헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병, Haemophilus influenzae infections
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Chapter 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염의 개요와 원인
-
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균(Haemophilus Influenzae)은 일종의 박테리아이다.
-
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균은 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균과 비 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균이 있다. 즉, B형 인플루엔자균은 B 혈청 형과 비(非) B 혈청형으로 분류된다.
-
이 두 가지 형의 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균은 사람에게 감염되어 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병을 일으킨다.
-
특히 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균에 감염되면 소아청소년들에서 여러 종류의 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
B형 인플루엔자균을 편의상 히브균(HIb)이라고도 칭한다.
-
많은 사람들이 B형 인플루엔자균과 독감의 원인이 되는 인플루엔자바이러스를 혼동한다. 다시 설명하면 독감(인플루엔자)은 인플루엔자바이러스 감염으로 생긴 바이러스성 감염병이다.
-
B형 인플루엔자균(Hib)은 건강한 사람들의 상기도의 점막층에서 정상적으로 발견될 수 있는 상존 세균이다.
-
B형 인플루엔자균 감염병의 거의가 B형 인플루엔자균 감염병을 앓는 사람들과 근접하거나 접촉될 때 감염될 수 있고 그 사람들이 B형 인플루엔자균을 다른 사람들에게 감염시킬 수 있다.
-
그 두 종류의 혈청형 중, B형 인플루엔자균은 특히, 영유아들에게 더 잘 감염되어 생명에 위험한 여러 가지의 히브 감염병을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
B형 인플루엔자균 감염으로 중이염, 패혈증, 축농증, 폐렴 그와 다른 B형 인플루엔자균 감염병들이 생길 수 있다. 봉소염(봉와염), 급성 후두개염으로 인해서 생기는 크루프 참조.)
-
B형 인플루엔자균은 의료인들에게는 많이 알려진 무서운 세균인데 비 의료인들에게는 잘 알려지지 않은 박테리아이다.
-
B형 인플루엔자균과 그 박테리아 감염으로 생기는 감염병에 대하여 부모들도 알아 둘 필요가 있다.
-
B형 인플루엔자균 감염병을 히브 백신으로 예방해 주기 전에는 B형 인플루엔자균은 신생아기 이후부터 3세 이전 영유아들에게 생기는 박테리아 뇌막염의 주원인이 되는 세균이었고, 패혈증, 후두개염, 폐렴, 늑막염, 복막염, 근육염, 관절염, 골수염, 심낭염, 중이염, 부비동염, 결막염, 안와 주위 봉소염 등의 소아청소년 감염병의 주 원인되는 세균이었다.
-
특히, 이 세균은 3∼6세 이전 학령기 전 유아들에게 여러 가지 감염병을 일으킬 수 있었다.
-
요즘에도 영유아들을 비롯해 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들, 성인들까지 이 세균에 감염되어 생명을 위협할 정도의 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
잠복기는 확실히 모른다.
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병의 증상 징후 진단
-
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균(히브균 Hib bacteria)이 신체의 어느 부위에 감염되어 그로 인해 어떤 종류의 감염병이 생겼는지에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
자세한 증상 징후는 “B형 인플루엔자균 감염으로 생긴 각종 감염병“의 각 항을 참조.
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 이 세균 감염으로 생긴 감염병의 병소에서 채취한 피나 고름 등 피검 물 또는 체액 등 피검 물로 세균검사를 하여 이 병을 확진하고 치료하는 것이 이상적 진단 치료 방법이다.
사진 2-71. CBC, 혈액 전해질 농도 검사, 혈액 세균 배양 검사 등을 필요에 따라 해 진단한다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균이 B혈청형에 속하는지 또는 비 B혈청형에 속하는지에 따라 치료 방법에 차이가 다소 난다.
-
또 그때그때 생긴 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병을 일으킨 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균의 종류에 따라 그 세균을 죽일 수 있는 항생제의 선택이 다를 수 있다.
-
따라서 항생제로 치료하기 전 가능한 한 어떤 종류의 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균에 의해 히브 감염병이 생겼는지 알아보기 위해 감염병의 병소에서 피검 물을 채취한 후 바로 경험에 의해 적절한 항생제로 치료를 시작하는 것이 이상적 치료이다.
