파상풍, Tetanus
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Chapter 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
파상풍의 원인
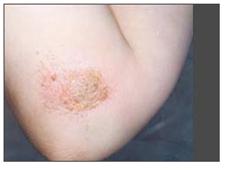
사진 2-82. 자상, 열상 또는 찰과상 등 상처를 적절히 처치하지 않으면 파상풍에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
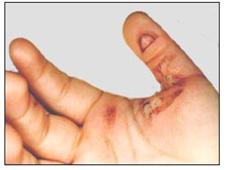
사진 2-83. 화상을 잘못 처치하면 파상풍에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
파상풍균(Clostridium tetanus)이라는 박테리아가 일으킨 감염병을 파상풍이라고 한다.
-
파상풍균은 포자를 형성하는 그람 양성, 혐기성 세균의 일종이다.
-
흙, 먼지, 사람이나 짐승의 위장관 속에 상재하는 세균이다.
-
상처 입은 피부층, 점막층 또는 신체의 다른 부위를 통해 몸속으로 감염될 때 파상풍균 독소가 만들어지고 그 균독소로 파상풍에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
파상풍균이 감염된 상처의 조직이 파괴되지도 않고 거기에 염증도 생기지 않는다. 그러나 파상풍균에서 테타노스파스민(Tetanospasmin) 외독소(Exotoxin)가 분비된다. 그 외독소를 파상풍균 강직독소라고 한다. 파상풍균 강직독소는 횡문근의 운동신경 종판과 척수에 작용하여 운동신경과 근육에 작용해서 심한 근육경련 및 개구 불능증 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
그 외독소가 전신으로 퍼질 수 있고 그로 중추신경이 마비될 수 있다.
-
권장한 대로 파상풍 예방접종을 받았지만 파상풍균에 완전 면역이 생기지 않았을 때
-
권장한 파상풍 예방접종 배열에 의해서 파상풍 예방접종을 다 접종받지 않았거나
-
파상풍 예방접종을 한 번도 접종 받은 적이 없는 아이들에게 파상풍이 생길 수 있다.
-
못이나 예리한 나뭇조각 등으로 자상을 입거나 열상, 또는 찰과상 등을 입었을 때, 파상풍균이 상처를 통해 신체에 감염될 때 파상풍에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
불결한 장소에서 분만하여 태어난 신생아나 갓 태어난 신생아의 탯줄을 불결한 가위 등으로 처리했을 때
-
탯줄이 아직 떨어지지 않은 배꼽을 적절히 살균 소독해 주지 않았을 때 [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질환–신생아 파상풍 참조
-
화상을 입었을 때
-
벌 등 곤충에 쏘인 상처를 통해서 파상풍균에 감염되어 파상풍이 생길 수 있다.
-
자상이나 열상 등으로 생긴 상처가 크면 클수록 상처가 불결하면 불결할수록 파상풍균이 더 잘 감염될 수 있고 파상풍이 발생되면 중증도 더 심한 것이 보통이다.
-
아주 작은 자상, 열상 등의 상처를 통해서도 파상풍균이 감염될 수 있다.
-
2005년 9월 파키스탄에서 일어난 지진으로 외상을 입은 아이들 중 수십 명이 파상풍에 걸렸다. 평소에 파상풍을 잘 예방했으면 이 병에 걸리지 않았을 것이다.
파상풍의 증상 징후
-
파상풍균이 만들어 낸 세균의 외독소에 의해 목과 입 등의 근육에 강직성 경련이 생기고 목과 입이 뻣뻣해지고 입을 벌리기가 힘든 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
파상풍 중증도가 점점 더 진전되면 전신 근육에 강직성 경련이 와서 몸 전체가 활같이 구부러질 수 있다.
-
정상적으로 호흡할 때 주로 쓰는 근육에 경련이 생겨 호흡곤란이 생기고 그로 인해서 질식사망을 할 수 있다.
-
입을 정상적으로 벌릴 수 없어 음식물을 먹지 못하는 개구 불능증도 생기고 방광 근육에 경련이 생겨 소변보는데도 곤란이 생길 수 있다.
