피가 소변에 나올 때(혈뇨/ 피가 오줌에 나올 때) Hematuria(Blood in urine)
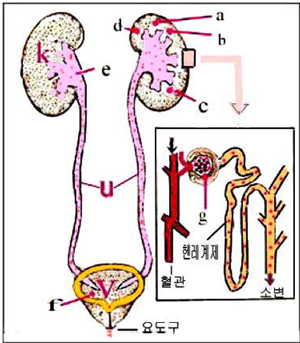
그림 1-26. 혈뇨의 원인과 비뇨계의 구조.
혈뇨의 개요와 원인
- 소변검사에는
-
- 물리학적 소변 검사(Physical urine tests),
- 현미경적 소변 검사(Microscopic urine tests),
- 화학적 소변 검사(Chemical urine tests),
- 세균배양검사 등이 있다.
- 피가 소변에 섞여 나오는 것을 혈뇨라고 한다.
- 육안으로 볼 수 있을 정도로 빨간 피가 소변에 섞여 나오는 혈뇨도 있고 소변을 딥스틱(Dipstix), 멀티스틱(Multistix) 또는 켐스트맆(Chemstrip) 등으로 화학적 소변 검사(Chemical urine tests)를 할 때나 현미경적 소변 검사로 소변을 검사 할 때 소변에 피가 나와 있는지 알 수 있는 혈뇨를 잠재성 혈뇨라고 한다.
- 육안으로는 볼 수 없을 정도로 아주 조금 피가 소변에 섞여 나올 때의 혈뇨를 “잠재성 혈뇨” 또는 요잠혈이라고 한다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제10권 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기계 질환-소변검사 참조).
- 신장 타박상,
- 신장이나 방광 등에 생긴 요로 종양,
- 급성 사구체신염,
- 요로 감염,
- 바이러스 방광염,
- 박테리아 방광염,
- 약물 중독,
- 다낭성 신장병,
- 혈액 응고인자 결핍증,
- 혈소판 감소증,
- 헤모글로빈 이상,
- 요석증,
- 비뇨기 내 이물,
- 육체적 운동,
- 수음,
- 알레르기,
- 폴립,
- 칼슘 과다증,
- 양성 비특이성 혈뇨 등으로 요로에서 피가 나와 혈뇨가 생길 수 있다.
- 혈뇨의 원인 중 가장 흔한 원인은 박테리아 요로 감염병이다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제10권 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기계 질환-혈뇨, 제13권 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환-급성 출혈에 의한 빈혈 참조).
혈뇨의 증상 징후
- 혈뇨는 병이 아니고 어떤 원인으로 생기는 징후라고 할 수 있다.
- 혈뇨를 일으키는 원인과 혈뇨의 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 다르게 나타난다.
- 새빨간 피가 소변에 많이 섞여 나오는 혈뇨,
- 커피색과 비슷한 검붉은 피가 소변에 나오는 혈뇨,
- 피가 소변에 섞여 나와 있어도 소변에 피가 있는지 육안으로 식별 할 수 없을 정도로 아주 소량의 피가 소변에 있는 혈뇨도 있다.
혈뇨의 진단
- 빨간 피가 나온 혈뇨, 커피색과 비슷한 적갈색 혈뇨가 있을 때는 소변에 피가 있는지 육안으로 쉽게 알 수 있다.
- 잠재성 혈뇨가 있을 때는 소변 검사나 소변 잠혈 검사를 하지 않고 소변에 피가 나와 있는지 알 수 없다.
- 소변에 피가 많이 나온다고 추정하면 진단 치료를 응급으로 받아야한다.
- 그래서 그 원인을 알아야 한다.
- 집에서 본 소변을 버리지 말고 깨끗한, 가능한 무균 플라스틱 컵 등에 받아가지고 병원으로 가지고 가면 그 피검물로 소변 검사를 바로 해 소변에 피가 나오는지 금방 알아볼 수 있다.
- 소변에 피가 나오는지 알아보기 위해 소변검사를 할 때 소변 화학적 검사, 소변 현미경 검사와 소변 세균 배양 검사 등을 동시 검사해 요로 감염으로 피가 나오는지 또는 다른 원인으로 소변에 피가 나오는지 알아볼 수 있다.
