현기증(어지러움) Dizziness (Vertigo)
현기증(어지러움)의 개요
- 자기의 주위에 있는 것들이 자기를 중심으로 빙빙 돌아가는 느낌을 갖는 것을 어지러움 또는 현기증이라 한다.
그림171. 자기의 주위에 있는 것들이 자기를 중심으로 빙빙 돌아가는 느낌이 드는 증상을 어지러움 또는 현기증이라 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
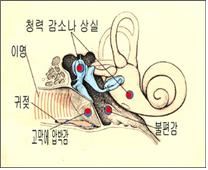
그림172. 귀에 이런 증상과 징후가 있으면 중이나 내이에 생긴 병으로 어지러운 병이 생기는지 알아본다.
Differential diagnosis of Vertigo. Hospital Medicine. Octover 1970
-
현기증이 생기면 때로는 몸이 위로 아래로 올라갔다 내려왔다 하는 느낌, 좌우로 움직이는 느낌, 좌우로 위 아래로 조금 움직이는 느낌이 있을 수 있고, 또 경미한 두통이 있을 수 있다.
-
현기증이 갑자기 올 수도 있고 서서히 올 수도 있다. 몇 초, 몇 분, 몇 시간, 몇 주, 또는 몇 년 동안 있을 수 있다.
-
머리를 좌우로나 한 쪽으로 움직이면 더 어지러울 수 있고,
-
또는 서거나 앉거나 눌 때 어지러움이 더 할 수도 있고 덜 할 수도 있다.
-
구기, 구토, 실신, 이명, 또는 경련도 동반할 수 있다.
-
어지러움은 어떤 병이 아니고 증상이다.
-
어지러움은 소아들보다 성인들에게 더 흔히 생기는 증상이다.
-
그러나 어지러움은 일반적으로 성인들에게 생기는 만큼 소아들에게도 흔히 생길 수 있다.
-
특히 영유아들에게 어지러움이 생겨도 그들은 어려서 그런 어지럼증이 있다는 것을 부모들에게 말로 잘 표현할 수 없기 때문에 영유아들에게 어지러움이 생기고 있는지 잘 모르고 지낼 수 있다.
-
어지러움은 신체에 어떤 기질적 병이 없이 생겼다가 자연히 회복되는 양성 급성 현기증 즉 양성 현기증 어떤 병으로 생기는 병적 현기증으로 나눌 수 있다.
-
양성 급성 현기증 참조.
현기증(어지러움)이 원인
-
뇌막염, 뇌종양, 뇌농양, 뇌염 등 중추신경계 감염병
-
뇌진탕, 두개골 골절, 특히 측두 골절 등 두부 외상, 전정 소뇌 보행 실조증, 고 뇌압증 등 중추신경계 이상
-
다발성 경과증
-
내이 이상, 전정 신경염, 급성 중이염, 만성 삼출성 중이염, 내이 외상, 메니에르 병, 미로염, 내이 출혈 등 귀 이상
-
체위 변경성 어지러움
-
대상포진 등 감염병
-
알코올, 피임약, 정신 안정제, 아스피린 등 약물 중독이나 부작용,
-
부정맥, 고혈압 등 심장혈관계 이상
-
저혈당증, 갑상선 이상, 그 외 내분비 이상
-
빈혈
-
스트레스 등 정신적 문제
-
양성 급성 현기증
-
원인 불명
-
두통을 앓는 어떤 아이에게는 두통의 증상은 거의 나타나지 않고 어지러운 증상만 주로 나타날 수 있고 두통과 어지러운 증상이 동시 나타날 수 있다.
-
그 외
현기증(어지러움) 진단
-
과거, 현재 가족의 병력과 증상 징후 진찰 소견 등을 종합해서 진단할 수 있다.
-
필요에 따라 뇌 MRI 검사, 내이 MRI 검사, CBC 피 검사, 소변검사, 뇌파검사, 심전도검사 등으로 진단하는데 도움을 얻는다.
-
어지러움이 심하거나 계속되면 소아청소년과 전문의, 이비인후과 전문의, 소아 신경내과 전문의의 진단을 받을 수 있다.
현기증(어지러움) 치료
-
원인에 따라 치료한다.
Dizziness (Vertigo) 현기증(어지러움)
Overview of dizziness (dizziness)
• Feeling that things around you revolve around you is called dizziness or dizziness.

Figure 171. A symptom in which you feel that things around you revolve around you is called dizziness or dizziness. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 172. If you have any of these symptoms and signs in your ears, look for dizziness due to a disease in your middle or inner ear. Differential diagnosis of Vertigo. Hospital Medicine. Octover 1970
• If you have dizziness, you may sometimes feel that your body is moving up and down, moving from side to side, moving up and down from side to side, and you may also have a mild headache.
• Dizziness may come suddenly or slowly. It can be in seconds, minutes, hours, weeks, or years.
• Moving your head from side to side or to one side can make you more dizzy,
• Or you may feel more or less dizzy when standing, sitting, or pressing.
• May also accompany vomiting, vomiting, fainting, tinnitus, or convulsions.
• Dizziness is not a disease, it is a symptom.
• Dizziness is a more common symptom in adults than in children.
• However, dizziness is as common in children as it usually occurs in adults.
• Even if dizziness occurs especially in infants and toddlers, they may not know if dizziness is occurring in infants because they are young and cannot communicate well to their parents that they have such dizziness.
• Dizziness can be divided into benign acute vertigo, that is, benign vertigo, which occurs without any organic ailments in the body and recovers spontaneously, or pathological vertigo caused by certain diseases.
• See benign acute vertigo.
The cause of Dizziness (dizziness)
• Infectious diseases of the central nervous system such as meningitis, brain tumor, brain abscess, encephalitis
• Central nervous system abnormalities such as concussion, skull fracture, head trauma, especially temporal fracture, vestibular cerebellar ataxia, and hypertension
• Multiple progression
• Ear abnormalities such as inner ear abnormalities, vestibular neuritis, acute otitis media, chronic exudative otitis media, inner ear trauma, Meniere’s disease, labyrinthitis, inner ear bleeding
• Postural change dizziness
• Infectious diseases such as shingles
• Drug addiction or side effects, such as alcohol, birth control pills, mental tranquilizers, and aspirin,
• Cardiovascular abnormalities such as arrhythmia and high blood pressure
• Hypoglycemia, thyroid abnormalities, and other endocrine abnormalities
• anemia
• Mental problems such as stress
• Benign acute dizziness
• Unknown cause
• In some children with headaches, symptoms of headache are rarely seen, only dizziness may be present, and headache and dizziness may occur simultaneously.
• etc
Diagnosis of dizziness (dizziness)
• It is possible to comprehensively diagnose the past and present family medical history, symptoms, symptoms, examination findings, etc.
• If necessary, get help in diagnosing brain MRI, inner ear MRI, CBC blood test, urine test, electroencephalogram, electrocardiogram, etc.
• If dizziness is severe or persists, you may be diagnosed with a pediatrician, an otolaryngologist, or a pediatric neurologist.
Dizziness treatment
• Treat according to the cause.
출처와 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Handbook of Pediatric Neurology, Katherine B. Sims, MD
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”