풍진(3일 홍역), Rubella (German measles/Three-day measles)
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
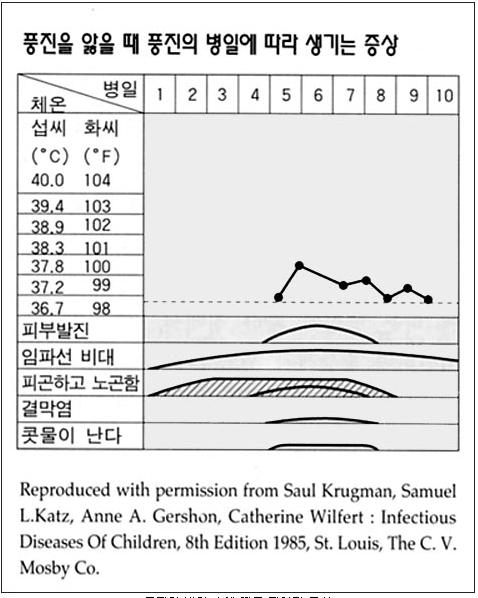
그림 3-19. 풍진의 병일 수에 따른 전형적 증상
Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children, 8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co. Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz and others
풍진 (3일 홍역)의 원인
-
풍진바이러스(Rubella virus) 감염으로 생기는 전신 급성 바이러스성 감염병을 풍진이라고 한다.
-
1969년에 풍진 백신이 처음으로 개발된 이후 거의 모든 아이들에게 풍진 백신으로 기본 예방접종을 해 주기 때문에 요즘 풍진을 앓는 아이들을 보기 드물다.
-
풍진을 앓는 환아들의 콧물이나 가래 등에서 나온 비말 속에 들어 있는 풍진 바이러스 감염에 의해 감염될 수 있다.
-
또 풍진을 앓는 환자에게 근접해도 감염될 수 있다.
-
동물을 통해서는 감염되지 않는다.
-
임신 첫 3개월 동안 임신부가 풍진에 걸리면 태아도 풍진에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 질환–선천성 풍진증후군, 제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환–난청과 귀머거리 참조).
-
출생 이후 신생아들이나 영유아들뿐만 아니라 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들 그리고 성인들도 풍진에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
풍진에 걸리면 증상 징후가 조금 나타나든지 조금도 나타나지 않을 수 있고 다만 풍진 면역체가 신체에 생기고 풍진이 자연히 낫는 경우도 많다.
풍진 (3일 홍역)의 증상 징후
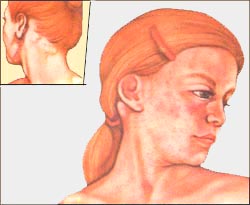
그림 3-20. 풍진으로 생긴 피부 발진과 귓바퀴 뒤 부위와 목 사이에 생긴 림프절 비대
Used with permission from Health information service, Merk Sharp & Dome, West Point, PA,
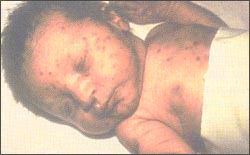
사진 3-22. 선천성 풍진증후군 으로 생긴 피부 발진
참조문헌– CDC USA
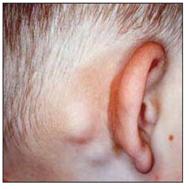
사진 3-21. 풍진으로 인해 귓바퀴 뒤 부위에 있는 두발의 가장자리 부위에 생긴 림프절 비대
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
풍진의 초기의 증상 징후는 감기의 증상 징후와 비슷한 데가 많다.
-
그렇지만 조금 진행되면 귓바퀴 뒤 부위나 뒤통수의 두발의 가장자리의 아래 부위와 뒷목 사이에 있는 림프절들이 메주콩알만 하게 부을 수 있다.
-
이와 같이 부었던 림프절들은 10일 정도 지나면 정상 크기로 돌아간다.
-
풍진이 발병된 후 3~4일경 미열이 나고, 연분홍색 피부 발진이 얼굴, 목, 몸통, 배, 팔다리 등에 날 수 있다.