-
햇빛이나 다른 종류의 광선, 아주 작은 소리나 사소한 외부의 자극을 받으면 그로 심한 전신경련이 생길 수 있다.
-
신생아가 파상풍에 걸리면 사망률이 거의 60% 정도이고 신생아기 이후의 아이들이 파상풍에 걸리면 사망률이 거의 20%정도 된다.
-
잠복기는 약 2일∼몇 개월이다. 평균 14일이다. 신생아 파상풍의 잠복기는 5~14일이다.
파상풍의 진단 치료
-
병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 환부에서 나온 분비물이나 피·고름 등의 피검물을 채취해서 그람 염색 현미경 파상풍균 세균검사 및 세균 배양 검사로 확진한다.
-
병원 중환자실 입원 치료를 받는다.
-
포도당 전해질용액 혈관주사 수화치료로 탈수를 예방하고 파상풍 인간면역 글로불린(TIG) 주사로 치료한다.
-
호흡곤란이 심하면 기관 절개 수술로 호흡개구를 만들고 그를 통해 호흡할 때도 있다.
-
진정제·근육 이완제·페니실린 등의 항생제로 필요에 따라 치료한다.
-
사소한 외부의 자극에도 전신경련이 생길 수 있기 때문에 광선, 소리 등 외부에서 들어오는 모든 자극에 노출되지 않게 격리 치료한다.
-
환자를 가능한 한 아주 조용한 병실에서 치료하고 입원실도 어둡게 해서 될 수 있는 한 조그마한 자극도 받지 않게 한다.
-
파상풍 사람 면역 글로불린으로 치료할 수 없을 때는 파상풍 항독소 혈청주사(TAT)로 치료한다. 혈관 면역 글로불린으로 치료하기도 한다.
-
Metronidazole, 페니실린이나, 또는 다른 적절한 항생제로 치료할 수 있다.
-
파상풍의 증상 징후가 아주 심할 경우에는 사람 파상풍 면역 글로불린과 파상풍 항독소 혈청주사를 함께 주어 치료할 수 있다.
-
외상으로 생긴 환부가 불결하면 착면 절제수술 치료를 한다.
파상풍 환아의 격리
-
환아도, 환아와 접촉한 사람도 격리할 필요가 없다.
-
또 환자와 접촉했다고 해서 파상풍 백신을 응급을 접종해 줄 필요 없다.
파상풍 백신의 예방 접종
- 2014년 미 소아청소년과 학회에서 권장하는 소아청소년 감염병 예방접종 스케줄 표 참조
-
생후 2·4·6개월에 DTaP 백신으로 각각 1차, 2차, 3차 접종해서 총 3차 접종하고 생후 15~18개월에 4차 접종하고, 유치원에 들어갈 때쯤 4∼6세 사이에 5차 파상풍 백신으로 기본 예방접종을 해 준다.
-
그 이후에는 매 10년마다 디프테리아 백신과 파상풍 백신이 섞인 Td 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주든지 Tdap 백신으로 추가 접종해 준다(예방접종 기록 카드 참조).
-
권장한 대로 정기적으로 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주어도, 피부나 점막 또는 신체에 생긴 자상이나 열상 또 찰과상 등의 상처가 상당히 크거나 또 그 상처가 상당히 불결할 때는 파상풍 백신으로 추가 접종해 줄 수 있다.
-
따라서 화상·절상·자상·찰과상 등의 상처를 입었을 때마다 의사에게 문의하여 파상풍 예방접종을 추가로 접종받아야 되는지 꼭 알아보아야 한다. 자상이나 찰과상 등으로 상처를 입은 아이가 파상풍 백신으로 과거에 예방접종을 한 번도 받지 않았을 때는 파상풍 톡소이드와 파상풍 사람 면역 글로불린을 동시에 주어 파상풍을 예방하는 것이 통상적이다.
-
갓 태어난 신생아의 탯줄을 자를 때는 반드시 소독된 가위나 소독된 의료기구를 사용해야 한다. 탯줄이 다 말라 배꼽에서 떨어지기 전 배꼽 건사 처치는 의사의 지시에 따라 깨끗이 해야 한다.
