철 결핍성 빈혈(철 결핍 빈혈) Iron deficiency anemia
철 결핍성 빈혈(철 결핍 빈혈)의 원인
-
철 부족으로 생기는 빈혈을 철 결핍 빈혈성이라고 한다.
-
건강한 임신부에게 태어난 정상 만삭 신생아들은 생후 6개월까지 철 결핍성 빈혈에 걸리지 않는 것이 보통이다. 만삭 태아들은 출생하기 전까지 모체로부터 철분을 충분히 공급받고 태어나는 것이 보통이기 때문이다.
-
비록 임산부에게 철분 부족이 있어도 태아는 충분한 철분을 모체로부터 공급 받고 태어나기도 한다.
-
건강하고 균형 잡힌 음식물을 섭취하는 수유모의 젖을 먹는 생후 0~6개월까지 영아들이나 인공영양만 먹는 영아들에게 철 결핍성 빈혈이 거의 생기지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
따라서 생후 0~6개월 동안 만삭으로 태어난 영아들에게 철분제를 추가로 더 먹이지 않아도 철 결핍성 빈혈에 걸리지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
생후 6~9개월 이후 모유만 먹는 영아들이나 인공영양을 적절이 먹지 않고 전 우유를 많이 먹는 영아들, 철분이든 고형 이유식을 적절이 먹지 않는 영아들, 균형 잡힌 음식물을 먹지 않는 영유아들, 미숙 신생아로 태어난 영유아들에게 철 결핍성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
생후 6개월 이후 모유만 먹는 영아들
-
생후 6개월 이후 철분이 든 고형 이유식을 먹지 않고 전 우유를 섭취하는 영유아들
-
균형잡힌 영양분을 적절하게. 충분히 먹지 않는 저체중 신생아, 아주 작은 저체중 미숙아, 또는 쌍 태아로 태어난 영아들
-
출생 시 어떤 원인으로 내·외출혈이 있었던 병력이 있는 영아들
-
Rh 부적합이나 A B O부적합으로 생긴 용혈성 빈혈이 있던 병력이 있는 영아들
-
심한 황달 치료를 받기 위해 교환수혈치료를 받은 병력이 있는 영아들에게는 생후 6개월 이전에도 철 결핍성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
소화성 위궤양, 십이지장 궤양, 십이지장충증, 그 외 기생충증 등으로 위장관 점막층에서 피가 장기간 조금씩 나거나 다량으로 나거나
-
신체의 어떤 부위에서든지 소량으로 또는 대량으로 출혈되면 철 결핍성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
편식을 하거나 비타민 결핍증이 있거나
-
월경을 비정상으로 오래하거나 월경 량이 비정상적으로 많으면 철 결핍성 빈혈이 사춘기 여아들에게 생길 수 있다.
-
만성 신장염, 만성 위장염, 류마티스 관절염 또, 연소성 류마토이드 관절염 등으로 철 결핍성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
그 외 원인
철 결핍성 빈혈(철 결핍 빈혈)의 증상 징후
-
철 결핍성 빈혈은 연령층을 가리지 않고 남녀노소 누구에게나 생길 수 있고 빈혈의 원인과 정도에 따라 증상이 다양하다.
-
철 결핍성 빈혈은 생후 12개월에서 2세까지 영유아들에게 9%,
-
3~4세 이후의 유아들의 4% 정도 생긴다(Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine April 2008 p.374).
-
4~6세 유아들과 학령기 아이들 또는 사춘기 아이들에게 빈혈이 생기면 철 결핍성 빈혈이 있다고 진단을 부치기 전에 다른 원인으로 생긴 빈혈인지 꼭 알아보아야 한다.
-
생후 4-6세 이후 철 결핍성 빈혈은 드물게 생기기 때문이다.
-
철 결핍성 빈혈이 경미하게 생기면 신경 발육에도 이상이 생길 수 있고, 학습장애, 정신적 문제, 운동성 발육지연이 생길 수 있고, 사회정신 발육지연이 생길 수 있다.
