포도상구균 감염병(포도알구균 감염병) Staphylococcal infections
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Chapter 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or 제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)

그림 2-43. 보통 현미경으로 본 황색 포도상구균
메티실린(Methicillin)에 내성이 있는 황색 포도상구균과 메티실린에 내성이 없는 황색 포도상구균으로 분류된다. 메티실린은 페니실린 계에 속하는 일종의 항생제이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

그림 2-42. 전자 현미경으로 본 황색 포도상구균
메티실린Methicillin에 내성이 있는 황색 포도상구균과 메티실린에 내성이 없는 황색 포도상구균으로 분류하기도 한다. 메티실린은 페니실린 계에 속하는 일종의 항생제이다. 출처– 미 CDC
포도상구균에 의한 감염병의 개요와 원인
-
포도상구균은 일종의 그람 양성 박테리아다.
-
참고로 포도상구균을 포도알구균, 또는 포도구균이라고도 한다.
-
포도상구균에는 황색 포도상구균(Staphylococcus aureus), 표피 포도상구균(Staphylococcus epidermidis), 용혈성 포도상구균(Staphylococcus haemolyticus), 부패성 포도상구균(Staphylococcus saprophyticus) 등 여러 종류가 있다.
-
포도상구균은 혈장응고효소(Coagulase) 양성 균과 음성 균으로 나눈다.
-
그 중 황색 포도상구균은 혈장응고효소(Coagulase) 양성 균에 속한다.
-
여러 종류의 포도상구균 중 황색 포도상구균이 감염병을 더 잘 일으킬 수 있다.
-
황색 포도상구균은 또 다시 여러 균종으로 세분된다.
-
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병을 여기서 주로 설명한다.
-
편의상 황색 포도상구균을 포도상구균, 또는 황색 포도상구균이라고 칭한다.
-
황색 포도상구균이 20~50%의 건강한 사람들의 손, 콧구멍, 비강 속, 콧구멍 근처에서 발견된다. 하지만, 황색 포도상구균은 건강한 사람들의 건전한 피부나 점막층을 통과해서 신체 속으로 감염되어 황색 포도상구균 감염병을 잘 일으키지 않는다.
-
그렇지만, 피부 자상 상처나 찰과상 상처 또는 절상 등 피부 외상 상처에 감염되어 거기에 황색 포도상구균 감염병이 생길 수도 있고 그 상처를 통해 신체 내로 감염되어 다음과 같은 여러 종류의 황색 포도상구균 감염병을 일으킬 수 있다.
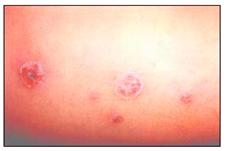
사진 2-44. 황색 포도상구균 감염에 의한 농가진
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
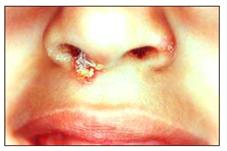
사진 2-45. 콧구멍과 콧구멍 가장자리에 난 황색 포도상구균 피부 감염병으로 생긴 농가진
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
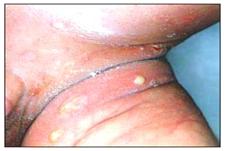
사진 2-46. 신생아에게 생긴 황색 포도상구균 기저귀 피부염은일종의 신생아 농가진
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
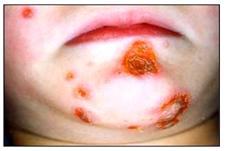
사진 2-47. 얼굴과 턱에 난 황색 포도상구균 농가진
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병
-
-
포도상구균 농가진(부스럼/Staphylococcal impetigo)(제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질환–신생아 농가진, 제17권 소아청소년 피부질환–농가진 참조)
-
포도상구균 종기(Staphylococcal abscesses)(호발주/뾰루지) (p.00 종기, p.00 농가진 참조)
-
포도상구균 골수염과 관절염(Staphylococcal osteomyelitis and arthritis)(제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환–골수염, 급성 관절염 참조)
-
포도상구균 폐렴과 농흉(Staphylococcal pneumonia and empyema)(제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환–포도상구균 폐렴, 늑막염과 농흉 참조)
-
포도상구균 안와 주위 봉소염(Staphylococcal periorbital cellulitis)(제19권 소아청소년 안과질환–안와 주위 봉소염 참조)
-
포도상구균 근육염(Staphylococcal myositis)
-
포도상구균 패혈증(Staphylococcal septicemia)(p.00 패혈증 참조)
