홍역, Measles(Rubeola)
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
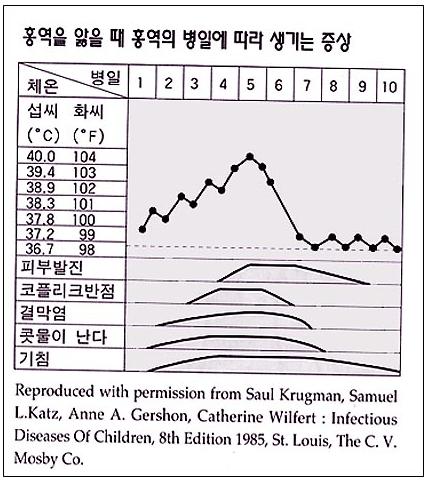
그림 3-14. 병 일에 따른 전형적인 홍역의 증상 징후
Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children,8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz and others
홍역의 원인
-
홍역바이러스 감염으로 생기는 전신 급성 바이러스성 감염병을 홍역이라고 한다.
-
과거에는 누구든 꼭 한 번 알아야 하는 감염 병이었고 아주 흔한 바이러스성 감염병들 중 하나였다.
-
그러나 지금은 홍역 예방접종 백신으로 홍역이 잘 예방될 수 있기 때문에 홍역은 보기 드문 감염병이다.
-
홍역바이러스는 자연 홍역 바이러스와 생 홍역 백신 홍역 바이러스 두 종가 있다.
-
자연 홍역바이러스 감염으로 생긴 홍역을 앓는 환아에서 나온 콧물, 기침, 가래, 비말 속에 들어 있는 자연 홍역바이러스에 면역체가 없는 아이들에게 감염되면 “자연 홍역“(Wild measles) 또는 야생주 홍역(Wild-type measles)이 생길 수 있다.
-
홍역 환아가 기침을 할 때 뱉은 가래침이나 비말이 묻은 가구 등에서 홍역 바이러스에 감염되어도 홍역에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
과거에는 자연 홍역은 겨울철과 이른 봄철에 주로 유행됐었으나 요즘은 계절에 관계없이 사시사철에 발생될 수 있다.
-
권장한 대로 홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 한 번도 접종 받지 않은 아이,
-
홍역 백신으로 권장한 백신 배열대로 접종받지 않은 아이는 자연 홍역에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
드물게 권장한 홍역 백신 예방접종배열대로 다 접종받은 아이가 “비정형 홍역(Atypical measles)”을 앓을 수 있다.
-
아이들이 비정형 홍역에 걸리면 홍역 바이러스 면역체의 정도에 따라 홍역 증상 징후가 다를 수 있다.
-
자연 홍역을 앓을 때에 생길 수 있는 2차 박테리아 감염병의 유무에 따라 증상 징후가 퍽 다르다.
-
요즘에는 영유아들뿐만 아니라 사춘기 아이들과 성인들까지 자연 홍역에 걸려 앓을 수 있다.
-
드물게는 홍역 예방접종 백신을 제대로 받은 아이들이나 성인들도 비정형 홍역에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 받은 사람이 홍역에 걸리면 홍역의 증상 징후가 비정형적으로 나타날 수 있다.
홍역의 증상 징후
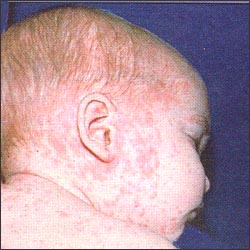
사진 3-16. 홍역 꽃.출처: USA. CDC
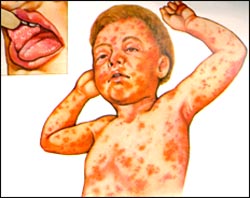
그림 3-15. 홍역으로 생길 수 있는 피부 발진과 입안
점막에 생긴 코플릭 반점 (Koplik Spots)
Used with permission from Health information Service, Merk Sharp & Dome, West Point, PA, USA와 소아가정간호백과
-
홍역 백신으로 접종 받을 수 있는 적령기가 되 기 전 생긴 자연 홍역, 홍역 예방접종 백신을 받을 적령기가 지난 후 홍역 백신으로 어떤 이유로 전혀 접종받지 않아 홍역바이러스 면역체가 체내에 하나도 없어 생긴 홍역을 편의상 “자연 홍역” 또는 “자연 주 홍역”이라 하고,
-
홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 적기에 적절히 받은 후 홍역바이러스 면역체가 체내 불충분해 홍역 면역 기능이 없어 생긴 홍역과 생 홍역 백신에 있는 홍역바이러스로 생긴 홍역을 편의상 “비정형 홍역“이라고 한다.
-
자연 홍역의 증상 징후는 거의 비슷하게 나타난다.
-
비정형 홍역으로 생기는 홍역 증상 징후는 자연 홍역을 앓을 때 생기는 홍역 증상 징후와 다른 점이 많다.
-
기침(Cough), 콧물(Coryza), 결막염(Conjunctivitis)은 자연 홍역의 초기의 주 증상이다. 이 주 증상을 자연홍역의 3Cs 증상이라고 한다. 홍역의 초기에는 이 3Cs 주 증상 징후가 거의 다 있다. 그리고 감기의 증상 징후와 거의 비슷한 다른 증상 징후도 생긴다.
-
때문에 감기나 다른 종류의 바이러스성 상기도염이나 바이러스성 하기도염의 증상 징후와 홍역의 초기의 증상 징후를 확실히 감별하기가 어려운 때도 있다.