-
모든 아이들이 초등학교에 입학하기 전 디프테리아, 백일해와 파상풍을 비롯한 다른 여러 종류의 감염병을 권장에 따라 접종해 주어야 한다(예방접종 표 참조).
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 Recommended immunization schedule for 0~18 year old Americal children in Jan 1st 2021
|
☞ 각 나라에 따라 권장 기본 예방접종 스케줄이 다를 수 있다. |
| 예방접종 백신 종류/ 예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1차 접종 | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus²(RV) RV-1(2회분 배열 접종); RV-5(3 회분 배열 접종)/ 로타바이러스 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³(DTaP;<7세)/파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | ←1차 접종→ | →2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ←5차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap;7세나 >7세 파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ 히브 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 5 | ←3차 또는 4차 접종 → 각주 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) /폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 세)/소아마비 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 예방 접종 백신 종류/예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||
| Influenza⁸(IIV; LAIV) 1부에게는 2회분,각주 8 /인플루엔자 | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (11V 만)→ | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (II V 또는 LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ 홍역, 풍진, 유행성 이하선염 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /수두 | ←1 차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/A형 간염 | ←2 회분→ 주서 11 | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; 여성에게만 (HPV4; 여성과 남성 에게)/사람유두종 바이러스 감염병 | ←3회 분 배열 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 생후 9 개월이나 그후후. MenACWY-CRM-D는 생후 2개월이나 그 이후. MenACWY-TT는 은 생후 2세나 그 이후. /수막구균 뇌막염과 그 외 감염병
—————————- Meningococcal B 백신에는 MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, Trumenba 백신이 있다. 10세나 그 이상에 접조한다. Bexsero백신은 2회 접종하고 Trumenba 백신은 총 3회 접종한다. 위험도다 없는 사춘기아이들이나 청년들은 16-23세에 접종받는다. 소스: CDC, AAP News 3/2021
——————————2021년 5월 부터 미 12-15세 사춘기 이이들은 COVI 19 예방 접종을 2회 접종 받을 수 있다. |
←주서 13→ | ←1차 접종→ | 추가 접종 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
접종을 권장 하는 나이의 범위, | ||
|
|
건강상 고 위험 군 아이들에게 접종을 권장하는 나이 |
박테리아 감염병과 바이러스성 감염병을 예방하는 종합 백신
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해 (DTaP) 백신성분이 든 GSK 종합백신-페디아릭스 PEDIARIX, 인팬릭스 INFANRIX, 킨릭스 KINRIX
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해 (DTaP) 백신성분이 든 GSK 종합백신-
|
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해 (DTaP) 백신 성분이 든 GSK 종합백신 |
백신의 성분
|
예방할 수 있는 감염병의 종류 |
예방접종을 받을 수 있는 나이 |
접종경로와 접종 권장 횟수 |
|
PEDIARIX 페디아릭스 |
Diphtheria, Tetanus Toxoids, Acellular Pertussis Adsorbed, Hepatitis B (Recombinant) and Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Combined |
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해, B형 간염, 소아마비 |
생후 6주부터 7세나 그 이전 |
근육주사, 총 3회 접종 생후 2,4,6 개월에 접종하되 접종 간격은 6~8주 |
|
INFANRIX 인팬릭스
|
Diphtheria, Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed |
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해 |
생후 6주부터 7세 이전 |
근육주사, 총 5회.접종 1차 3회 배열 접종을 할 때는 생후 2,4,6개월에 접종하고 추가 접종은 생후 15~20개월에 접종하고 그 다음은 4~6세에 접종한다. |
|
KINRIX 킨릭스
|
Diphtheria, tetanus toxoids acellular pertussis adsorbed and inactivated poliovirus vaccine |
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해, 소아마비 |
4~6세 |
근육주사 1회 디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해, (DTaP) 배열접종을 받을 때 5차 접종백신으로 쓸 수 있다. |
소스:MMWR. 2013:62;1`19
파상풍 백신 예방접종의 부작용
-
각 예방접종 백신의 종류에 따라 부작용이 다르게 생길 수 있다.
-
그러나 백신주사를 맞은 국소가 아프고 발적되고 부을 수 있다.
-
열이 날 수 있고 보챌 수 있는 부작용은 흔히 생기는 부작용이다.
