토혈(피를 토할 때), Hematemesis (Vomiting blood)
토혈의 개요
- 위장 관에서 흘린 피를 입안이나 입 밖으로 토하고 뱉어내는 증상 징후를 토혈(Hematemesis)이라고 한다.
- 토혈은 증상 징후이다. 병명은 아니다.
- 참고로, 하 기도나 폐에서 나온 피를 입안으로 또는 입 밖으로 토하고 뱉어내는 증상 징후는 객혈(Hemoptysis)이라고 한다.
- 한두 방울의 피가 섞인 위액을 토할 수도 있고 피만 소량 토할 수 있고 피를 다량 토할 수 있다.
- 때로는 커피색 같은 피를 소량 또는 다량 토할 수 있다.
- 토혈의 원인은 많고 나이에 따라 원인이 다르다.
- 신생아가 피를 토하는 원인과 신생아기 이후 영유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들이 피를 토하는 원인에 관해 알아본다.
토혈의 원인
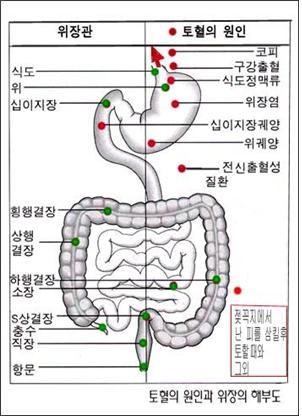
▴ 그림 1-24. 신생아가 피를 토하는 원인과 신생아기 이후 피를 토하는 원인.
분만 중 태어나는 아기가 모체의 산도에서 나온 모체 피를 삼킨 후 태어난 신생아가 피를 토할 수 있고 모유 수유 중 수유모의 젖꼭지에서 나는 엄마의 피를 삼킨 후 신생아가 피를 토할 수 있다.
신생아나 신생아기 이후 코피, 구강 출혈, 식도 정맥류 출혈,위장염, 12지장 궤양, 위궤양, 전신 출혈성 질환 등으로 피를 토 할 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAPP
신생아가 피를 토하는 원인
- 태어나서 28일까지의 기간을 신생아기라고 한다.
- 신생아기의 아기들을 신생아라고 한다.
- 태어나서부터 생후 첫 3일까지의 신생아가 피를 토하는 원인의 대부분과 생후 3~4일 이후에서 28일까지의 신생아들이나 신생아기 이후 영유아들, 학령기 아이들, 또는 사춘기 아이들이 피를 토하는 원인의 대부분은 다른 점이 많다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 질병 -피를 토할 때, 신생아가 출혈할 때 참조).
- 드물게, 갓 태어난 신생아가 비타민 K 결핍증으로 위장 관에서 피가 날 수 있고 위장 관 내로 흘린 피를 토할 수 있다.
- 분만 중 모체의 산도에서 나는 피를 태어나는 아기가 삼킬 수 있다. 산도에서 모체의 피를 삼키고 태어난 신생아가 생후 1~3일 동안 피를 토할 수 있다.
- 모유를 먹는 아기가 엄마의 젖꼭지에서 나는 엄마 피를 삼킨 후 삼킨 엄마 피를 토할 수 있다. 갓 태어난 신생아의 위장 관이 삼킨 엄마의 피로 자극 받고 삼킨 엄마 피를 토할 수 있다.
- 갓 태어난 신생아가 토한 피가 아기 자신의 입안, 인두 강, 비강, 위장 관 등에서 흘린 피를 토하는지, 그렇지 않으면, 분만 중 모체의 산도에서 흘린 모체 피를 삼킨 후 신생아가 삼킨 모체의 피를 토하는지 감별해야한다.
- 분만 중 모체의 산도에서 흘린 모체 피를 삼킨 후 태어난 신생아들의 대부분은, 대개, 생후 1~3일 이내 삼켰던 모체 피를 토하는 것이 보통이다.
- 그렇지 않으면, 태어나는 중 산도에 흘린 모체 피를 삼킨 후 태어난 신생아들의 대부분은 모체 피의 일부를 토하고 나머지는 삼킨 피가 대변으로 배설되기도 하고, 또는 삼킨 모체 피의 전부가 위장 관을 통과한 다음 항문을 통과해 혈변으로 배설된다.
- 원인을 확실히 알 수 없이, 생후 2~3일 경에, 신생아가 한두 방울의 피를 토하다가 자연히 그치는 경우도 있다.
- 위궤양, 십이지장 궤양, 위장염, 선천성 위장 관 기형, 위장 관 내 이물, 위장 관 혈관 기형, 또는 전신 출혈성 질환 등으로 신생아가 피를 토할 수 있다. 그런 경우는 아주 드물다.
신생아기 이후 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들 및 사춘기 아이들이 피를 토하는 원인
- 선천성 담도 폐쇄증이 있을 때,
- 간 정맥의 압이 비정상적으로 높아서 생긴 식도하단 정맥류가 터지면 피를 다량 토할 수 있다. 이런 병으로 소아청소년들이 피를 토하는 경우는 사실 아주 드물다.
