퍼세스병(레그퍼세스 병/ 소아 대퇴골두 무혈성 괴사증) Perthes’s disease (Legg-Calve Perthes disease)
- 좌골과 대퇴골을 연결하는 관절을 고관절이라고 한다.
- 고관절 낭 속에 들어가 있는 대퇴골 두부의 혈액순환에 이상이 생겨 대퇴골 두부의 일부 또는 전부가 괴사되고 손상되는 병을 퍼세스병, 소아성 대퇴골두 무혈성 괴사증, 또는 레그-퍼세스병이라고 한다.
퍼세스병의 원인
- 대퇴골 두부 혈액순환에 장애가 생기는 원인은 아직도 확실히 모른다.
- 그러나 이병이 있을 때 대퇴골 두부 혈액순환 장애가 있어서 대퇴골 두부가 괴사되고, 부스러지고, 납작해진다는 것은 확실하다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
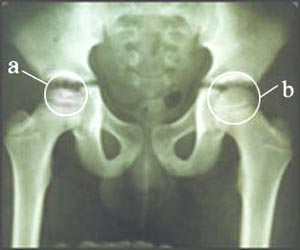
사진 291. 우 대퇴골 두부에 생긴 레그-퍼세스병
a내-레그-퍼세스 병으로 대퇴골의 두부가 비정상적으로 괴사되고 납작해졌다,
b내-정상 대퇴골 두부
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
퍼세스병의 증상 징후
- 이 병은 한 번 걸리면 몇 개월 내지 몇 년을 두고 서서히 진행된다.
- 때문에 병의 진행 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 2~12살 연령층 아이에게 더 잘 생길 수 있지만 4~8세 유아나 학령기 아이에게 더 잘 생긴다.
- 여아보다 남아에게 더 잘 생긴다.
- 이 병은 한쪽 고관절에만 생길 수도 있고 양쪽 고관절에 동시 생길 수 있다.
- 이 병이 생긴 고관절은 진행 정도에 따라 다를 수 있지만, 은근히 아프고 그쪽 다리를 절 수 있다.
- 박테리아 고관절염이 있을 때의 증상 징후와 달리 열이 나지 않고 고관절이 붓지 않는다.
- 아픈 고관절을 정상적으로 움직일 수 없다.
- 어떤 경우에는 이 병이 있는 고관절은 아프지도 않고 그쪽 무릎만 아프다고 호소할 수 있다.
퍼세스병의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 고관절 X선 사진이나 CT 스캔 검사 등으로 진단한다.
- 초기에 찍은 고관절 X선 사진은 정상으로 나타날 수도 있다.
- 퍼세스병이 점점 더 진행되어 3~4주 이상 지난 후 재차 검사한 고관절 X선 사진은 비정상으로 나타나는 경우가 많다.
- 이때에 비로소 이 병을 처음으로 진단하는 경우도 있다.
- 요즘, 고관절 CT 스캔 검사로 이 병을 조기에 진단을 할 수 있다.
- 퍼세스병과 결핵균성 고관절염, 고관절 탈구, 라임병성 고관절염 등을 감별 진단하기 위해 투베르쿨린 검사, 피 검사, 소변 검사, 가래 세균 검사, 가슴 X선 사진 검사 등을 할 때도 있다.
퍼세스병의 치료
- 이 병이 의심될 때는 소아청소년과 전문의, 정형외과 전문의의 세밀한 진찰을 받아야 한다.
- 얼마동안 퍼세스병이 있는 쪽의 다리로 걷지 말고 그쪽 다리를 쓰지 말고 쉬어야 한다.
- 허리에서부터 퍼세스병이 생긴 고관절과 그쪽 다리의 전체를 석고 붕대 고정치료를 받든지 브레이스 장치 고정 치료를 받는다.
- 학령기 아이는 목발을 짚고 학교에 다니게 한다.
- 이런 식으로 1~2년 동안 계속 치료하면 이 병은 거의 완치된다.
- 경우에 따라 수술로 치료한다.
- 극소수의 환아는 어떤 방법으로 치료를 해 주어도 완치되지 않는다.
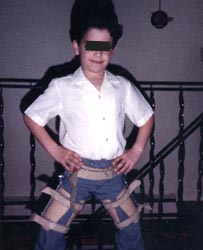
사진 292. 레그-퍼세스병을 브레이스로 치료한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Perthes disease (Legg-Calve Perthes disease)퍼세스병(레그퍼세스 병/ 소아 대퇴골두 무혈성 괴사증)
• The joint connecting the ischial bone and the femur is called the hip joint.
• A disease in which part or all of the femoral head is necrotic and damaged due to abnormal blood circulation of the femoral head in the hip joint capsule is called Perceth’s disease, juvenile femoral head avascular necrosis, or Leg-Percet’s disease.
Causes of Perthes disease
• The cause of the disorder of the femoral head blood circulation is still unknown.
• However, it is certain that the femoral head is necrotic, brittle, and flattened due to impaired blood circulation in the femoral head in the presence of this disease.

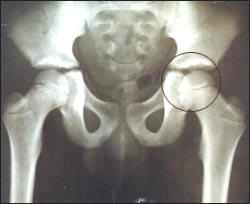
Picture 290. X-ray of both hips (The area marked with O is the left hip joint) Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 291. Leg-Perses disease in the head of the right femur aThe head of the femur was abnormally necrotic and flattened due to In-Leg-Perthes disease In b-normal femoral head Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Signs, Symptoms of Perthes disease
• The disease, once diagnosed, progresses slowly over months or years.
• Because of this, symptoms and signs differ depending on the degree of disease progression.
• It is more likely to occur in children between the ages of 2 to 12, but is more common in infants aged 4 to 8 and school-age children.
• It occurs more often in boys than in girls. • This disease can occur in only one hip joint or in both hip joints simultaneously.
• The hip joint affected by this disease may vary depending on the degree of progression, but it is mildly painful and you can limp your leg.
• Contrary to the symptoms of bacterial hip arthritis, there is no fever and no swelling of the hip joint.
• Inability to move the sore hip joint normally.
• In some cases, the patient may complain that the hip joint with this disease does not hurt and only the knee hurts.
Diagnosis of Perthes disease
• If the disease is suspected by combining the medical history, symptomatic signs, and examination findings, it is diagnosed with an X-ray X-ray of the hip joint or a CT scan.
• Early X-rays of the hip may appear normal.
• The X-ray of the hip joint after 3~4 weeks or more as the progress of Perses’s disease has passed, and the X-ray of the hip joint is often abnormal.
• In some cases, this is the first time the disease is diagnosed.
• These days, a CT scan of the hip can diagnose this disease early
• Tuberculin test, blood test, urine test, sputum bacterium test, chest X-ray test, etc. are sometimes performed to differentially diagnose Perthes disease, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, hip dislocation, and Lyme disease.
Treatment of Perthes disease
• When this disease is suspected, a detailed examination by a pediatrician and an orthopedic specialist should be sought.
• For a while, you should rest without walking on the leg on the side of the person with Perses’ disease and not using that leg.
• From the lower back, the hip joint affected by Perthes disease and the entire leg are treated with a plaster bandage or receive a brace fixation treatment.
• Have school-aged children go to school on crutches.
• If you continue treatment in this way for 1 to 2 years, the disease is almost completely cured.
• In some cases, it is treated with surgery.
• A very small number of children cannot be cured by any means of treatment.

Picture 292. Leg-Perthes disease is treated with braces. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”