파상풍 백신 예방접종의 금기
-
백신의 성분 중 이스트(곰팡이), Neomycin, Polymyxin B에 알레르기가 있는 아이들은 이 백신으로 예방접종을 받아서는 안 된다. 또 각 백신의 종류에 따라 다른 금기가 있다.
-
더 자세한 정보는 www.aapnews.org
심한 DTaP 백신부작용이 생기면 어떻게 하나
-
DTaP 백신 주사를 맞은 후 심한 DTaP 백신으로 부작용이 생긴 아이에게 파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일해를 예방하기 위해 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 더 이상 해 줄 수 없다. 그러나 DTaP 예방접종 백신 중 백일해 백신의 성분인 P가 들어 있지 않은 TD 백신으로 파상풍과 디프테리아를 예방해 줄 수 있다.
-
DTaP 백신 주사를 맞고 생긴 심한 부작용을 예방접종 기록카드에 자세히 기록했다가 다음 백신으로 예방접종을 받기 전에 의사에게 DTaP 백신으로 부작용이 심하게 생겼었다는 사실을 알려야 한다.
-
과거에 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 받고 심한 DTaP 백신부작용이 있었던 7세 이하 아이들에게는 백일해 예방접종 백신 성분인 P 백신 성분이 들어 있지 않은 TD 백신으로 파상풍과 디프테리아를 예방한다.
-
심한 DTaP백신 부작용이 생겨서 TD 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 때는 백일해를 예방할 수 있는 면역체가 그 아이에게 생기지 않기 때문에 백일해균에 감염될 수 있다.
표 2-13. 자상, 절상, 찰과상 등 외상을 입었을 때 사춘기 이전 소아들과 사춘기 아이들에게 통상적으로 접종해 주는 파상풍 백신 예방접종(표1)
| 침강 테타누스 톡소이드 백신으로 접종 받았던 횟수 | 깨끗하고, 작은 상처Td백신 또는 Tdap 백신2 TIG3 |
그 외 모든 상처1 Td백신 또는 Tdap 백신2 ,또는 TIG3 |
| 3회 이하 또는 확실히 모름 | Yes No | Yes Yes |
|
3회 또는 그 이상4 |
No5 No | No6 No |
-
Td 백신 : 파상풍이나 디프테리아가 만 7세나 그 이상 소아 청소년에게 발생되지 않게 파상풍이나 디프테리아를 예방접종할 때 쓰는 파상풍과 디프테리아의 종합 백신이다.
-
자상, 절상, 찰과상 등 외상을 입은 아이가 7세 이하일 때는 TD 백신이나 DTaP 백신으로 파상풍을 예방접종한다.
-
TIG : 파상풍 면역 글로불린(사람)
-
Tdap 백신 :추가 테타누스 톡소이드백신, 감량된 디프테리아 백신과 톡소이드와 무세포성 백일해 백신.
주석
- 1-쓰레기, 흙, 대변, 또는 침 등이 묻은 자상, 절상, 찰과상, 총상, 화상, 또는 동상 등 외상을 입었을 경우
- 2-과거에 한 번도 추가 테타누스 톡소이드(T) 백신으로 접종 받지 않은 사춘기 아이들에게는 TD 백신으로 접종하는 대신 Tdap 백신으로 접종한다. Tdap 백신이 없거나 이전에 Tdap 백신으로 접종받은 사춘기 아이들에게는 테타누드 톡소이이드(TT) 백신으로 접종 받는 대신 Td 백신으로 접종한다.
- 3-TIG가 없으면 면역 글로불린주사를 맞아야 한다.
- 4-이전에 테타누스 톡소이드를 3차만 접종받았으면, 4차 테타누스 톡소이드 백신으로 접종을 받아야 한다.
- 5-마지막 테타누스 백신이 든 백신으로 접종받은 지 10년이나 그 이상 경과했으면, yes다
- 6-마지막 테타누스 백신이 든 백신으로 접종받은 지 5년이나 그 이상 경과했으면, 추가 예방접종이 필요치 않다.
