혈뇨, 육안적 혈뇨, 현미경적 혈뇨, 잠재 혈뇨, 무해성 혈뇨 Hematuria, Gross hematuria, Microscopic hematuria, Occult hematuria, Benign hematuria
혈뇨의 종류
-
피가 섞여 있는 소변을 혈뇨라고 한다.
-
육안으로 쉽게 보고 알 수 있을 정도 피가 소변에 많이 섞여 있는 혈뇨를 육안적 혈뇨(Gross hematuria)라 하고,
-
소변에 피가 섞여 있지만 육안으로 볼 수 없을 정도의 피가 극소량 소변에 섞여 있을 때의 혈뇨를 잠재 혈뇨(Occult hematuria/뇨 잠혈/잠혈성 혈뇨),
-
현미경 검사로 소변에 피가 있다고 알 수 있는 혈뇨를 현미경적 혈뇨(Microscpic hematuria)라고 한다.
-
현미경 검사로 소변을 들여다보면 건강한 소아청소년들이나 성인들의 소변에 적혈구가 몇 개 정도 있는 것은 정상이다.
-
소변에 피가 극소량 섞여 있는 잠재 혈뇨의 색은 정상 소변색과 동등한 것이 보통이다.
-
그러나 소변에 피가 많이 섞여 있는 육안적 혈뇨의 색은 빨갛거나, 커피색 같이 적갈색일 수 있다.
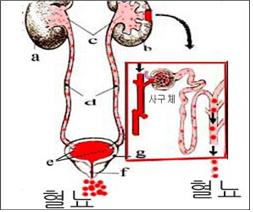
그림 1-14. 신장, 비뇨계 해부도
a-우 신장,
b-좌 신장,
c-신우,
d-요관,
e-요관구,
f-요도,
g-방광
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD. FAAP
출처 및 참조문헌, 피가 소변에 나올 때
혈뇨의 원인
-
혈뇨는 병이 아니라 하나의 징후이다. 다음과 같은 경우에 혈뇨가 있을 수 있다.
-
바이러스 상기도 감염병이나 바이러스 위장염 등을 앓을 때
-
박테리아 상기도 감염병이나 박테리아 위장염을 앓을 때
-
심한 육체적 운동을 하는 중 또는 하고 난 후
-
신장·요관·방광·요도·요도구 또는 그 외 외생식기에 외상을 입을 때
-
요로 감염이 있을 때
-
신장 요로에 종양이 있을 때
-
전신 출혈성 질환이 있을 때
-
급성 사구체 신염이 있을 때
-
무해성 혈뇨가 있을 때
-
혈중 고 칼슘증이 있을 때
-
비뇨기계 우유 알레르기가 생겼을 때
-
외 요도구가 물리적 자극을 받았을 때
-
낭포성 신장병이 있을 때
-
신장 정맥 혈전이 있을 때
-
부신 출혈이 있을 때
-
그 외
붉은 기저귀 증후군
- 세라티아 마르세센스균 비뇨기 감염병(Serratia marcescens urinary tract infection)이 있을 때 소변에 피가 없는데 그 소변이 기저귀에 묻으면 기저귀에 붉은 반점이 나타날 수 있다.
- 이것을 붉은 기저귀 증후군이라 한다.
- 여러 가지 혈뇨 원인들 중 가장 흔한 소아청소년 혈뇨의 원인은 요로 감염이다.
Hematuria, gross hematuria, microscopic hematuria, latent hematuria, harmless hematuria 혈뇨, 육안적 혈뇨, 현미경적 혈뇨, 잠재 혈뇨, 무해성 혈뇨
Hematuria, Gross hematuria, Microscopic hematuria, Occult hematuria, Benign hematuria
Type of hematuria
• Urine mixed with blood is called hematuria.
• Hematuria in which urine contains a lot of blood that can be easily seen with the naked eye is called gross hematuria,
• Hematuria when urine contains blood but a very small amount of blood that cannot be seen by the naked eye is called occult hematuria,
• Hematuria, which can be determined by microscopic examination, that there is blood in the urine is called microscpic hematuria.
• It is normal for healthy children and adults to have a few red blood cells in the urine of healthy children and adolescents if they look in the urine under a microscopic examination.
• The color of latent hematuria, which contains a very small amount of blood in the urine, is usually the same as that of normal urine.
• However, the color of gross hematuria, with a lot of blood in the urine, may be red or reddish-brown, such as coffee.

Figure 1-14. Kidney, urinary system anatomy a-right kidney, b-left kidney, c-Shinwoo, d-ureter, e-ureter, f-urethra, g-bladder Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD. FAAP Sources and references, when blood comes in urine
Causes of hematuria
• Hematuria is not an illness, but a sign. Hematuria may be present in the following cases:
• When suffering from viral upper respiratory infections or viral gastroenteritis
• When you have a bacterial upper respiratory infection or bacterial gastroenteritis
• During or after doing heavy physical exercise
• When trauma to the kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra, urethra, or other exogenous organs
• When you have a urinary tract infection
• When there is a tumor in the kidney urinary tract
• When you have a systemic hemorrhagic disease
• When you have acute glomerulonephritis
• When you have harmless hematuria
• When you have hypercalcemia in the blood
• When you have a milk allergy in the urinary system
• When the external urinary device is physically stimulated
• When you have cystic kidney disease
• When there is a blood clot in the renal vein
• When you have adrenal bleeding
• etc
Red diaper syndrome
• When you have a Serratia marcescens urinary tract infection, there is no blood in your urine, but if the urine gets on the diaper, red spots may appear on the diaper.
• This is called red diaper syndrome.
• Urinary tract infections are the most common cause of hematuria in children and adolescents among several causes.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”