탈구, Dislocations
탈구의 개요와 그 원인
- 뼈의 머리(골두)의 일부가 정상적 관절 위치로부터 전위되거나 이탈되는 되는 것을 탈골 또는 탈구라고 한다. 인체의 한 부분이 정상 위치로부터 전위될 수도 있다.
- 관절 낭(Articular capsule) 속에 들어있는 뼈의 머리(골두)가 갑자기 세게 당기거나 밀리거나 비틀릴 때 골두가 관절낭 속에 있는 소켓(확)에서 그 주위로 조금 빠져나오든지 또는 많이 빠져 나오는 것을 탈구라고 한다.
- 팔꿈치 관절(주관절), 수지관절(손가락 마디관절), 발 뼈 관절(족관절), 엉덩관절(고관절), 무릎 관절(슬관절), 어깨 관절(견관결), 측두하악관절, 발목 관절, 손목 관절 등 여러 종류의 관절이 우리 몸에 있다.
- 이론적으로 탈구가 어느 관절에도 생길 수 있다. 각 관절에 생긴 탈구의 증상 증후에도 차이가 난다.
- 모든 종류의 탈구의 증상 징후 진단 치료를 여기에서 다 설명할 수 없다. 그래서 몇 종류관절의 탈구와 탈구의 일반적 응급 처치법을 설명한다.
- 관절낭이 파괴될 수 있는 관절염, 관절 주위 근육염이 있을 때 탈구가 더 쉽게 될 수 있고, 선천성으로도 탈구 될 수 있고 신경이나 근육에 이상이 있어도 탈구 될 수 있고 중추 신경 이상이 있어도 탈구 될 수 있다.
- 탈구가 생긴 관절 주위에 있는 인대, 근육과 관절낭, 말초신경, 혈관과 연 조직이 동시 손상될 수 있다 ([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환-선천성 고관절 탈구, 고관절 이상 형성, 후천성 고관절 탈구, 일과성 활막염, 탈구, 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호-붕대 참조).
탈구의 증상 징후
- 관절이 삐었을 때처럼 탈구가 되었을 때도 탈구된 관절을 정상적으로 잘 움직일 수 없다.
- 능동적으로 움직일 수 있는 운동 범위도 제한 받는다.
- 일반적으로 삐었을 때보다 탈구되었을 때의 관절은 더 붓고 더 아프고 탈구된 관절을 정상적으로 거의 쓰지 못하는 것이 보통이다.
탈구의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해 진단한다.
- 탈구됐다고 의심하면 관절 X선 사진 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
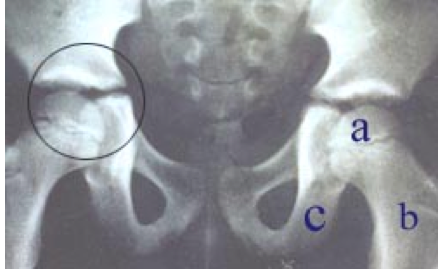
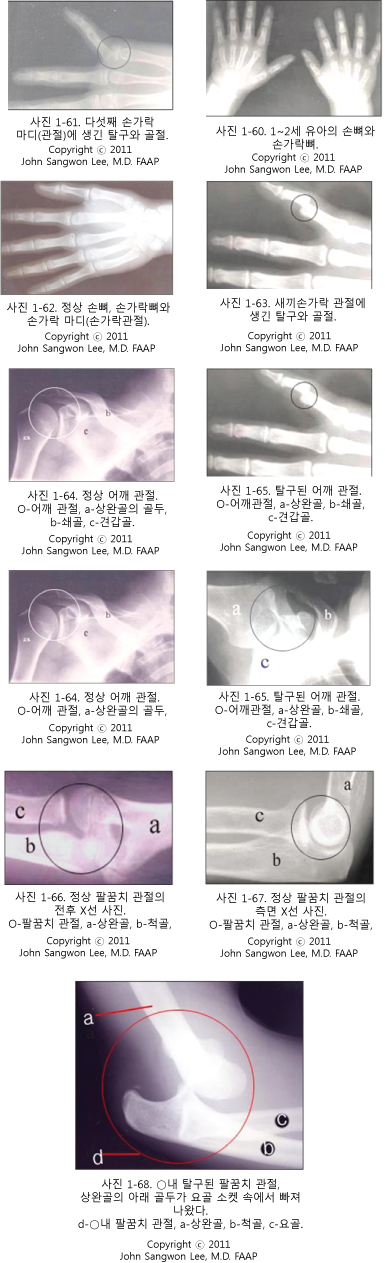
사진 1-69. 정상 고관절(엉덩관절) X선 사진.
◯-고관절(엉덩관절), a-대퇴골 근위 두부, b-대퇴골, c-좌골.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 우선, 탈구가 생겼다고 의심하면 환아를 안정시킨다.
- 가능하면 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과에 응급으로 전화해 응급처치에 관해 전와 문의를 해 그들의 지시에 따라 사고 현장에서 1차 최초 응급치료를 시작한다.
- 의사도 탈구된 관절을 시진하고 촉진 해 관절에 염좌가 생겼는지, 탈구가 생겼는지, 괸절을 형성하고 있는 관절 뼈에 골절이 생겼는지, 또는 삐고 골절되고 탈구가 동시 생겨 있는지 확실히 쉽게 감별 진단할 수 없다.
- 상황에 따라, 가능하면, 단골 소아청소년과 의사나 의료구급대가 현장에 도착할 때까지, 또는 의사의 지시가 있을 때까지 탈구가 되어 있다고 의심되는 관절이나 관절 부위를 될 수 있는 한 조금도 움직이지 말고 처음 목격한 외상 자세 그대로 관찰 치료를 한다.
- 단골 소아청소년과, 의료구급대, 또는 병원 응급실에 전화 해 긴급 도움을 받든지, 그런 도움도 다른 종류의 도움을 도저히 받을 수 없을 때는 사고 현장에서, 탈구되었다고 의심되는 관절과 그 관절의 위아래에 있는 성한 신체 부위에 부목을 조심히 대든지, 또는 가능한 한 상처 입은 직후 체위를 그대로 유지하면서 치료할 수 있는 병원 응급실로 이송한다.
- 부목을 댈 때 탈구된 관절과 그 부근 부위를 밀거나 당기거나 뒤틀어서는 안 된다.
- 가능한 한, 처음 목격한 신체 자세 그대로 놓고 부목을 대어야 한다.
- 응급처치에 쓸 수 있는 부목용 물체가 없어 부목을 댈 수 없으면 탈구된 상태 그 대로 놓고 탈구된 관절이 잘 움직이지 않도록 모래주머니나 베개, 돌돌 말은 담요 등을 부목으로 이용한다.
- 그런 것으로 탈구된 관절 부위를 받쳐 임시로 고정해 주는 정도로 응급처치를 하고 병원 응급실로 데리고 간다.
- 병원에서는 관절이 삐었는지, 탈구되었는지, 골절되어 있는지를 확실히 감별 진단하기 위해 관절 X선 사진 검사 등을 할 수 있다.
- 어느 관절이, 얼마나 심하게 탈구되었는지, 증상 징후의 정도 등에 따라 석고붕대치료, 수술치료, 목발사용치료, 부목치료 등으로 치료한다.
- 탈구가 됐을 때는 일반적으로 정형외과 전문의의 치료를 받는 것이 이상적이다.
Dislocations 탈구
Overview of dislocation and its causes
- Dislocation or dislocation of a part of the bone’s head from the normal joint position is called dislocation or dislocation.
- A part of the human body may be displaced from its normal position.
-
When the head of the bone in the articular capsule is suddenly pulled, pushed, or twisted, the head of the bone comes out of the socket in the articular capsule slightly or out of the surrounding area is called dislocation.
- Elbow joint, finger joint, hip joint, knee joint, shoulder joint, temporomandibular joint, ankle joint, wrist joint, etc.
- There are many types of joints in our body.
- Theoretically, dislocations can occur in any joint.
- There are also differences in the symptoms and signs of dislocation in each joint.
- All types of dislocation symptoms, signs, diagnoses, treatments cannot be described here.
- So, some types of joint dislocations and general first aid methods for dislocations will be described.
- When there is arthritis or myositis around the joints, which can destroy the joint capsule, dislocation can happen, it can be congenital dislocation, or dislocation even if there is an abnormality in nerves or muscles, and it can be dislocated even if there is an abnormality in the central nerve.

