탈구 Dislocation
탈구의 원인
-
우리 신체에 있는 긴뼈를 장골이라 한다.
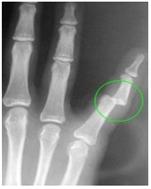
그림 170. 새끼 손가락뼈 사이에 있는 ◯내 관절(지골 관절)에 탈구가 생겼다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D.. FAAP
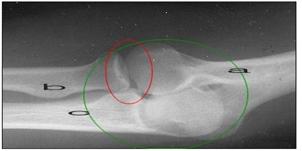
사진 171. ◯내 팔꿈치 관절(주 관절)
a-요골, b-상완골, c-척골
요골 두부가 부전 탈구된 것을 요골 두부 부전탈구라 한다.
◯내에 요골 두부가 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D.. FAAP
-
모든 장골은 골 두부·골 경부·골 간 등으로 구성된다.
-
골 두부(骨頭部)는 관절낭 속에 들어가 있다.
-
골 두부가 관절낭 속에서 빠져 나온 상태를 탈구라고 한다.
-
골 두부가 탈구로 인해 관절낭 속에서 완전히 빠져 나온 탈구를 완전 탈구 또는 아 탈구라 한다.
-
일부 빠져 나온 탈구를 일부 탈구라고 한다.
-
선천성으로 생긴 탈구를 선천성 탈구, 후천성으로 생긴 탈구를 후천성 탈구라고 한다.
-
이와 같이 여러 종류의 탈구가 있다.
-
타박상·교통사고·심한 운동·장난 등 사고로 팔다리나 신체 다른 부위에 있는 관절낭 속에 있는 골 두부가 갑자기 심하게 당겨지거나 틀리거나 밀릴 때 관절낭 속 골 두부가 경미하게 일부, 또는 심하게 전부 빠져 나올 수 있다.
-
고관절을 형성하고 있는 근육이나 활막, 인대, 조직 등이 선천적으로 미약하거나, 고관절낭 속에 들어있는 대퇴골 두부가 제대로 형성되지 않았거나, 대퇴골 두부가 들어가 있는 관절구 등이 제대로 형성되지 않았을 때는 대퇴골 두부가 고관절 낭 속에서 쉽게 빠져 나와 고관절에 탈구가 생길 수 있다.
-
선천성 고관절 탈구나 고관절 발육형성 장애 등은 출생 시 발견될 수 있다(p.00 탈구, 선천성 고관절 탈구, 선천성 고관절 탈구, p.00 일과성 활막염 참조).
-
그 밖에 신체 다른 여러 종류의 관절에 선천성으로 또는 후천성으로 탈구가 생길 수 있다.
- 여기서는 고관절 탈구 이외 다른 관절의 탈구에 대해서 주로 설명한다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료–탈구 참조).
탈구의 증상 징후
-
탈구된 정도, 탈구된 관절의 종류, 탈구와 동시 생긴 다른 합병증 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
이론적으로 우리 몸에 있는 어느 관절이든지 탈구될 수 있다.
-
탈구가 갑자기 생기면 탈구된 관절과 그 탈구된 관절 부위가 몹시 아프고, 붓고, 잘 움직일 수 없다.
탈구의 진단 치료
-
병력·증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 탈구를 진단한다.
-
탈구만 되었는지, 삐기만 했는지, 골절만 되었는지, 탈구와 골절이 같이 되어 있는지 육안으로 보고 확실히 감별 진단할 수 없는 때가 많다.
-
따라서 탈구가 됐다고 의심하면 골절됐을 때와 같이, 또는 거의 같게 현장에서 응급 처치를 시작한다.
-
아주 위급한 상황이 아니면 가능한 한 단골 소아청소년과, 의료구급대, 병원 응급실이나 단골 의사와 응급전화 진료 상담을 하고 그 지시에 따라 응급처치를 현장에서 시작한다.
-
그들의 지시에 따라, 탈구가 됐다고 의심되는 관절과 그 관절의 위아래에 있는 성한 신체 부위에 부목을 충분히 대고 붕대· 수건·천 등으로 탈구된 관절을 적절히 고정시킨 후 병원 응급실이나 적절한 병원으로 이송한다.
-
부목을 댈 때 잘못 대면 탈구된 부위나 골절된 부위를 더 손상시킬 수 있다.
-
응급처치를 어떻게 할지 잘 모르면, 가능한 한 탈구된 상태 그대로 두고 기다리고 있다가 의료구급대나 구급차, 또는 의사 등이 현장으로 올 때까지 기다리든지 또는 의사 등의 지시에 따라서 응급처치를 시작한다.
-
병원에서는 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 탈구가 의심되는 관절의 X선 사진 검사 등으로 진단한다.
-
탈구가 경미하게 되었을 때 최초 찍은 X선 사진 검사로 탈구만 되어 있는지, 골절만 되어 있는지, 또는 정상인지 확실히 알 수 없을 때도 있다.
-
따라서 추적 X선 사진 검사를 또 해 탈구를 진단할 수 있다.
-
탈구의 정도, 탈구가 된 관절의 종류, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르고 치료도 다르다.
-
탈구 이외 호흡곤란, 출혈 등이 있으면 병원 응급실이나 소아청소년과로 데리고 가기 전에 그런 문제는 우선 응급으로 처치해야 한다.
-
그런 후속 조치도 가능한 한 의료구급대원이나 병원 응급실, 또는 의사의 지시에 따라 현장에서 시작한다.