-
피검 물로 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균 배양검사, 세균 항생제 감수성 검사를 해보고 그 세균 항생제 감수성 검사 결과에 따라 적절한 항생제를 다시 선택해서 이 세균 감염에 의한 감염병을 치료하는 것이 이상적 치료 방법이다.
-
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병의 병소가 신체 어느 국소에 있는지에 따라 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사나 세균 배양 검사를 할 피검 물을 채취하는 방법이 다르다.
-
피, 뇌척수액, 소변 등에서 피검물을 조금 채취해서 세균 배양 검사를 하고 필요에 따라 가슴 X선 사진, 초음파 사진, 에코카디오그람 등 적절한 여러 가지 검사로 진단한다.
-
여러 가지 이유로 항시 이런 식의 진단 치료가 가능할 수 없는 때도 있다.
-
Slide agglutination serotyping (SAST) 검사나 polymerase chain reaction (PCR)로도 진단할 수 있다.
-
무균 뇌막염 (Aseptic meningitis)및 박테리아(성) 뇌막염(Bacterial meningitis)감별진단.
-
무균 뇌막염과 박테리아(성) 뇌막염의 감별진단(Differential diagnosis of aseptic meningitis and bacterial meningitis).
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병의 치료
-
이 히브 세균이 신체 어느 부위에 감염되어 어떤 종류의 감염병을 일으켰느냐에 따라 치료 방법이 다르다.
-
즉, B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염에 의해서 생긴 뇌막염, 폐렴, 패혈증, 관절염, 안와 주위 봉소염, 후두개염 등의 치료 방법이 다르다.
-
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 뇌막염이나 후두개염 등 생명을 위협받을 수 있는 아주 위중한 B 형헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병을 앓을 때는 응급으로 집중 치료를 받아야 한다. 임상 경험에 토대를 두고 선택한 Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, 클로람페니콜, 앰피실린, Meropenem, 또는 그 외 다른 항생제로 치료할 수 있다.
-
때로는 두세 가지의 항생제 혈관주사로 응급 치료를 시작 한다.
-
그 다음, 세균 항생제 감수성 검사 결과에 따라 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병 치료에 가장 알 맞는 한두 가지의 항생제를 선택해 10일이나 그 이상 동안 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
-
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 뇌막염을 항생제로 치료하면서 Dexamethasone제로 치료한다.
-
히브 세균 감염으로 생긴 경미한 중이염이나 경미한 결막염, 또는 경미한 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병은 의사의 처방에 따라 아목시실린이나 Ceclor, 그 외 다른 적절한 항생제로 10일 정도 가정에서 의사의 지시에 따라 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
-
참조 문헌
Red book 29th edition 2012,
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
Others
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병 환자와 접촉한 경우
-
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 뇌막염이나 후두개염 등 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 위중한 감염병을 앓는 환자에 근접했거나 접촉됐던 사람에게 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병이 발병되는지 조심해서 관찰해야 한다.
-
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병을 앓는 환자와 접촉된 사람에게는 의사의 처방에 따라 리팜핀이나 다른 종류의 항생제로 이 히브 세균에 감염되지 않도록 예방적 치료를 해야 한다.
-
더 자세한 예방법은 표1~4 참조.
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병의 예방
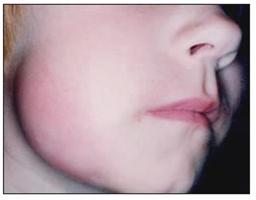
사진 2-72. B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 좌 얼굴 봉소염.
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균(HIB, 히브균) 감염에 의해 뇌막염, 중이염, 균혈증, 관절염, 봉소염 등이 생길 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 및 안전사고 예방-2011년 1월 미 소아청소년과 학회에서 권장하는 0~6세 소아 감염병 예방접종 스케줄-1과 스케줄 2, 3, 4 및 표 1~4 참조.
-
1985년에 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균에 의한 감염병을 예방하는 히브 백신이 처음 개발되었다. 그 후 생후 2개월부터 7세 되기 전까지 모든 아이들에게 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염에 의해서 생기는 히브 감염병을 예방해 줄 수 있는 B형 인플루엔자 백신으로 예방접종을 기본적으로 접종해 주도록 권장하고 있다.
