폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병), Pneumococcal infections(Streptococcus pneumoniae infection)
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Chapter 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병)의 원인
그림 2-106. 폐렴 연쇄상구균이 기침할 때 나온 가래나 기말을 통해서 다른 사람들에게 감염시킬 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균(Streptococcus pneumoniae)을 폐렴 연쇄구균, 폐렴 연구균, 폐렴구균, 또는 폐렴 쌍구균이라 한다.
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병을 폐렴 연쇄구균 감염병이라 한다.
-
폐가 폐렴 연쇄상구균에 감염되면 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 폐렴 이 외 다른 여러 가지의 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
대부분의 건강한 사람들은 인두 점막층에 폐렴 연쇄상구균을 평소에 보균하고 있을 수 있고 보통 때는 아무런 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병을 일으키지 않는다.
-
감기나 다른 종류의 바이러스성 상기도염 등을 앓는 사람의 상기도의 점막층에 있던 폐렴 연쇄상구균이 신체 속으로 감염될 때 폐렴 연쇄상구균성 폐렴이나 폐렴 연쇄상구균성 패혈증 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균을 보균한 사람이나 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병을 앓는 사람들이 폐렴 연쇄상구균을 다른 사람들에게 감염시킬 수 있다.
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균에 감염되면 폐렴, 급성 중이염, 결막염, 축농증(부비동염), 뇌막염, 패혈증, 관절염, 복막염, 또는 심낭염 등의 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
잠복기는 약 1∼3일이다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병)의 증상 징후
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병의 종류, 병의 진행 정도 중증도·병일·환자의 나이 등에 따라 증상 징후가 상당히 다르다.
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병의 구체적인 증상 징후는 폐렴 연쇄상구균성 감염으로 생긴 각 감염병을 참고한다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병)의 진단
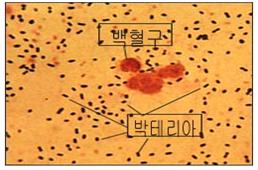
그림 2-107. 현미경으로 본 그람 염색 폐렴 연쇄상구균 사진. 출처–미 CDC 50
-
병력·증상·징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생긴 감염병이 있다고 의심되면 가래·피·뇌척수액 및 병원소 등에서 나온 피고름 등 피검 물을 채취해 그 피검 물로 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사, 세균 배양 검사 등을 해서 진단할 수 있다.
-
이 세균 감염으로 생긴 병소가 신체 어느 부위에 있는지에 따라 그 부위 X-선 사진검사·초음파 사진 검사 등으로 진단한다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병)의 치료
-
이 세균에 감염돼 생긴 감염병의 종류에 따라 치료 방법이 다르다.
-
몇 년 전까지만 해도, 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염에 의해 생긴 감염병의 치료에 페니실린이 특효약이었다.
-
그러나 요즘에는 페니실린 치료에 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병의 50% 이상은 치료가 되지 않고, 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병의 50% 정도는 Cefotaxime나 Ceftriaxone 등 항생제로도 치료되지 않는다.
-
요즘, 침입성 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병이 있다고 의심하거나 확진되면 우선 Vancomycin과 Cefotaxime이나 Vancomycin과 Ceftriaxone 광범위 항생제로 치료를 시작하는 것이 보통이다.
-
그런 다음, 항생제 감수성 검사에서 나온 결과에 따라 항생제를 재 선택해 치료하는 것이 기본이다.
-
물론, 의사에 따라 경험에 비춰 적절한 항생제를 선택해 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병을 치료하는 것이 원칙이다.
-
페니실린에 알레르기가 있는 아이들의 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병은 페니실린으로 치료하는 대신에 에리스로마이신 등 다른 항생제로 치료한다.
