폐렴 Pneumonia
폐렴의 개요와 원인
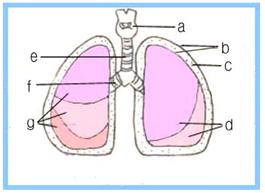
그림100.하기도와 폐
a-후두, b-늑막(흉막), c-늑막강(흉막강), d- 좌 폐, e-기관, f-기관지, g-우폐. 오른쪽 폐에는 세 개의 폐 대엽이 있고 왼쪽 폐에는 두 개 폐 대엽이 있다.
Copyrightⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
-
바이러스, 박테리아, 마이코플라스마(미코플라스마), 곰팡이(진균), 클라미디아, 리케차, 기생충, 원충, 그 외 다른 여러 종류의 병원체, 유기물질이나 무기물질, 알레르기, 이물 등에 의해서 생긴 폐의 염증을 폐렴이라고 한다.
-
항생제가 발명된 이후 박테리아 감염성 폐렴으로 사망하는 경우가 훨씬 적어졌지만 아직도 폐렴은 사망의 주원인 중 하나이다.
-
폐렴의 원인, 폐렴이 생긴 폐의 부위, 중증도, 나이, 합병증 유무 등에 따라 폐렴을 여러 종류의 폐렴으로 분류할 수 있다.
-
소아 청소년들의 폐렴의 가장 흔한 원인은 바이러스 감염이고 그 다음으로는 박테리아 감염고, 그 다음으로 흔한 원인은 마이코플라스마 폐렴이다.
-
그 외 괴사성 폐렴(Necrotizing pneumonia)이란 폐렴도 있다. 괴사성 폐렴은 심한 폐렴의 일종이다.
-
폐렴연쇄상구균(Streptococcus pneumonia), 황색 포도상구균(Staphyllococcus aureus), 또는 마이코플라스마(Mycoplasma) 등의 박테리아 감염이 폐에 생겨 폐렴이 생기고 그와 동시 늑막강(흉막강) 내 농액이 고이고 흉막염도 생길 수 있다.
-
물에 빠졌을 때 침수가 기도 내로 흡인될 때, 불이 났을 때 화염과 독가스 등이 기도 내로 흡인됐을 때, 가솔린이나 등유, 화학물질 등이 폐 속으로 흡인될 때 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
폐렴의 원인을 확실히 알 수 없는 때도 있다.
-
신생아의 폐렴의 원인, 증상 징후, 진단, 치료, 예후는 신생아기 이후 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들의 폐렴의 원인, 증상 징후, 진단, 치료, 예후와 다른 점이 많다.
-
신생아의 폐렴,
-
급성 세기관지염 참조
영유기· 학령기· 사춘기의 아이들의 폐렴의 분류 그리고 폐렴애 대한 더 자세한 정보는 아래 각 폐렴을 참조
- 바이러스(성) 폐렴
- 급성 세기관지염
- 폐렴연쇄상구균 폐렴
- 황색 포도상구균 폐렴
- 마이코플라스마 폐렴
- 흡인성 폐렴(신생아의 흡인성 폐렴, 흡인성 폐렴 참조)
- 지역 사회 획득 소아 청소년 폐렴
- 약물에 의한 폐렴
- 클라미디아 폐렴
- 그 외 폐렴
Pneumonia Pneumonia
Overview and causes of pneumonia

Figure 100.
Lower respiratory tract and lungs a-larynx, b-pleural (pleural), c-pleural (pleural), d- left lung, e-trache, f-bronchi, g-right lung.
The right lung has three lung lobes and the left lung has two lung lobes. Copyrightⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Pneumonia in the lungs caused by viruses, bacteria, mycoplasma (mycoplasma), fungi (fungi), chlamydia, rickettsia, parasites, protozoa, and many other pathogens, organic or inorganic substances, allergies, foreign bodies, etc. It is called.
• Pneumonia is still one of the leading causes of death, although there have been far fewer deaths from bacterial infectious pneumonia since the invention of antibiotics.
• Pneumonia can be classified into several types of pneumonia depending on the cause of pneumonia, the part of the lung where the pneumonia occurred, the severity, age, and the presence or absence of complications.
• The most common cause of pneumonia in children and adolescents is viral infection, followed by bacterial infection, followed by mycoplasma pneumonia.
• There is also a pneumonia called Necrotizing pneumonia. Necrotizing pneumonia is a type of severe pneumonia.
• Bacterial infection, such as Streptococcus pneumonia, Staphyllococcus aureus, or Mycoplasma, occurs in the lungs, causing pneumonia, and at the same time, pus in the pleural cavity (pleural cavity) and pleurisy are formed. I can.
• Pneumonia can occur when submerged water is sucked into the airways when submerged in water, when flames and poisonous gases are sucked into the airways during a fire, or when gasoline, kerosene, or chemicals are aspirated into the lungs.
• Sometimes the cause of pneumonia is not known for certain.
• The causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of pneumonia in newborns are different from the causes, symptoms, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of pneumonia in infants and toddlers or school-age children after the neonatal period.
• pneumonia in newborns,
• See acute bronchiolitis
The classification of pneumonia and pneumonia in children of infancy, school age, and adolescence, For more information on refer to each pneumonia below
1. Viral pneumonia
2. Acute bronchiolitis
3. Streptococcal pneumonia
4. Staphylococcal pneumonia
5. Mycoplasma pneumonia
6. Aspiration pneumonia (refer to aspiration pneumonia and aspiration pneumonia in newborns)
7. Community Acquired Child and Adolescent Pneumonia
8. Drug-induced pneumonia
9. Chlamydia pneumonia
10. Other pneumonia
11. Corona virus(COVID-19) peumonia
12 others
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd editio
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”