-
그 후 2~3일 정도 지나면 피부 발진은 자연히 없어진다.
-
콧물이 나고 결막염이 생길 수 있다.
-
풍진으로 생기는 증상 징후는 홍역을 앓을 때 생기는 증상 징후에 비하면 전반적으로 더 경미하다.
-
임신 첫 3개월 중 태아가 풍진에 걸리면 귀머거리, 백내장, 소두증, 선천성 심장 기형 등 여러 가지의 선천성 기형이 생길 수 있다.
-
태아 풍진은 TORCH(Toxoplasmosis, Others such as Syphilis, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus(CMV), Herpes simplex virus (HSV)에 속한다참조.
-
미국에서는 풍진을 앓는 환자를 요즘 더 이상 볼 수 없다고 한다.
-
잠복기는 약 14~21일이다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병, 안전사고 예방–풍진 예방접종 참조, 풍진 예방접종 참조.
풍진 (3일 홍역)의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병을 진단한다.
-
때로는 성홍열, 홍역, 또는 다른 여러 종류의 피부 발진성 감염병과 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
풍진 바이러스 IgM, IgG 항체 검사, 풍진 바이러스 RNA 검사로 진단할 수 있고, 피, 소변, 뇌척수액, 비강, 인두 등에서 채취한 피검 물로 풍진 바이러스 배양검사를 해 확진할 수 있다.
-
풍진 바이러스에 대한 면역체가 없는 임신부가 임신 첫 3개월 동안에 풍진에 걸렸다고 의심되면 진짜로 풍진에 걸렸는지 안 걸렸는지를 확실히 알아봐야 한다.
풍진 (3일 홍역)의 치료
-
풍진은 원래 급성 바이러스성 감염병이다.
-
증상 징후가 경미하기 때문에 특별한 치료가 요하지 않는다.
-
그렇지만 두통, 열, 관절통 등의 증상 징후가 있을 때는 타이레놀 등으로 진통시키고 대증 치료한다.
-
풍진으로 생긴 피부 발진도 그대로 두고 관찰하면 자연히 치료된다.
풍진(3일 홍역) 환아의 격리
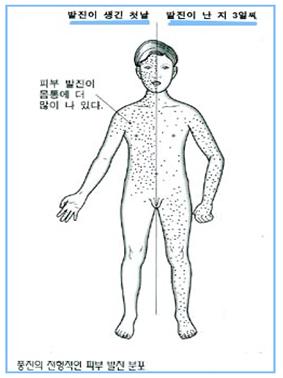
그림 3-23. 풍진 병일에 따른 풍진의 전형적인 피부 발진
Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children, 8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co. Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz and others
-
학령기 아이에게 풍진이 발생되면 피부 발진이 나기 시작한 날부터 5일 동안 학교에 보내지 말아야 한다.
-
어떤 이유로 풍진을 앓고 있는 환아를 병원에 입원시켰을 때는 그 환아를 다른 환자로부터 격리시켜야 한다.
-
선천성 풍진 증후군을 갖고 태어난 신생아들은 풍진 바이러스를 다른 사람들에게 출생 후 상당한 기간 동안 감염시킬 수 있다.
-
따라서 선천성 풍진 증후군이 있는 신생아를 다른 신생아들로부터 격리시켜야 한다.
-
풍진을 앓고 있는 환아를 탁아소나 학교 같이 아이들이 많이 모인 장소에 보내지 말아야 한다.
-
풍진 바이러스 면역체가 있지 않은 임신부는 풍진 바이러스에 감염되지 않도록 임신 중 특히 조심해야 한다.
-
그러나 생 풍진 바이러스 백신으로 예방 접종을 임신부에게 해주어서는 안 된다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 25권 임신, 분만, 신생아 돌보기 참고.
풍진(3일 홍역)환아와 접촉한 경우
-
임신 첫 3개월 동안 임신부가 풍진 환자와 접촉됐으면 의사에게 곧 문의해야 한다.
-
임신부가 과거에 풍진을 앓았었는지 확인하기 위해 풍진 혈청 항체 검사를 임신 초기에 기본적으로 한다.