-
자연 홍역으로 콧물이 나고 재채기와 기침을 하고 미열 내지 고열이 나는 것이 보통이다.
-
이런 증상 징후가 3~4일 동안 계속되다가 전형적인 홍역 꽃이 나타난다.
-
전형적 홍역 꽃은 분홍색 홍반과 구진이고 그 피부 발진이 귓바퀴 부위 피부에서부터 나기 시작하는 것이 보통이다. 그 다음으로 얼굴, 목, 몸통, 팔, 다리 등으로 점점 확 더 퍼져 난다.
-
결막염이 생겨 눈이 빨갛고 각막염도 생겨 햇빛이나 강한 불빛에 예민해지고 불빛을 보기 싫어한다.
-
미열 내지 고열이 계속 나면서 복통, 설사, 구토와 그 외 다른 여러 증상 징후가 생기며 식욕이 감퇴된다.
-
홍역이 점점 더 진행되면 홍역 꽃은 필연적으로 나타나는 징후의 하나이다. 그러나 홍역 꽃을 더 빨리 나게 하고 더 빨리 없어지게 할 수 있는 약물은 없다.
-
환아를 더 덥게 하든지 더 춥게 하든지, 아니면 어떤 사약이나 묘약으로 홍역을 더 빨리 낫도록 할 수 없다.
-
홍역 꽃이 많이 나거나 적게 났다고 해서 홍역의 예후가 나쁘거나 좋다고 판단할 수 없다. 또 홍역 꽃이 많이 또는 적게 났다고 해서 홍역의 증세가 더 심한 것도 아니고 더 덜한 것도 아니다.
-
홍역이 발병된 후 5~6일 동안 고열이 계속되는 것이 보통이다.
-
피부 발진은 홍역이 발병된 후 3, 4일 이후부터 나기 시작해서 7~10일 지나면 거의 없어진다.
-
홍역의 초기에서부터 기침과 재채기, 콧물이 나기 시작해서 발병된 이후 10일까지 계속되는 것이 보통이다.
-
홍역을 앓는 중 2차 박테리아 감염으로 박테리아 중이염, 박테리아 폐렴, 또는 박테리아 뇌막염이 생길 수 있고 드물게는 홍역 바이러스성 뇌염 등의 합병증이 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 2차 박테리아 감염이나 홍역바이러스성 뇌염 등 합병증이 생기지 않으면 자연 홍역은 자연히 낫는 것이 보통이다.
-
잠복기는 약 8~12일이다.
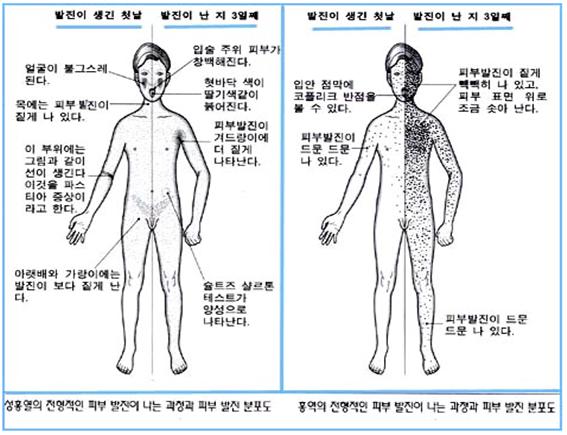
그림 3-17. 성홍열(좌)과 자연 홍역(우)의 전형적인 피부 발진
출처: 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다와
Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children,8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz and others
홍역의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 홍역이 의심되면 피, 대소변, 홍역바이러스 면역체 검사, 홍역바이러스 배양검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
-
자연 홍역의 초기 증상 징후는 감기나 독감 등의 바이러스성 상기도염의 증상 징후와 거의 비슷해 때로는 서로 감별 진단하기가 곤란할 때가 있다.
-
그러나 홍역의 경과가 좀 더 진행되면 홍역의 특이한 여러 증상 징후가 나타나 진단하기가 쉬워진다.
-
즉, 홍역 꽃이 나기 바로 24~48시간 전에 입안 점막에 코플리크 반점(Koplik spots)이 생긴다.
-
코플리크 반점이 난 후 1, 2일쯤에 전형적인 홍역 꽃이 피부에 나타나기 시작한다.
-
코플리크 반점이 나타나면 홍역을 하루 이틀 더 일찍 확진할 수 있고 또 홍역 꽃이 언제쯤 나기 시작할 것이라는 것도 예상할 수 있다.
-
최근에는 거의 모든 아이들에게 홍역 백신으로 기본 접종을 해 주기 때문에 전형적 자연 홍역의 증상 징후를 보기가 힘들어졌다. 홍역 예방접종을 적령에 적절히 접종해 주었으나 홍역바이러스 감염에 대항할 수 있는 홍역 면역체가 충분하게 생기지 않은 아이에게 “비정형 홍역“이 생길 수 있다. 비정형 홍역의 증상 징후와 홍역 예방접종 백신을 한 번도 접종해 주지 않은 아이에게 생긴 “자연 홍역“의 증상 징후가 많이 다르다.
-
이런 이유로 어떤 때는 자연 홍역을 확실히 진단하기가 곤란할 때가 있다. 자연 홍역을 진단하기 위해 환자의 피나 인두에서 채취한 점액으로 홍역 바이러스 배양검사를 해서 진단할 수 있다. 그러나 자연 홍역바이러스를 배양 검사해서 자연 홍역을 진단하려면 14일 정도 걸리고 특수 의료 기술과 설비, 많은 경비가 들기 때문에 이 방법으로는 드물게 진단한다. 그래서 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해 다른 병들과 감별 진단해서 진단할 때가 많다.
