팔로 4징과 팔로 3징 Tetralogy of Fallot and Trilogy of Fallot
- 팔로 4징
-
심실 중격 결손,
-
폐동맥 협착,
-
대동맥 우위,
-
우심실 비대 이 네 가지 선천성 심장 기형이 함께 있는 선천성 심장 기형을 팔로 4징 또는 활로 4징이라고 한다.(그림 44, 45 참고)
-
-
팔로 3징(Trilogy Fallot)
-
심방 중격 결손,
-
폐동맥 협착과
-
우심방 속에서 좌심방 속으로 피가 흘러가는 선천성 심장 기형을 팔로 3징(Trilogy Fallot)이라고 한다.
-
팔로 4징과 팔로 3징의 원인
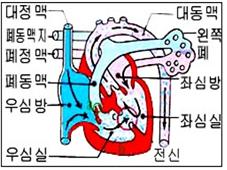
그림 45. 심장 혈관과 팔로 4징, 혈류의 흐름
a-폐동맥 협착, b-심실 비대, c◯–심실중격 결손
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
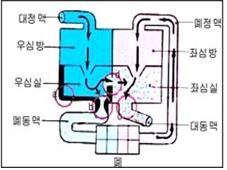
그림 44. 심장 혈관과 팔로 4징, 혈류의 흐름
a◯–우심실 비대, b◯–폐동맥 협착, c◯–대동맥 우위, d◯–심실 중격 결손
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
원인은 확실히 모른다.
-
그러나 당뇨병이 있는 임산부에게 태어난 아이에게 팔로 4징이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
심장이 정상일 때, 전신에서 대정맥을 통과해 우심방 속으로 돌아온 정맥혈이 우심방 속→ 우심실 속→ 주 폐동맥→ 폐동맥 분지(폐동맥 가지/폐동맥 지)→ 폐 순서로 흘러가는 혈액순환이 생긴다.
-
팔로 4징이 있으면
- 전신에서 흘러 들어온 우심방 속 정맥혈은 우심방 속에서 우심실 속으로 일단 흘러간다. 그 다음,
- 폐동맥 협착과 심실중격 결손 기형이 있기 때문에 우심실 속 정맥혈의 대부분이 심실중격 결손을 통과해서 좌심실 속으로 흘러가게 된다.
- 결국, 좌심방 속에서 정상적으로 흘러 들어온 좌심실 속 동맥혈과 우심실 속에서 비정상적으로 흘러 들어온 정맥혈이 섞이게 된다.
- 좌심실 속에는 동맥혈과 정맥혈이 섞인 동맥혈 정맥혈 혼합혈이 생기고 그 피가 대동맥을 통과해서 전신으로 흘러간다.
- 동맥혈 정맥혈 혼합혈을 받은 전신 각 계통의 각 기관과 조직에 파래지거나 창백해지는 중추성 청색증이 생긴다.
- 중추성 청색증이 나타나기 때문에 팔로 4징은 청색증 형 선천성 심장 기형에 속한다.
팔로 4징과 팔로 3징의 증상 징후
-
심실 중격 결손과 폐동맥 협착의 정도, 환아의 나이, 팔로 4징과 함께 있는 다른 선천성 심장혈관 기형의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
팔로 4징을 가지고 태어난 신생아에게 중추성 청색증이 출생 후 바로 나타날 수도 있고, 출생 후 점차로 더 심하게 나타나기도 한다.
-
팔로 4징을 적기에 심장 수술로 치료하지 않는 한 중추성 청색증은 계속 나타나고 다른 증상 징후도 점점 더 심해지는 것이 보통이다.
-
팔로 4징을 가진 신생아나 영아는 젖을 빨아 먹을 힘도 없고 우유병 꼭지를 빨 힘도 없이 쇠약하고 숨을 빠르게 쉬는 것이 보통이다.
-
팔로 4징을 가진 영유아는 잠시 동안 놀다가 숨이 차서 쪼그리고 앉아 자주 쉬는 경향이 있다.
-
어떤 경우는 갑자기 숨이 넘어갈 듯 숨을 가쁘게 쉴 때도 있다.
-
이 기형을 가진 영유아는 또래들보다도 성장 발육이 현저하게 지연된다.
-
적기에 심장 수술로 적절히 치료하지 않으면 사춘기 까지 성장하기 전에 거의 다 사망한다.
-
팔로 4징이 있는 아이에게 뇌농양, 전염성 심내막염, 심부전증 등 생명을 위협할 수 있는 위중한 합병증이 생길 수 있다.