-
생후 2개월∼7세가 되기 전까지 영유아들에게 히브 백신을 근육주사로 접종해 준다. 예방접종 방법 및 접종 횟수는 예방접종 백신의 종류에 따라 다르다.
-
현재까지 히브 백신의 면역효과가 대단히 좋다. 그리고 부작용은 아주 적은 편이다
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병 및 안전사고 예방 B형 헤모필러스(헤모필루스) 인플루엔자균에 의한 감염병 예방접종(히브 예방접종).
-
2011년 1월 미 CDC, 미소아청소년과 학회에서 권장하는 소아청소년 예방접종 스케줄의 표 1, 2, 3, 4를 참조
-
B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염으로 인해 급성 뇌막염, 급성 후두개염, 급성 폐렴, 급성 안와 주위 봉와직염(봉소염), 급성 심낭염, 급성 관절염, 급성 중이염 등의 히브 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
히브 예방접종 백신(B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 백신)은 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자 균을 인공으로 배양한 후 그 배양 된 세균을 살균시켜 만든 일종의 사(불활성) 백신이다.
-
B형 헤모필러스 헤모필러스 인플루엔자 박테리아 감염병 백신에는
-
프로히비트(ProHiBit),
-
프로히비터(HIBTITER),
-
페드 백스히브(PedvaxHIB),
-
액티히브(ActHIB),
-
옴니히브(OmniHIB) 등 여러 종류가 있다. 이 여러 종류의 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병 백신들을 통틀어 히브(Hib) 백신, 또는 히브 예방접종 백신이라고 한다.
-
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병 백신 접종 연령
-
생 후 2, 4, 6개월에 각각 1차, 2차, 3차 접종을 받고 12~15 개월에 추가 접종 받아서 총 4회 히브 예방접종을 받는다. 모든 아이들은 생후 2개월에서 6세까지 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병을 예방하는 히브 백신 예방접종을 받아야 한다.
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염접종 방법
-
정기 건강검진을 받고 열이 있는지 알아보기 위해 체온을 잰다.
-
발열성 감염병이 없고 히브 백신에 알레르기가 없고 히브 백신 예방 접종에 금기 사항이 없으면 히브 백신 예방 접종 방법에 따라 근육이나 피하주사로 접종 받는다.
-
페드백스 히브 백신으로 생후 2, 4, 12~15개월에 각각 1차, 2차, 3차로 총 3차 접종 받고,
-
히브타이터나 프로히비트 히브 백신으로 생후 2, 4, 6, 12~15개월에 각각 1차, 2차, 3차, 3차로 총 4차 접종 받는다.
-
이와 같이 히브 백신의 종류에 따라 히브 백신 예방접종 횟수가 다르고 받는 나이도 다르다. 히브 백신으로 전에 한 번도 예방접종 받지 않았을 때의 히브 백신 예방접종 스케줄을 참조한다(표 (1), (2), (3), (4) 참조).
-
테트라뮨 히브 백신으로 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균에 의한 감염병을 예방접종할 때는 테트라뮨 히브 예방접종 백신으로 생후 2, 4, 6, 15~18개월에 각각 1차, 2차, 3차, 4차 접종 받아서 총 4차 근육주사로 접종 받는다.
-
테트라뮨 히브 백신에는 히브 백신 성분과 DTP 백신 성분이 들어있다. 그 때문에 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균에 의한 감염병과 디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해를 동시에 예방해주는 셈이다.
헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병 백신 부작용과 금기
-
히브 예방접종 백신을 받은 후 주사를 맞은 국소가 조금 붓고 아플 수 있다. 미열이 날 수 있다.
-
쇼크 등의 부작용이 날 수 있고 고열이 나는 등 위중한 부작용이 드물게 날 수 있다.
-
다행히 이런 부작용은 극히 드물다.
-
히브 백신에 알레르기가 있으면 히브 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 수 없다. 그밖에 다른 뚜렷한 금기 사항이 없다.
Haemophilus influenzae infections 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균 감염병
Overview and causes of Haemophilus influenzae infection
• Haemophilus Influenzae is a type of bacteria.