-
급성기 홍역 바이러스 혈청검사 결과와 회복기 홍역 바이러스 혈청검사 결과를 비교해서 비교적 쉽게 진단할 수 있다. 이 역시 이런 검사를 하는데도 2주 정도 걸린다.
-
홍역 바이러스 IgM 항체검사, 홍역 바이러스 RNA 검사로 진단할 수 있다. 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 다른 감염병으로 생긴 감염병이 아니라고 진단한 후 역으로 홍역이라고 진단하는 경우도 있다.
홍역의 치료
-
홍역은 급성 전신 바이러스성 감염병의 일종이다.
-
항생제 치료에 치료효력이 없다.
-
홍역을 치료할 수 있는 특효약도 없다.
-
Rivbavirin 이란 항 바이러스제로 치료하면 치료효과가 있다.
-
증상 징후가 심한 홍역환자나 면역체계 이상이 있는 홍역 환자를 치료할 때 Rivbavirin을 사용할 수 있다.
-
그렇지 않으면 대개는 그때그때 생긴 홍역 증상에 대한 대증 치료로 치료한다.
-
홍역을 앓을 때 2차성 박테리아 감염에 의한 합병증이 생기지 않는 한 홍역을 항생제로 치료하지 않는다.
-
열이 나고 보채고 머리가 아프면 타이레놀 등으로 해열 진통시킨다.
-
기침과 콧물이 나면 의사의 처방에 따라 기침 콧물 치료제로 치료할 수 있다.
-
식욕이 떨어지기 때문에 잘 먹지도 않고, 고열로 쉽게 탈수 될 수 있다.
-
이 때는 페디아라이트 등 경구용 포도당 전해질 용액으로 재수화 치료를 하든지 과일즙이나 주스, 고기국물, 보리차, 소다수, 쌀죽 등 자극성이 적은 전 유동음식물 내지 반 유동음식물, 또는 보통 음식물을 조금씩 자주 주어 탈수를 예방하고 탈수가 되어 있으면 그도 치료한다.
-
홍역의 경과와 병세, 환아의 나이 그리고 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 페디아라이트 등 경구용 포도당 전해질용액이나 전 유동 음식물로 재수화 치료를 하다가 반 유동음식물로 바꾸어 주고 점차로 보통 때 먹는 보통 음식물로 바꾸어 준다.
-
합병증이 생겨 있을 때는 합병증에서 생기는 여러 가지의 증상 징후가 자연 홍역의 증상 징후와 함께 나타날 수 있다.
-
이 때 2차 박테리아 감염병이 신체 어느 부위에 있느냐, 그의 정도, 또 그에 따른 증상 징후에 따라 집에서 혹은 병원에 입원하여 항생제와 포도당 전해질용액 혈관주사로 치료할 수 있다.
홍역 환아의 격리
-
홍역 꽃이 나기 4일 전부터 홍역 꽃이 나기 시작한 후 4일이 될 때까지, 총 8일 동안 홍역바이러스가 다른 사람들에게 더 쉽게 감염될 수 있다. 이 기간 동안에는 자연 홍역을 앓는 환자를 다른 사람으로부터 격리시켜야 한다.
-
나이가 어리면 어릴수록 자연 홍역을 더 심하게 앓을 수 있고, 자연 홍역을 앓는 중 2차 박테리아 감염으로 합병증이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
될 수 있는 한 영유아들이 자연 홍역을 앓는 환자와 접촉되지 않도록 격리시켜야 한다.
홍역 환아와 접촉한 경우
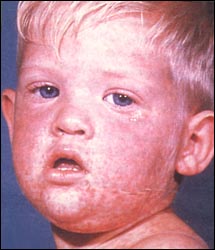
사진 3-18. 홍역을 앓는 아이. 출처–미 CDC
-
한 번도 홍역 백신으로 접종 받지 않아 홍역 바이러스 항체가 없는 아이가 자연 홍역을 앓는 환자와 접촉됐을 때는 의사에게 곧 문의해서 적절하게 예방 조치를 취해야 한다.
-
자연 홍역 환자와 접촉한 이후 약 72시간 이내에 홍역 예방접종 백신으로 접종해 줄 수 있다.
-
환자와 접촉을 한 후 72시간 이내에 홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주면 68% 정도 자연 홍역에 예방된다.
-
과거에 한 번도 홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 받지 않은 돌 이전의 영아가 자연 홍역 환자와 접촉 된지 6일 이내에 체중 매 1kg당 감마 글로불린 0.25cc를 1회 근육주사로 접종받으면 자연 홍역에 예방되든지 자연 홍역에 걸려도 경미하게 앓을 수 있다.
-
돌 이전 영아들이 자연 홍역 환자와 접촉한 바로 후에 권장한 대로 감마 글로불린 근육 주사를 맞은 영아들이나, 홍역 백신 예방접종을 받은 첫돌 이전 영아들은 생후 15개월이 될 때까지 자연 홍역에 걸려 앓지 않으면 이런 치료 조치를 받지 않은 다른 유아들과 마찬가지로 생후 15개월 될 때 홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주는 것이 보통이다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 및 안전사고 예방–홍역 예방접종 참조).
-
홍역 백신으로 한 번도 예방접종을 받지 않은 아이가 첫돌 지난 이후에 자연 홍역 환자와 접촉한 후 72시간 내에 홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주어도 된다.