그림48. 팔로 4징이나 다른 종류의 청색형 선천성 심장 기형이 있을 때 혈액 순환 증진을 위해 쪼그리고 앉는 증상 징후도 생긴다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
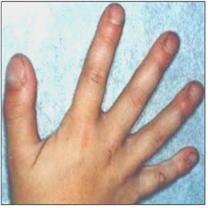
사진 46. 경도 손가락 곤봉 상지
청색형 심장병, 만성 위장병 또는 만성 폐병 등으로 손가락 끝 마디나 발가락 끝 마디가 사진에서 보는 것같이 곤봉형태로 커질 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
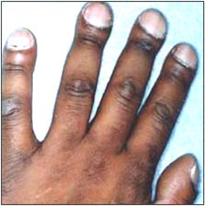
사진 47. 중등도 손가락 곤봉 상지
청색형 심장 기형, 만성 위장병 또는 폐병 등으로 손가락 끝 마디나 발가락 끝 마디가 사진에서 보는 것같이 곤봉형태로 커질 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
팔로 4징과 팔로 3징의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해 이 병이 의심되면, 가슴 X-선 사진검사, 심도자법검사, 심초음파검사 등으로 확진할 수 있다.
팔로 4징과 팔로 3징의 치료
-
팔로 4징의 중증도, 환아의 나이, 합병증 유무 등에 따라 치료한다.
-
일반적인 치료에 관해 주로 설명한다.
-
팔로 4징을 가진 영유아가 갑자기 숨을 가쁘게 쉬면서 기진맥진할 때는 의료 구급대, 병원 응급실이나 단골 의사의 긴급 전환 진료를 받아 그들의 지시에 따라 현장에서 응급치료를 시작한다.
-
이 때 꼭 조이는 옷은 느슨히 풀어 주고 바닥에 두 팔꿈치를 대고 무릎을 꿇고 엎드리도록 응급처치를 한다.
-
산소가 있으면 산소호흡 치료를 한다.
-
의사의 처방에 따라 몰핀이나 그밖에 약물로 응급치료를 한다.
-
의사의 지시에 따라 구급차로든지 다른 적절한 교통 수단으로 병원 응급실로 급히 이송 한다.
-
팔로 4징이 있는 환아는 감기나 위장염 등 바이러스성 전염병에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
-
그런 감염병으로 경미한 설사, 구토 등 이 생기면 짧은 시간 내 심히 탈수될 수 있다.
-
감기와 같은 바이러스성 상기도 염이나 다른 종류의 바이러스성 전염병으로도 음식물을 잘 먹지 않는 경향이 있다.
-
때문에 하찮은 바이러스성 감염병으로도 짧은 시간 내 심하게 탈수될 수 있다.
-
팔로 4징을 가진 환아는 경도 탈수로 혈관 속에 혈전이 쉽게 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 혈전이 뇌혈관 속에도 생겨 뇌혈관의 일부가 막일 수 있다.
-
팔로 4징을 가진 환아가 사소한 병에 걸려 앓을 때도 의사에게 곧 긴급 전화 진료를 받고 그에 따라 적극적으로 치료해야 한다.
-
팔로 4징을 가진 환아의 헤모글로빈 농도는 건강한 아이들의 헤모글로빈 농도보다 더 높을 수 있다.그러나 그 해모글로불린 농도에도 빈혈에 걸려 있을 수 있다. 의사의 처방에 따라 철분제 로 빈혈치료를 받아야 할 때도 있다.
-
환아의 건강상태가 심장 수술을 받을 수 있을 정도로 전반적으로 좋으면, 심실 중격 결손을 막아 주는 수술치료를 받고 협착된 폐동맥을 크게 넓혀 주는 수술치료를 받거나 대동맥 속에 있는 혈이 폐동맥 속으로 흐를 수 있도록 대동맥과 폐동맥 두 동맥 사이에 측로를 만들어 주는 혈관 수술 치료를 우선 하고 적절한 시기에 근본적인 심장 수술치료를 선택적으로 해 준다.
Tetralogy of Fallot and Trilogy of Fallot 팔로 4징과 팔로 3징
Tetralogy of Fallot
o ventricular septal defect,
o pulmonary artery stenosis,
o Right position of aortic,
o Right ventricular hypertrophy
Congenital heart anomaly with these four congenital heart anomalies is called Tetralogy of Fallot
(see Figs. 44 and 45).
• Trilogy Fallot
o atrial septal defect,
o Pulmonary artery stenosis
o Congenital heart anomalies in which blood flows from the right atrium into the left atrium is called Trilogy Fallot.
Causes of Tetralogy of Fallot and Trilogy of Fallot

Figure 45. Cardiovascular and following, blood flow a-pulmonary artery stenosis, b-ventricular hypertrophy, c ◯-ventricular septal defect Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 44. Cardiovascular and following, blood flow a ◯-right ventricular hypertrophy, b ◯-pulmonary artery stenosis, c ◯-aortic dominance, d ◯-ventricular septal defect Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• The cause is not clear.
• However, a child born to a pregnant woman with diabetes may be more prone to have it.