표 2-14. 자상, 절상, 찰과상 등의 외상을 입었을 때 파상풍을 예방해 주는 파상풍 예방접종(표2)
| 외상의 정도 | 열상, 자상, 찰과상, 화상 등 외상이 비교적 깨끗하고 경미할 때 | 열상, 자상, 찰과상, 화상 등 외상이 불결할 때 | |||
| 예방접종백신의 이름 | Td 주사 | TIG 주사 | Td 주사 | TIG 주사 | |
| 태어나서부터 현재까지 맞은 파상풍 예방접종의 횟수 | 확실히 모를 때 | 맞아야 한다. | 맞을 필요 없다 | 맞아야 한다. | 맞아야 한다. |
| 0 ~ 1 회 맞았을 때 | 맞아야 한다. | 맞을 필요 없다. | 맞아야 한다. | 맞아야 한다. | |
| 2 회 맞았을 때 | 맞아야 한다. | 맞을 필요 없다. | 맞아야 한다. | 외상을 입은 후 24시간이 지났으면 맞을 필요 없다. | |
| 3 회 또는 그 이상 맞았을 때 | 최종 파상풍 예방접종을 맞은 후 10년이 지났을 경우에 맞아야 한다 | 맞을 필요 없다. | 최종 파상풍 예방접종을 맞은 후 5년이 지났을 경우에 맞아야 한다. | 맞을 필요 없다. | |
- Td 백신: 파상풍이나 디프테리아를 만 7세나 그 이상 소아청소년에게 발생되지 않게 파상풍이나 디프테리아를 예방할 때 쓰는 파상풍과 디프테리아 종합 백신이다. 자상, 절상, 찰과상 등 외상을 입은 아이가 7세 이하일 때는 TD 백신이나 DTaP 백신으로 파상풍을 예방접종한다.
-
TIG : 파상풍 면역글로불린.
Tetanus 파상풍
Causes of tetanus

Photo 2-82. If the wound such as cuts, lacerations, or abrasions is not properly treated, your child can get tetanus. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-83. Incorrect treatment of burns can lead to tetanus. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• An infectious disease caused by a bacterium called Clostridium tetanus is called tetanus.
• Tetanus bacteria are Gram-positive, anaerobic bacteria that form spores.
• Dirt, dust, and bacteria that live in the gastrointestinal tract of humans or animals.
• When infected into the body through a wounded layer of skin, mucous membranes, or other parts of the body, tetanus toxin is produced and the toxin can lead to tetanus.
• Tetanus-infected wound tissue is neither destroyed nor inflamed.
However, tetanospasmin exotoxin is secreted from tetanus bacteria.
The exotoxin is called tetanus toxin. Tetanus ankylosing toxin acts on the motor nerve endings and spinal cord of the rhabdomyoma muscle and acts on the motor nerves and muscles, resulting in symptoms such as severe muscle spasms and inability to open.
• The exotoxin can spread throughout the body, resulting in paralysis of the central nervous system
• You have been vaccinated against tetanus as recommended, but you are not completely immune to tetanus bacteria.
• Not all of the tetanus vaccinations have been received according to the recommended tetanus vaccination arrangement.
• Tetanus can develop in children who have never been vaccinated against tetanus.
• You can get tetanus when you get cuts, lacerations, or abrasions from nails or sharp pieces of wood, or when tetanus bacteria infect your body through the wound.
• When the umbilical cord of a newborn or newborn baby born from delivery in a dirty place is treated with dirty scissors, etc.
• When the umbilical cord has not been properly sterilized and sterilized when the umbilical cord has not yet fallen, see [Parents should also be at least the hsalf-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing]-Volume 6, Newborn Growth and Disease-Newborn Tetanus
• When you get burned
• Tetanus can occur due to infection with tetanus through wounds from insects such as bees.
• The larger the wound caused by a cut or laceration, the more dirty the wound is, the more likely it is that tetanus can be infected, and when tetanus occurs, the severity is usually more severe.
• Even small cuts, lacerations, and other wounds can cause tetanus infection.
• Dozens of children traumatized by an earthquake in Pakistan in September 2005 became tetanus. If tetanus had been well prevented, you wouldn’t have gotten this disease.