-
만약 자연 홍역 환자와 접촉한 지 6일이 지나지 않은 경우에는 의사의 처방에 따라 그 아이에게 감마 글로불린 근육주사로 홍역을 예방해 주는 것이 보통이다.
-
감마 글로불린 근육 주사를 맞은 날로부터 5~6개월이 지난 이후에는 홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주어도 된다.
-
감마 글로불린 근육 주사를 맞았다고 해서 홍역이 완전히 예방되는 것이 아니고 자연 홍역에 걸릴 수도 있으나 자연 홍역에 걸려도 경미하게 앓을 수 있다.
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 Recommended immunization schedule for 0~18 year old Americal children in Jan 1st 2021
|
☞ 각 나라에 따라 권장 기본 예방접종 스케줄이 다를 수 있다. |
2014년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2014
| 예방접종 백신 종류/ 예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1차 접종 | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus²(RV) RV-1(2회분 배열 접종); RV-5(3 회분 배열 접종)/ 로타바이러스 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³(DTaP;<7세)/파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | ←1차 접종→ | →2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ←5차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap;7세나 >7세 파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ 히브 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 5 | ←3차 또는 4차 접종 → 각주 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) /폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 세)/소아마비 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 예방 접종 백신 종류/예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||
| Influenza⁸(IIV; LAIV) 1부에게는 2회분,각주 8 /인플루엔자 | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (11V 만)→ | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (II V 또는 LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ 홍역, 풍진, 유행성 이하선염 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /수두 | ←1 차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/A형 간염 | ←2 회분→ 주서 11 | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; 여성에게만 (HPV4; 여성과 남성 에게)/사람유두종 바이러스 감염병 | ←3회 분 배열 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 생후 9 개월이나 그후후. MenACWY-CRM-D는 생후 2개월이나 그 이후. MenACWY-TT는 은 생후 2세나 그 이후. /수막구균 뇌막염과 그 외 감염병
—————————- Meningococcal B 백신에는 MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, Trumenba 백신이 있다. 10세나 그 이상에 접조한다. Bexsero백신은 2회 접종하고 Trumenba 백신은 총 3회 접종한다. 위험도다 없는 사춘기아이들이나 청년들은 16-23세에 접종받는다. 소스: CDC, AAP News 3/2021 |
←주서 13→ | ←1차 접종→ | 추가 접종 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
접종을 권장 하는 나이의 범위, | ||
|
|
건강상 고 위험 군 아이들에게 접종을 권장하는 나이 |
홍역예방 백신(홍역 백신)
-
홍역 백신은 홍역 바이러스를 인공적으로 배양한 후 그 바이러스 균독을 감독시켜 만든 생 홍역바이러스 백신이다.
-
홍역 바이러스 백신으로 홍역 예방접종을 해주면 생 홍역 바이러스 백신 속에 든 생 홍역바이러스 감염으로 인하여 홍역에 걸리지는 않지만 홍역 항체(홍역 면역체)가 체내에 생긴다.
-
그 홍역 항체는 인체 내로 감염되어 들어온 야생 홍역 바이러스를 죽여 자연 홍역 바이러스에 감염되지 않게 된다.
-
홍역 백신에는 홍역만 예방할 수 있는 단가 생 홍역바이러스 백신,
-
홍역백신과 풍진 백신을 동시에 예방접종하는데 쓰는 홍역, 풍진 백신인 MR 백신,
-
홍역, 풍진, 볼거리를 동시에 예방할 수 있는 MMR 종합 백신이 있고,
-
홍역, 풍진, 볼거리(유행성 이하선염)와 수두 이 4가지 바이러스 감염병을 예방하는데 쓰는 MMRV(ProQuad) 종합 백신이 있다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 및 안전사고 예방–홍역 참조).
-
홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 때 MMR 백신으로나 MMRV 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 수 있다.
홍역 백신으로 예방 접종 받을 수 있는 연령
-
일반적으로 생후 12~15개월에 MMR 백신으로 1차 홍역, 픙진, 볼거리를 예방할 수 있는 접종을 받고,
-
생후 4~6세에 2차 홍역, 픙진, 볼거리를 동시 예방할 수 예방접종을 기본적으로 받을 수 있다.
-
예상치 않게 갑자기 홍역이 유행될 때는 생후 6~12개월 된 영아들도 홍역 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 수 있고,
-
또 홍역을 앓는 환자에 근접했었거나 환자와 접촉한 생후 6~12개월 된 영아들도 홍역 예방접종을 의사의 지시에 따라 특별히 접종 받을 수 있다.
-
권장한 나이 보다 조기에 홍역 백신으로 접종 받았을 때, 즉 예를 들면 생후 9개월에 홍역 예방접종 백신으로 접종 받았을 때는 생후 15개월경에 MMR 백신으로 홍역, 유행성 이하선염, 풍진을 예방하는 예방접종을 받으라고 권장한다.
-
이 경우에는 4~6세에 3차 MMR 백신 추가 백신으로 접종 받는 것이 보통이다.
-
그 외 경우 [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 및 안전사고 예방, 2011년 미 CDC, 미소아청소년과 학회 등에서 권장하는 소아 예방접종 스케줄의 표 (1)~(4)를 참조한다.
-
MMRV(ProQuad) 종합 백신으로 홍역, 풍진, 볼거리(유행성 이하선염)와 수두를 예방접종해 줄 때는 ProQuad 백신 용법에 따라 접종한다.
홍역백신 예방 접종방법
-
소아 건강검진을 받고 열이 있나 알아보기 위해 체온을 재고 발열성 감염병이 없고 MMR 백신에 알레르기가 없고 접종 금기 사항이 없으면 MMR 백신으로 상박부나 대퇴부에 예방접종을 받는다.