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균 뇌막염이나 관절염, 패혈증, 또는 심한 폐렴을 앓을 때는 병원에 입원하여 적절한 항생제 혈관주사로 치료해야 한다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병) 환아의 격리
-
이 병을 적절한 항생제로 치료 시작한 24시간 이후 치료경과가 좋으면 환아를 더 이상 격리시킬 필요가 없다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병) 백신 Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
-
2014년 미 소아청소년과 학회에서 권장하는 소아청소년 감염병 예방접종 참조
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균의 균종은 90여종이 넘는다.
-
90여 폐렴 연쇄상구균 균종 중 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F 균종에 속하고 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생기는 감염병을 예방할 수 있는 PCV7(프레브날 백신/Prevnar vaccine)백신이 있다.
-
PCV7 백신으로 권장한 대로 접종하면 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생기는 중이염, 축농증, 폐렴, 관절염, 패혈증, 뇌막염 등 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병을 예방할 수 있다.
-
또 23 균종의 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생기는 감염병을 예방할 수 있는 23PS(23 Valent pneumococcal Polysaccharide vaccine) 백신도 있다.
-
현재 미국에서는 프레브날 백신(PCV7)으로 2세 이하의 영유아들에게 접종한다.
-
PCV7백신으로 생후 2, 4, 6, 12~15개월에 각각 1회씩 총 4차로 기본 접종한다.
-
23ps 백신으로는 2세 이상에서 생후 59개월 유아들에게 주로 예방접종한다.
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 Recommended immunization schedule for 0~18 year old Americal children in Jan 1st 2021
|
☞ 각 나라에 따라 권장 기본 예방접종 스케줄이 다를 수 있다. |
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2021
| 예방접종 백신 종류/ 예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1차 접종 | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus²(RV) RV-1(2회분 배열 접종); RV-5(3 회분 배열 접종)/ 로타바이러스 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³(DTaP;<7세)/파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | ←1차 접종→ | →2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ←5차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap;7세나 >7세 파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ 히브 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 5 | ←3차 또는 4차 접종 → 각주 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) /폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 세)/소아마비 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 예방 접종 백신 종류/예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||
| Influenza⁸(IIV; LAIV) 1부에게는 2회분,각주 8 /인플루엔자 | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (11V 만)→ | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (II V 또는 LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ 홍역, 풍진, 유행성 이하선염 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /수두 | ←1 차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/A형 간염 | ←2 회분→ 주서 11 | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; 여성에게만 (HPV4; 여성과 남성 에게)/사람유두종 바이러스 감염병 | ←3회 분 배열 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 생후 9 개월이나 그후후. MenACWY-CRM-D는 생후 2개월이나 그 이후. MenACWY-TT는 은 생후 2세나 그 이후. /수막구균 뇌막염과 그 외 감염병
—————————- Meningococcal B 백신에는 MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, Trumenba 백신이 있다. 10세나 그 이상에 접조한다. Bexsero백신은 2회 접종하고 Trumenba 백신은 총 3회 접종한다. 위험도다 없는 사춘기아이들이나 청년들은 16-23세에 접종받는다. 소스: CDC, AAP News 3/2021 |
←주서 13→ | ←1차 접종→ | 추가 접종 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
접종을 권장 하는 나이의 범위, | ||
|
|
건강상 고 위험 군 아이들에게 접종을 권장하는 나이 |
다음과 같은 경우 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병을 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병 백신으로 예방 접종을 꼭 해줘야 한다
-
후천성 면역 결핍증이나 선천성 면역 결핍증이 있거나
-
선천성으로 비장이 없이 태어나거나 비장을 수술로 적출해서 후천성으로 비장이 없거나
-
비장 기능 저하증이 있거나
-
선천성으로나 후천성으로 면역체 결핍증이 있거나
-
신증후군, 만성 신장 부전증, 기관 이식, 만성 폐렴, 심장 울혈증, 뇌척수액이 새는 병 누출관 등이 있거나
-
호지킨스 병이나 다른 종류의 암을 항암제로 치료 시작하기 바로 전이나 항암제 치료나 방사능 치료 또는 코르티코스테로이드제 치료를 장기간 받거나
-
에이즈나 악성 종양을 앓거나
-
당뇨병 등 만성 대사성 질병을 앓거나
-
3세 이하의 모든 건강한 영유아들
-
특히 탁아소나 어린이집 등 집단생활을 하는 어린이들
-
그 외
-
폐렴 연쇄상구균의 종류가 많기 때문에 모든 종류의 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염에 대한 예방접종 백신을 다 해 줄 수도 없고, 비록 해 주더라도 모든 종류의 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병을 완전히 예방해 주기가 어렵다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병, 안전사고 예방–비장이 없는 아이 참조.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병) 백신 예방접종 연령
-
생후 2, 4, 6, 12~15 개월에 각각 1회씩 총 4차 접종한다.
