포도상구균 식중독 Staphylococcal food poisoning (Staphylococcal foodborne illness)
포도상구균 식중독(포도상구균 식중독)의 원인
- (표 2-2, 2-3 참조) [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병- 포도상구균에 의한 감염병 참조)
- 포도상구균에는 황색 포도상구균 등 여러 종류의 균종이 있다.
- 그중 황색 포도상구균에 의해 주로 식중독이 생길 수 있다.
- 황색 포도상구균에 의해 생긴 식중독을 포도상구균 식중독(포도상구균 식중독/Staphylococcal food poisoning) 이라한다.
- 건강한 사람들의 20~50%는 평소에 황색 포도상구균을 적어도 신체 한 부위에 보균하고 있다.
- 특히, 콧구멍이나 그 가장자리 부위, 콧구멍 전정, 손 등에서 황색 포도상구균이 발견될 수 있다.
- 집파리 등이 황색 포도상구균을 사람들에게 옮길 수 있고, 가구나 실내 먼지에도 황색 포도상구균에 오염되어 있을 수 있다.
- 종기나 여드름 등 환부 속에 있는 황색 포도상구균이 다른 사람들에게 감염될 수 있다.
- 종기, 농가진, 또는 곪은 여드름 등에서 흘러나온 황색 포도상구균이 든 피고름 등을 손으로 만진 후 그 오염된 손을 씻지 않고 그 손으로 음식물을 요리하거나 만지면 음식물에 황색 포도상구균이 오염될 수 있고, 그 손에 묻은 황색 포도상구균이 본인에게 자가 감염이 될 수 있고 다른 사람들에게도 감염될 수 있다.
- 콧구멍 속이나 인두 점막 등에 상존하고 있는 황색 포도상구균이 기침, 재채기, 또는 대화 등을 할 때 비말을 통해 다른 사람에게 감염될 수 있다.
- 황색 포도상구균이 오염된 손으로 다른 사람의 신체나 자신의 신체의 다른 부위를 만져도 감염될 수 있다.
- 공기, 먼지, 파리 등에 오염되었던 황색 포도상구균이 음식물에 오염될 수 있다.
- 이때 황색 포도상구균에 의해 생성된 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신(장독소/장관독소, Enterotoxin)이 음식물에 오염될 수 있다.
- 이런 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신이 오염된 음식물을 먹으면 황색 포도상구균 식중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 황색 포도상구균이 자라기 좋은 장소에 황색 포도상구균이 오염된 음식물을 오랫동안 보관하면 황색 포도상구균에서 포도상구균 엔테로톡신이 음식물에 오염된다.
- 황색 포도상구균 이외 다른 포도상구균으로도 식중독이 생길 수 있다.
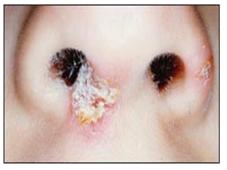
사진 2-56. 황색 포도상구균 농가진 등 피부 감염병을 손으로 만진 후 그 손을 잘 씻지 않고 음식물을 요리해 먹을 때 황색 포도상구균 식중독에 걸릴 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
포도상구균 식중독의 증상 징후
- 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신에 오염된 음식물을 먹은 후 30분∼8시간 경에 식중독 증상 징후가 나타날 수 있다.
- 평균 잠복기는 2~4시간이다.
- 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신 중독의 전형적인 증상 징후는 심한 구토, 복통, 허탈 등이다.
- 이런 증상 징후가 갑자기 나타나면서 심한 설사를 하고 탈진되면서 식은땀이 날 수 있다.
- 미열이 날 수 있으나 고열은 나지 않는다.
- 심할 때는 체온이 떨어져 몸이 차고 혈압이 비정상적으로 떨어지고 쇼크에 빠질 수 있다.
- 이런 정도로 앓을 때는 대개 입원치료를 받는다.
- 적절히 바로 치료받아도 이런 식중독 증상들이 24~48시간 동안 지속되는 것이 보통이다.
- 환자가 먹었던 음식물을 함께 먹었던 다른 사람들에게도 황색 포도상구균 식중독이 거의 동등하게 나타날 수 있다.
포도상구균 식중독의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병을 진단할 수 있다.
- 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 종기나 여드름 등 환부를 손으로 만진 후 그 손을 씻지 않고 그 손으로 요리한 음식물을 먹었는지, 또는 실내 온도에 오랫동안 보관해 놓았던 음식물을 먹었는지 등을 알면 진단하는데 도움이 된다.
- 화학물질 식중독(Chemical food poisoning), 클로스트리듐 페르프린젠스(Clostridium perfringens) 식중독, 살모네라 식증독, 시겔라 식증독 등 다른 원인에 의해 생긴 식중독의 증상 징후와 서로 비슷한 점이 많기 때문에 황색 포도상구균 식중독과 감별진단 해야 한다(표 2-2, 2-3 참조).
- 때로는 황색 포도상구균 식중독을 정확히, 신속히 진단하기 어려운 때도 있다.
- 환자의 구토물이나 대변으로 황색 포도상구균 세균배양검사를 하여 진단할 수 있고. 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신을 검출해 진단할 수 있다.
- 황색 포도상구균을 감염시킨 사람의 환부에서 황색 포도상구균 세균 배양검사를 해서 진단하는 데 도움을 얻을 수 있다.
- 또 황색 포도상구균과 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신을 음식물에서 검출하여 진단할 수 있다.
포도상구균 식중독의 치료
- 증상 징후에 따라 대증치료를 한다.
- 심할 때는 병원에 입원해 포도당 전해질용액 혈관주사로 탈수를 치료 예방한다.
