파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염 Paratyphoid fever, Paratyphoid food poisoning, Paratyphoid gastroenteritis
파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염의 원인
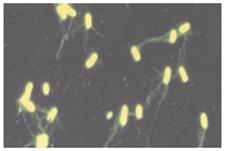
사진 2-98. 살모넬라균
출처– CDC와 Infectious Diseases In Children, May, 2005.Vol.18.#5

사진2-105.거북이도 파라티푸스균을 보균할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
파라티푸스균(Sallmonella Paratyphoid)은 살모넬라균 속(屬)에 속한 일종의 박테리아이다.
-
파라티푸스균에 감염되어 생기는 급성 위장 감염병을 파라티푸스(파라장티푸스)라고 한다.
-
파라티푸스균은 파라티푸스균성 위장염(파라티푸스 위장염)을 일으킬 수 있고,
-
파라티푸스균 식중독(파라티푸스 식중독), 또 파라티푸스 열(파라티푸스)도 일으킬 수 있다.
-
위장관 속에 파라티푸스균을 보균하고 있지만 아무 병도 증상도 없이 지내는 건강한 사람들도 많다.
-
닭·칠면조·오리·소·돼지 등 가축이나 가금류 등이 이 세균을 보균하고 있을 수 있다.
-
고양이·곤충도 이 세균을 보균할 수 있다.
-
미국서 연간 1.2백만 여명에게 살모넬라균성 감염병이 발생되고 그 중 약 6%는 애완용 거북이 등 파충류에 의해 감염된다.
-
파라티푸스균을 보균한 사람들이나 동물들이 이 균을 다른 사람들이나 동물들에게 감염시킬 수 있다.
그림 2-99. 파라티푸스균에 오염된 달걀 껍데기이나 잘 익히지 않은 생달걀로 만든 음식물로 인해 파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
그림 2-100. 파라티푸스균에 오염된 생우유로 인해 파라티푸스균 감염, 파라티푸스 식중독, 또는 파라티푸스 위장염에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
그림 2-101. 파라티푸스균을 보균한 개로 인해 파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 또는 파라티푸스 위장염에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
그림 2-102. 파라티푸스균을 보균한 고양이로 인해 파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 또는 파라티푸스 위장염에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
그림 2-103. 파라티푸스균을 보균한 돼지, 소, 말 등으로부터 파라티푸스균에 감염되어 파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 또는 파라티푸스 위장염에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
그림 2-104. 파라티푸스균을 보균한 새, 닭, 칠면조 등으로 인해 파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 또는 파라티푸스 위장염에 걸릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 닭고기·돼지고기·쇠고기, 또는 달걀 등에 파라티푸스균이 오염되어 있을 수 있다.
- 파라티푸스균에 오염된 고기 음식물을 완전히 익히지 않은 채로, 또는 날 것으로 먹을 때 파라티푸스균에 감염될 수 있다.
- 사람이 이런 파라티푸스균에 감염되어도 파라티푸스나 파라티푸스 감염병이 발생되지 않을 수 있다.
- 감염된 파라티푸스균의 수에 따라 파라티푸스균 독소의 강약에 따라, 이 균에 감염된 사람의 면역 기능 능력 등에 따라 파라티푸스를 앓을 수 있고 앓지 않을 수 있다.
파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염의 증상 징후
- 이 세균에 의한 감염병의 종류와 정도, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다양하다.
- 파라티푸스균에 오염된 음식물을 먹은 후 6∼72시간쯤에 구토, 구기 또는 심한 복통과 다른 여러 가지의 식중독 증상 징후가 나타날 수 있다.
- 중증도와 앓는 기간이 환아에 따라 조금 다를 수 있다.
- 합병증이 생기지 않는 한 5일 정도 앓다가 회복되는 것이 보통이다.
- 배만 조금 아픈 증상만 있을 뿐 다른 증상 징후는 거의 없을 수 있고,
- 고열·복통·설사·경기 등의 증상 징후가 심하게 나타날 수 있다.
- 또 심하게 탈수될 수 있고 탈수로 인해 다른 여러 증상 징후가 생겨 병원에 입원해 치료받아야 하는 경우도 있다.
- 때로는 피 똥과 곱똥 섞인 설사를 심하게 할 수 있다.
- 파라티푸스균 감염병으로 위장염은 생기지 않고, 신체 다른 부위에 감염되어 패혈증·뇌막염·골수염·농양 등 생명에 위중한 침입성 파라티푸스균 감염병을 일으킬 수 있다.
