| 10~12years old | 13 | 9.5 | 32 | 9.5 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 100 |
| 12~18years old and >18 years old | 9 | 9 | 36 | 9 | 18 | 18 | 1 | 100 |
The size of the surface area of the burned skin is set at 1~100%.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th-21 ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다
www.koreapediatrics.com
Copyright ⓒ 2021 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.