-
포도상구균 식중독(Staphylococcal food poisoning)(p.00 식중독 참조)
-
포도상구균 열상감염이나 자상 감염(Staphylococcal infection of laceration or punctured wound)(제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료–자상, 절상 참조)
-
포도상구균 림프절염(Staphylococcal lymphadenitis)(제13권 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환–목에 있는 림프절 비대와 림프절염 참조)
-
포도상구균 간농양(Staphylococcal liver abscesses)
-
포도상구균 뇌농양(Staphylococcal brain abscesses)
-
포도상구균 독성 쇼크 증후군(Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome)
-
포도상구균 화상 피부 증후군(Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome/ssss)(제15권 소아청소년 알레르기 질환 참조)
-
포도상구균 괴사성 근막염 (Staphylococcal necrotizing fasciitis)
-
포도상구균 괴사성 폐렴 (Staphylococcal necrotizing pneumonia)
-
포도상구균 전격성 자반병 (Staphylococcal purpura fulminans)
-
포도상구균 심장 내막염(Staphylococcal endocarditis)(제11권 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환 참조)
-
포도상구균 급성 신장염(Acute staphylococcal nephritis)
-
다형 홍반(Erythema multiforme)(제17권 소아청소년 피부질환 참조)
-
포도상구균 척추염(Staphylococcal vertebritis)(제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환 참조)
-
그 외
-
-
평소에도 20~50%의 사람들의 비강의 앞쪽 부분이나 콧구멍의 가장자리, 손 등 신체의 여러 부위에 황색 포도상구균을 보균하고 있다.
-
황색 포도상구균을 보균한 사람이 다른 사람들에게 황색 포도상구균을 감염시킬 수 있다.
-
많은 경우, 본인이 자기 자신에게 자가 감염시킬 수 있다.
-
일반적으로 황색 포도상구균은 피부나 점막 상처가 전혀 나지 않은 건강한 피부나 점막을 통해 체내로 잘 감염되지 않지만 불결한 피부의 상처를 통해서나 상처 입은 점막을 통해 잘 감염될 수 있다.
-
황색 포도상구균이 피부나 연조직에 감염되어 농가진, 종기, 봉소염 등 황색 포도상구균 피부염 및, 또는 다른 여러 종류의 황색 포도상구균 감염병이 피부 및 그 외 신체의 여러 부분에 생길 수 있다.
-
황색 포도상구균을 보균한 사람이나 황색 포도상구균 감염병 환부에서 나온 피나 고름 등을 손으로 만지거나 피나 고름이 신체 다른 어느 부위에 직접 접촉될 때 황색 포도상구균에 감염될 수 있다.
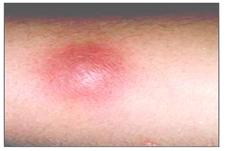
사진 2-48. 황색 포도상구균 종기
세균 감염으로 종기가 날 때는 1-아프다, 2-붓는다, 3-붉어진다, 4-국소염이 난다. 이 4가지 증상 징후가 종기 등을 진단하는 임상 기준이 될 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
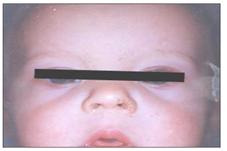
사진 2-49. 콧구멍 속과 콧구멍 가장자리에 난 황색 포도상구균 감염병
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병의 잠복기
-
황색 포도상구균 감염병이 신체 어느 부위에 생겨 있나, 신체의 어떤 계통의 어떤 기관이나 조직에 생겨 있는지에 따라 잠복기가 다르다.
-
농가진이나 화상 피부 증후군의 잠복기는 1~10일이고
-
그 밖의 포도상구균 감염병의 잠복기는 때에 따라 다르다.
-
포도상구균 식중독의 잠복기는 30분~8시간이다.
-
포도상구균 화상 피부 증후군(Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome/ssss)의 잠복기는 1~10일이다.
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병의 증상 징후
-
황색 포도상구균 감염병의 증상 징후는 감염병이 생긴 신체의 부위와 기관,
-
감염병의 정도, 병일 등에 따라 다르다.
-
앞서 나열한 각 황색 포도상구균 감염병의 증상 징후는 황색 포도상구균 감염병의 각항을 참조.
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 진단하는 것이 보통이다.
-
황색 포도상구균 감염병의 종류 및, 또는 신체의 어느 부위에 생겼는지에 따라 진단 치료 방법이 다를 수 있다.