-
혈중 헤모글로빈 농도가 정상일 때도 철분 결핍성 빈혈의 증상 징후가 현저히 나타날 수 있다.
-
1~3세 비만 소아들의 20%, 1~4세 백인 유아들의 6%에서 철 결핍이 생긴다. 또 저소득층 자녀들에게는 철 결핍이 더 많이 더 잘 생길 것이라고 한다(출처;Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine April 2008 p.374, Pediatrics News October 2008).
-
철 결핍성 빈혈이 심하게 생기면 안색이 창백해진다.
-
영유아들은 자주 보채고 잘 운다.
-
철 결핍성 빈혈이 더 심하면 식욕이 감퇴되고, 잘 먹지 않고, 맥박이 정상 이상으로 빠르고 숨이 가빠지고 기운이 없고 각종 감염병에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
-
철 결핍성 빈혈이 있는 어떤 아이에게 얼음이나 흙 등 영양가치가 조금도 없는 것을 먹는 이미증이 생기기도 한다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제12권 소아 신경 정신, 행동, 수면 문제–이미증 참조
철 결핍성 빈혈(철 결핍 빈혈)의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 철 결핍성 빈혈이 의심되면, CBC 피 검사 및, 또는 혈장 철농도, 철 결합능, 철과 결합할 수 있는 단백질(Apo-ferritin), 저당혈 층 적혈구혈, 철결합 단백질 등을 검사해 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
-
대변에 피가 나오나 알아보는 분변 잠혈 검사(Fecal occult blood test-FOBT),
-
소변에 피가 나오나 또는 요로 감염이 있나 알아보는 소변 검사를 한다.
-
요즘, CBC 피 검사에 헤모글로빈의 농도가 비정상적으로 낮지도 않은데 철 결핍성 빈혈의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있는 연구가 나왔다.
-
즉, CBC 피 검사나 헤모글로빈 농도 검사의 결과가 정상이라도 철 결핍이 생길 수 있다.
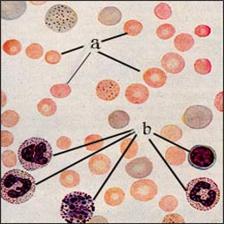
사진 1-21. CBC 피검사
철결핍 빈혈이 있을 때 적혈구가 비정상적으로 더 작고 적혈구 내 헤모글로빈 농도가 비정상적으로 더 낮은 것이 보통이다. a-적혈구, b-백혈구
출처; Clinical atlas of Blood diseases, 6th edition
-
그로 인해 철결핍 빈혈 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
다음과 같은 가족 병력과 과거 병력이 있을 때 철결핍 빈혈을 진단하는데 큰 도움이 될 수 있다.
-
아이가 태어날 때 출혈했던 병력이 있었는지,
-
임신 중 임신부가 출혈했었는지,
-
Rh 부적합이나 ABO 부적합 등으로 용혈성 빈혈이나 어떤 종류의 황달을 앓은 적이 있는지,
-
만삭에 정상적으로 태어났는지,
-
균형 잡힌 음식물을 먹고 있는지 등이다.
-
전술한 바와 같이 4세 이후 건강한 아이들에게는 철결핍 빈혈이 잘 생기지 않는다.
-
그러므로 4세 이후 유아들이나 학령기 아이들 또는 사춘기 아이들에게 빈혈이 생기면 위장에서 피가 나는지, 납중독에 걸렸는지, 또는 다른 원인으로 빈혈이 생겼는지 우선 알아보아야 한다.
-
철 결핍성 빈혈이 생겼을 때, 대부분의 경우, CBC 피 검사를 하면 적혈구의 크기가 정상크기 보다 훨씬 더 작고, 적혈구 속에 헤모글로빈 농도가 정상치 보다 훨씬 낮기 때문에 적혈구 속이 텅 빈 것 같다.
-
혈중 철 농도와 철 결핍으로 인한 빈혈에 관련된 다른 피검사 등을 해서 진단할 수 있다.
-
요로감염이나 신장염 등이 있는지 알아보기 위해 소변검사를 한다.