-
임신부에게 풍진 면역체(항체)가 있을 때도 태아에게 풍진이 생길 수 있으나 일반적으로 드물게 생기므로 태아가 풍진 바이러스에 감염되었는지 걱정할 필요가 거의 없다.
-
풍진 바이러스 면역체가 없는 임신부가 풍진 환자에게 근접됐을 때는 임신부에게 감마글로불린 주사를 주는 경우도 있다.
-
과거에 풍진을 앓았던 병력도 없고, 풍진 예방접종을 받지 않아서 풍진 면역체가 없는 임신부가 임신 첫 3개월 동안에 풍진에 걸리면 태아를 낙태시켜야 한다고 주장하기도 있다.
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 Recommended immunization schedule for 0~18 year old Americal children in Jan 1st 2021
|
☞ 각 나라에 따라 권장 기본 예방접종 스케줄이 다를 수 있다. |
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2021
| 예방접종 백신 종류/ 예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1차 접종 | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus²(RV) RV-1(2회분 배열 접종); RV-5(3 회분 배열 접종)/ 로타바이러스 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³(DTaP;<7세)/파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | ←1차 접종→ | →2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ←5차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap;7세나 >7세 파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ 히브 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 5 | ←3차 또는 4차 접종 → 각주 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) /폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 세)/소아마비 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 예방 접종 백신 종류/예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||
| Influenza⁸(IIV; LAIV) 1부에게는 2회분,각주 8 /인플루엔자 | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (11V 만)→ | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (II V 또는 LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ 홍역, 풍진, 유행성 이하선염 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /수두 | ←1 차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/A형 간염 | ←2 회분→ 주서 11 | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; 여성에게만 (HPV4; 여성과 남성 에게)/사람유두종 바이러스 감염병 | ←3회 분 배열 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 생후 9 개월이나 그후후. MenACWY-CRM-D는 생후 2개월이나 그 이후. MenACWY-TT는 은 생후 2세나 그 이후. /수막구균 뇌막염과 그 외 감염병
—————————- Meningococcal B 백신에는 MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, Trumenba 백신이 있다. 10세나 그 이상에 접조한다. Bexsero백신은 2회 접종하고 Trumenba 백신은 총 3회 접종한다. 위험도다 없는 사춘기아이들이나 청년들은 16-23세에 접종받는다. 소스: CDC, AAP News 3/2021 Covid-19 예방 접종은 12-15세에 2회 접종해도 된다. 5/.2021 |
←주서 13→ | ←1차 접종→ | 추가 접종 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
접종을 권장 하는 나이의 범위, | ||
|
|
건강상 고 위험 군 아이들에게 접종을 권장하는 나이 |
풍진(3일 홍역)의 예방 접종
-
예방접종 스케줄 표 (1)~(4), [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병, 안전사고 예방-2008년 미 소아청소년과 학회에서 권장하는 소아 감염병 예방접종 스케줄 표 (1)~(4) 참조
-
생후 12~15개월 사이에 풍진 백신, 홍역 백신과 볼거리 백신이 든 혼합 예방접종 백신인 MMR 백신으로 1차 접종하든지,
-
또는 풍진 백신 성분만 든 단가 풍진 생 백신으로 접종을 하든지, ProQuad 종합 백신으로 수두, 홍역, 유행성 이하선염(볼거리), 풍진을 동시 예방 접종을 해 줄 수 있다.
-
초등학교에 들어갈 때쯤 4~6세 경 2차 풍진 예방접종을 MMR 백신이나 ProQuad 백신으로 2차로 접종해 줄 수 있다.
-
결혼하기 바로 직전이나 임신한 모든 여성은 풍진 바이러스 면역체(항체)를 가지고 있는지 알기 위해 풍진 혈청검사를 통상적으로 받아야 한다.
-
미국에서는 혼인 신고를 할 때도 풍진 혈청검사 결과를 법적으로 제출하도록 규정되어 있다. 결혼할 여성에게 풍진 바이러스 면역체가 없으면 결혼하기 전에 법적으로 풍진 백신을 접종 받아야 한다.