-
예를 들면, 황색 포도상구균 골수염, 황색 포도상구균 관절염, 또는 황색 포도상구균 폐렴 등 생명을 위협할 수 있는 위중한 포도상구균 감염병을 앓을 때는 항생제 치료를 시작하기 바로 전에, 가능한 한 환부나 병소 또는 적절한 신체의 부위에서 피, 고름, 또는 가피 등 세균검사용 피검 물을 적절히 채취해 황색 포도상구균 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사와 세균 배양검사 등을 하면서 어떤 종류의 황색 포도상구균 감염에 의해 감염병이 생겼는지 알아보면서 항생제 치료를 시작할 수 있다.
-
그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사, 세균 배양검사, 황색 포도상구균 항생제 감수성 검사의 결과에 따라 그 황색 포도상구균 감염병 치료에 가장 잘 듣는 항생제를 선택해 그 항생제로 치료하고 필요에 따라 배농 수술 치료를 적절히 하는 것이 가장 이상적 치료다.
-
그러나 이런 검사를 하기 전 가장 많이 권장하는 항생제를 경험적으로 선택해 치료를 시작하는 것이 보통이다. 황색 포도상구균이 “커뮤니티 관련성 황색 포도상구균(CMMRSA)”에 속하는지 아닌지 알아보는데 “D 테스트“를 하기도 한다. p.00 세균검사 참조.
-
메티실린(Methilcillin) 내성 황색 포도상구균에 감염됐을 때 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균에 감염됐는지, 메티실린 내성이 없는 보통 황색 포도상구균에 감염됐는지 2시간 내 알아볼 수 있는 BD GeneOhm Staph SR 검사법이 미 FDA의 허가를 받았다(Pediatric News, February 2008, p.5).
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병의 치료
-
메티실린(Methicillin), Oxacillin, Dicloxacillin, Cefazolin, Vancomycin 등 여러 종류의 항생제들 중 한 종류나 두 종류의 항생제를 선택해서 황색 포도상구균 감염병을 치료할 수 있다.
-
황색 포도상구균은 황아가 살고 있는 지방이나 나라에 따라, 그때그때에 따라, 또 해마다 메티실린 항생제에 내성이 생길 수 있다.
-
그래서 이상 열거한 항생제에 황색 포도상구균이 죽지 않아 황색 포도상구균 감염병이 치료되지 않을 수 있다.
-
이런 황색 포도상구균을 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균이라고 한다.
-
메티실린 내성 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 점염병을 항생제로 치료 할 때 심각한 황색 포도상구균 감염병 치료 문제가 오늘날 생기고 있다.
-
병원 내에서 황색 포도상구균이 감염되지 않고 병원 바깥, 즉 평소 살고 있는 지역에서 감염되어 생긴 황색 포도상구균 감염병이 메티실린 항생제로 치료 되지 않을 때가 가끔 있다.
-
이런 황색 포도상구균을 “커뮤니티 관련 메티실린 내성 포도상구균(Community-acquired methicillin-resistant staphyllococcus aureus/CA-MRSA) “이라한다.
-
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, Clindamycin, Minocycline, Doxycycline, Linezolid, daptomycin, Quinupristin-dalfopristin, Vancomycin 등의 항생제 중 한 종류를 선택해서 “커뮤니티 관련 메티실린 내성 포도상구균” 감염병을 요즘 치료하기도 한다.
-
몇 년 전에는, 메티실린(Methicillin sodium) 내성 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병을 Vancomycin 제로 치료했으나 최근에는 Daptomycin으로 치료하기도 한다. 출처: Infectious disease in children, June 2008.
-
이런저런 이유로, 어디까지나 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병을 치료할 때는 그때그때 상황에 따라 적절한 항생제를 선택해서 치료 한다.
-
항생제로 치료를 시작하기 전에 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병의 병소에서 가능한 한 피, 고름 등 적절한 세균 검사용 피검물을 채취해서 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사, 세균 배양검사, 및 항생제 세균 감수성 검사로 진단 치료 하는 것이 이상적 치료 방법이다.
-
이런 식으로 치료하려면 치료비용이 상당하다. 그리고 이런 식의 치료를 할 수 있는 의료 시설이 갖추어져야 한다.
-
황색 포도상구균 종기나 봉소염 등으로 고름이 잡혀있으면 배농 수술 치료를 하고 필요에 따라 더운찜질 치료를 하고 적절한 항생제로 치료할 수 있다.