-
잠재성 위장 출혈이 있는지를 알아보기 위해 대변에서 대변 잠혈 검사도 한다.
-
기생충 알이나 기생충 성충이 있는지 알아보기 위해 대변 기생충검사를 한다.
-
빈혈이 있을 때는 이런 검사 등으로 빈혈을 일으킨 근본 원인이 무엇인지 꼭 알아내야 한다.
-
참고로 철 결핍성 빈혈이 생겼을 때는 골수검사는 통상적으로 하지 않고 진단할 수 있다.
표 1-4. 혈청 철 농도와 철 결합능 Serum iron level and Iron-binding capacity
| 나이 | 혈청 철 농도(㎍/100mL) | 철 결핍능(㎍/100mL) |
| 신생아 | 90 | 225 |
| 생후 1일 | 50 | 50 |
| 생후 2주 | 125 | 230 |
| 생후 3개월 | 50 | 250 |
| 생후 1세 | 70 | 250 |
| 2세 | 100 | 250 |
| 10세 | 110 | 280 |
| 성인 여자 | 110 | 330 |
| 성인 남자 | 125 | 300 |
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition, p.400
Nelson text book, 15th edition
철결핍 빈혈(철결핍성 빈혈)의 원인에 따라 치료한다.
- 철결핍 빈혈이 생겼을 때는 철결핍이 생긴 이유, 그 원인을 알아서 치료 한다.
- 생후 6개월 이후 모유만 먹거나 전우유만 먹어 철결핍 빈혈이 생겼을 때는 경구용 철분제로 치료하면서 철분이 많이 든 이유식이나 다른 종류의 음식물도 함께 주어야 한다.
- 생후 6개월 이후에 모유만 먹는 아기에게는 철과 비타민을 보충해 주어야 한다.
전 우유를 과량 섭취해 생기는 철결핍 빈혈(철결핍 빈혈)의 치료.
- 생후 6개월 이후 영아들이나 첫 돌이 지난 유아들이 전우유를 많이 먹어 철결핍 빈혈이 생기면 전 우유(Whole milk)의 섭취량을 최소한도로 줄이고 나이에 따라 균형 잡힌 이유식이나 식구들이 먹는 밥상음식물을 먹여야 한다.
- 첫 돌이 지난 유아들이 균형 잡힌 음식물을 잘 먹지 않고 전 우유만 오랫동안 많이 먹어 철결핍 빈혈이 생기면 전 우유를 얼마 동안 조금도 먹이지 말고 균형 잡힌 음식물만 주어야 한다.
- 영아들이나 첫 돌이 지난 유아들에게 전 우유를 주지 않으면 처음 며칠 동안은 다른 음식물도 먹지 않고 전 우유만 달라고 졸라대는 경우도 있다.
- 그래도 전 우유를 2~3일 동안 일절 주지 않으면 결국 새로 주는 음식물을 먹게 된다.
- 이때부터 인내심을 갖고 전 우유를 적어도 4주 동안 일절 주지 말고 균형 잡힌 음식물을 주면서 경구용 철분제와 종합비타민제로 치료하면 철결핍 빈혈이 치료된다.
- 물론 빈혈이 치료된 후 균형 잡힌 음식물을 섭취하고 전 우유의 섭취량을 적당히 줄일 수 있다.
- 우유는 매일 꼭 먹어야 하는 음식물이 아니다.
편식으로 생기는 철결핍 빈혈(철결핍성 빈혈)의 치료
- 편식으로 철결핍 빈혈이 생길 때는 균형 잡힌 음식물을 섭취하면서 의사의 처방에 따라 경구용 철분제로 치료한다.
- 일반적으로 페로우스 설페이트(Ferrous sulfate) 경구용 철분제로 철결핍 빈혈을 치료한다. 경구용 철분제로 치료 시작한지 7일 정도 되면 철분제 경구치료의 효과가 현저하게 나타나기 시작한다.
- 3~4주 경구용 철분제 치료를 하는 동안 빈혈의 증상 징후가 하나 둘씩 점차로 없어지고 헤모글로빈 농도가 정상치로 돌아가고 철결핍 빈혈이 거의 완치될 수 있다.
