포도상구균성 폐렴 Staphylococcus pneumonia
| 포도상구균성 폐렴의 원인 |
- 포도상구균에는 황색 포도상구균(S. aureus), 표피 포도상구균(S. epidermidis), 사람 포도상구균(S. homins), 용혈성 포도상구균(S. haemolyticus) 등 여러 종류가 있다. 그 중 황색 포도상구균이란 박테리아 감염이 임상적으로 문제가 가장 많이 생긴다.
- 여기서는 황색 포도상구균 감염에 관해 주로 설명한다. 황색 포도상구균 감염에 의해 생긴 폐감염병을 황색 포도상구균 폐렴이라고 한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 폐렴은 일종의 박테리아 폐렴이다. 이 폐렴에 걸리면 어느 연령층이든 상당히 심하게 앓을 수 있다. 초기에 적절히 속히 치료해 주지 않으면 여러 종류의 합병증이 생길 수도 있고 사망하는 경우도 많다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아 청소년 감염병-황색 포도상구균에 의한 감염병 참조
- 그 여러 종류의 포도상구균 균종 중 황색 포도상구균이 주로 감염병을 일으킨다. 아무런 감염병이 나타나지 않는 데도 많은 사람들은 피부, 콧구멍과 그 가장자리, 코 전정, 비강 점막층, 인두 점막층, 손 등에 황색 포도상구균을 보균하고 있다.
- 나이에 따라 좀 다르지만 20~30%의 소아 청소년들이 황색 포도상구균에 의한 감염병이 없이 평소에도 위에서 설명한 신체부위에 보균하고 있다. 누구든지 황색 포도상구균 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있지만 신생아들, 돌 이전 영아들, 특히 생후 3개월 이전 영아들, 바이러스 상기도염을 앓고 있는 영유아들, 영양실조 영유아들, 쇠약한 아이들이 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
- 농가진이나 종기 등 황색 포도상구균 피부염을 앓을 때 그 피부염을 일으켰던 황색 포도상구균이 폐에 감염되어 황색 포도상구균 폐렴을 일으킬 수 있다.
- 한 집안 식구들 중 누구든지 농가진을 앓을 때 농가진을 일으킨 황색 포도상구균이 다른 식구에게 감염 되어 그 식구가 황색 포도상구균 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 자기가 가지고 있는 황색 포도상구균 감염병에 있던 황색 포도상구균이 자신에게도 감염되는 자가 감염도 생길 수도 있다.
포도상구균 폐렴의 증상 징후
- 나이, 중증도, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 다른 종류의 박테리아 폐렴을 앓을 때와 거의 마찬가지로 갑자기 고열이 나면서 기침을 심하게 하며 숨이 찰 수 있다. 피부가 창백하면서 정신이 불안해지고 기면 상태에 빠지면서 보채고 몹시 아파 보이고 독성 상태에 빠지게 된다.
- 숨 쉴 때마다 갈비뼈 사이에 있는 늑골 근육이 흉강 속을 향해서 빨려 들어갔다 나왔다 하면서 심한 호흡곤란이 생길 수 있다.
- 구토, 설사, 복통의 증상 징후도 있고 어딘가 몹시 아픈 것 같아 보인다. 신생아들이나 영아들이 이 폐렴에 걸리면 기운이 하나도 없이 잠만 계속 자면서 음식물을 통 먹지 않을 수 있다.
- 이 병을 빨리 적절히 치료해 주지 않으면 황색 포도상구균 농흉, 폐농양, 그 밖의 다른 여러 종류의 황색 포도상구균 감염성 합병증이 생길 수 있다. 그리고 심지어는 쇼크에 빠지고 사망하게 된다.
- 흡인성 폐렴, 기흉 참조
| 포도상구균성 폐렴의 진단 |
- 병력, 증상징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 폐렴이 의심되면 가슴 X-선 사진, CBC 피 검사, 가래를 채취하여 그 피 검물로 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균 배양검사 등으로 진단한다. 나이, 환자 자신이나 식구들 중 누군가가 황색 포도상구균에 의한 피부 감염병 등을 앓고 있을 때는 이 폐렴을 진단하는데 큰 도움이 된다.