- 잠복기는 약 6∼72시간이다.
파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염의 진단
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면, 환자에게서 피검 물용 설사 변 등을 채취해서 그 피검 물로 그램 염색 현미경 세균 검사도 하고 세균배양검사를 해서 진단할 수 있다.
- 대변으로 세균 배양검사를 바로 할 필요가 있지만, 검사할 수 있는 피검 물용 대변을 바로 배변 받을 수 없을 때는 항문 속에 피 검물 채취용 면봉 팁을 넣었다 뺀 후 그 면봉 팁에 묻은 대변 피검 물로 세균배양검사를 해 이 병을 진단하기도 한다.
- 신체의 어느 부위에 파라티푸스균 감염병이 있느냐에 따라, 진단 방법이 다소 다를 수 있다.
- 몸의 어느 부위에 감염병이 있었는지에 따라 대변·소변·피·골수 등 피검 물을 채취해 그 피검 물로 세균배양검사를 하여 진단할 수 있다. 파라티푸스균 감염병으로 생긴 파라티푸스균 병원소에서 고름 등을 채취해 파라티푸스균 세균배양검사를 해 이 병을 확진할 수 있다.
- 효소면역 분석검사, 라텍스응집 검사, 단클론항체검사 등으로도 진단한다.
파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염의 치료
- 파라티푸스균 감염으로 생긴 파라티푸스균 위장염의 증상 징후가 경미할 때는 가능한 한 항생제로 치료하지 않는 것이 보통이다.
- 그 대신, 페디아라이트나 다른 종류의 경구용 포도당 전해질용액으로 재수화 치료와 현상유지 수화 치료를 하거나 포도당 전해질용액 혈관주사 재수화 치료로 탈수를 치료하고 탈수를 예방하기도 한다.
- 열이 나고 아프면 타이레놀 등 해열 진통제로 해열·진통시킨다.
- 침입성 파라티푸스균 감염병이 있거나 침입성 파라티푸스균 감염병이 없더라도 증상 징후가 심하고 열이 많이 나면 병원에 입원시켜 앰피실린이나 클로람페니콜, 또는 세포택심 항생제들 중 적절한 항생제 한 가지를 선택해서 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
- 신생아들이나 생후 3개월 이전 영아들에게 파라티푸스균 감염병이 생기면 고열이 나면서 생명에 위험할 정도로 위중하게 앓을 수 있다. 특히 생후 3개월 이전 신생아나 영아들에게 파라티푸스균 감염병이 생기면 입원해 항생제 정맥주사 치료 하는 것이 보통이다.
- 파라티푸스균 뇌막염이나 패혈증·뇌막염·골수염 등 위중한 파라티푸스균 감염병을 앓을 때는 항생제 혈관주사 치료를 한다.
- 증상 징후가 경미한 파라티푸스균 위장염은 통상적으로 항생제치료를 하지 않는다.
- 경미한 파라티푸스균 위장염을 항생제로 치료하면 파라티푸스균이 소장관이나 담낭관 또는 담낭 속에서 오랫동안 살아남아 있으면서 다른 사람들에게 파라티푸스균을 감염시킬 수 있는 보균자가 될 수 있다.
- 또 항생제로 치료할 때나 치료하지 않을 때의 증상 징후, 병세와 병의 진행경과가 거의 같기 때문에 증상이 경미하면 항생제 치료를 하지 않는 것이 보통이다.
- 그리고 항생제 치료를 할 때 그 항생제 자체로 부작용이 위장관에 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 설사할 수 있다.
- 따라서 파라티푸스균 위장염을 경미하게 앓는 환자는 가능한 한 항생제 치료를 받지 않고 대증치료만 받는 것이 보통이다.
파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염의 합병증
- 파라티푸스균 위장염을 앓을 때 패혈증·골수염, 또는 뇌막염 등의 합병증이 생길 수 있고 그런 합병증에 의해 생명이 위험할 수 있다.
- 이런 복잡한 치료는 그때그때 의사의 판단에 따라 해야 한다.
파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염 환자와 격리
- 이 병을 앓는 환자의 대변이나 소변 등에 파라티푸스균이 섞여 나올 수 있기 때문에 그런 배설물을 조심히 취급한다.
- 특히, 환아를 직접 간호하는 사람들은 손을 깨끗이 씻어야 한다. 환아가 병원에 입원했을 때는 그 환자를 다른 사람들로부터 격리시켜야 한다.