- 이때부터 1~2개월 정도 경구용 철분제 치료를 더 계속 하다가 의사의 지시에 따라 철분제 치료를 더 이상 하지 않는다.
- 철결핍 빈혈을 철분제로 치료하는 동안 CBC 피 검사 등을 해서 빈혈이 계속 나아가는지 완치되었는지 확인해야 한다.
철결핍 빈혈(철결핍성 빈혈)은 철분제로 치료 한다
- 철결핍 빈혈은 주로 경구용 철분제정이나 철분제액제로 치료한다.
- 철분제 주사액으로 철분 결핍성 빈혈을 치료해 줄 수 있지만 철분제 주사로 치료할 때 심한 부작용이 생길 수 있다.
- 가능한 한 철분제 주사로 치료 하지 않는 것이 좋다.
- 경구용 철분제정이나 철분제 액으로 치료할 때 대변과 치아가 일시적으로 검게 될 수 있다.
- 경구용 철분제 치료를 중지하면 검은 대변 색이나 치아의 색이 정상 색으로 곧 돌아간다.
철결핍 빈혈(철결핍성 빈혈)을 철분제로 예방한다.
- 철결핍 빈혈이 미숙 신생아나 저 체중 신생아에게 생기기 쉽다.
- 생후 1~2개월부터 의사의 처방에 따라 종합비타민과 철분제를 먹여 빈혈이 생기지 않도록 예방한다.
- 아주 드물게는 철 결핍으로 생긴 심한 빈혈을 수혈로 치료하기도 한다.
|
다음은“빈혈에 대해서 질문이 있습니다.”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 빈혈에 대해서 질문이 있습니다.
Q.
- 아기가 지금 빈혈이래요.. ㅜㅜ
- 34주에 2.48의 미숙아로 태어나서 건강하게 잘 지내고 있었는데.. 처음 태어났을 때 빈혈(인큐베이터에 3주 있으면서 수혈을 한번 받았습니다.)이 좀 있었다고 하셔서 그것과 같이 다른 항체 검사를 했는데 아이가 빈혈이라네요.. 8.1이라는 수치가 나왔습니다.
- 대변 검사는 해서 이상이 없었구요..
- 지금은 재훈이에게 철제를 먹이고 있습니다.
- 1cc 씩이요~ (지금 72.5센티에 10킬로 나갑니다) 한 달 동안 먹인 후 다시 검사하자고 하셨는데요.. 다름이 아니라 모유를 먹이면 빈혈이 있을 수 있다고 해서 엄마가 할 수 있는 방법이 뭐가 있나 궁금해서 여쭙니다.
- 1. 제가 철제를 복용하는 것이 도움이 될까요?
- 2. 혹은 제가 철이 많이 있다는 음식을 먹는 것도 도움이 될까요? (주위에서 소간을 삶아서 이유식에 갈아 죽을 써주라고 하는데..)
- 요즘은 그래서 재훈이에게 하루에 계란 노른자를 하나씩 먹이고 있습니다.(혹시 도움이 되지 않을까 싶어서요~^^) 이유식 먹일 때 조금씩 숟가락에 얹어 아침 점심으로 먹여요..
- 지금 9개월이 좀 넘었거든요..
- 얼마 전부터 이유식은 하루에 세 번 먹이는데 아주 잘 먹습니다..(2번 먹일 때도 있습니다. ) 쌀 위주구요.. 간식으로 치즈라든가..과일도 조금씩 먹입니다.
- 선생님이 정상 수치가 어떤데 재훈이 수치는 어떻다 얘길 하시는데 너무 수치가 낮은 거 같아서 걱정이 앞섭니다.
- 그래서 엄마로서 약 먹이는 거 외에 도움이 되는 것을 좀 하고 싶습니다. 재훈이가 단순히 모유를 먹여서나 미숙아라서 철이 부족한거 라면 어떻게 해야 하는지 선생님의 답변 부탁드립니다.
- 감사합니다…!
A.