-
MMR 백신으로 홍역, 볼거리와 풍진만 예방접종해 주는 대신 수두, 홍역, 유행성 이하선염, 풍진을 예방할 수 있는 MMRV 종합 백신 주사를 한번 맞아 예방할 줄 수 있다.
홍역 백신 예방접종 부작용
-
MMR 백신으로 홍역, 볼거리와 풍진 예방접종을 받은 후 1~2주 내에 홍역을 앓을 때 나타날 수 있는 비슷한 피부 발진과 미열이 날 수 있다.
-
MMR 백신을 만드는 과정에 MMR 백신 속에 든 극소량의 항생제나 달걀 단백이나 오리알 단백으로 인해서 알레르기가 생길 수 있다.
-
MMR 백신으로 홍역 예방접종을 받을 때는 풍진과 이하선염 예방접종 백신으로 인하여 부작용도 생길 수 있다.
-
MMRV(ProQuad) 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 때는 그로 인한 부작용이 생길 수 있다.
-
참고로, MMR 백신으로 예방 접종을 받는 것과 소아 자폐증의 원인과는 무관하다.
엠엠알(MMR)백신으로 홍역 예방 접종을 받을 수 없는 경우
① 선천성으로나 후천성으로 면역체 결핍증이 있을 때
② 백혈병이나 악성 종양을 앓을 때
③ 코르티코스테로이드제 치료나 항암제 치료, 또는 방사능 치료를 받을 때
④ 발열성 감염병을 앓을 때
⑤ 예방접종을 받는 날로부터 3개월 이내에 면역 글로불린 주사를 맞았을 때
⑥ 홍역 예방접종 백신을 만드는 과정에서 사용된 달걀 단백이나 오리알 단백, 또는 항생제 등에 알레르기가 있을 때
⑦ 임신 중
⑧ 그 외
다음은 “홍역”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다.
Q&A. 홍역이라고 하는데요.
Q.
전번 문의 드렸던 사람입니다. (9개월 여아) 답변은 감사합니다.
병원에서 홍역이라고 하네요.
그런데 아이가 목이 부어서 항생제를 하루 먹이고 있던 중이거든요.
홍역이라서 항생제를 먹이지 말라고 하셨습니다.
우유 먹고 나서도 목이 아픈지 자꾸만 음음~하면서 소리를 냅니다.
일요일까지는 홍역이 없어질 거라고 하셨는데…
그때까지 목 아픈 거는 당분간 치료할 수 없나요?
답변 기다리겠습니다.
그럼 수고하세요.
A.
승호님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 많은 정보가 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 주신 정보를 참작해 답변을 드립니다.
병원에서 홍역이라고 진단을 받았으면 홍역 치료를 받아야 합니다.
홍역은 바이러스 감염으로 생기는 전신 급성 바이러스성 감염병이고 그에 대한 특효약은 없습니다.
Rivbavirin 항 바이러스제로 치료하면 치료효과가 있습니다.
증상 징후가 심한 홍역환자나 면역체계 이상이 있는 홍역 환아를 치료할 때 Rivbavirin 항 바이러스제로 치료하기도 합니다.
WHO에서 비타민 A를 충분히 섭취하지 않는 아이들이 홍역에 걸리면 비타민 A 200,000 IU를 1회 용량을 경구 복용하라고 권장합니다.
열이 나면 타이레놀로 해열시키고 충분한 수분을 공급하고 전 유동음식물 내지 반 유동음식물로 영양공급을 적절히 해서 홍역을 치료하는 것이 보통입니다.
생후 6~24개월 영유아들이 홍역에 걸리면 2차 박테리아 감염병 등 합병증이 생길 가능성이 더 많기 때문에 때로는 병원 입원 치료를 할 수 있습니다.
목 안이 아픈 증상이나 다른 증상에 관한 치료는 단골 의사에게 전적으로 맡겨 치료받는 것이 가장 좋습니다.
홍역에 더 자세한 정보가 있습니다. 참고하시면 많은 도움이 될 것입니다.
계속 치료하면서 의사와 상담하시기 바랍니다.질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다.이상원 드림
Measles (Rubeola) 홍역
Figure 3-14. Typical symptoms of measles depending on the day of the illness Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children, 8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz and others Causes of measles
• A systemic acute viral infection caused by measles virus infection is called measles.
• In the past, it was an infectious disease that anyone should know once, and it was one of the most common viral infectious diseases.
• But now, measles is a rare infectious disease because the measles vaccination vaccine can prevent measles well.
• There are two types of measles virus: natural measles virus and live measles vaccine measles virus.
• Natural measles virus infection in children who are not immune to the natural measles virus contained in a runny nose, cough, sputum, or droplet from a child with measles caused by natural measles virus infection can lead to “wild measles” or wild-type measles. measles) can occur.
• Measles can also occur when a child with measles coughs and is infected with the measles virus from spit spit or furniture with splashes.
• In the past, natural measles was predominantly prevalent in winter and early spring, but these days it can occur in all seasons regardless of the season.
• Children who have never been vaccinated with the measles vaccine as recommended,
• Children who are not vaccinated in the vaccine arrangement recommended for the measles vaccine can get spontaneous measles.
• Rarely, a child who is fully vaccinated in the recommended measles vaccine vaccination arrangement may develop “atypical measles”. • If children have atypical measles, the symptoms of measles may differ depending on the level of the measles virus immunity.