- 항생제 치료는 효과 없다.
- 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신이 위장관 속에 있을 때는 그 엔테로톡신이 위장관 외로 빨리 배설되도록 설사 하게 하는 약물 치료를 할 수 있다.
- 환자가 먹다 남긴 음식물은 전부 버려야 한다.
- 이런 식으로 치료하면 보통 1~2일 이내 완전히 회복되는 것이 보통이다.
포도상구균 식중독의 예방
- 특히, 음식물을 요리하고 취급하는 사람들은 손을 깨끗이 씻어야 한다.
- 종기, 고름 나는 병소를 손으로 만졌을 때는 손을 더 깨끗이 씻어야 한다.
- 평소에, 먹다 남은 음식물은 냉장고에 보관하든지 그렇지 않으면 버린다.
- 실내 온도에 오랫동안 놓아두었던 음식물은 버린다.
- 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신에 오염된 음식물은 30분 동안 물에 끓여도 황색 포도상구균 엔테로톡신이 없어지지 않는다.
Staphylococcal food poisoning (Staphylococcal foodborne illness) 포도상구균 식중독
Causes of staphylococcal food poisoning
• (Refer to Tables 2-2 and 2-3) [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Pediatric and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Vol. 7 Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-Infectious Diseases caused by Staphylococcus)
• Staphylococcus aureus has several types of fungi, including Staphylococcus aureus.
• Food poisoning can be caused mainly by Staphylococcus aureus.
• Food poisoning caused by Staphylococcus aureus is called staphylococcal food poisoning.
• 20-50% of healthy people usually carry Staphylococcus aureus on at least one part of the body.
• In particular, Staphylococcus aureus may be found in the nostrils or edges thereof, in the vestibule of the nostrils, in the hands, etc.
• Houseflies, etc., can transmit Staphylococcus aureus to people, and furniture or indoor dust can be contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus.
• Staphylococcus aureus in the affected area, such as a boil or acne, can infect others.
• If you touch or cook food with your hands without washing the contaminated hands after touching the blood pus containing Staphylococcus aureus from boils, impetigo, or festering acne, staphylococcus aureus may be contaminated in the food. Staphylococcus aureus on your hands can self-infect yourself and can infect others.
• Staphylococcus aureus, which is present in the nostrils or pharyngeal mucosa, can infect other people through droplets when coughing, sneezing, or having a conversation.
• Staphylococcus aureus-contaminated hands can be infected by touching someone else’s body or other parts of your body.
• Staphylococcus aureus, which has been contaminated with air, dust, and flies, can be contaminated with food.
• At this time, Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin (enterotoxin/enterotoxin, Enterotoxin) produced by Staphylococcus aureus may be contaminated with food.
• Eating foods contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin can lead to Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning.
• If foods contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus are stored for a long time in a place where Staphylococcus aureus grows, staphylococcus enterotoxin is contaminated with food.
• Staphylococcus aureus other than Staphylococcus aureus can also cause food poisoning.

Photo 2-56. Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning can occur when you cook and eat food without washing your hands well after touching skin infections such as Staphylococcus aureus impetigo. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Symptoms signs of staphylococcal food poisoning
• Symptoms of food poisoning may appear 30 minutes to 8 hours after eating food contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin.
• The average incubation period is 2 to 4 hours.
• Typical symptomatic signs of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin poisoning are severe vomiting, abdominal pain, and collapse.
• Sudden signs of these symptoms may cause severe diarrhea, exhaustion, and cold sweat.
• You may have a mild fever, but you do not have a high fever.
• In severe cases, the body temperature drops, the body becomes cold, blood pressure drops abnormally, and shock may occur.
• If you are sick with this level, you are usually hospitalized.
• Even with appropriate immediate treatment, these symptoms of food poisoning usually persist for 24 to 48 hours.
• Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning can appear almost equally in other people with whom the patient ate food. Diagnosis of staphylococcal food poisoning
• The disease can be diagnosed by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
• After touching the affected area such as a boil or acne caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection, knowing whether you ate food cooked with your hand without washing your hand, or ate food that had been stored at room temperature for a long time, etc., is helpful in diagnosing.
• The symptoms of food poisoning caused by other causes such as Chemical food poisoning, Clostridium perfringens food poisoning, Salmonella food poisoning, and Shigella food poisoning are similar to each other. Aureus food poisoning should be differentially diagnosed (refer to Tables 2-2 and 2-3).
• Sometimes it is difficult to diagnose Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning accurately and quickly.
• It can be diagnosed by performing a Staphylococcus aureus bacterial culture test with the patient’s vomit or feces. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin can be detected and diagnosed.
• A culture of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria in the affected area of a person infected with Staphylococcus aureus can be used to help diagnose.
• It can also be diagnosed by detecting Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin in food. Treatment of staphylococcal food poisoning
• Treat symptomatically according to symptoms.
• In severe cases, hospitalized to prevent dehydration by intravenous injection of glucose electrolyte solution.
• Antibiotic treatment is ineffective.
• When Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin is present in the gastrointestinal tract, diarrhea medications may be given so that the enterotoxin is quickly excreted outside the gastrointestinal tract.
• All food left behind by the patient must be thrown away.
• When treated in this way, it usually recovers completely within 1 to 2 days. Prevention of staphylococcal food poisoning
• In particular, those who cook and handle food should wash their hands thoroughly.
• Wash your hands more thoroughly when you touch a boil or a pus-blowing area.
• Usually, keep leftovers in the refrigerator or discard them.
• Throw away food that has been left at room temperature for a long time.
• Foods contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin do not disappear after boiling in water for 30 minutes.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”