- 필요에 따라, CBC 혈액 검사와 출혈 스크린 검사를 해 전신 출혈 질환이 있는지, 그로 인해 혈뇨가 생기는지 알아볼 수 있다(표 23 참조).
- 소변에 피가 많이 나오지만 원인을 확실히 모르면 필요에 따라
-
- 보이딩 시스토유레스로그램(Voiding Cystourethrogram/VCUG),
- 신장 요관 초음파 검사와 신장 요관 CT 스캔 검사 등으로 비뇨기에 어떤 이상이 있는지 알아보고 혈뇨의 원인을 찾기도 한다.
|
다음은 “오줌에서 피가 나요(피가 소변에 나올 때)”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 오줌에서 피가 나요(피가 소변에 나올 때)에 관한 질문
Q.
4세 된 남아입니다. 제 아이의 증상 징후는 오늘 오후 갑자기 오줌에서 피가 나오고 있습니다. 피가 조금 섞여 나오는 것이 아니고 아예 오줌이 피로 나오고 있습니다. 아기가 먹기도 잘하고 놀기도 잘하는데 왜 오줌에서 피가 나오는 것이지요. 걱정이 많이 됩니다. 오줌에서 피가 나오는 이유가 무엇이고 어떻게 하여야 하는 건가요.
빠른 대답 부탁드립니다.
A. 송자님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 더 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
급성 사구체 신염, 바이러스 방광염, 요로 감염, 요로 외상, 요로 종양 등으로 소변에 피가 나올 수 있습니다.
육안으로 볼 수 있을 정도로 소변에 피가 나오면 응급으로 진단 치료 받아야 합니다.
소아청소년과나 병원 응급실에서 진찰 진단을 받으시고 이 문제에 관해서 상담하시기 바랍니다.
피가 소변에 나올 때. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제10권 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기계 질환–혈뇨, 급성 사구체 신염 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
사진 1-172. 영유아의 소변 검사를 하기 위해 피검물용 소변을 받을 때 쓸 수 있는 영유아용 오줌주머니.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 1-173. 혈뇨, 단백뇨, 또는 당뇨 등을 검사할 때 쓸 수 있는 소변 화학 검사 딥스틱(담금띠/ Dipstick).
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
혈뇨의 치료
- 혈뇨의 원인과 증상 징후 등에 따라 치료한다.
- 소변에 피가 다량으로 나오고 혈압이 많이 떨어지면서 환아가 많이 아플 때는 의료구급대, 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 전화해 그들의 지시에 따라 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 간다.
- 소변에 피가 나오는 정도나 원인에 따라 치료한다.
Hematuria (Blood in urine) 피가 소변에 나올 때(혈뇨/ 피가 오줌에 나올 때)

Figure 1-26. The causes of hematuria and the structure of the urinary system. k-kidney, u-ureter, v-bladder a-bacterial nephritis (bacterial urinary tract infection), b-positive nonspecific hematuria, c-physical motility hematuria, d-kidney and urinary tract trauma, e-drugs and allergies, f-cystitis, g-acute glomerulonephritis, etc. Blood may come out. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Overview and causes of hematuria
- Urine test –1. Microscopic urine tests, 2. Chemical urine tests,.3. There are bacterial culture tests. 4. Blood mixed with urine is called hematuria.
- There is also hematuria, in which red blood is mixed in the urine enough to be seen with the naked eye,
- and when urine is subjected to chemical urine tests with a Dipstix, Multistix, or Chemstrip, or under a microscope.
- Hematuria, which can tell if blood is present in the urine when the urine is tested with a red urine test, is called latent hematuria.
- Hematuria when very little blood is mixed in the urine so that it cannot be seen with the naked eye is called “latent hematuria” or urinary occult blood ([Parents should also be at least the half doctors-Department of Pediatrics and Family Nursing)]-Volume 10 Pediatric and Adolescent Kidney Diseases of the genitourinary system-see urine test).