Tetanus Symptoms, Signs
• Due to the bacterial exotoxin produced by tetanus bacteria, stiff cramps in the muscles of the neck and mouth, stiff neck and mouth, and difficulty opening the mouth may occur.
• As the severity of tetanus develops more and more, a tonic cramp can occur in the muscles of the whole body, causing the entire body to bow like a bow.
• When you breathe normally, you may have convulsions in the muscles you use, which can lead to shortness of breath, which can lead to suffocation.
• There is also an inability to eat due to the inability to open the mouth normally, and a cramp in the bladder muscles may cause difficulty in urinating.
• Sunlight, other types of rays, very small sounds, or minor external stimuli can cause severe systemic cramps.
• When newborns get tetanus, the mortality rate is almost 60%, and when children after neonatal periods get tetanus, the mortality rate is almost 20%.
• The incubation period is about 2 days to several months. It averages 14 days. The incubation period for neonatal tetanus is 5-14 days.
Diagnosis, treatment of tetanus
• Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, medical findings, etc.
If this disease is suspected, specimens such as secretions, blood, pus, etc. from the affected area are collected and confirmed by Gram staining microscopy tetanus bacteria test and bacterial culture test.
• Get inpatient treatment in a hospital intensive care unit.
• Glucose electrolyte solution vascular injection hydration is used to prevent dehydration, and tetanus human immunoglobulin (TIG) injection is used to treat it.
• When breathing is severe, a tracheostomy is used to make a breathing opening and breathe through it.
• Treat as needed with antibiotics such as sedatives, muscle relaxants, and penicillin. • Since even minor external stimuli can cause systemic cramps, treat in isolation so as not to be exposed to all external stimuli such as light rays and sounds.
• Treat the patient in as quiet a room as possible and darken the hospital room so that it does not receive as little irritation as possible.
• When treatment with tetanus human immunoglobulins is not possible, treatment with tetanus antitoxin serum injection (TAT). It is sometimes treated with vascular immunoglobulins.
• Can be treated with Metronidazole, penicillin, or another suitable antibiotic.
• If the symptoms of tetanus are very severe, human tetanus immunoglobulin and tetanus antitoxin serum injection can be given together to treat severe symptoms.
• If the affected area caused by the trauma is unclean, treat with chamferectomy surgery.
Isolation of children with tetanus
• Neither the patient nor the person in contact with the patient need to be isolated.
• Also, you do not need to give an emergency tetanus vaccine just because you have been in contact with the patient.
Vaccination of tetanus vaccine
• Refer to the pediatric and adolescent infectious disease vaccination schedule recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents in 2014.
• At 2, 4, and 6 months of age, the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd doses of DTaP vaccine are given, respectively, for a total of 3 doses, and 4th doses at 15-18 months of age. Tea tetanus vaccine provides basic vaccination.
• Thereafter, every 10 years, either vaccinated with the Td vaccine mixed with the diphtheria vaccine and the tetanus vaccine or boosted with the Tdap vaccine (see immunization record card).
• Even if you are vaccinated with the DTaP vaccine regularly as recommended, additional vaccinations with tetanus vaccine can be given if the cut, laceration, or abrasion on the skin, mucous membrane, or body is very large or the wound is very dirty. have.
• Therefore, whenever you suffer from burns, cuts, cuts, abrasions, etc., you should ask your doctor to see if you need to receive additional tetanus vaccinations.
When a child who has been injured due to a cut or abrasion has never been vaccinated with a tetanus vaccine in the past, it is common to give tetanus toxoid and tetanus human immunoglobulin at the same time to prevent tetanus.
• When cutting the umbilical cord of a newborn baby, you must use sterile scissors or sterile medical equipment. Before the umbilical cord dries out and falls off the navel, the umbilical cord should be cleaned according to the doctor’s instructions.
• All children should be vaccinated against diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus and other infectious diseases as recommended before entering elementary school (see Vaccination Table).