-
생후 6주에 1차 접종할 수 있다.
-
적어도 4∼8주 간격을 두고 접종 받을 수 있다.
-
4차 접종은 3차 접종을 받은 후 적어도 2개월 간격 후에 한다.
-
건강상 고위험군은 2~6세 사이에 ppsv로 접종 받는다(소스;MMVR 2 10, 2012).
표 2-17. 생후 7개월까지 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병 백신 예방 접종을 한 번도
받지 않은 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들은 다음 표와 같이 접종 받는다.
| 1차 접종받을 때 나이 | 총 예방 접종을 받을 횟수 |
| 생후 7~11개월 | 3+ |
| 생후 12~23개월 | 2++ |
| 생후 12 개월~9세 | 1 |
+: 1차와 2차 접종은 적어도 4주 간격을 두고 받는다.
3차 접종을 생 후 12개월 후에 받을 때는 적어도 2개월 간격을 두고 접종받는다.
++: 적어도 2개월 간격을 두고 접종받는다.
더 자세한 정보는 www.prevnar.com을 방문세요.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병) 백신 예방접종의 금기
-
임신
-
디프테리아 톡소이드나 프레브날(PCV7) 백신에 알레르기가 있을 때
-
고열이 나면서 감염병을 앓을 때는 그 감염병이 다 나은 후에 접종한다.
-
열이 나지 않고 감기를 경미하게 앓을 때는 브레브날 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 수 있다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병) 백신 예방접종의 방법
-
소아 건강검진을 받고 열이 있나 체온을 재고 발열성 감염병이 없고 백신에 알레르기가 없고 접종 금기가 없으면 프레브날 백신(PCV7) 0.5cc를 근육주사로 접종 받는다.
-
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해, 히브, 소아마비, 홍역, 풍진, 볼거리, 수두 또는 B형 간염 등을 예방해 줄 수 있는 백신과 프레브날 백신을 동시 접종해 줄 수 있다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병) 백신 부작용
-
접종을 받은 국소에 부종, 압통, 발적이 생길 수 있다. 열, 기면증, 식욕감퇴, 과민, 구토, 설사, 발진 등 경미한 부작용이 생길 수 있다. 드물게 알레르기 반응이 생길 수 있다.
폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병) 백신 예방접종 효과
PCV7 백신으로 폐렴연쇄상구균 예방접종을 받은 후 면역 효과는 거의 100% 나타나지만 나머지 83여종의 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염으로 인해서 생기는 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병을 예방할 수 있는 면역 효과는 없다.
지역사회 획득 소아 폐렴(병원 외 획득 소아 폐렴/병원 외 소아 폐렴)의 감별진단 Differential diagnosis of community-acquired Pneumonia in children
-
소아청소년들에게 지역사회 획득 소아 폐렴이 생기면 다음과 같은 병과 감별 진단한다.
- 소아청소년의 나이, 사는 지역, 계절, 예방 접종 상태, 현재 병력, 가족병력, 과거 병력, 증상, 징후, 진찰 소견 등을 종합해 필요한 임상 검사를 해 감별 진단하는 것이 보통이다.