• When the heart is normal, the venous blood returned from the whole body to the right atrium through the vena cava flows in the order of the right atrium → right ventricle → main pulmonary artery → pulmonary artery branch (pulmonary artery branch/pulmonary artery branch) → lung in the order.
• If you have Tetralogy of Fallot
as a follower
o Venous blood in the right atrium flows from the whole body and once flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle. next,
o Due to pulmonary artery stenosis and ventricular septal defect deformity, most of the venous blood in the right ventricle passes through the ventricular septal defect and flows into the left ventricle.
o Eventually, arterial blood in the left ventricle that normally flows from the left atrium and venous blood that flows abnormally from the right ventricle is mixed.
o In the left ventricle, arterial blood and venous blood mixed with arterial blood and venous blood are formed, and the blood flows through the aorta to the whole body.
o Arterial blood, venous blood, Central cyanosis, which becomes blue or pale, occurs in each organ and tissue of each systemic system that received mixed blood.
o Because central cyanosis is present,
Tetralogy of Fallot is a cyanotic congenital heart malformation.
Symptoms and signs of Tetralogy of Fallot and Trilogy Fallot
• Symptoms differ depending on the degree of ventricular septal defect and pulmonary artery stenosis, the child’s age, and the presence or absence of other congenital cardiovascular anomalies along with the palatosis.
• In newborns born with four paws, central cyanosis may appear immediately after birth or may appear gradually more severe after birth.
• Central cyanosis will continue to appear and other symptomatic signs will usually become more and more severe unless the pallor is treated with heart surgery in a timely manner.
• Newborns or infants with four fingers on their arms are usually weak and breathe quickly without the power to suck the milk and the teat of the milk bottle.
• Infants and toddlers with four arms tend to play for a while, then squat out of breath and take frequent breaks. • In some cases, you may breathe quickly as if you are suddenly out of breath.
• Infants and toddlers with this deformity are significantly delayed in growth and development than their peers.
• If not properly treated with heart surgery in a timely manner, almost all of them die before they grow up to puberty.
• A child with four signs can develop serious, life-threatening complications such as brain abscess, infectious endocarditis, and heart failure.

Figure 48. There are also signs of squatting to improve blood circulation when a person has four palates or other types of blue-shaped congenital heart anomalies. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 46. Mild club fingers and cyanotic heart disease, chronic gastrointestinal disease, or chronic lung disease can cause the tip of the finger or the tip of the toe to become larger in the form of a club as shown in the picture. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 47. Moderate club fingers and cyanotic heart disease, chronic gastrointestinal disease, or lung disease can cause the tip of the finger or the tip of the toe to grow in the shape of a club as shown in the picture. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of Tetralogy of Fallot and Trilogy Fallot
• If the disease is suspected by taking the medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings together, it can be confirmed by chest X-ray examination, echocardiography, and echocardiography.
Treatment of the Tetralogy of Fallot and Trilogy Fallot
• Treat according to the severity of the following four signs, the child’s age, and the presence of complications.
• Explain mainly about general treatment.
• When infants and toddlers with four pals are suddenly exhausted with a short breath, seek emergency switching care from a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or a regular doctor, and initiate emergency treatment at the site according to their instructions.
• At this time, loosen tight clothes and give first aid to kneel down with both elbows on the floor.
• If you have oxygen, take oxygen breathing treatment.
• Provide emergency treatment with morphine or other drugs as prescribed by your doctor.
• Urgently transported to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation as directed by the doctor.
• Infants with four fingers are more susceptible to viral infectious diseases such as colds and gastroenteritis.
• Minor diarrhea and vomiting caused by such an infectious disease can lead to severe dehydration within a short period of time.
• People tend not to eat well with viral upper respiratory tract infections such as colds or other types of viral infectious diseases.
• Because of this, even a minor viral infectious disease can cause severe dehydration within a short period of time.
• In children with four fingers, mild dehydration can easily cause blood clots to form in blood vessels.
• These blood clots can also form in the blood vessels in the brain, which can block part of the blood vessels in the brain.
• Even when a child with 4 symptoms is ill from a minor illness, he or she should immediately seek emergency phone care from a doctor and be actively treated accordingly.
• Hemoglobin levels in children with paloculo 4 may be higher than hemoglobin levels in healthy children, but even those hemoglobulin levels may have anemia. In some cases, according to the doctor’s prescription, treatment for anemia with iron medications may be required.
• If the child’s health is generally good enough to undergo heart surgery, receive surgical treatment to prevent ventricular septal defects and undergo surgical treatment to widen the narrowed pulmonary artery, or to allow blood in the aorta to flow into the pulmonary artery. It prioritizes the vascular surgery treatment that creates a lateral path between the two arteries of the pulmonary artery and the pulmonary artery, and selects the fundamental heart surgery treatment at an appropriate time.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”