-
부스럼과 같이 경미한 황색 포도상구균 피부 감염병은 경구용 항생제 및, 또는 박트로반 항생제 연고(Bactroban ointment/Mupirocin ointment) 등으로 치료할 수 있다.
-
이런 항생제로 치료할 때도 어디까지나 의사의 판단에 따라 치료한다.
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병을 앓는 환아 격리
-
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병의 환부에서 나온 황색 포도상구균이 손이나 의복 등에 묻거나 그 환부가 신체의 다른 어느 부위에 직접 접촉될 때 황색 포도상구균이 환아 자신이나 다른 사람들에게 쉽게 감염될 수 있다.
-
또 환부에서 나오는 진물이나 피고름 등을 닦은 치료용 거즈나 종기나 부스럼 등을 치료할 때 쓴 의료 기구에 접촉해도 감염될 수 있다.
-
다 낫지 않은 농가진이나 종기 등 포도상구균 피부염을 거즈나 반창고 등으로 덮어서 황색 포도상구균이 환아 본인이나 다른 사람들에게 더 이상 감염되지 않도록 예방해야 한다.
-
황색 포도상구균 감염병을 치료하기 위해서 병원에 입원할 때는 의사의 지시에 따라 그 환아를 다른 환자로부터 격리시켜 치료해야 한다.
-
주치의와 주치 간호사 자신에게 감염되지 않게 장갑을 끼는 등 세심한 감염 예방을 해야 한다.
-
황색 포도상구균 감염병을 앓는 아이와 접촉했을 때는 황색 포도상구균에 접촉된 사람에게 감염될 수 있다.
-
따라서 접촉된 후 10일 간 조심히 관찰해야 한다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 질환–신생아 농가진,
-
제17권 소아청소년 피부질환–농가진 참조.
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병의 예방
-
아직까지 예방접종 백신은 없다.
-
이 병을 항생제로 예방하지 않는다.
-
가장 좋은 예방 방법은 손을 평소에 깨끗이 씻는 방법이다.
-
다음과 같은 면에서 특히 위생관리를 더 잘 해야 한다.
-
수건, 면도, 비누, 화장도구 등을 서로 같이 쓰지 않는다.
-
피부에 상처가 생기면 물과 비누로 깨끗이 씻고 적절한 살균제로 바로 살균 치료한다. 파이소헥스 살균제 또는 베타다인 살균제를 사용할 수 있다.
-
Chlohexdine이나 황색 포도상구균을 죽일 수 있는 비누를 적절히 사용한다.
-
Mupirocin 연고(Bactroban)를 코 구멍 속과 그 주위에 필요에 따라 바른다.
-
손을 더 깨끗이 씻는다.
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병 및 질병의 합병증
-
포도상 구균이 신체의 다른 부위로 자가 감염될 수 있고 다음과 같은 합병증이 생길 수 있다.
-
포도상 구균 패혈증.
-
폐, 신장, 간장 등 각 계통의 각종 내장에 포도상 구균 농양.
-
포도상 구균 골수염.
-
포도상 구균 심내막염 .
-
뇌 포도상 구균 농양.
-
포도상 구균 척추 농양.
-
그 외
아토피성 피부염과 화농성 피부염
-
아토피성 피부염이 있는 사람들의 피부층에 피부 펩티드(Skin peptide)의 농도는 비정상적으로 더 낮다. 그래서 그들의 피부에 화농성 피부염이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
아토피성 피부염의 주 증상의 하나가 가려운 증상, 즉 소양감이다.
-
피부에 가려운 증상 징후가 생기면 긁고, 긁으면 긁힌 피부에 상처가 나고, 그 상처를 통해 황색 포도상구균이나 A군 연구균 등 화농성 세균이 감염되어 농가진, 종기, 모낭염, 또는 뾰루지 등이 날 수 있다.
-
이런 이유로, 아토피성 피부염이 있지 않은 소아청소년들보다 아토피성 피부염이 있는 소아청소년들의 피부에 황색 포도상구균 피부염이 더 잘 생긴다.
-
다시 설명하면, 화농성 세균성 피부염을 예방할 수 있는 피부 펩티드 농도가 아토피성 피부염이 있는 소아청소년들의 피부층에는 정상보다 더 낮기 때문에 그로 인해 아토피성 피부염이 있는 소아청소년들이나 아토피성 피부염의 병력이 있는 소아청소년들에게 화농성 세균성 피부염이 더 잘 생긴다.