• Symptoms vary greatly depending on the presence or absence of a secondary bacterial infection that can occur when suffering from spontaneous measles.
• Nowadays, not only infants, but also adolescents and adults can get natural measles.
• Rarely, children and adults who have been properly vaccinated against measles can also get atypical measles.
• If a person vaccinated with the measles vaccine gets measles, the symptoms of measles may be atypical.
Symptoms, signs of measles
Photo 3-16. Measles flowers. Source: USA. CDC
Figure 3-15. Skin rash and mouth that can result from measles Koplik spots on the mucous membrane Used with permission from Health information Service, Merk Sharp & Dome, West Point, PA, USA and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia
• Natural measles that occurred before the age to receive measles vaccine, measles vaccination After the age of age to receive the measles vaccination, the measles vaccine was not vaccinated at all for some reason. Called measles” or “natural main measles”,
• Measles caused by the lack of measles immune function because the measles virus immune system is insufficient after receiving vaccination with the measles vaccine in a timely manner, and measles caused by the measles virus in the live measles vaccine are called “atypical measles” for convenience.
• Symptoms of natural measles are almost the same.
• The signs of measles symptoms caused by atypical measles are different from those of measles symptoms caused by spontaneous measles.
• Cough, runny nose (Coryza), and conjunctivitis are the first major symptoms of spontaneous measles.
This main symptom is called the 3Cs symptom of spontaneous measles. In the early stages of measles, there are almost all of the main symptoms of this 3Cs. And there are other symptoms that are almost identical to those of a cold.
• Because of the cold or other types of viral upper respiratory tract or viral lower respiratory tract symptoms, it is sometimes difficult to reliably discriminate between the symptoms and the initial symptoms of measles.
• Natural measles usually causes a runny nose, sneezing and coughing, and mild to high fever.
• Symptoms of these symptoms persist for 3 to 4 days before typical measles blooms appear.
• Typical measles flowers are pink erythema and papules, and the skin rash usually starts from the skin of the auricle. Then, it spreads more and more to the face, neck, torso, arms, and legs.
• Because of conjunctivitis, the eyes are red, and keratitis also occurs, making you sensitive to sunlight or strong light, and you do not like to see the lights.
• A mild to high fever continues, causing abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and other signs of symptoms, and loss of appetite. • As measles progresses more and more, measles flowers are one of the inevitable signs. However, there are no drugs that can make measles bloom faster and disappear faster.
• No matter how hotter or colder the child is, or with any medicine or potion, the measles cannot be healed faster.
• Measles with a lot or less flowers cannot be judged as having a bad or good prognosis for measles. Also, having more or less measles flowers does not mean that the symptoms of measles are more severe or less.
• It is common for the fever to continue for 5 to 6 days after the onset of measles.
• Skin rash begins to appear 3 to 4 days after the onset of measles, and disappears almost 7 to 10 days after the onset of measles.
• From the beginning of measles, coughing, sneezing, and a runny nose usually begin to last until 10 days after the onset.
• A secondary bacterial infection during measles can lead to bacterial otitis media, bacterial pneumonia, or bacterial meningitis, and in rare cases, complications such as measles viral encephalitis.
• If complications such as secondary bacterial infection or measles viral encephalitis do not occur, natural measles usually heals naturally.
• The incubation period is about 8 to 12 days.
Figure 3-17. Typical skin rash of scarlet fever (left) and natural measles (right) Source: Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia-Parents should also be anti-doctors Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children, 8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz and others
Diagnosis of measles
• If measles is suspected by combining medical history, symptoms, and medical examination findings, it can be diagnosed with blood, feces, measles virus immune body test, and measles virus culture test.
• The initial symptoms of spontaneous measles are similar to those of viral upper respiratory tract infections such as a cold or flu, and sometimes it is difficult to differentiate and diagnose each other.
• However, as the course of measles progresses further, a number of symptoms of measles may appear, making it easier to diagnose.
• That is, Koplik spots appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth 24 to 48 hours before the measles bloom.
• A typical measles flower begins to appear on the skin around 1 or 2 days after the copley spot.
• When Copley spots appear, measles can be confirmed a day or two earlier, and you can expect to see measles bloom at some point.
• In recent years, almost all children are given the basic measles vaccine, making it difficult to see the typical signs of natural measles symptoms. “Atypical measles” can occur in children who have been properly vaccinated against the measles virus, but do not have enough measles immune systems to fight the measles virus infection.
Symptoms of atypical measles are very different from those of “natural measles” in a child who has never been vaccinated against the measles vaccine.
• For this reason, it is sometimes difficult to reliably diagnose natural measles.
To diagnose natural measles, it can be diagnosed by performing a measles virus culture test with mucus collected from the patient’s blood or pharynx.
However, it takes about 14 days to diagnose natural measles by culture testing the natural measles virus, and it is rarely diagnosed with this method because it requires special medical technology, equipment, and a lot of expenses.
Therefore, it is often diagnosed by differential diagnosis from other diseases by synthesizing the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings.
• It can be diagnosed relatively easily by comparing the results of the acute measles virus serologic test and the convalescent measles virus serologic test results. It also takes about two weeks to do this test.
• Measles virus IgM antibody test, measles virus RNA test can be diagnosed. In some cases, it is diagnosed as measles after the diagnosis is not caused by other infectious diseases by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, symptoms, and examination findings.
Measles treatment
• Measles is a type of acute systemic viral infectious disease.
• There is no therapeutic effect on antibiotic treatment.
• There are no special drugs that can cure measles.
• Treatment with an antiviral drug called Rivbavirin has a therapeutic effect.