- 환자와 접촉한 경우, 손을 잘 씻고 위생관리를 잘 하는 것 이외 특별히 달리 할 것은 없다.
파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염의 예방
- 예방접종 백신은 아직 없다.
- 보균자의 대변을 통해 나온 파라티푸스균이 수개월 내지 수 년 동안 다른 사람들에게 감염될 수 있다.
- 평소, 대변을 본 후 손을 항상 깨끗이 씻는 습관은 이 병을 예방하는데 도움이 된다.
- 파라티푸스균에 오염된 날고기를 실내온도에 오랫동안 보관하면 파라티푸스균이 날고기 속에서 짧은 기간 내 많이 증식될 수 있다.
- 이렇게 파라티푸스균에 오염된 음식물을 잘 익히지 않고 먹을 때 파라티푸스에 걸릴 수 있으므로 주의해야 한다. 그리고 오염된 물은 반드시 끓여 마셔야 한다.
Paratyphoid fever, Paratyphoid food poisoning, Paratyphoid gastroenteritis파라티푸스, 파라티푸스 식중독, 파라티푸스 위장염
Causes of paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, and paratyphoid gastroenteritis

Photo 2-98. Salmonella Source- CDC and Infectious Diseases In Children, May, 2005.Vol.18.#5

Picture 2-105.Turtles can also carry paratyphoid bacteria. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Salmonella Paratyphoid is a type of bacteria belonging to the genus Salmonella.
• An acute gastrointestinal infection caused by infection with paratyphoid bacteria is called paratyphoid.
• Paratyphoid bacteria can cause Paratyphoid gastroenteritis (Paratyphoid gastroenteritis),
• Paratyphoid bacteria can cause food poisoning (paratyphoid food poisoning) and also paratyphoid fever (paratyphoid fever).
• There are many healthy people who carry paratyphoid bacteria in their gastrointestinal tract, but have no disease or symptoms.
• Livestock and poultry, such as chickens, turkeys, ducks, cows, and pigs, may carry these bacteria.
• Cats and insects can also carry these bacteria.
• About 1.2 million people in the United States are infected with salmonella per year, and about 6% of them are infected by reptiles such as pet turtles.
• People and animals that carry Paratyphoid bacteria can infect other people and animals with the bacteria.

Figure 2-99. Paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, and paratyphoid gastroenteritis can result from foods made from eggshells contaminated with paratyphoid bacteria or raw eggs that are not well-cooked. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 2-100. Live milk contaminated with paratyphoid bacteria can lead to paratyphoid infection, paratyphoid food poisoning, or paratyphoid gastroenteritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 2-101. Dogs with paratyphoid bacteria can develop paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, or paratyphoid gastroenteritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 2-102. Cats carrying paratyphoid bacteria can develop paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, or paratyphoid gastroenteritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 2-103. Pigs, cattle, and horses carrying paratyphoid bacteria may be infected with paratyphoid bacteria, resulting in paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, or paratyphoid gastroenteritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 2-104. Birds, chickens, and turkeys carrying paratyphoid bacteria can cause paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, or paratyphoid gastroenteritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Chicken, pork, beef, or eggs may be contaminated with paratyphoid bacteria.
• Paratyphoid-contaminated meat You can become infected with paratyphoid bacteria when food is eaten raw or raw.
• Even if a person is infected with these paratyphoid bacteria, they may not develop paratyphoid or paratyphoid infections.
• Depending on the number of infected paratyphoid bacteria, depending on the strength of the paratyphoid toxin, and the immune function of a person infected with this bacteria, you may or may not have paratyphoid.
Symptoms signs of paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, and paratyphoid gastroenteritis
• Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of infectious diseases caused by this bacterium and the presence or absence of complications.
• About 6 to 72 hours after eating food contaminated with paratyphoid bacteria, vomiting, goji, or severe abdominal pain and several other signs of food poisoning may appear.
• The severity and duration of illness may vary slightly depending on the patient.
• Unless there are complications, it usually takes about 5 days and then recovers.
• There may be only symptoms of a little stomach ache, but few other signs of symptoms,
• Symptoms such as high fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and sports may be severe.
• In addition, dehydration may result in severe dehydration and other symptoms may result, requiring hospitalization to be treated.
• Sometimes it can cause severe diarrhea, which is a mixture of blood and dung.