- 간 경변증, 혈우병, 패혈증, 혈소판 감소증, 위궤양, 위염, 십이지장 궤양, 십이지장 염, 전신 출혈성 질환, 부식성 식도염, 위장염, 약물 중독, 아스피린 등 약물 부작용, 위장 관 내 이물, 위장 관 혈관 기형, 지속성 구토 등으로 피를 토할 수 있다.
- 신생아기 이후 소아들의 경우, 이를 뺄 때, 아데노이드 절제 수술, 편도 절제 수술을 받을 때 흘린 피를 삼키거나 삼킨 코피로 위장 관이 자극받고 삼킨 피를 토할 수 있다.
토혈의 진단
- 토혈은 어떤 병의 증상 징후이고 병명은 아니다.
- 피를 토할 때는 토한 피가 신체 어느 부위에서 어떻게 해서 나온 피인지 알아봐야 한다.
- 피를 토할 때 토한 피는 구강, 인두, 식도, 위장관 등 소화기계에서 나온 피일수도 있고 상·하기도 등 호흡기에서 나온 피일 수 있다.
- 즉 입안, 인두, 식도, 위, 작은창자 등의 소화기계의 위장관에서 나온 피를 토할 수도 있고, 비강, 인두, 후두, 기관, 기관지, 폐 등의 호흡기에서 나온 피를 토할 수 있다.
- 호흡기 질환을 앓을 때 기침하면서 토한 피는 호흡기에서 나온 피(객혈)일 가능성이 더 많다.
- 소화기 질병을 앓는 중 구토와 구역질을 하다가 토한 피는 소화기의 위장관에서 나온 피(토혈)일 가능성이 더 많다.
- 그렇지만 신생아들이나 영유아들이 피를 토할 때 토한 피가 호흡기에서 나온 피인지, 위장 관에서 나온 피인지 확실히 쉽게 감별하기가 힘들다.
- 배가 아프면서 토한 피, 위궤양이나 십이지장 궤양 등을 앓고 있는 병력이 있으면서 토한 피는 위장 관에서 나온 피일 가능성이 상당히 더 많다.
토혈의 치료
- 토혈의 원인과 토한 피의 량, 토혈할 때의 건강상태, 출혈 스크린 검사, 간 기능 검사 결과 등에 따라 치료가 다르다.
- 갓 태어난 신생아든 그 이후 신생아이든 영유아든 아무런 증상 징후가 없이 피를 토하면 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 전화 연락해서 그들의 지시에 따라 토혈의 원인이 무엇인지 알아보고 원인에 따라 치료한다.
- 피를 다량으로 토하고 의식이 몽롱하거나 쇼크에 빠질 때는 기본 심폐 소생술 처치법을 하고 상반신을 하반신보다 15~30도 정도 낮게 눕히고 의료구급대, 병원 응급 의료실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과에 긴급으로 전화해 그들의 지시에 따라 응급처치를 현장에서 하면서 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단으로 병원 응급실로 급히 이송한다.
- 병원 응급실에서는 토혈의 원인과 정도에 따라 산소호흡치료, 수혈치료를 한다.
- 피가 없어 수혈치료를 할 수 없으면 알부민을 피 대신 쓰기도 한다.
- 토혈의 원인에 따라 치료한다.
Hematemesis(Vomiting blood) 토혈 (피를 토할 때)
Overview of hematopoiesis
- The symptom of vomiting and spitting blood from the gastrointestinal tract into or out of the mouth is called hematemesis.
- Hematemesis is a symptom, a sign. It is not a disease name.
- For reference, a symptom of vomiting and spitting blood from the lower respiratory tract or lungs into or out of the mouth is called hemoptysis.
- You can vomit a gastric juice mixed with one or two drops of blood, only a small amount of blood, or a large amount of blood.
- Sometimes, you can vomit small or large amounts of coffee-colored blood.
- There are many causes of hematemesis, and the causes vary according to age.
- Find out what causes newborns to vomit blood and what causes infants, school-age children, and adolescents to vomit blood after the neonatal period.
Causes of hematemesis

▴ Figure 1-24. What causes newborns to vomit blood and what causes newborns to vomit blood. Newborns born after a baby is born during delivery swallows maternal blood from the mother’s birth canal may vomit blood, and newborns may vomit blood after swallowing the mother’s blood from the nursing mother’s nipples during breastfeeding. After the newborn or neonatal period, blood can be vomited from nosebleeds, oral bleeding, esophageal variceal bleeding, gastroenteritis, ulcers in the duodenum, gastric ulcers, and systemic hemorrhagic diseases.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAPP
What causes newborns to vomit blood
- The period from birth to 28 days is called the newborn period. Newborn babies are called newborns. Most of the causes of vomiting blood in newborns from birth to the first 3 days of life, and most of the causes of blood vomiting in newborns from 3 to 4 days to 28 days after birth, infants, school-age children, or adolescent children
- There are many differences.