• Rivbavirin may be used to treat measles patients with severe symptomatic symptoms or measles patients with immune system abnormalities.
• Otherwise, it is usually treated with symptomatic treatment for symptoms of measles that have occurred on the fly.
• Measles is not treated with antibiotics unless complications from a secondary bacterial infection occur when you have measles.
• If you have a fever, fluff, and head ache, use Tylenol to relieve fever.
• Cough and runny nose can be treated with a cough runny nose remedy as prescribed by your doctor.
• You don’t eat well because you lose your appetite, and you can easily become dehydrated due to high fever.
• In this case, rehydration is performed with oral glucose electrolyte solutions such as Pedialite, or whole or semi-fluid foods with little irritation such as fruit juice, juice, meat broth, barley tea, soda water, rice porridge, etc.
If you are dehydrated, treat him as well.
• Depending on the course and condition of measles, the age of the child, and the presence or absence of complications, rehydration treatment with oral glucose electrolyte solutions such as Pedialite or whole-fluid foods, then change them to semi-fluid foods and gradually change them to regular foods that you eat normally.
• When complications arise, a number of symptoms arising from the complication may appear along with the symptoms of spontaneous measles.
• At this time, depending on where the secondary bacterial infectious disease is located in the body, its severity, and the symptoms associated with it, it can be treated at home or in a hospital with an intravenous injection of antibiotics and glucose electrolyte solution. Isolation of children with measles
• Measles virus can be more susceptible to other people for a total of 8 days, from 4 days before measles blooms to 4 days after measles blooms.
During this period, patients with spontaneous measles should be isolated from others.
• The younger you are, the more severe you are with natural measles, and the more complications you have from secondary bacterial infections while suffering from natural measles.
• To the extent possible, infants and toddlers should be isolated from contact with patients with natural measles.
In case of contact with a child with measles

Photo 3-18. A child suffering from measles. Source-US CDC
• If a child who has never been vaccinated against the measles vaccine and does not have measles virus antibodies has come into contact with a patient with spontaneous measles, they should contact their doctor immediately and take appropriate preventive measures.
• The measles vaccine can be given within about 72 hours after contact with a natural measles patient.
• If vaccinated with measles vaccine within 72 hours after contact with a patient, about 68% of natural measles are prevented.
• If infants before stones who have never been vaccinated with the measles vaccine in the past receive a single intramuscular injection of 0.25 cc of gamma globulin per 1 kg of body weight within 6 days of contact with a natural measles patient, it will be prevented from natural measles or natural measles.
You can get mildly ill even if you get sick.
• Infants who received intramuscular injections of gamma globulin as recommended immediately after contact with patients with natural measles pre-dolescence, or pre-first-dolescence infants vaccinated with the measles vaccine, are treated with this treatment if they do not develop natural measles until 15 months of age.
Like other infants who have not been treated, it is common to receive measles vaccine vaccination at 15 months of age www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 2 Prevention of pediatric and adolescent diseases and safety accidents. -See Measles Vaccination).
• A child who has never been vaccinated with the measles vaccine may be vaccinated with the measles vaccine within 72 hours of contact with a natural measles patient after the first birthday.
• If six days have not passed since contact with a natural measles patient, it is common to prevent measles with intramuscular gamma globulin injection to the child according to the doctor’s prescription. • You may be vaccinated with the measles vaccine 5 to 6 months after the intramuscular injection of gamma globulin has passed.
• Having an intramuscular injection of gamma globulin does not completely prevent measles, and you can get spontaneous measles, but you can get mildly affected by spontaneous measles.
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2021,
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 1 5 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19~23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | |||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←←3rd vaccination→→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus² (RV) RV-1 (two batch sequence inoculation); RV-5 (3-batch sequence vaccination)/ Rotavirus infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³ (DTaP; <7 years old)/tetanus, diphtheria, pertussi | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ←5th vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap; 7 years old> 7 years old tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ Hib infectious disease | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 5 | ←3rd or 4th vaccination→ Footnote 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/Pneumococcal infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) / Streptococcal pneumonia infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 years old)/Polio | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 2 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 15 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19-23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | ||
| Influenza⁸ (IIV; LAIV) for 1 copy, 2 servings, footnote 8 / Influenza | ←Get inoculated every year (11V 만)→ | ←Get inoculated every year(II V or LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ Measles, Rubella, Mumps | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /Varicella | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/Hepatitis A | ←2 doses→ | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; women only (HPV4; women and men))/Human papillomavirus infectious disease | ←3rd vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 9 months or later. MenACWY-CRM-D is 2 months or later. MenACWY-TT is 2 years old or later. / Meningococcal meningitis and other infectious diseases) —————————- Meningococcal B vaccines include MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, and Trumenba vaccines. We touch on 10 years of age or older. The Bexsero vaccine is inoculated twice and the Trumenba vaccine has inoculated a total of three times. Adolescents and young adults with no risk are vaccinated at age 16-23. Source: CDC, AAP News 3/2021
——————Beginning in May 2021, adolescents aged 12 to 15 years old can receive the COVID-19 vaccination twice. |
←1st vaccination→ | Booster vaccination | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
The age range for which vaccination is recommended, | ||
|
|
Age recommending vaccination for children in the high risk group |
Recommended immunization schedule for 0-18 year old Americal children in Jan 1st 2021
☞ The recommended basic vaccination schedule may differ depending on each country.Source: CDC, AAP News 3/2021
Measles prevention vaccine (measles vaccine)
• Measles vaccine is a live measles virus vaccine created by artificially culturing the measles virus and then supervising the viral poison.