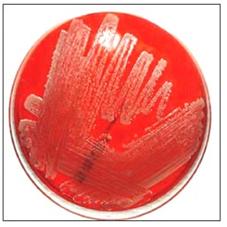
사진 107. 황색 포도상구균성 감염으로 생긴 병소에서 피나 고름 등으로 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균 배양검사를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
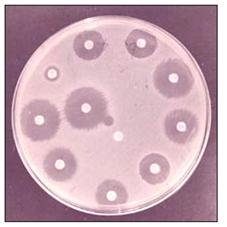
사진 108. 세균 배양검사에서 배양된 세균을 가장 잘 죽일 수 있는 항생제를 찾는 항균제감수성 검사를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
| 포도상구균성 폐렴의 치료 |
- 황색 포도상구균에 의해 생긴 폐렴은 응급으로 진단 치료 한다.
- 요즘 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균(Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus/MRSA)에 감염되면 적절한 항생제를 선택하는 데도 어렵다. 그래서 치료 문제가 전 세계적으로 생길 수도 있다.
- 병원에 입원해서 나프실린(Nafcillin), 옥사실린(Oxacillin), Vancomycin, Clindamycin, Gentamicin, Rifamfin, Cephalosporin, Sulbactam, 또는 Trimethoprime-sulfamethoxazole, Linezolid 등 항생제들 중 한 가지 또는 두세 가지 항생제를 임상 경험을 토대로 선택해 치료를 시작하는 것이 보통이다.
- 적절한 항생제들 중 선택한 한 가지 항생제를 정맥주사로 치료하거나 두세 가지 항생제 정맥주사로 치료하기 시작하고 병소에서 얻은 피검 물로 세균 배양검사를 하고 그 검사에서 나온 황색 포도상구균으로 항균제 감수성 검사를 하고 그 결과에 따라 적절한 항생제를 선택해 치료한다.
- 필요에 따라 산소호흡치료를 하고, 머리와 상체를 하체보다 15도 정도 낮게 눕히고 컵과 같이 살짝 오므린 손바닥으로 앞가슴과 등을 살살 두들겨 기도 속에 괸 가래를 더 쉽게 뱉어내도록 도와주는 물리치료도 한다.
- 증상 징후에 따라 탈수를 예방 치료해 주기 위해서 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 치료한다.
- 음식물은 먹을 수 있는 양만큼 처음에는 전 유동 음식물을 먹다가 그 다음 반 유동 음식물로 바꾸어 주고 그 다음에는 보통 때 먹던 음식물로 점차로 바꾸어 준다.
- 황색 포도상구균은 감염성이 아주 강한 박테리아이다. 그러므로 환아를 다른 사람으로부터 격리 치료해야 한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 폐렴을 앓을 때 농흉이나 기흉 등 합병증이 없을 때는 황색 포도상구균 폐렴 초기에는 적절한 항생제로 잘 치료해 주면 잘 나을 수 있다.
- 농흉이나 기흉 등의 합병증이 생기고 폐렴이 상당히 진행되었을 때는 농흉 속에 괸 고름을 수술로 빼주는 치료를 한다.
- 어떤 경우는 황색 포도상구균으로 곪은 폐 부분을 절제치료 한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 폐렴을 앓는 환자의 폐렴 병소에서 가래나 고름 등이 더 이상 나오지 않을 때까지 다른 사람들로부터 환자를 격리 치료한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 피부염, 또는 황색 포도상구균 관절염을 앓는 환아도 격리 치료 한다.
- 이런 병을 앓고 있는 사람과 접촉한 사람에게 황색 포도상구균이 감염될 가능성이 있으므로 황색 포도상구균 감염병이 그들에게 생기는지 조심히 관찰한다.
- 예방접종 백신은 아직 없다.
포도상구균성 폐렴 Staphylococcus pneumonia
| 포도상구균성 폐렴의 원인 |
- 포도상구균에는 황색 포도상구균(S. aureus), 표피 포도상구균(S. epidermidis), 사람 포도상구균(S. homins), 용혈성 포도상구균(S. haemolyticus) 등 여러 종류가 있다. 그 중 황색 포도상구균이란 박테리아 감염이 임상적으로 문제가 가장 많이 생긴다.