- 훈님
- 안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다.
- 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 많은 정보가 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 주신 정보를 참작해 답변을 드립니다.
- 아기가 벌써 9개월이 됐군요.
- 보통 만삭 신생아들이 돌이 될 때 체중이 출생 시 체중의 3배정도 되는 것이 보통인데 아기의 경우 9개월인데 벌써 4배나 되는 체중이군요.
- 잘 아시겠지만 임신 37~40주 사이에 태아는 모체로부터 철분을 충분히 얻어 가지고 출생합니다. 그래서 만삭에 태어난 아기들은 생후 6개월이 될 때까지 철분을 보통 이상으로 섭취하지 않더라도 철결핍 빈혈에 걸리지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
- 아기의 경우, 미숙 신생아로 태어났고 성장속도가 상당히 빨랐기 때문에 철분 결핍으로 철분 결핍성 빈혈에 걸린 것 같습니다.
- 생후 6개월에서 2년 되는 영유아들의 정상 평균 헤모글로빈 농도는 12.0g%입니다. 아기의 헤모글로빈 농도는 비정상적으로 낮으나 10.5g%까지 정상으로 봅니다.
- 만삭에 태어난 신생아들도 생후 9개월까지 모유만 먹이면 철결핍으로 빈혈이 생길 수 있습니다. 더군다나 미숙 신생아로 태어난 아기에게 모유만 수유하면 철결핍으로 인한 빈혈이 생길 가능성이 아주 많습니다.
- 미숙 신생아로 태어나면 아기들에게 종합 비타민과 철 점액제(Iron drops)를 적어도 생후 3~4개월부터 예방적 치료를 하기위해 먹이기 시작하면 철분 결핍성 빈혈이 예방될 수 있습니다.
- 철분 첨가 곡분 고형 이유식과 다른 종류의 이유식도 나이에 적절하게 먹이고 모유를 계속 수유 하면 철 결핍으로 빈혈이 잘 생기지 않습니다.
- 빈혈이 있으면 어떤 원인으로 빈혈이 생겼나 적어도 CBC 피 검사 등을 해서 꼭 원인을 알아서 그 원인에 따라 치료하는 것이 원칙입니다.
- 적절한 철 용량으로 치료를 시작한 후 1~2주된 후 CBC 피 검사를 해보면 철분제 치료 효과가 당장에 나타나는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 필요에 따라 피검사도 하고 소변검사를 꼭 해보시는 것이 또한 중요합니다.
- 모유수유를 하는 수유모는 자신의 건강을 위해서 철분과 비타민 등이 충분히 든 균현 잡힌 음식을 먹는 것이 중요하고 또 젖 먹는 아기에게도 물론 좋습니다.
- 특별하게 계란 노른자를 빈혈에 좋다고 꼭 먹일 필요는 없습니다.
- 알레르기가 많은 아기들에게는 계란 흰자뿐만 아니라 계란 노른자를 어린 나이에 먹이면 그로 인해서 알레르기 반응이 생길 가능성이 많을 수 있습니다.
- 그러나 노른자를 먹고 아무 이상이 없으면 계속 먹여도 될 것입니다.
- 요즘 곡분류 고형 이유식에 철분이 많이 들어 있고 또 때로는 철분을 첨가해서 만들기 때문에 곡분고형 이유식을 먹는 아기들에게 계란 노른자를 꼭 먹일 필요가 없습니다.
- 소아청소년과에서 계속 진찰 진단 치료를 받으시고 그 문제에 관해 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
다음은“밥 거부와 소아 빈혈에 관하여 알려주세요. 빈혈, 음식물을 잘 먹지 않는 아이”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 밥 거부와 소아 빈혈에 관하여 알려주세요. 빈혈, 음식물을 잘 먹지 않는 아이.
Q.
- 선생님 안녕하세요?
- 30개월 된 남자아기 입니다. 원래 우유나 음식을 많이 먹는 편은 아닌데 2개월 전까지 거의 우유 위주로 먹고 요즈음은 3끼 밥을 먹이고 우유 및 과일 등(주스, 치즈 등)을 먹이는 데 밥을 먹을 때마다 조금 먹고는(4~5수저) 안 먹으려고 도리질을 하고는 밥 수저를 들이대면 헛구역질을 합니다.