1. Bacterial pneumonia,
2. Viral, pneumonia,
3. Pulmonary tuberculosis,
4. Eosinophilic pneumonia,
5. Cryptococcal Pneumonia,
6. Pneumocystis Carinii pneumonia,
7. Granulomatous disease,
8. Typhus Pneumonia,
9. Typhoid Pneumonia,
10. Atypical pneumonia,
11. Legionella Pneumonia,
12. Q fever Pneumonia,
13. Neonatal adenovirus pneumonia,
14. Chlamydia pneumonia,
15. Fungi pneumonia,
16. Mycobacterial Pneumonia,
17. Tuberculosis pulmonary,
18. Parasitic Pneumonia,
19. Lung Abscess,
20. Histoplasmosis,
21. Aspergillosis,
22. Staphlococcus Pneumonia,
23. Aspiration,
24. Aspiration Pneumonia,
25. Legionella species,
26. Bronchiolitis obliterans,
27. Pulmonary embolism,
28. Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia,
29. Malignant lymphoma,
30. Bronchopulmonary sequestration,
31. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia,
32. Acute respiratory distress Syndrome,
33. Empyema and abscess,
34. Asthma,
35. Immunocompromised pneumonia,
36. Bronchitis,
37. Respiratory distress syndrome,
38. Smoke inhalation,
39. Acute respiratory failure,
40. Pneumocystis,
41. CMV pneumonia,
42. Trauma causes pneumonia,
43. Pulmonary contusion,
44. Electromagnetic, Physics, trauma, radiation of lungs,
45. High altitude pulmonary edema, 46. Bacterial tracheitis,
47. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP),
48. Pertussis,
49. Ascariasis,
50. Pulmonary larval infestation,
51. Fungal lung infection,
52. Parasitic lung infection,
53. Psittacosis/ornithosis,
54. Infected organ, abscesses,
55. Bronchitis, acute,
56. Granulomatous,
57. Inflammatory Disorders,
58. Hemorrhagic pancreatitis, necrotizing,
59. Pulmonary eosinophilic granuloma,
60. Sarcoidosis,
61. Sarcoidosis, pulmonary,
62. Wegeners granulomatosis,
63. Wegener’s pulmonary (isolated) disease,
64. Neoplastic disorders,
65. Carcinoma, oat cell (small cell), lung,
66. Pleural effusion, malignant,
67. Carcinoma lung squamous cell/large cell,
68. Meigs’Pleural effusion syndrome,
69. Allergic, collagen, auto-Immune disorders,
70. Collagen-vascular disease,
71. Dressler’s syndrome,
72. Goodpasture’s syndrome,
73. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis/alveolitis,
74. Pneumonitis, collagen vascular disease,
75. Carrington’s pulmonary eosinophilia,
76. Pulmonary arteritis/vasculitis,
77. Scleroderma, pulmonary,
78. Metabolic, storage disorders,
79. Hemosiderosis, pulmonary,
80. Congenital, developmental disorders,
81. Pulmonary A/V malformation,
82. Anatomic, foreign body, structural disorders,
83. Pulmonary embolism, 84. Pleural effusion,
85. Mallory Weiss syndrome (esophageal tear),
86. Arteriosclerotic, vascular, venous disorders,
87. Pulmonary infarction,
88. Reference to the organ system,
89. Pericarditis, acute,
90. Pulmonary edema,
91. Respiratory distress(adult)syndrome,
92. Chronic pulmonary edema,
93. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis,
94. Organ Poisoning (Intoxication),
95. Drug-induced Interstitial disease,
96. Toxic Peripheral / polyneuropathy,
97. External Links Related to Pneumonia, bacteria,
98. Vascular ring,
99. Tumor,
100. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis / Rheumatoid lung disease / Pneumoconiosis, rheumatoid,
101. Bronchiectasis,
102. Pulmonary hemosiderosis,
103. Chemical pneumonitis,
104. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia,
105. Tracheoesophageal fistula,
106. Bronchogenic cyst,
107. 그 외
- 이상은 감별 진단해야 할 질병의 목록이다. 이렇게 많은 종류의 병들과 소아 지역사회 획득 소아 폐렴과 감별진단을 쉽게 한다는 것은 소아청소년과 전문의에게도 물론 어려운 문제이고 또한 소아 감염병 전문의에게도 어려운 문제 중 하나이다. 전문적인 소아청소년 건강 문제는 여기서 다루는 목적은 부모들이 자녀를 양육하는 동안 자녀에게 폐렴이 생기면 참고하는 데 도움이 되게 다룬다.