- 여기서는 황색 포도상구균 감염에 관해 주로 설명한다. 황색 포도상구균 감염에 의해 생긴 폐감염병을 황색 포도상구균 폐렴이라고 한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 폐렴은 일종의 박테리아 폐렴이다. 이 폐렴에 걸리면 어느 연령층이든 상당히 심하게 앓을 수 있다. 초기에 적절히 속히 치료해 주지 않으면 여러 종류의 합병증이 생길 수도 있고 사망하는 경우도 많다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아 청소년 감염병-황색 포도상구균에 의한 감염병 참조
- 그 여러 종류의 포도상구균 균종 중 황색 포도상구균이 주로 감염병을 일으킨다. 아무런 감염병이 나타나지 않는 데도 많은 사람들은 피부, 콧구멍과 그 가장자리, 코 전정, 비강 점막층, 인두 점막층, 손 등에 황색 포도상구균을 보균하고 있다.
- 나이에 따라 좀 다르지만 20~30%의 소아 청소년들이 황색 포도상구균에 의한 감염병이 없이 평소에도 위에서 설명한 신체부위에 보균하고 있다. 누구든지 황색 포도상구균 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있지만 신생아들, 돌 이전 영아들, 특히 생후 3개월 이전 영아들, 바이러스 상기도염을 앓고 있는 영유아들, 영양실조 영유아들, 쇠약한 아이들이 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
- 농가진이나 종기 등 황색 포도상구균 피부염을 앓을 때 그 피부염을 일으켰던 황색 포도상구균이 폐에 감염되어 황색 포도상구균 폐렴을 일으킬 수 있다.
- 한 집안 식구들 중 누구든지 농가진을 앓을 때 농가진을 일으킨 황색 포도상구균이 다른 식구에게 감염 되어 그 식구가 황색 포도상구균 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 자기가 가지고 있는 황색 포도상구균 감염병에 있던 황색 포도상구균이 자신에게도 감염되는 자가 감염도 생길 수도 있다.
포도상구균 폐렴의 증상 징후
- 나이, 중증도, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 다른 종류의 박테리아 폐렴을 앓을 때와 거의 마찬가지로 갑자기 고열이 나면서 기침을 심하게 하며 숨이 찰 수 있다. 피부가 창백하면서 정신이 불안해지고 기면 상태에 빠지면서 보채고 몹시 아파 보이고 독성 상태에 빠지게 된다.
- 숨 쉴 때마다 갈비뼈 사이에 있는 늑골 근육이 흉강 속을 향해서 빨려 들어갔다 나왔다 하면서 심한 호흡곤란이 생길 수 있다.
- 구토, 설사, 복통의 증상 징후도 있고 어딘가 몹시 아픈 것 같아 보인다. 신생아들이나 영아들이 이 폐렴에 걸리면 기운이 하나도 없이 잠만 계속 자면서 음식물을 통 먹지 않을 수 있다.
- 이 병을 빨리 적절히 치료해 주지 않으면 황색 포도상구균 농흉, 폐농양, 그 밖의 다른 여러 종류의 황색 포도상구균 감염성 합병증이 생길 수 있다. 그리고 심지어는 쇼크에 빠지고 사망하게 된다.
- 흡인성 폐렴, 기흉 참조
| 포도상구균성 폐렴의 진단 |
- 병력, 증상징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 폐렴이 의심되면 가슴 X-선 사진, CBC 피 검사, 가래를 채취하여 그 피 검물로 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균 배양검사 등으로 진단한다. 나이, 환자 자신이나 식구들 중 누군가가 황색 포도상구균에 의한 피부 감염병 등을 앓고 있을 때는 이 폐렴을 진단하는데 큰 도움이 된다.
사진 107. 황색 포도상구균성 감염으로 생긴 병소에서 피나 고름 등으로 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균 배양검사를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
사진 108. 세균 배양검사에서 배양된 세균을 가장 잘 죽일 수 있는 항생제를 찾는 항균제감수성 검사를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
| 포도상구균성 폐렴의 치료 |
- 황색 포도상구균에 의해 생긴 폐렴은 응급으로 진단 치료 한다.