-
그리고 임신됐을 때는 반드시 풍진 면역체가 있는지 검사해야 한다.
Rubella (German measles/Three-day measles) 풍진 (3일 홍역)

Figure 3-19. Typical symptoms depending on the number of days of rubella Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children, 8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co. Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz and others
Causes of rubella (3-day measles)
• A systemic acute viral infection caused by infection with the Rubella virus is called rubella.
• Since the rubella vaccine was first developed in 1969, it is rare to see children with rubella these days because almost all children are given basic immunizations with the rubella vaccine.
• Children with rubella may be infected by a rubella virus infection, which is contained in droplets from runny nose or phlegm.
• You can also get infected by getting close to a patient with rubella. • No infection through animals.
• If a pregnant woman gets rubella during the first three months of pregnancy, the fetus can get rubella as well.
www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 6 Newborn growth and developmental disease-Congenital rubella syndrome, Vol.
• Postnatal newborns and infants, as well as school-age children, adolescents, and adults can get rubella.
• If you get rubella, you may have little or no symptoms, but there are many cases where the rubella immune system develops in the body and the rubella heals spontaneously.
Symptoms signs of rubella (3-day measles)

Figure 3-20. Skin rash caused by rubella and enlarged lymph nodes in the area behind the auricle and between the neck Used with permission from Health information service, Merk Sharp & Dome, West Point, PA,

Photo 3-22. Skin rash caused by congenital rubella syndrome References-CDC USA

Photo 3-21. Enlarged lymph nodes at the edge of the head in the area behind the auricle due to rubella Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• The initial symptoms of rubella are often similar to those of a cold.
• However, if it progresses slightly, the lymph nodes between the back of the auricle or the lower edge of the head of the back of the head and the back of the neck may swell to the size of a soybean meal.
• These swollen lymph nodes return to their normal size after about 10 days. • A mild fever occurs 3 to 4 days after the onset of rubella, and a pale pink skin rash may occur on the face, neck, torso, stomach, and limbs.
• After 2 to 3 days, the skin rash disappears spontaneously.
• Runny nose and conjunctivitis may develop.
• Symptoms of rubella are generally milder than those of measles.
• Rubella in the fetus during the first three months of pregnancy can lead to a number of congenital anomalies, including deafness, cataracts, microcephaly, and congenital heart anomalies.
• Fetal rubella belongs to TORCH (Toxoplasmosis, Others such as Syphilis, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Herpes simplex virus (HSV)).
• In the United States, it is said that patients with rubella are no longer seen these days. • The incubation period is about 14 to 21 days. www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 2 Child and adolescent disease, prevention of safety accidents-See Rubella vaccination, see Rubella vaccination.
Diagnosis of rubella (3-day measles)
Diagnose this disease by synthesizing medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
Sometimes you need to differentiate it from scarlet fever, measles, or several other types of skin rash infections.
• It can be diagnosed with rubella virus IgM, IgG antibody test, and rubella virus RNA test, and can be confirmed by performing a rubella virus culture test with specimens collected from blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, nasal cavity, and pharynx.
• If a pregnant woman who is not immune to the rubella virus is suspected of having rubella during the first three months of pregnancy, it is important to determine whether or not she really has rubella.
Treatment of rubella (3-day measles)
• Rubella is originally an acute viral infection. • No special treatment is required because the symptoms are mild.
• However, when symptoms such as headache, fever, joint pain, etc. are present, pain is relieved with Tylenol and symptomatic treatment.
• If the skin rash caused by rubella is left and observed, it will heal naturally.
Isolation of children with rubella (3-day measles)

Figure 3-23. Typical skin rash of rubella following rubella disease Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children, 8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co. Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, and others
• If rubella develops in school-age children, they should not be sent to school for 5 days from the day the skin rash begins to develop.
• When a child suffering from rubella is admitted to the hospital for any reason, the child must be isolated from other patients. • Newborns born with congenital rubella syndrome can infect others with the rubella virus for a considerable period of time after birth.
• Therefore, newborns with congenital rubella syndrome should be isolated from other newborns.