• Haemophilus influenzae is classified into B-type Haemophilus influenzae and non-B-type Haemophilus influenzae. That is, type B influenza bacteria are classified into B serotypes and non-B serotypes.
• These two types of Haemophilus influenzae bacteria infect humans and cause Haemophilus influenzae infectious diseases.
• Several types of infectious diseases can develop in children and adolescents, especially when infected with Haemophilus influenzae B.
• Influenza type B is also called HIb for convenience.
• Many people confuse influenza B with the influenza virus that causes the flu. In other words, flu (influenza) is a viral infectious disease caused by influenza virus infection.
• Influenza B (Hib) is a persistent bacteria that can normally be found in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract of healthy people.
• Most of the influenza B infections can be infected when they are in close proximity or come into contact with people with influenza B infections, and those people can infect other people with influenza B.
• Of the two types of serotypes, influenza B is more infected, especially in infants and young children, and can cause several life-threatening HIV infections.
• Influenza B infection can lead to otitis media, sepsis, sinusitis, pneumonia, and other influenza B infections, Cellulitis, see Croup caused by acute epiglottis.
• Influenza B is a scary bacterium that is well known to medical professionals but is not well known to non-medical professionals.
• Parents also need to know about influenza B and infectious diseases caused by bacterial infection.
• Prior to the prevention of influenza B infectious diseases with the HIb vaccine, influenza B was the main cause of bacterial meningitis in infants and toddlers from newborn to 3 years old. Sepsis, epiglottis, pneumonia, pleurisy, peritonitis, and myositis, Arthritis, osteomyelitis, pericarditis, otitis media, sinusitis, conjunctivitis, and peri-orbital cellulitis
• In particular, the bacteria could cause a number of infectious diseases in preschool children before the age of 3-6.
• Even nowadays, even infants, school-age children, adolescents, and adults can become infected with this bacterium, resulting in life-threatening infectious diseases.
• The incubation period is not clear.
Diagnosis of symptoms and signs of Haemophilus influenzae infectious disease
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on where in the body Haemophilus influenzae B (Hib bacteria) is infected and what kind of infectious disease is caused by it.
• For detailed symptoms and signs, refer to each section of “Various infectious diseases caused by influenza B infection”.
• If the disease is suspected by combining the medical history, symptoms, signs, examination findings, etc., it is recommended to confirm and treat the disease by performing a bacteriological test with specimens such as blood or pus collected from the lesion of the infectious disease caused by the bacterial infection, or body fluids. It is an ideal diagnostic treatment method.

Photo 2-71. CBC, blood electrolyte concentration test, blood bacterial culture test, etc. are performed as necessary to diagnose. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• There are some differences in treatment methods depending on whether Haemophilus influenzae belongs to the B serum type or the non-B serum type.
• In addition, depending on the type of Haemophilus influenzae B, which caused Haemophilus influenzae infectious disease that occurred then, the choice of antibiotics that can kill the bacteria may be different.
• Therefore, before treatment with antibiotics, it is recommended to start treatment with appropriate antibiotics according to experience immediately after collecting a specimen from the infectious disease site in order to find out what type of Haemophilus influenzae is caused by the type of Haemophilus influenzae. It is an ideal treatment.
• The ideal treatment method is to treat the infectious disease caused by this bacterial infection by performing a Gram stain microscopic examination with the specimen, a bacterial culture test, and a bacterial antibiotic susceptibility test, and then selecting an appropriate antibiotic again according to the bacterial antibiotic susceptibility test result. •
Depending on where the lesion of Haemophilus influenzae B infectious disease is located in the body, the method of collecting specimens for gram-stained microscopic bacterial examination or bacterial culture examination differs.
• A small amount of a specimen is collected from blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, etc., and a bacterial culture test is performed. If necessary, a chest X-ray photograph, an ultrasound photograph, an echocardiogram, etc. are used to diagnose.
• There are times when this type of diagnostic treatment is not always possible for a number of reasons.
• It can also be diagnosed by slide agglutination serotyping (SAST) test or polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
• Differential diagnosis of aseptic meningitis and bacterial (sex) meningitis.