The following condition may be associated with hematuris
- Kidney bruises,
- Urinary tract tumors in the kidneys or bladder,
- Acute glomerulonephritis,
- Urinary tract infections,
- Viral cystitis,
- Bacterial cystitis,
- Drug addiction,
- Polycystic kidney disease,
- Blood clotting factor deficiency,
- Thrombocytopenia,
- Hemoglobin abnormalities,
- Urolithiasis,
- Foreign bodies in the urinary tract,
- Physical Exercise,
- masturbation,
- allergy,
- polyp,
- Hypercalcemia,
- Blood from the urinary tract, such as benign nonspecific hematuria, can lead to hematuria.
- Among the causes of hematuria, the most common cause is bacterial urinary tract infection ([Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Pediatric and Family Nursing Encyclopedia)-Vol. 10 Child and Adolescent Kidney Urogenital Diseases-Hematuria, Vol. 13 Children and Adolescent Blood, Lymphatic, and Tumor Diseases -See anemia due to acute bleeding).
- Symptoms signs of hematuria Hematuria is not a disease, but a symptom of a cause.
Symptoms and signs
- Appear differently depending on the cause of the hematuria and the degree of hematuria.
- Hematuria, where a lot of bright red blood is mixed in the urine,
- Hematuria in the urine with dark red blood similar to coffee color,
- There is also hematuria in which a very small amount of blood is present in the urine so that the naked eye cannot discern whether there is blood in the urine even if the blood is mixed in the urine.
Diagnosis of hematuria
- If you have hematuria with red blood or reddish-brown hematuria similar to coffee color, you can easily tell if there is blood in your urine.
- When you have latent hematuria, you cannot tell if there is blood in your urine without a urine test or a urine occult blood test.
- Assuming that there is a lot of blood in your urine, you should seek medical attention as an emergency. So you need to know the cause.
- Instead of throwing away the urine you saw at home, take it in a clean, sterile plastic cup, etc., and take it to the hospital, so you can immediately do a urine test with the specimen to see if there is blood in the urine.
- When urinalysis is performed to determine whether blood is bleeding in the urine, urine chemistry, urine microscopy, and urine bacterial culture can be simultaneously tested to determine if blood is bleeding from a urinary tract infection or from other causes.
- If necessary, a CBC blood test and a bleeding screen can be performed to determine if there is a systemic bleeding disorder and if it causes hematuria (see Table 23). There is a lot of blood in the urine, but if you are not sure of the cause,
- Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG), ultrasonography of the renal ureter and CT scan of the renal ureter is used to check for any abnormalities in the urinary system and to find the cause of hematuria.
The following is an example of the question-and-answer on the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling on “I bleed from my urine (when blood comes out of my urine)”.
Q&A.
Questions about bleeding from the urine (when blood comes out of the urine)
Q.
This is a 4-year-old boy.
My child’s symptom is suddenly bleeding from his urine this afternoon.
The blood doesn’t mix a little, but urine is coming out of blood.
The baby is good at eating and playing, but why is the urine bleeding? I’m worried a lot. What is the reason for blood coming out of the urine and what should I do?
I would like a quick answer.
A.
Songja-nim Good morning.
Thanks for asking.
That’s a good question.
The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer.
We will respond based on the information you provided. Acute glomerulonephritis, viral cystitis, urinary tract infection, urinary tract trauma, urinary tract tumor, etc. can cause blood to bleed in the urine. If the urine bleeds enough to be visible to the naked eye, you should seek medical attention as an emergency.
Please consult the pediatrics department or hospital emergency room for medical examination and consultation regarding this problem.
When blood comes out of the urine. [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Pediatrics and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Vol. 10 Children and adolescents Kidney urogenital diseases-Hematuria, Acute glomerulonephritis, etc. Please refer to.
If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won

Photo 1-172. A urine bag for infants and toddlers that can be used to receive urine for specimens to perform urine tests for infants and toddlers. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-173. A urine chemistry dipstick that can be used to test for hematuria, proteinuria, or diabetes. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Treatment of hematuria
Treatment according to the cause and symptoms of hematuria.
When a child is very ill due to a large amount of blood coming out of the urine and blood pressure drops a lot, call the medical paramedic, hospital emergency room or regular pediatrician and take them to the hospital emergency room according to their instructions.
Treatment depends on the degree or cause of blood bleeding in the urine.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.157
- Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.263-267
- Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.67,157, 220, 225
-
Nelson textbook, 14th edition, p.1326-1339
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”