Pneumococcal infections (Streptococcus pneumoniae infection) 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병(폐렴구균 감염병)
Causes of pneumonia streptococcal infectious disease (pneumococcal infectious disease)

Figure 2-106. Streptococcus pneumonia can infect others through sputum from coughing or through the end of the cough. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Streptococcus pneumoniae is cause of Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumonia
• An infectious disease caused by a streptococcal pneumonia infection is called a streptococcal pneumonia infection.
• Pneumonia can develop when the lungs are infected with pneumonia streptococcus.
• Streptococcal pneumonia infection can lead to many other streptococcal pneumonia infections.
• Most healthy people may have streptococcal pneumonia on a regular basis in the pharyngeal mucosa and usually do not develop any streptococcal pneumonia.
• Streptococcal pneumonia can occur when streptococcal pneumonia in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract of a person with a cold or another type of viral upper respiratory infection into the body.
• People with streptococci pneumonia or people with streptococcal pneumonia can infect other people with pneumonia.
• Streptococcal pneumonia infection can lead to streptococcal pneumonia such as pneumonia, acute otitis media, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, meningitis, sepsis, arthritis, peritonitis, or pericarditis.
The incubation period is about 1 to 3 days.
Symptoms and signs of streptococcal pneumonia (pneumococcal infection)
• Symptoms and signs vary considerably depending on the type of infectious disease caused by a streptococcal pneumonia infection, the severity of the disease progression, the disease day, and the patient’s age.
• For specific symptoms and signs of streptococcal pneumonia, refer to each infectious disease caused by streptococcal pneumonia infection.
Diagnosis of pneumonia streptococcal infectious disease (pneumococcal infectious disease)

Figure 2-107. Gram-stained pneumonia streptococci picture seen under a microscope. Source-US CDC 50
• If you suspect that there is an infectious disease caused by pneumonia streptococcal infection by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings, collect a sample such as sputum, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood pus from a hospital, etc. It can be diagnosed by performing a bacterial culture test or the like.
• Depending on which part of the body the lesion caused by this bacterial infection is located, it is diagnosed with an X-ray photo test or an ultrasonic photo test.
Treatment of streptococcal pneumonia (pneumococcal infection)
• The treatment method differs depending on the type of infectious disease caused by infection with this bacteria.
• Until a few years ago, penicillin was the best medicine for the treatment of infectious diseases caused by pneumonia streptococcal infection.
• However, these days, more than 50% of streptococcal pneumonia infections are not treated with penicillin treatment, and 50% of streptococcal pneumonia infections are not treated with antibiotics such as Cefotaxime or Ceftriaxone.
• Nowadays, it is common to start treatment with Vancomycin and Cefotaxime or Vancomycin and Ceftriaxone broad-spectrum antibiotics first when suspected or confirmed that you have an invasive streptococcal infection.
• Then, according to the results of the antibiotic susceptibility test, it is basic to reselect and treat antibiotics.
• Of course, according to the doctor’s experience, it is a principle to select appropriate antibiotics to treat streptococcal pneumonia.
• Streptococcal pneumonia in children allergic to penicillin is treated with other antibiotics such as erythromycin instead of penicillin.
• Pneumonia If you have streptococcal meningitis, arthritis, sepsis, or severe pneumonia, you should be admitted to a hospital and treated with appropriate antibiotic vascular injections.