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2021,
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 1 5 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19~23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | |||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←←3rd vaccination→→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus² (RV) RV-1 (two batch sequence inoculation); RV-5 (3-batch sequence vaccination)/ Rotavirus infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³ (DTaP; <7 years old)/tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ←5th vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap; 7 years old> 7 years old tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ Hib infectious disease | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 5 | ←3rd or 4th vaccination→ Footnote 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/Pneumococcal infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) / Streptococcal pneumonia infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 years old)/Polio | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 2 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 15 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19-23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | ||
| Influenza⁸ (IIV; LAIV) for 1 copy, 2 servings, footnote 8 / Influenza | ←Get inoculated every year (11V 만)→ | ←Get inoculated every year(II V or LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ Measles, Rubella, Mumps | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /Varicella | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/Hepatitis A | ←2 doses→ | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; women only (HPV4; women and men))/Human papillomavirus infectious disease | ←3rd vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 9 months or later. MenACWY-CRM-D is 2 months or later. MenACWY-TT is 2 years old or later. / Meningococcal meningitis and other infectious diseases) —————————- Meningococcal B vaccines include MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, and Trumenba vaccines. We touch on 10 years of age or older. The Bexsero vaccine is inoculated twice and the Trumenba vaccine has inoculated a total of three times. Adolescents and young adults with no risk are vaccinated at age 16-23. Source: CDC, AAP News 3/2021
——————Beginning in May 2021, adolescents aged 12 to 15 years old can receive the COVID 19 vaccination twice. |
←1st vaccination→ | Booster vaccination | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
The age range for which vaccination is recommended, | ||
|
|
Age recommending vaccination for children in the high-risk group |
The multiple vaccines to prevent bacterial and viral infectious diseases
GSK comprehensive vaccine containing Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (DTaP)-PEDIARIX, INFANRIX, KINRIX
Comprehensive GSK vaccine containing vaccine ingredients for diphtheria, tetanus, and whooping cough (DTaP)
디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해 (DTaP) 백신성분이 든 GSK 종합백신-
|
GSK Comprehensive Vaccine Containing Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTaP) Vaccine |
Ingredients of the vaccine
|
Types of infectious diseases that can be prevented |
Age at which you can get the vaccine |
Vaccination route and recommended number of vaccinations |
|
PEDIARIX
|
Diphtheria, Tetanus Toxoids, Acellular Pertussis Adsorbed, Hepatitis B (Recombinant) and Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Combined |
diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, Hepatitis B, polio |
From 6 weeks of age to 7 years of age or older |
Intramuscular Injection, A total of 3 vaccinations Inoculation at 2, 4, 6 months after birth, but every 6 to 8 weeks |
|
INFANRIX
|
Diphtheria, Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed |
diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough |
From 6 weeks of age to 7 years old |
Intramuscular Injection, A total of 5 vaccinations. When performing the first 3 batch vaccinations, vaccination should be performed at 2, 4, 6 months of age. Additional vaccination should be done at 15-20 months of age. Then, inoculate at the age of 4-6. |
|
KINRIX
|
Diphtheria, tetanus toxoids acellular pertussis adsorbed and inactivated poliovirus vaccine |
diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio |
4~6years old |
ntramuscular injection 1 time Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, (DTaP) can be used as the 5th vaccination when receiving an array of vaccinations. |
Source: MMWR. 2013:62;1`19
Side Effects of Tetanus Vaccination
• Side effects may occur differently depending on the type of vaccine for each vaccination.
• However, the vaccinated area may be sore, red, and swollen.
• The side effects that can cause fever and replenishment are common side effects. Contraindications to tetanus vaccination
• Children who are allergic to yeast (fungi), Neomycin and Polymyxin B among the components of the vaccine should not be vaccinated with this vaccine.
There are also different contraindications for each type of vaccine.
• For more information, please visit www.aapnews.org
What to do if you have severe DTaP vaccine side effects
• In order to prevent tetanus, diphtheria, and whooping cough after receiving DTaP vaccine injection, children with severe DTaP vaccine side effects can no longer be vaccinated with the DTaP vaccine.
However, among the DTaP vaccination vaccines, a TD vaccine that does not contain P, a component of the pertussis vaccine, can prevent tetanus and diphtheria.
• Record the severe side effects of getting the DTaP vaccine in detail on your vaccination record card and let your doctor know that the side effects of the DTaP vaccine are serious before getting vaccinated with the next vaccine.