- 먹지 않아 변비도 있는 상태이다 보니까 걱정이 되고 엄마입장에서는 살도 찌지 않고 마르고 한 모습이다 보니(10.5kg) 속도 상한 상태입니다.
- 혹여 영양 상태에 심각한 문제가 있을까 걱정이 됩니다. 어떻게 해야 아이가 밥도 잘 먹고 다른 아이들처럼 살도 찔지 걱정스럽고 궁금합니다. 도움주세요!
A.
- 지원님
- 안녕하세요. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
- 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
- 이 나이 유아들은 부모가 먹는 밥상 음식을 먹어야 합니다.
- 아이 자신이 수저나 컵이나 손으로 먹도록 훈련시켜야 하고 그렇게 먹도록 해야 합니다.
- 자녀 스스로 수저로 먹도록 해야 합니다. 그 나이 자녀에게 부모가 수저로 떠 먹여서는 안 됩니다.
- 자녀는 독립된 한 인간이고 부모는 그 자녀를 사랑하고 보살피고 양육할 수 있지만 소유할 수는 없습니다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 키우세요–소유적 사랑 참조.
- 그들은 그 나이에도 부모로부터 독립을 계속 추구합니다. 조금씩 점진적으로 독립을 추구하도록 훈련을 시키는 것이 대단히 중요합니다.
- 우리 부모들 모두가 잘못해서 자녀들에게 소유적 사랑을 하기 쉽습니다. 소유적 사랑을 해서는 안 됩니다.
- 우유는 균형 잡힌 음식물도 아니고 꼭 먹어야하는 음식물도 아닙니다.
- 때문에 하루에 적어도 주식 3번을 주고 그 외에 간식을 주면 됩니다.
- 우유는 하루에 1~2컵 이상 주지 않는 것이 좋습니다. 우유 음식물은 꼭 먹어야 하는 필수 음식물은 아닙니다.
- 우유를 많이 먹으면 매일매일 먹는 우유에서 자녀가 그날그날 필요로 하는 단백질, 지방, 탄수화물 등의 영양분의 대부분을 섭취할 수 있기 때문에 우유 이외 다른 종류의 음식물을 먹을 수 있는 여유가 없습니다.
- 따라서 자연적으로 우유 이 외 음식물은 먹지 않게 됩니다. 우유 성분 속에 철분이 충분히 들어있지 않기 때문에 우유를 많이 마시면 빈혈이 생길 수 있습니다. 때로는 우유알레르기, 유당 불내증으르 고생할 수 있습니다.
- 자녀가 배가 고플 때 아침, 저녁, 점심을 식구들과 같이 밥상 음식물을 먹도록 하고 간식을 하루 2번 정도 규칙적으로 주십시오.
- 성장차트에 의하면 자녀 체중은 5퍼센타일에 속합니다. 태어나서부터 지금까지 성장 차트의 몇 퍼센타일선을 따라 자라왔는지 확인해 보십시오.
- 자녀가 과거에도 지금도 같은 성장 차트의 퍼센타일을 따라 자라고 있으면 그 자녀의 현재 체중은 정상적인 체중이라고 생각할 수 있습니다. 각 자녀의 성장속도는 선천적으로 정해져 있습니다.
- 그 성장속도를 확 바꾼다는 것은 거의 불가능하고 부모도 그 자녀 자신도 바꿀 수가 없습니다. 다시 말씀드리면 그 자녀는 그 자녀가 태어난 성장속도로 자라야 합니다.
- 소아청소년과에서 정기 건강검진을 해 주실 때 소변검사, 빈혈검사도 하고 이런 문제에 대해서 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아 청소년 질병 안전사고 예방–정기 건강검진 참조.