Isolation of Children with Streptococcal Pneumonia Infectious Disease (Pneumococcal Infectious Disease)
• If the disease has been treated well 24 hours after the start of treatment with appropriate antibiotics, it is no longer necessary to isolate the patient.
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
• Refer to pediatric and adolescent infectious disease vaccination recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents in 2014.
• There are over 90 types of streptococcus pneumonia.
• There is a PCV7 (Prevnar vaccine) vaccine, which belongs to 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F, and can prevent infectious diseases caused by streptococcal pneumonia infection.
• If vaccinated as recommended with the PCV7 vaccine, streptococcal pneumonia infections such as otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia, arthritis, sepsis, and meningitis caused by streptococcal pneumonia infection can be prevented.
• There is also the 23 Valent Pneumococcal Polysaccharide vaccine (23PS) vaccine, which can prevent infectious diseases caused by streptococcal pneumonia infections of 23 strains.
• In the United States, the Prevenal vaccine (PCV7) is currently administered to infants and young children under 2 years of age.
• The PCV7 vaccine is given at 2, 4, 6, 12 to 15 months of age, once each, for a total of 4 doses.
• The 23ps vaccine is mainly vaccinated against infants aged 2 years and older to 59 months of age.
Recommended immunization schedule for 0-18-year-old Americal children in Jan 1st, 2021
☞ The recommended basic vaccination schedule may differ depending on each country.
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 1 5 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19~23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | |||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←←3rd vaccination→→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus² (RV) RV-1 (two batch sequence inoculation); RV-5 (3-batch sequence vaccination)/ Rotavirus infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³ (DTaP; <7 years old)/tetanus, diphtheria, pertussi | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ←5th vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap; 7 years old> 7 years old tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ Hib infectious disease | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 5 | ←3rd or 4th vaccination→ Footnote 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/Pneumococcal infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) / Streptococcal pneumonia infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 years old)/Polio | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 2 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 15 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19-23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | ||
| Influenza⁸ (IIV; LAIV) for 1 copy, 2 servings, footnote 8 / Influenza | ←Get inoculated every year (11V 만)→ | ←Get inoculated every year(II V or LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ Measles, Rubella, Mumps | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /Varicella | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/Hepatitis A | ←2 doses→ | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; women only (HPV4; women and men))/Human papillomavirus infectious disease | ←3rd vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 9 months or later. MenACWY-CRM-D is 2 months or later. MenACWY-TT is 2 years old or later. / Meningococcal meningitis and other infectious diseases) —————————- Meningococcal B vaccines include MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, and Trumenba vaccines. We touch on 10 years of age or older. The Bexsero vaccine is inoculated twice and the Trumenba vaccine has inoculated a total of three times. Adolescents and young adults with no risk are vaccinated at age 16-23. Source: CDC, AAP News 3/2021 | ←1st vaccination→ | Booster vaccination | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
The age range for which vaccination is recommended, | ||
|
|
Age recommending vaccination for children in the high-risk group |
DTaP vaccine (diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus vaccine) vaccination
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Acellular Pertussis Immunization
In the following cases, vaccination against streptococcal pneumonia should be performed with a vaccine against streptococcal pneumonia.
• have an acquired immunodeficiency or congenital immunodeficiency, or
• Born without a spleen due to congenital or acquired spleen due to surgical removal of the spleen
• you have hyposplenism function or
• Congenital or acquired immune system deficiency, or
• Nephrotic syndrome, chronic kidney failure, organ transplantation, chronic pneumonia, heart congestion, or leaking ducts of cerebrospinal fluid.
• Immediately before starting treatment with anticancer drugs for Hodgkin’s disease or other types of cancer, or for prolonged periods of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or corticosteroid therapy.