황색 포도상구균이 여러 종류의 항생제 내성이 생겨 그로 인한 황색 포도상 균 감염병을 치료하는데 요즘 심각한 임상 건강 문제가 생길 수 있다.
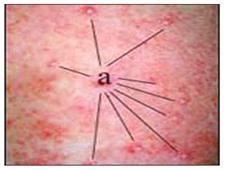
사진 2-50. 황색 포도상구균 모낭염(여포염)
아토피성 피부염이 있는 소아청소년들의 피부에 황색 포도상구균 감염이 더 잘 생길 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병을 치료하는데 특별히 효과가 있었던 항생제로 잘 알려졌던 메티실린(Methicillin)이나 밴코마이신(Vancomycin) 등 항생제 치료에도 황색 포도상구균이 내성이 생겨 큰 걱정거리이다.
-
요즘, 메티실린 항생제나 밴코마이신에 내성이 있는 “병원 관련성 황색 포도상구균감염“으로 생긴 감염병이 병원 중환자실, 신생아실 지붕 치료실, 또는 일반 환자실 등에 입원한 사람들에게 점점 더 많이 발생되는 추세다.
-
그뿐만 아니라, 병원의 바깥 지역사회에서 사는 사람들에게 생긴 “커뮤니티 관련성 황색 포도상구균” 감염병 병소에서 발견된 황색 포도상구균이 메티실린 항생제 치료에 내성이 생기고 있다.
-
메티실린 내성이 있는 “병원 관련성 황색 포도상구균 감염병에서 발견된 황색 포도상구균이 메티실린 내성이 있을 때 그 황색 포도상구균을 “병원 관련성 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균(HMRSA)이라한다.
-
병원의 바깥 지역사회에서 사는 사람들에게 생긴 황색 포도상구균 감염병에서 발견된 황색 포도상구균이 메티실린에 내성이 있을 때 메티실린에 내성이 있는 황색 포도상구균을 “지역사회 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균” 또는 “커뮤니티 관련성 황색 포도상구균(CMMRSA)“이라고 한다. 황색 포도상구균 감염병이 있을 때 이렇게 분류 하는 것은 황색 포도상구균 감염병 치료에 상당히 도움 된다.
-
메티실린에 내성 있는 황색 포도상구균(Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus)감염으로 생긴 종기 등을 Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, Minocycline, 또는 Clindamycin 등 항생제로 치료하기도 한다.
-
그래서 내성이 생겨 이런 항생제 치료에 치료되지 않는 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 폐렴이나 관절염 등을 치료하는 데 큰 문제가 생기고, 이런 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 종기 등을 치료하는 데도 문제가 생기고 있다.
-
요즘, 메티실린에 내성이 있는 황색 포도상구균 감염병은 클린다마이신(Clindamycin) 항생제로 치료할 수 있고, 피부에 생긴 경미한 황색 포도상구균 감염병은 뮤피로신(Mupirocin 연고/박트로반 연고) 등으로 치료하기도 한다.
-
때로는 그런 종류의 항생제에도 내성이 생길 수 있다.
Staphylococcal infections 포도상구균 감염병(포도알구균 감염병)

- Figure 2-43. Staphylococcus aureus as seen under a normal microscope. It is classified into Staphylococcus aureus, which is resistant to methicillin, and Staphylococcus aureus, which is not resistant to methicillin. Methicillin is a type of antibiotic belonging to the penicillin family. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 2-42. Staphylococcus aureus seen under an electron microscope. It is also classified as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-not-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Methicillin is a type of antibiotic belonging to the penicillin family. Source- US CDC Overview and causes of infectious diseases caused by staphylococcus Staphylococcus is a type of Gram-positive bacteria. For reference, staphylococcus is also called staphylococcus. There are several types of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, etc. Staphylococcus aureus is divided into plasma coagulase positive bacteria and negative bacteria.
- Among them, Staphylococcus aureus belongs to plasma coagulase positive bacteria. Of the many types of staphylococcus, Staphylococcus aureus is more likely to cause infectious diseases.
- Staphylococcus aureus is again subdivided into several species. Infectious diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection are mainly described here.
- For convenience, Staphylococcus aureus is referred to as Staphylococcus aureus.
- Staphylococcus aureus is found in the hands, nostrils, nasal passages, and near the nostrils of 20-50% of healthy people.