- [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing]-Volume 6 Diseases with good growth and development for newborns-Refer to when vomiting blood or bleeding newborns)
- Rarely, newborn babies with vitamin K deficiency can bleed in the gastrointestinal tract and vomit blood spilled into the gastrointestinal tract. During delivery, blood from the mother’s birth canal can be swallowed by a born baby. After swallowing the mother’s blood in the birth canal, newborns can vomit blood for 1 to 3 days after birth.
- A breastfed baby may swallow the mother’s blood from the mother’s nipple and then vomit the swallowed mother’s blood.
- The gastrointestinal tract of a newborn baby may be irritated by the mother’s blood and vomit the swallowed mother’s blood.
- Whether the newborn’s vomiting blood vomits blood from the baby’s own mouth, pharyngeal cavity, nasal cavity, gastrointestinal tract, etc., or whether the newborn vomits maternal blood after swallowing the maternal bloodshed from the mother’s birth canal during delivery.
- You have to discriminate.
- Most of the newborns born after swallowing maternal blood from the mother’s birth canal during delivery usually vomit maternal blood that was swallowed within 1 to 3 days of birth.
- Otherwise, most of the newborns born after swallowing maternal blood that spilled into the birth canal during birth vomit part of the maternal blood, and the rest of the maternal blood may be excreted in feces, or all of the maternal blood swallowed passes through the gastrointestinal tract and then through the anus and Excreted blood thru anus.
- There are cases when the cause is not known for sure, and around 2-3 days after birth, newborns vomit one or two drops of blood and then stop spontaneously.
- Newborns can vomit blood from gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, gastroenteritis, congenital gastrointestinal anomalies, foreign objects in the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal vascular anomalies, or systemic bleeding disorders.
- Such cases are very rare.
Causes of vomiting blood in infants, school-age children, and adolescent children after the neonatal period
- When you have congenital biliary atresia,
- Abnormally high pressure in the hepatic vein can cause a large amount of blood to be vomited when a varicose vein in the lower esophagus bursts. In fact, it is very rare for children and adolescents to vomit blood from this disease.
- Liver cirrhosis, hemophilia, sepsis, thrombocytopenia, gastric ulcer, gastritis, duodenal ulcer, duodenitis, systemic hemorrhagic disease, corrosive esophagitis, gastroenteritis, drug posons, drug side effects such as aspirin, foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal vascular malformation, persistent vomiting, etc.
- Your child can vomit blood. In the case of children after the neonatal period, the gastrointestinal tract may be irritated and vomit of swallowed blood by swallowing or swallowing blood that was shed during adenoidectomy or tonsillectomy when it is removed.
Diagnosis of hematemesis
- Hematemesis is a symptom of a disease and not a disease name.
- When vomiting blood, you need to find out how and where the vomited blood came from.
- When vomiting blood, the blood that vomited may be blood from the digestive system such as the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, and gastrointestinal tract, or it may be blood from the respiratory tract such as the upper and lower respiratory tract.
- In other words, you can vomit blood from the gastrointestinal tract of the digestive system, such as the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, and small intestines, and blood from the respiratory tract such as the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
- The blood that coughs and vomits when suffering from respiratory problems is more likely to be blood from the respiratory tract (hemoptysis).
- The blood that vomits and vomits while suffering from gastrointestinal ailments and then vomits is more likely to be blood from the gastrointestinal tract of the digestive tract (hematosis).
- However, when newborns or infants vomit blood, it is difficult to clearly distinguish whether the vomited blood is from the respiratory tract or from the gastrointestinal tract.
- With a history of vomiting blood, stomach ulcers or duodenal ulcers while having a stomach ache, vomiting blood is considerably more likely to be blood from the gastrointestinal tract.
Hematotemesis treatment
- Treatment differs depending on the cause of the hematemesis, the amount of vomiting blood, the health status when hematemesis, the bleeding screen test, and the results of the liver function test
- If you vomit blood without any signs, symptoms, whether a newborn baby or a later newborn or infant, call your regular pediatrician and follow their instructions to find out what is causing the hemorrhage and treat it according to the cause.
- When vomiting a large amount of blood and feeling dizzy or in shock, perform basic CPR treatment, lay the upper body 15 to 30 degrees lower than the lower body, and call a medical paramedic, hospital emergency medical room, or a regular pediatrics department in an emergency and follow their instructions.
- As a result, first aid is provided on-site and urgently transferred to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation.
- In the hospital emergency room, oxygen respiration therapy and blood transfusion therapy are performed depending on the cause and degree of hematemesis.
- If blood transfusion cannot be performed because there is no blood, albumin may be used instead of blood. Treated according to the cause of hematemesis.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.150-151
- Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.250-257
- Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.218-219
- Nelson textbook, 15th edition p.939, 940
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
- Red book 29th-31st Ed 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”