- 요즘 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균(Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus/MRSA)에 감염되면 적절한 항생제를 선택하는 데도 어렵다. 그래서 치료 문제가 전 세계적으로 생길 수도 있다.
- 병원에 입원해서 나프실린(Nafcillin), 옥사실린(Oxacillin), Vancomycin, Clindamycin, Gentamicin, Rifamfin, Cephalosporin, Sulbactam, 또는 Trimethoprime-sulfamethoxazole, Linezolid 등 항생제들 중 한 가지 또는 두세 가지 항생제를 임상 경험을 토대로 선택해 치료를 시작하는 것이 보통이다.
- 적절한 항생제들 중 선택한 한 가지 항생제를 정맥주사로 치료하거나 두세 가지 항생제 정맥주사로 치료하기 시작하고 병소에서 얻은 피검 물로 세균 배양검사를 하고 그 검사에서 나온 황색 포도상구균으로 항균제 감수성 검사를 하고 그 결과에 따라 적절한 항생제를 선택해 치료한다.
- 필요에 따라 산소호흡치료를 하고, 머리와 상체를 하체보다 15도 정도 낮게 눕히고 컵과 같이 살짝 오므린 손바닥으로 앞가슴과 등을 살살 두들겨 기도 속에 괸 가래를 더 쉽게 뱉어내도록 도와주는 물리치료도 한다.
- 증상 징후에 따라 탈수를 예방 치료해 주기 위해서 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 치료한다.
- 음식물은 먹을 수 있는 양만큼 처음에는 전 유동 음식물을 먹다가 그 다음 반 유동 음식물로 바꾸어 주고 그 다음에는 보통 때 먹던 음식물로 점차로 바꾸어 준다.
- 황색 포도상구균은 감염성이 아주 강한 박테리아이다. 그러므로 환아를 다른 사람으로부터 격리 치료해야 한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 폐렴을 앓을 때 농흉이나 기흉 등 합병증이 없을 때는 황색 포도상구균 폐렴 초기에는 적절한 항생제로 잘 치료해 주면 잘 나을 수 있다.
- 농흉이나 기흉 등의 합병증이 생기고 폐렴이 상당히 진행되었을 때는 농흉 속에 괸 고름을 수술로 빼주는 치료를 한다.
- 어떤 경우는 황색 포도상구균으로 곪은 폐 부분을 절제치료 한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 폐렴을 앓는 환자의 폐렴 병소에서 가래나 고름 등이 더 이상 나오지 않을 때까지 다른 사람들로부터 환자를 격리 치료한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 피부염, 또는 황색 포도상구균 관절염을 앓는 환아도 격리 치료 한다.
- 이런 병을 앓고 있는 사람과 접촉한 사람에게 황색 포도상구균이 감염될 가능성이 있으므로 황색 포도상구균 감염병이 그들에게 생기는지 조심히 관찰한다.
- 예방접종 백신은 아직 없다.
Staphylococcus pneumonia 포도상구균성 폐렴
Causes of staphylococcal pneumonia
• Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), epidermal staphylococcus (S. epidermidis), human staphylococcus (S. homins), hemolytic staphylococci (S. haemolyticus), etc.
There are several types. Among them, a bacterial infection called Staphylococcus aureus causes the most clinical problems.
• This section mainly deals with Staphylococcus aureus infection. A pulmonary infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection is called Staphylococcus pneumonia.
• Staphylococcal pneumonia is a type of bacterial pneumonia. Any age group can get quite severely ill with this pneumonia. If it is not treated properly and promptly in the early stage, various complications may occur and many deaths occur.
• [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 7 Children and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-Refer to Infectious Diseases Caused by Yellow Staphylococcus
• Among the various types of staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus aureus mainly causes infectious diseases. Although no infectious disease appears, many people carry Staphylococcus aureus on the skin, nostrils and edges, nasal vestibule, nasal mucosa, pharyngeal mucosa, and hands.