• If you are vaccinated against measles with the measles virus vaccine, you will not get measles due to the live measles virus infection contained in the live measles virus vaccine, but measles antibodies (measles immune body) will be produced in your body.
• The measles antibody kills the wild measles virus that has been infected and enters the human body, thus preventing infection with the natural measles virus.
• Measles vaccine includes a single-cost live measles virus vaccine that can only prevent measles,
• MR vaccine, a measles and rubella vaccine, used to immunize both measles and rubella vaccines at the same time,
• There is a comprehensive MMR vaccine that can prevent measles, rubella and mumps at the same time,
• There is a comprehensive vaccine for MMRV (ProQuad), which is used to prevent measles, rubella, mumps (mumps) and chickenpox. And safety accident prevention-measles).
• When you are vaccinated with the measles vaccine, you can be vaccinated with either the MMR vaccine or the MMRV vaccine.
Age to be vaccinated against the measles vaccine
• In general, at 12 to 15 months of age, the first dose of the MMR vaccine is given to prevent measles, sores, and mumps.
• At the age of 4-6 years old, you can get a basic vaccination that can prevent 2nd measles, sores, and mumps at the same time.
• When a measles outbreak unexpectedly occurs, infants 6 to 12 months old can also be vaccinated with the measles vaccine.
• In addition, infants aged 6 to 12 months who have been in close proximity to or have been in contact with a patient suffering from measles can also receive the measles vaccination as directed by a doctor.
• If you were vaccinated with the measles vaccine earlier than the recommended age, for example, when you were vaccinated with the measles vaccination at 9 months of age, you should be vaccinated against measles, mumps and rubella with the MMR vaccine at around 15 months of age. It is recommended to receive.
• In this case, it is common to get the 3rd MMR vaccine supplemental vaccine at the age of 4-6 years old.
• In other cases, www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 2 Prevention of pediatric and adolescent diseases and safety accidents, Table of pediatric vaccination schedules recommended by the US CDC in 2011 and the Academy of Small Children and Adolescents (1 Refer to )~(4).
• When vaccinating measles, rubella, mumps (mumps) and chickenpox as a comprehensive MMRV (ProQuad) vaccine, follow the ProQuad vaccine method.
Measles vaccine vaccination method
• If you have a child’s body temperature to check for fever and have a fever, do not have a febrile infectious disease, are not allergic to MMR vaccine, and there are no contraindications to vaccination, you will be vaccinated at the upper arm or thigh with MMR vaccine.
• Instead of vaccinating only measles, mumps, and rubella with the MMR vaccine, you can get a single injection of the MMRV comprehensive vaccine that can prevent chickenpox, measles, mumps, and rubella.
Measles Vaccination Side Effects
• Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination with the MMR vaccine, you may develop a similar skin rash and mild fever that can occur with measles within 1 to 2 weeks.
• In the process of making the MMR vaccine, allergies may occur due to trace amounts of antibiotics or egg protein or duck egg protein contained in the MMR vaccine.
• Measles vaccination with the MMR vaccine may cause side effects from the rubella and mumps vaccination.
• When vaccinated with the MMRV (ProQuad) vaccine, side effects may occur. • For reference, being vaccinated with the MMR vaccine is not related to the cause of childhood autism. If you cannot receive measles vaccination with the MMR vaccine
① Congenital or acquired immune system deficiency
② When suffering from leukemia or malignant tumors
③ When receiving corticosteroid therapy, anticancer therapy, or radiation therapy ④ When suffering from a febrile infectious disease
⑤ When you receive an injection of immunoglobulin within 3 months from the date of vaccination
⑥ When you are allergic to egg protein, duck egg protein, or antibiotics used in the process of making the measles vaccination vaccine
⑦ during pregnancy
⑧ Others
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer on “measles”.
Q&A.
It’s called measles.
Q.
This is the person I contacted the previous time. (9 months girl) Thank you for the answer. The hospital says it’s measles. But my child has a swollen throat and is taking antibiotics for a day. She told me not to take antibiotics because she had measles.
Even after eating milk, it keeps making noises and makes noises as if it’s a sore throat. He said the measles would be gone by Sunday, but… Until then, can’t the sore throat be cured for the time being? Answers I’ll wait. Then, have a good time at work.
A.
Seungho Good morning. Thank you for asking. If you have a lot of information, such as your child’s age, gender, past and family history, medical examination findings, and clinical test results, we can give you a better answer.
We will respond by taking the information you provided into consideration. If you have been diagnosed with measles at the hospital, you will need treatment for measles. Measles is a systemic acute viral infectious disease caused by viral infection, and there is no specific drug for it. Treatment with Rivbavirin antiviral drugs has a therapeutic effect. Rivbavirin antiviral drugs are sometimes used to treat patients with measles with severe symptoms or with measles with immune system abnormalities.
WHO recommends taking a single dose of 200,000 IU of vitamin A by mouth if children who do not get enough vitamin A get measles.
When you have a fever, it is common to treat measles by decomposing with Tylenol, supplying sufficient moisture, and supplying adequate nutrition with whole or semi-fluid foods. Infants 6 to 24 months of age can sometimes be hospitalized because they are more likely to develop complications such as secondary bacterial infections when they get measles. Treatment for sore throat or other symptoms is best left to a regular doctor for treatment. Th
ere is more information on measles.
It will be very helpful if you refer to it. Please consult your doctor as you continue treatment, and visit again if you have more questions. Thank you, Lee Sang-won.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th – 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”