-
탈구가 되어 있는지 또는 골절이 되었는지 확실히 모르면서 상처 입은 관절을 손으로 주물러 치료해서는 절대 안 되고,
-
골 두부를 관절낭 속에 다시 넣기 위해 탈구된 부위를 잡아당기거나 넣었다 뺐다 해도 절대로 안 된다.
-
탈구된 관절이나 그 주위 연조직이 더 손상될 수 있기 때문이다.
-
탈구가 되었다고 의심되면 가능한 한 병원 응급실이나 의사의 지시에 따라 구급차로 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 가는 것이 가장 이상적이다.
-
탈구된 관절의 종류와 탈구의 정도 등에 따라 수술 치료를 하지 않고 탈구된 골 두부를 겉에서 관절낭 속에 다시 넣는 치료를 하든지, 또는 수술로 탈구된 골 두부를 관절 낭 속에 다시 넣고 석고 붕대로 고정시켜 치료할 수 있다.
Dislocation탈구
Causes of dislocation
• Long bones in our body are called long bones.

Figure 170. A dislocation occurs in the ◯ inner joint (phalangeal joint) between the little finger bones. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 171. ◯My elbow joint (main joint) a – radius, b – humerus, c – ulna If the radial head is dislocated, it is called a radial head dislocation. ◯There is a radial head inside. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D.. FAAP
• All iliac bones are composed of the head, neck, and liver. • Bone head (骨頭部) is in the joint capsule.
• The state in which the bone head is protruded from the joint capsule is called dislocation.
• A dislocation in which the bone head completely comes out of the joint capsule due to dislocation is called complete dislocation or subluxation.
• A partial dislocation is called a partial dislocation.
• Congenital dislocation is called congenital dislocation, and acquired dislocation is called acquired dislocation.
• There are several types of dislocations.
• When the bone head in the joint capsule in the limbs or other parts of the body is suddenly pulled, misplaced, or pushed due to an accident such as a bruise, traffic accident, heavy exercise, or play, the bone head in the joint capsule may come out slightly or severely .
• If the muscles, synovial membrane, ligaments, and tissues forming the hip joint are congenitally weak, the femoral head in the hip joint capsule is not properly formed, or the condyle containing the femur head is not properly formed. The hip joint can easily slip out of the hip capsule and cause dislocation of the hip joint.
• Congenital hip dislocation or hip dysplasia can be detected at birth (see
dislocation, congenital hip dislocation, congenital hip dislocation, transient synovitis).
• In addition, congenital or acquired dislocations can occur in many other types of joints in the body.
Here, dislocations of joints other than hip dislocation are mainly explained www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents – Dislocations).
Symptoms, signs of dislocation
• Symptoms vary depending on the degree of dislocation, the type of dislocated joint, and other complications occurring simultaneously with the dislocation.
• Theoretically, any joint in our body can be dislocated.
• When a dislocation occurs suddenly, the dislocated joint and the dislocated joint area are very painful, swollen, and unable to move.
Diagnosis and treatment of dislocation
• Diagnosis of dislocation by synthesizing medical history, symptoms, signs and examination findings.
• In many cases, it is not possible to diagnose with the naked eye whether only dislocation, sprain, fracture, or dislocation and fracture are combined.
• Therefore, if you suspect that you have had a dislocation, start first aid on the spot as if you had a fracture, or about the same.
• Unless it is a very urgent situation, if possible, consult with a regular pediatrician, medical emergency department, hospital emergency room, or a regular doctor on the emergency phone, and start emergency treatment on the spot according to their instructions.
• According to their instructions, apply a sufficient splint to the joint suspected of being dislocated and the healthy body part above and below the joint, and properly immobilize the dislocated joint with a bandage, towel, or cloth, and then transport to the hospital emergency room or appropriate hospital.
• Improper placement of the splint can further damage the dislocated or fractured area.
• If you do not know how to administer first aid, leave the dislocated state as much as possible and wait until the medical paramedics, ambulances, or doctors come to the scene, or start first aid according to the instructions of the doctor.
• The hospital diagnoses with X-ray examination of the joint suspected of dislocation by synthesizing the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings.
• When the dislocation is mild, it is sometimes not clear whether the dislocation is only a dislocation, only a fracture, or is normal on the first X-ray examination.
• Therefore, follow-up X-ray examination can be performed again to diagnose dislocation. • Symptoms and signs vary depending on the degree of dislocation, the type of dislocated joint, and the presence or absence of complications.
• If you have dyspnea or bleeding other than dislocation, treat them first before taking them to the hospital emergency room or pediatric department.
• Such follow-up is also initiated on-site as directed by paramedics, hospital emergency rooms, or physicians whenever possible. • Never treat an injured joint by hand rubbing it without knowing for sure whether it is dislocated or fractured;
• Never pull or insert and remove the dislocated area to put the bone head back in the joint capsule.
• This is because the dislocated joint or surrounding soft tissues may be further damaged.
• If you suspect that you have had a dislocation, it is ideal to take you to the hospital emergency room by ambulance as soon as possible or as directed by your doctor.
• Depending on the type of dislocated joint and the degree of dislocation, the dislocated head is placed back into the joint capsule from the outside without surgical treatment, or the surgically dislocated head is placed back into the joint capsule and fixed with a plaster bandage. can be treated
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”