• Although slightly different depending on age, 20-30% of children and adolescents carry on the above-described body parts without infectious diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Anyone can get Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia, but newborns, pre-dwelling infants, especially infants before 3 months of age, infants with viral upper respiratory tract infections, malnutrition infants, and debilitating children are more likely to get it.
• When you have Staphylococcus aureus dermatitis, such as impetigo or boil, Staphylococcus aureus, which caused the dermatitis, can infect your lungs and cause Staphylococcal pneumonia.
• When any member of the household has impetigo, Staphylococcus aureus, the cause of impetigo, can be infected by another family member, causing the family member to develop Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia.
• There may also be self-infection, in which Staphylococcus aureus, which was in your own Staphylococcus aureus infectious disease, infects you as well.
Symptoms signs of staphylococcal pneumonia
• Symptoms differ depending on age, severity, and the presence or absence of complications.
• As with any other type of bacterial pneumonia, a sudden high fever can cause severe coughing and shortness of breath. As the skin becomes pale, the mind becomes unstable, drowsiness, and fluffiness, very painful, and toxic.
• Whenever you breathe, the rib muscles between the ribs are sucked into and out of the chest cavity, which can lead to severe breathing difficulties.
• There are also signs of vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, and it looks like something very painful. When newborns or infants get this pneumonia, they can sleep without energy and stop eating whole foods.
• If the disease is not treated promptly and appropriately, staphylococcal empyema, lung abscess, and many other types of Staphylococcus aureus infectious complications can occur. And they even fall into shock and die.
• See aspiration pneumonia, pneumothorax.
Diagnosis of staphylococcal pneumonia
• If this pneumonia is suspected by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, chest X-rays, CBC blood tests, and sputum are collected and diagnosed with Gram staining microscopy, bacterial culture tests, etc. It is very helpful in diagnosing this pneumonia when the age, the patient himself or someone in his household has a skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus

.Photo 107. Gram staining microscopic bacterial examination and bacterial culture examination with blood or pus in the lesion caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 108. In the bacterial culture test, an antimicrobial susceptibility test is performed to find the antibiotic that can best kill the cultured bacteria. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Treatment of staphylococcal pneumonia
• Pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus is diagnosed and treated as an emergency.
• If you are infected with Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) these days, it is difficult to select an appropriate antibiotic. So, treatment problems may arise all over the world.
• Based on clinical experience, one or two or three antibiotics such as Nafcillin, Oxacillin, Vancomycin, Clindamycin, Gentamicin, Rifamfin, Cephalosporin, Sulbactam, or Trimethoprime-sulfamethoxazole, Linezolid, etc. It is common to choose and start treatment. • Treatment of one antibiotic selected from the appropriate antibiotics intravenously or with two or three antibiotics intravenously is started, a bacterial culture test is performed with the specimen obtained from the lesion, and an antimicrobial susceptibility test is performed with Staphylococcus aureus from the test. Select an appropriate antibiotic according to the treatment.
• Oxygen breathing treatment as needed, and physical therapy to help spit out phlegm in the airways by gently tapping the forelimbs and back with the palms slightly constricted like a cup.
• In order to prevent and treat dehydration depending on the symptoms, it is treated with a glucose electrolyte solution intravenously.
• As for food, the amount that can be eaten is first eaten with full-fluid food, then replaced with semi-fluid food, and then gradually changed to the usual food.
• Staphylococcus aureus is a highly infectious bacterium. Therefore, the patient should be treated in isolation from others.
• Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia If there are no complications such as empyema or pneumothorax, it can be well treated with appropriate antibiotics in the early stages of Staphylococcal pneumonia.
• When complications such as empyema or pneumothorax occur and pneumonia has progressed considerably, treatment is performed to remove the pus from the empyema with surgery.
• In some cases, a section of the lung festered by Staphylococcus aureus is excised.
• Patients with Staphylococcal pneumonia are treated in isolation from others until no more sputum or pus comes out of the pneumonia lesion.
• Patients with Staphylococcal dermatitis or Staphylococcal arthritis are also treated in isolation.
• People who have come into contact with those who have this disease may be infected with Staphylococcus aureus, so watch carefully for a Staphylococcus aureus infection in them.
• There is still no vaccination vaccine.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”