- However, staphylococcus does not easily cause Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease by passing through healthy skin or mucous membranes and infecting the body.
- However, a staphylococcus aureus infectious disease may occur thereby being infected with a cutaneous cut, abrasion, or cut, or a Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease in the body through the wound, which can cause several types of Staphylococcus aureus infectious diseases, such as:

Photo 2-44. Impetigo due to Staphylococcus aureus infection. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-45. Impetigo caused by a Staphylococcus aureus skin infection on the nostrils and edges of the nostrils. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-46. Staphylococcus aureus diaper dermatitis in newborns is a type of newborn impetigo. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-47. Staphylococcus aureus impetigo on the face and chin. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Infectious diseases and diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection
Staphylococcal impetigo (refer to Volume 6, Newborn Growth and Development and Disease-Newborn Impetigo, Volume 17 Pediatric and Adolescent Skin Diseases-Impetigo)
- Staphylococcal abscesses (refer to p. Staphylococcal osteomyelitis and arthritis (See Vol. 16, Children’s and Adolescent Orthopedic Diseases-Osteomyelitis, Acute Arthritis)
- Staphylococcal pneumonia and empyema (refer to Volume 8 Child and Adolescent Respiratory Disease-Staphylococcal pneumonia, pleurisy and empyema)
- Staphylococcal periorbital cellulitis (refer to Volume 19 Child and Adolescent Eye Diseases-Orbital Cellulitis)
- Staphylococcal myositis Staphylococcal septicemia (refer to p.00, septicemia) Staphylococcal food poisoning (refer to p.00 Food poisoning)
- Staphylococcal infection of laceration or puncture wound (See Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents-Cuts, Cuts)
- Staphylococcal lymphadenitis (See Vol. 13 Children and Adolescent Blood, Lymph, Tumor Diseases-Lymph Node Enlargement and Lymphadenitis in the Neck)
- Staphylococcal liver abscesses Staphylococcal brain abscesses
- Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome/ssss (See Volume 15, Children’s and Adolescent Allergic Diseases)
- Staphylococcal necrotizing fasciitis
- Staphylococcal necrotizing pneumonia Staphylococcal purpura fulminans
- Staphylococcal endocarditis (see Volume 11 Cardiovascular Disease in Children and Adolescents)
- Acute staphylococcal nephritis
- Erythema multiforme (refer to Volume 17, Pediatric and Adolescent Skin Diseases) Staphylococcal vertebritis (see Volume 16, Pediatric and Adolescent Orthopedic Diseases) etc. Usually, 20-50% of people carry
- Staphylococcus aureus in various parts of the body, such as the front part of the nasal cavity, the edge of the nostril, and the hand.
- People with Staphylococcus aureus can infect others with Staphylococcus aureus. In many cases, you can self-infect yourself. In general,
- Staphylococcus aureus is not easily infected into the body through healthy skin or mucous membranes that have no skin or mucous membrane wounds but can be easily infected through wounds of unclean skin or through wounded mucous membranes.
- Staphylococcus aureus dermatitis, such as impetigo, boils, blepharitis, and several other types of Staphylococcus aureus infectious diseases can occur on the skin and other parts of the body due to infection of Staphylococcus aureus to the skin or soft tissue.
- People who have Staphylococcus aureus or when they touch blood or pus from an affected area of Staphylococcus aureus infection with their hands, or when blood or pus comes into direct contact with any other part of the body, they can become infected with Staphylococcus aureus.

Photo 2-48. Staphylococcus aureus boils. When a boil occurs due to a bacterial infection, 1-sick, 2-swelling, 3-red, 4-localized. These four symptom signs can serve as a clinical criterion for diagnosing boils, etc. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-49. Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease in the nostrils and on the edges of the nostrils Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
The incubation period of infectious diseases and diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection
- The incubation period differs depending on where the Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease occurs in the body, and in which organs or tissues of the body. The incubation period for impetigo or burn skin syndrome is 1-10 days.
- The incubation period for other staphylococcal infectious diseases varies from time to time. The incubation period for staphylococcal food poisoning is 30 minutes to 8 hours. The incubation period for Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome/ssss is 1-10 days.
Symptoms. signs of infectious diseases and diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus
Symptoms and signs of Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease include the parts and organs of the body where the disease has occurred. It depends on the severity of the infectious disease and the day of the disease.
For symptoms and signs of each Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease listed above, refer to each section of Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease.