- Ligaments, muscles and joint capsules, peripheral nerves, blood vessels, and soft tissues around the dislocated joint may be simultaneously damaged
- ([Parents should also be at least the half-i-doctors-Pediatric Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Vol. 16 Pediatric Orthopedic Diseases- Congenital hip dislocation, hip joint abnormality formation, acquired hip dislocation, transient synovitis, dislocation, see Vol. 21, Child and Adolescent Home-School Nursing-Bandage).
- Symptoms signs of dislocation
- When a joint is dislocated, like when a joint is sprained, the dislocated joint cannot move properly.
- The range of motion that can be actively moved is also limited.
- In general, the dislocated joint is more swollen and more painful than the sprained joint, and the dislocated joint is rarely used normally.
Diagnosis of dislocation
- Comprehensive diagnosis, such as medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings. If you suspect that you are dislocated, you can diagnose it with a joint X-ray examination.

Photo 1-69. Normal hip joint (hip joint) X-ray.
◯- hip joint, a-proximal femur head, b-femur, c-sciatic bone. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Treatment of dislocation

- First of all, if you suspect that dislocation has occurred, stabilize the patient.
- If possible, call the medical paramedics, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrician in an emergency to make inquiries about first aid, and follow their instructions to start the first emergency treatment at the accident site.
- Even doctors cannot easily differentiate and diagnose whether there is a sprain in the joint by examining and facilitating the dislocated joint, whether there is a dislocation, a fracture in the joint bone forming the fracture, or a sprained fracture and a dislocation at the same time.
- Depending on the situation, if possible, do not move the suspected joint or joint area as little as possible until your regular pediatrician or medical paramedic arrives at the scene, or until your doctor’s instructions.
- Observational treatment is performed in the same position as the traumatic posture witnessed.
- Call the regular pediatrician, medical paramedics, or hospital emergency room for emergency help, or if you can’t get any other kind of help at the accident site, a joint suspected of being dislocated and the upper and lower parts of the joint.
- A splint is placed on the body part, or, as soon as possible, it is transferred to a hospital emergency room where it can be treated while maintaining the position as soon as possible.
- When applying a splint, do not push, pull, or twist the dislocated joint and the area around it.
- As much as possible, the body position you first witnessed should remain intact and a splint should be applied. If the splint cannot be applied because there is no object for first aid, put it in the dislocated state, and use a sandbag, pillow, or blanket as a splint to prevent the dislocated joint from moving well.
- As such, first aid is given to the extent that the dislocated joint is supported and temporarily fixed, and taken to the hospital emergency room.
- In hospitals, joint X-ray examinations can be done to reliably diagnose whether a joint is sprained, dislocated, or fractured.
- Treatment with plaster bandage treatment, surgical treatment, crutches treatment, splint treatment, etc., depending on which joint is severely dislocated and the severity of symptoms.
- When dislocated, it is generally ideal to seek medical attention from an orthopedic surgeon.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D.
- Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th Edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons.
- Nelson textbook, 15 edition
- Signs & Symptoms in Pediatrics 2nd edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”