• Differential diagnosis of aseptic meningitis and bacterial meningitis. Treatment of Haemophilus influenza infectious disease
• The treatment method differs depending on which part of the body the HIV bacteria infects and causes what kind of infectious disease.
• In other words, treatment methods for meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, arthritis, periorbital cellulitis, epiglottis, etc. caused by Haemophilus influenzae B infection are different.
• If you suffer from a very serious infection of Haemophilus B influenzae, such as meningitis or epiglottis, which can be life-threatening, you should seek emergency intensive care.
It can be treated with Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, Meropenem, or other antibiotics chosen based on clinical experience.
• Sometimes emergency treatment is initiated with two or three vascular injections of antibiotics.
• Next, according to the results of the bacterial antibiotic susceptibility test, it is common to select one or two antibiotics that are most suitable for the treatment of Haemophilus influenzae B infection and treat them for 10 days or longer.
• Haemophilus influenzae type B meningitis is treated with antibiotics and dexamethasone.
• Mild otitis media or mild conjunctivitis caused by HIb bacterial infection, or mild Haemophilus influenzae B infection, can be treated with amoxicillin, Ceclor, or other appropriate antibiotics as prescribed by a doctor for about 10 days at home as directed by a doctor. It is normal.
• References Red book 29th edition 2012, Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition Others In case of contact with a patient with Haemophilus influenzae infectious disease
• Haemophilus B influenza B. Infectious disease should be carefully observed in people who have been in close contact with or have been in contact with patients suffering from severe infectious diseases such as Haemophilus influenza B meningitis or epiglottis.
• Anyone who has come into contact with a patient suffering from Haemophilus influenzae B infection should be treated as a preventive treatment to prevent infection with the HIb bacteria with rifampin or other antibiotics as prescribed by a doctor.
• For more detailed prevention methods, see Tables 1~4. Prevention of Haemophilus influenzae infectious disease

Photo 2-72. Haemophilus influenzae type B left facial cellulitis. Meningitis, otitis media, bacteremia, arthritis, cellulitis, etc. can occur due to infection with Haemophilus influenzae (HIB, Hib). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 2 Prevention of pediatric and adolescent diseases and safety accidents-Infectious disease vaccination schedule for children aged 0-6 recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents in January 2011 See Schedules 2, 3, 4 and Tables 1-4.
• In 1985, the first HIb vaccine was developed to prevent infectious diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae B. After that, it is recommended that all children from 2 months of age to 7 years of age are basically vaccinated with a type of influenza B vaccine that can prevent the HIb infection caused by infection with Haemophilus influenzae.
• From 2 months to 7 years of age, infants and toddlers are given an intramuscular injection of the HIb vaccine. The method of vaccination and the number of vaccinations depends on the type of vaccination.
• So far, the immune effect of the HIb vaccine is very good. And the side effects are very few.
• [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 2 Prevention of childhood and adolescent diseases and safety accidents Vaccination against infectious diseases caused by influenza bacteria (Heb vaccination).
• Refer to Tables 1, 2, 3 and 4 of the pediatric and adolescent vaccination schedule recommended by the US CDC and the Society of Micro and Adolescents in January 2011.
• Acute meningitis, acute epiglottis, acute pneumonia, acute periorbital cellulitis acute pericarditis, acute arthritis, and acute otitis media can occur due to Haemophilus influenzae B infection.
• The HIb vaccination vaccine (Hemophilus influenza type B vaccine) is a type of dead (inactive) vaccine made by artificially culturing the hemophilus influenza type B and sterilizing the cultured bacteria.
o Haemophilus B Haemophilus Influenza Bacterial Infectious Disease Vaccine
o ProHiBit,
o HIBTITER,
o PedvaxHIB,
o ActHIB,
o There are several types, such as OmniHIB. These various types of Haemophilus influenzae infectious disease vaccines are collectively referred to as the Hib vaccine or the Hib vaccination vaccine. Haemophilus influenzae infectious disease vaccination age
• At 2, 4, 6 months of age, you will receive the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd vaccinations, respectively, and at 12-15 months of age, you will receive additional vaccinations for a total of 4 times. All children from 2 months to 6 years old are Type B
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”