Diagnosis of infectious diseases and diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus
- It is common to comprehensively diagnose medical history, symptoms, and medical findings.
- Depending on the type of Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease and where it occurs in the body, the diagnostic treatment method may be different.
- For example, if you suffer from serious life-threatening staphylococcal infections such as staphylococcal osteomyelitis, yellow staphylococcal arthritis, or staphylococcal pneumonia, immediately before starting antibiotic treatment,
- Antibiotic treatment is performed while appropriately collecting specimens for bacterial examination such as blood, pus, or crust from the site and performing a bacterial examination under a Staphylococcus aureus Gram staining microscope and a bacterial culture examination.
- According to the results of the Gram staining microscopy bacterial examination, bacterial culture examination, and susceptibility test for staphylococcus aureus antibiotics, it is most ideal to select the antibiotic that best suits the treatment of the Staphylococcus aureus infection, treat it with that antibiotic, and appropriately treats drainage surgery as needed.
- It’s treatment. However, it is common to start treatment by empirically selecting the most recommended antibiotic before performing such a test.
- A “D-test” is sometimes performed to determine whether Staphylococcus aureus belongs to “Community-related Staphylococcus aureus (CMMRSA)”.
- Refer to Bacterial test. If you are infected with Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, the BD GeneOhm Staph SR test method, which can be used to determine whether you are infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or infected with ordinary Staphylococcus aureus that is not methicillin-resistant, is the FDA With permission (Pediatric News, February 2008, p.5).
Treatment of infectious diseases and diseases caused by Staphylococcus
aureus
• You can treat Staphylococcus aureus infection by choosing one or two antibiotics from several types of antibiotics such as Methicillin, Oxacillin, Dicloxacillin, Cefazolin, and Vancomycin.
• Staphylococcus aureus can develop resistance to methicillin antibiotics, depending on the region or country in which the yellow baby lives, from time to time, and from year to year.
• Therefore, the antibiotics listed above do not kill Staphylococcus aureus, which may not cure Staphylococcus aureus infections.
• These Staphylococcus aureus are called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
• Severe Staphylococcus aureus infection treatment problems arise today when antibiotics are used to treat mucous infections caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcal infections.
• Sometimes in hospitals, Staphylococcus aureus infections are not infected, and Staphylococcus aureus infections caused by infections outside the hospital, ie in the area where they live, are sometimes not treated with methicillin antibiotics.
• These Staphylococcus aureus are called “Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus/CA-MRSA”.
• Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, Clindamycin, Minocycline, Doxycycline, Linezolid, daptomycin, Quinupristin-dalfopristin, Vancomycin, and other antibiotics are used to treat the “community-related methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus” infection.
• Several years ago, an infectious disease caused by a methicillin resistant staphylococcal infection was treated with Vancomycin, but recently Daptomycin has also been used. Source: Infectious disease in children, June 2008.
• For one reason or another, when treating infectious diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection for the last time, appropriate antibiotics are selected and treated according to the situation.
• Before starting treatment with antibiotics, collect appropriate bacterial test specimens such as blood and pus from the lesions caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection and diagnose them with Gram-stained microscopic bacterial tests, bacterial culture tests, and antibiotic bacterial susceptibility tests. Treatment is the ideal treatment method.
• Treatment in this way is expensive. And medical facilities that can do this kind of treatment should be equipped.
• If pus is caught due to Staphylococcus aureus boil or cellulitis, drainage surgery can be performed, if necessary, hot compresses can be treated, and appropriate antibiotics can be used.
• Mild Staphylococcus aureus skin infections such as swelling can be treated with oral antibiotics or Bactroban ointment/Mupirocin ointment.
• Even when treated with these antibiotics, it is treated according to the doctor’s judgment. Isolation of children suffering from infectious diseases and diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection
• Staphylococcus aureus can easily infect the child or others when Staphylococcus aureus from the affected area of an infectious disease caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection gets on hands or clothing, or when the affected area comes into direct contact with any other part of the body.
• You can also get infected by contacting medical devices used to treat swelling or swelling, or gauze used to wipe out the discharge or bloody pus from the affected area.
Staphylococcus aureus dermatitis, such as impetigo or boils that are not healed, should be covered with gauze or band-aids to prevent further infection of Staphylococcus aureus to the child or others.
When admitted to the hospital to treat Staphylococcus aureus infection,
the child must be isolated from other patients and treated according to the doctor’s instructions.