• As a paratyphoid infection, gastroenteritis does not occur, and can cause life-threatening invasive paratyphoid infections such as sepsis, meningitis, osteomyelitis, and abscess by infecting other parts of the body.
• The incubation period is about 6 to 72 hours.
Diagnosis of paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, and paratyphoid gastroenteritis
• If this disease is suspected by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, diarrhea, etc. for the subject are collected from the patient, and the sample can be diagnosed by performing a gram stain microscopic bacterial test and a bacterial culture test.
• It is necessary to perform a bacterial culture test with feces immediately, but if the feces for the subject that can be tested cannot be immediately defecated, insert and remove a cotton swab tip for collecting blood specimens into the anus, and then conduct a bacterial culture test with the stool specimen on the swab tip. The disease is also diagnosed by doing.
• Depending on which part of the body has a paratyphoid infection, the diagnosis method may be slightly different.
• Depending on which part of the body there was an infectious disease, it can be diagnosed by collecting specimens such as feces, urine, blood, and bone marrow, and performing a bacterial culture test with the specimen. The disease can be confirmed by collecting pus from a paratyphoid pathogen caused by a paratyphoid infectious disease and performing a paratyphoid bacterial culture test.
• Diagnosis is also carried out by enzyme immunity assay, latex aggregation test, and monoclonal antibody test.
Treatment of paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, and paratyphoid gastroenteritis
• When the symptoms of paratyphoid gastroenteritis caused by a paratyphoid infection are mild, it is usually not treated with antibiotics as much as possible.
• Instead, rehydration treatment and status maintenance hydration treatment with pedialite or other types of oral glucose electrolyte solutions, or intravascular rehydration treatment with glucose electrolyte solutions may treat dehydration and prevent dehydration.
• If you have a fever and are sick, use antipyretic analgesics such as Tylenol to reduce fever and pain.
• Even if you have an invasive paratyphoid infectious disease or do not have an invasive paratyphoid infectious disease, if symptoms are severe and you have a lot of fever, it is common to be admitted to a hospital and treated with one of the appropriate antibiotics from ampicillin, chloramphenicol, or cytotaxim antibiotics. • Paratyphoid infections in newborns or infants before 3 months of age can lead to high fever and life-threatening illness. In particular, if a paratyphoid infection occurs in newborns or infants before 3 months of age, it is common to be hospitalized and treated with intravenous antibiotics.
• If you suffer from severe paratyphoid infections such as paratyphoid meningitis, sepsis, meningitis, osteomyelitis, etc., antibiotic vascular injection treatment is given.
• Paratyphoid gastroenteritis with mild symptoms is not usually treated with antibiotics.
• Treating mild Paratyphoid gastroenteritis with antibiotics can make it a carrier that can infect other people with Paratyphoid bacteria while remaining alive in the small intestine, gallbladder, or gallbladder for a long time.
• In addition, since the symptoms, symptoms and progression of the disease are almost the same when treated with or without antibiotics, it is common not to take antibiotics if the symptoms are mild.
• And when taking antibiotic treatment, the antibiotic itself can have side effects in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in diarrhea.
• Therefore, patients with mild paratyphoid gastroenteritis are usually not treated with antibiotics as much as possible, but only symptomatic treatment.
Paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, complications of paratyphoid gastroenteritis
• When suffering from paratyphoid gastroenteritis, complications such as sepsis, osteomyelitis, or meningitis can occur, and such complications can be life-threatening.
• These complex treatments should be done at the discretion of the doctor. Isolation from patients with paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, and paratyphoid gastroenteritis
• Handle such excrement with care because paratyphoid bacteria may be mixed in the stool or urine of a patient with this disease.
• In particular, those who directly care for the child should wash their hands thoroughly.
When a patient is admitted to the hospital, the patient must be isolated from others.
• In case of contact with the patient, there is nothing else to do except wash your hands well and take good hygiene care.
Prevention of paratyphoid, paratyphoid food poisoning, and paratyphoid gastroenteritis
• There is still no vaccination vaccine.
• Paratyphoid bacteria from the carrier’s stool can infect others for months to years.
• The usual habit of washing your hands thoroughly after stooling can help prevent this disease.
• If raw meat contaminated with paratyphoid bacteria is kept at room temperature for a long period of time, paratypic bacteria can multiply in raw meat within a short period of time.
• When eating foods contaminated with paratyphoid bacteria without being cooked well, you may get paratyphoid, so be careful. And contaminated water must be boiled.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”