• have AIDS or malignant tumors,
• suffer from chronic metabolic diseases such as diabetes • All healthy infants and toddlers under the age of 3 • Children who live in group life, especially in daycare centers and daycare centers
• etc
• Because there are many types of pneumonia streptococci, it is not possible to provide all types of vaccination against streptococcal pneumonia infections, and even if they do, it is difficult to completely prevent all types of streptococcal pneumonia.
• www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 2 Prevention of pediatric and adolescent diseases and accidents-Refer to children without a spleen.
Pneumonia Streptococcus Infectious Disease (Pneumococcal Infectious Disease) Vaccination Age
• A total of 4 vaccinations are given once each at 2, 4, 6, 12 to 15 months of age.
• The first dose can be given at 6 weeks of age.
• You can get your vaccinations at least 4-8 weeks apart.
• The 4th vaccination should be done at least 2 months after receiving the 3rd vaccination.
• High-risk groups receive vaccination with ppsv between 2 and 6 years of age (source; MMVR 2 10, 2012).
Table 2-17. Until 7 months of age, never received a vaccine against streptococcal pneumonia.
표 2-17. 생후 7개월까지 폐렴 연쇄상구균 감염병 백신 예방 접종을 한 번도
받지 않은 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들은 다음 표와 같이 접종 받는다.
| Age at the time of primary vaccination | Total number of vaccinations |
| 7-11 months old | 3+ |
| 12~23 months after birth | 2++ |
| 12 months to 9 years old | 1 |
The 1st and 2nd vaccinations are given at least 4 weeks apart.
When receiving the 3rd vaccination 12 months after birth, the vaccination is given at least 2 months apart. ++: Get vaccinations at least 2 months apart. For more information, please visit www.prevnar.com.
Contraindications to vaccination against streptococcal pneumonia (pneumococcal infection) vaccination
• Pregnant
• You are allergic to diphtheria toxoid or prevent (PCV7) vaccine
• If you suffer from an infectious disease while having a high fever, take the vaccination after the infectious disease is over.
• If you don’t have a fever and have a mild cold, you can get vaccinated with the Brevenal vaccine.
Method of vaccination against pneumonia streptococcal infectious disease (pneumococcal infectious disease) vaccine
• If you have a child’s health checkup and have a fever, check your body temperature, do not have a feverish infectious disease, do not have any allergies to the vaccine, and there is no contraindication to vaccination, receive 0.5cc of Prevenal Vaccine (PCV7) by intramuscular injection.
• A vaccine that can prevent diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hives, polio, measles, rubella, mumps, chickenpox, or hepatitis B, and a prevent vaccine can be given at the same time.
Pneumonia streptococcal infection (pneumococcal infection) vaccine side effects
• Swelling, tenderness, and redness may occur in the area where the vaccine was given. Minor side effects such as fever, narcolepsy, loss of appetite, irritability, vomiting, diarrhea, and rash may occur. Rarely, an allergic reaction can occur.
Effect of vaccination against streptococcal pneumonia (pneumococcal infection) vaccine After receiving pneumococcal vaccination with PCV7 vaccine, the immune effect is almost 100%, but there is no immune effect that can prevent pneumonia streptococcal infection caused by the remaining 83 kinds of pneumococcal infection.
Differential diagnosis of community-acquired Pneumonia in children • When children and adolescents develop community-acquired childhood pneumonia, the following diseases are differentially diagnosed.