• Care should be taken to prevent infection, such as wearing gloves to prevent infection to the attending physician and the attending nurse himself.
• Contact with a child with Staphylococcus aureus infection can lead to infection in people who have come into contact with Staphylococcus aureus.
• Therefore, it should be observed carefully for 10 days after contact
• [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 6 Neonatal growth and development disease-Newborn impetigo, • See Volume 17 Child and Adolescent Skin Diseases-Impetigo.
Prevention of infectious diseases and diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection
• There is no vaccination vaccine yet.
• Do not prevent this disease with antibiotics.
• The best prevention is to wash your hands regularly.
• Better hygiene, especially in the following areas:
• Do not share towels, shaving, soap, and makeup tools.
• If there is a wound on the skin, wash it thoroughly with water and soap and immediately sterilize it with an appropriate disinfectant.
Phisohex disinfectant or betadine disinfectant may be used.
• Use chlorohexidine or soap that can kill Staphylococcus aureus properly.
• Apply Mupirocin ointment (Bactroban) into and around the nasal cavity as needed • Wash your hands more thoroughly.
Infectious diseases and complications of diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection
• Staphylococcus can infect other parts of the body and cause complications such as:
• Staphylococcal sepsis. Staphylococcal abscess in various intestines of each system, such as lungs, kidneys, and liver.
• Staphylococcal osteomyelitis.
• Staphylococcal endocarditis.
• Brain staphylococcal abscess.
• Staphylococcal spinal abscess.
• Atopic dermatitis and purulent dermatitis
• The concentration of skin peptides in the skin layers of people with atopic dermatitis is abnormally lower. So, purulent dermatitis is more likely to develop on their skin. • One of the main symptoms of atopic dermatitis is itching, that is, itching.
• If there are signs of itchy symptoms on the skin, it may be scratched, and if scratched, the scratched skin may be injured, and purulent bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or group A research bacteria may become infected, resulting in impetigo, boils, folliculitis, or rashes.
• For this reason,
Staphylococcus aureus dermatitis is more prevalent on the skin of children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis than children without atopic dermatitis.
• In other words, since the concentration of skin peptides that can prevent purulent bacterial dermatitis is lower than normal in the skin layer of children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis, this causes children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis or children and adolescents with a history of atopic dermatitis.
They are more prone to purulent bacterial dermatitis.
Staphylococcus aureus develops resistance to several types of antibiotics, which can cause serious clinical health problems to treat the resulting Staphylococcus aureus infection.

Photo 2-50. Staphylococcal folliculitis Children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis are more likely to develop Staphylococcus aureus infection on the skin. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Staphylococcus aureus has become resistant to antibiotic treatment such as Methicillin and Vancomycin, which are well known as antibiotics that have been particularly effective in treating infectious diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection, which is a big concern.
• Nowadays, infectious diseases caused by “hospital-related Staphylococcus aureus infection” resistant to methicillin antibiotics or vancomycin are becoming more common among people admitted to hospital intensive care units, neonatal roof treatment rooms, or general patient rooms.
• In addition, Staphylococcus aureus found in a “community-related Staphylococcus aureus” infectious disease lesion in people living in communities outside hospitals is becoming resistant to methicillin antibiotic treatment.
• Methicillin-Resistant “hospital-related Staphylococcus aureus When the Staphylococcus aureus found in a methicillin-resistant disease is methicillin-resistant, the Staphylococcus aureus is called “hospital-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (HMRSA).”
• Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is referred to as “community methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus” or when the Staphylococcus aureus found in a Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease in people living outside the hospital is resistant to methicillin.
It is called “Community-related Staphylococcus aureus (CMMRSA).”
This classification of Staphylococcus aureus infectious diseases is very helpful in treating Staphylococcus aureus infections.
• Boils caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection are sometimes treated with antibiotics such as Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, Minocycline, or Clindamycin.
• So, there is a big problem in treating pneumonia or arthritis caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection, which is not cured by these antibiotic treatments due to resistance, and there is also a problem in treating boils caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection.
• Nowadays, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections can be treated with Clindamycin antibiotics, and mild Staphylococcus aureus infections on the skin are sometimes treated with Mupirocin ointment/Bactroban ointment.
• Sometimes resistance to those kinds of antibiotics can develop.
infection One of several antibiotics, such as Methicillin, Oxacillin, Dicloxacillin, Cefazolin, and Vancomycin
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
-
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”