• Children under 7 years of age who have been vaccinated with DTaP vaccine in the past and had severe DTaP vaccine side effects are prevented from tetanus and diphtheria with a TD vaccine that does not contain the P vaccine component of whooping cough vaccination vaccine.
• When vaccinating with TD vaccine due to severe DTaP vaccine side effects, the child may be infected with pertussis because the child does not have an immune system that can prevent whooping cough.
Table 2-13. Tetanus vaccine vaccination that is routinely given to pre-adolescent children and adolescent children when trauma such as cuts, cuts, and abrasions has occurred (Table 1)
표 2-13. 자상, 절상, 찰과상 등 외상을 입었을 때 사춘기 이전 소아들과 사춘기 아이들에게 통상적으로 접종해 주는 파상풍 백신 예방접종(표1)
| Sedimentation Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine Number of times a person has been vaccinated | A clean, small wound Tdall other wounds1 Td vaccine or Tdap vaccine2, or TIG3 | All other wounds1 Td vaccine or Tdap vaccine 2, or TIG3 |
| 3 or less or not sure | Yes No | Yes Yes |
|
3 or more times 4 |
No5 No | No6 No |
• Td Vaccine: It is a comprehensive vaccine against tetanus and diphtheria used to prevent tetanus or diphtheria from occurring in children and adolescents aged 7 years or older.
• When a child with trauma such as cuts, cuts, and abrasions is under 7 years of age, vaccinate against tetanus with TD vaccine or DTaP vaccine.
• TIG: Tetanus immune globulin (human)
• Tdap Vaccine: Additional Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine, Reduced Diphtheria Vaccine and Toxoid and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine.
Remark
• 1- In case of trauma such as cuts, cuts, abrasions, gunshot wounds, burns, or frostbite with trash, dirt, feces, or saliva
• 2-Adolescent children who have never received an additional tetanus toxoid (T) vaccine in the past are given the Tdap vaccine instead of the TD vaccine. Adolescent children who do not have the Tdap vaccine or who have previously received the Tdap vaccine are given the Td vaccine instead of the tetanus toxoid (TT) vaccine.
• If you do not have
3-TIG, you will need an immunoglobulin injection.
• If you have only received the 3rd dose of tetanus toxoid prior to 4-4, you should be vaccinated with the 4th dose of tetanus toxoid vaccine.
• 5-Yes if 10 years or more have passed since the last vaccination with the tetanus vaccine.
• If more than 5 years have passed since you received the vaccine with the 6-last tetanus vaccine, no additional vaccinations are required.
Table 2-14. Tetanus vaccination to prevent tetanus in case of trauma such as cuts, cuts, and abrasions (Table 2)표 2-14. 자상, 절상, 찰과상 등의 외상을 입었을 때 파상풍을 예방해 주는 파상풍 예방접종(표2)
| The degree of trauma | When the trauma is relatively clean and minor such as lacerations, cuts, abrasions, and burns | When the trauma such as lacerations, cuts, abrasions, and burns is unclean | |||
| Name of vaccination vaccine | Td injection | TIG injection | Td injection | TIG injection | |
| Number of tetanus vaccinations from birth to present | When you don’t know for sure | Give vaccination | No need to Give vaccination | Give vaccination. | Give vaccination |
| When 0 ~ 1 vaccination | Give vaccination. | No need to Give vaccination | Give vaccination | Give vaccination | |
| When 2times vaccination | Give vaccination | No need to Give a vaccination. | Give vaccination | If 24 hours have passed since you suffered the trauma, you do not need vaccination. | |
| When more than 3 times vaccination
|
It should be taken if 10 years have passed since the last tetanus vaccination has passe | No need to Give vaccination | It should be correct if 5 years have passed since the last tetanus vaccination. | No need to Give a vaccination. | |
Td Vaccine: This is a comprehensive vaccine for tetanus and diphtheria, which is used to prevent tetanus and diphtheria so that tetanus and diphtheria do not occur in children 7 years of age or older. When a child with trauma such as cuts, cuts, abrasions, etc. is under 7 years of age, vaccinate against tetanus with a TD vaccine or a DTaP vaccine. TIG : tetanus immunoglobulin.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other