• Children suffering from rubella should not be sent to places with large numbers of children, such as daycare centers or schools.
• Pregnant women who do not have rubella virus immunity should be especially careful during pregnancy to avoid getting rubella virus infection.
• However, the live rubella virus vaccine should not be used to immunize pregnant women. www.drleepediatrics.com-Refer to Volume 25, Pregnancy, Delivery, and Caring for Newborns.
In case of contact with a child with rubella (3 days measles)
If a pregnant woman has been in contact with a rubella patient during the first 3 months of pregnancy, she should contact her doctor right away. Rubella serum antibody tests are done in the first trimester of pregnancy to determine if a pregnant woman has had rubella in the past.
Rubella can develop in the fetus even when a pregnant woman has rubella immune bodies (antibodies), but it is usually rare, so there is little need to worry about whether the fetus is infected with the rubella virus.
• When a pregnant woman without rubella virus immunity is close to a rubella patient, a gamma globulin injection may be given to the pregnant woman.
• It is argued that pregnant women who have no previous history of rubella and who do not have rubella immunity because they have not been vaccinated against rubella should have an abortion during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2021,
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표
1A
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 1 5 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19~23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | |||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←←3rd vaccination→→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus² (RV) RV-1 (two batch sequence inoculation); RV-5 (3-batch sequence vaccination)/ Rotavirus infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³ (DTaP; <7 years old)/tetanus, diphtheria, pertussi | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ←5th vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap; 7 years old> 7 years old tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ Hib infectious disease | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 5 | ←3rd or 4th vaccination→ Footnote 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/Pneumococcal infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) / Streptococcal pneumonia infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 years old)/Polio | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 2 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 15 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19-23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | ||
| Influenza⁸ (IIV; LAIV) for 1 copy, 2 servings, footnote 8 / Influenza | ←Get inoculated every year (11V 만)→ | ←Get inoculated every year(II V or LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ Measles, Rubella, Mumps | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /Varicella | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/Hepatitis A | ←2 doses→ | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; women only (HPV4; women and men))/Human papillomavirus infectious disease | ←3rd vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 9 months or later. MenACWY-CRM-D is 2 months or later. MenACWY-TT is 2 years old or later. / Meningococcal meningitis and other infectious diseases) —————————- Meningococcal B vaccines include MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, and Trumenba vaccines. We touch on 10 years of age or older. The Bexsero vaccine is inoculated twice and the Trumenba vaccine has inoculated a total of three times. Adolescents and young adults with no risk are vaccinated at age 16-23. Source: CDC, AAP News 3/2021
——————Beginning in May 2021, adolescents aged 12 to 15 years old can receive the COVID 19 vaccination twice. |
←1st vaccination→ | Booster vaccination | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
The age range for which vaccination is recommended, | ||
|
|
Age recommending vaccination for children in the high risk group |
Vaccination against rubella (3-day measles)
• Vaccination schedule table (1)~(4), [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Pediatric and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 2 Prevention of pediatric and adolescent diseases and safety accidents-Infectious diseases recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2008
Refer to the vaccination schedule table (1) to (4)
• Between 12 and 15 months of age, whether the first dose is given with the MMR vaccine, a combined immunization vaccine containing a rubella vaccine, a measles vaccine and a mumps vaccine,
• Or, whether you are vaccinated with a single-cost rubella vaccine containing the ingredients of a rubella vaccine, the ProQuad comprehensive vaccine can provide simultaneous vaccination against chickenpox, measles, mumps (mumps), and rubella.
• By the time they enter elementary school, around the age of 4 to 6 years old, a second dose of rubella vaccination can be given with the MMR vaccine or the ProQuad vaccine.
• Just before marriage or all pregnant women should routinely have a rubella serological test to see if they have the rubella virus immunity (antibodies).
• In the United States, it is legally required to submit rubella serologic results when registering a marriage. If a woman who will be married does not have the rubella virus immunity, they must be legally vaccinated against rubella before marriage.
• And when you are pregnant, you must be tested for rubella immunity.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th – 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”