• It is common to conduct a differential diagnosis by performing necessary clinical tests by combining the age of children and adolescents, living region, season, vaccination status, current medical history, family medical history, past medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
1. Bacterial pneumonia,
2. Viral, pneumonia,
3. Pulmonary tuberculosis,
4. Eosinophilic pneumonia,
5. Cryptococcal Pneumonia,
6. Pneumocystis Carinii pneumonia,
7. Granulomatous disease,
8. Typhus Pneumonia,
9. Typhoid Pneumonia,
10. Atypical pneumonia,
11. Legionella Pneumonia,
12. Q fever Pneumonia,
13. Neonatal adenovirus pneumonia,
14. Chlamydia pneumonia,
15. Fungi pneumonia,
16. Mycobacterial Pneumonia,
17. Tuberculosis pulmonary,
18. Parasitic Pneumonia,
19. Lung Abscess,
20. Histoplasmosis,
21. Aspergillosis,
22. Staphlococcus Pneumonia,
23. Aspiration,
24. Aspiration Pneumonia,
25. Legionella species,
26. Bronchiolitis obliterans,
27. Pulmonary embolism,
28. Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia,
29. Malignant lymphoma,
30. Bronchopulmonary sequestration,
31. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia,
32. Acute respiratory distress Syndrome,
33. Empyema and abscess,
34. Asthma,
35. Immunocompromised pneumonia,
36. Bronchitis,
37. Respiratory distress syndrome,
38. Smoke inhalation,
39. Acute respiratory failure,
40. Pneumocystis,
41. CMV pneumonia,
42. Trauma causes pneumonia,
43. Pulmonary contusion,
44. Electromagnetic, Physics, trauma, radiation of lungs,
45. High altitude pulmonary edema, 46. Bacterial tracheitis,
47. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP),
48. Pertussis,
49. Ascariasis,
50. Pulmonary larval infestation,
51. Fungal lung infection,
52. Parasitic lung infection,
53. Psittacosis/ornithosis,
54. Infected organ, abscesses,
55. Bronchitis, acute,
56. Granulomatous,
57. Inflammatory Disorders,
58. Hemorrhagic pancreatitis, necrotizing,
59. Pulmonary eosinophilic granuloma,
60. Sarcoidosis,
61. Sarcoidosis, pulmonary,
62. Wegeners granulomatosis,
63. Wegener’s a pulmonary (isolated) disease,
64. Neoplastic disorders,
65. Carcinoma, oat cell (small cell), lung,
66. Pleural effusion, malignant,
67. Carcinoma lung squamous cell/large cell,
68. Meigs’Pleural effusion syndrome,
69. Allergic, collagen, auto-Immune disorders,
70. Collagen-vascular disease,
71. Dressler’s syndrome,
72. Goodpasture’s syndrome,
73. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis/alveolitis,
74. Pneumonitis, collagen vascular disease,
75. Carrington’s pulmonary eosinophilia,
76. Pulmonary arteritis/vasculitis,
77. Scleroderma, pulmonary,
78. Metabolic, storage disorders,
79. Hemosiderosis, pulmonary,
80. Congenital, developmental disorders,
81. Pulmonary A/V malformation,
82. Anatomic, foreign body, structural disorders,
83. Pulmonary embolism, 84. Pleural effusion,
85. Mallory Weiss syndrome (esophageal tear),
86. Arteriosclerotic, vascular, venous disorders,
87. Pulmonary infarction,
88. Reference to the organ system,
89. Pericarditis, acute,
90. Pulmonary edema,
91. Respiratory distress(adult)syndrome,
92. Chronic pulmonary edema,
93. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis,
94. Organ Poisoning (Intoxication),
95. Drug-induced Interstitial disease,
96. Toxic Peripheral / polyneuropathy,
97. External Links Related to Pneumonia, bacteria,
98. Vascular ring,
99. Tumor,
100. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis / Rheumatoid lung disease / Pneumoconiosis, rheumatoid, 101. Bronchiectasis,
102. Pulmonary hemosiderosis,
103. Chemical pneumonitis,
104. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia,
105. Tracheoesophageal fistula,
106. Bronchogenic cyst,
107. etc
• The above is a list of diseases that need to be differentially diagnosed. Easier differential diagnosis of pediatric pneumonia and pediatric pneumonia acquired with so many kinds of diseases and pediatric community is a difficult problem for pediatricians and adolescents as well as for pediatric infectious disease specialists.
The purpose of addressing professional pediatric and adolescent health issues here is to help parents refer to pneumonia in their children while raising them
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 안효섭 외 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”