- 제3권 신생아, 영유아, 학령기아, 사춘기아, 성장발육육아–해당 연령 성장 발육. 빈혈. 제13권 소아 청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- 음식물을 잘 먹지 않는 아이, 체질, 성장 차트. 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요라–이유식을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단 치료를 받고 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Iron deficiency anemia 철 결핍성 빈혈(철 결핍 빈혈)
Causes of iron deficiency anemia (iron deficiency anemia)
• Anemia resulting from iron deficiency is called iron deficiency anemia.
• Normal term newborns born to healthy pregnant women usually do not develop iron deficiency anemia until 6 months of age. This is because it is common for full-term fetuses to be born with sufficient iron supply from the mother before birth.
• Even if a pregnant woman is deficient in iron, the fetus is still born with enough iron supplied by the mother.
• Iron deficiency anemia rarely develops in infants from 0 to 6 months of age when breastfeeding from a nursing mother who consumes a healthy and balanced diet, or in infants who only eat artificial nutrition
. • Therefore, it is common for infants born full-term during the age of 0 to 6 months to not get iron deficiency anemia without additional iron supplements.
• Infants who only eat breast milk after 6 to 9 months of age, infants who do not adequately eat artificial nutrition and eat a lot of whole milk, infants who do not adequately eat solid baby foods such as iron, infants who do not eat balanced foods, and immature newborns Iron deficiency anemia can develop in infants and toddlers born with
• Infants who only eat breast milk after 6 months of age
• Infants and toddlers who consume whole milk after 6 months of age without eating solid baby food containing iron
• Properly balanced nutrients. Underweight newborns who are not eating enough, very little underweight premature babies, or infants born with twin fetuses
• Infants with a history of internal or external bleeding due to any cause at birth
• Infants with a history of hemolytic anemia resulting from Rh incompatibility or A B O incompatibility
• Infants with a history of exchange transfusion therapy for severe jaundice treatment may develop iron deficiency anemia before 6 months of age.
• Peptic gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, hookworm disease, or other parasites such as small or large amounts of blood bleeding from the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract for a long period of time.
• Small or massive bleeding from any part of the body can lead to iron deficiency anemia.
• have a picky diet or a vitamin deficiency
• An abnormally prolonged period of menstruation or abnormally high menstruation can lead to iron deficiency anemia in adolescent girls.
• Chronic nephritis, chronic gastroenteritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or juvenile rheumatoid arthritis can lead to iron deficiency anemia.
• Other causes Signs of symptoms of iron deficiency anemia (iron deficiency anemia)
• Iron deficiency anemia can occur in any age group, young or old, and symptoms vary depending on the cause and severity of the anemia.
• Iron deficiency anemia is 9% in infants and toddlers from 12 months to 2 years of age,
• It occurs in 4% of infants after the age of 3-4 (Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine April 2008 p.374).
• If anemia develops in infants 4-6 years old, school-age children, or adolescent children, it is important to determine if anemia is caused by another cause before being diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia.
• Iron deficiency anemia rarely occurs after 4-6 years of age.
• If iron deficiency anemia occurs mildly, there may be abnormalities in neurodevelopment, learning disabilities, mental problems, motor development delays, and social and mental development delays.
• Even when the blood level of hemoglobin is normal, symptoms of iron deficiency anemia may be noticeable.
• Iron deficiency occurs in 20% of obese children aged 1 to 3 and 6% of white infants aged 1-4. It is also said that children from low-income families are more likely to develop iron deficiency (source; Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine April 2008 p.374, Pediatrics News October 2008).
• Severe iron deficiency anemia makes the complexion pale.
• Infants and toddlers often cries and cries well.
• If iron deficiency anemia is more severe, you may lose your appetite, eat poorly, have a faster pulse than normal, lose breath, lose energy, and become more susceptible to various infectious diseases.
• Some children with iron deficiency anemia may develop imitation of eating anything that does not have any nutritional value, such as ice or soil.www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 12 Pediatric Neuropsychiatric, Behavioral, and Sleep Problems-Refer to Immiosis
Diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia (iron deficiency anemia)
• If iron deficiency anemia is suspected by combining medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, CBC blood test and/or plasma iron concentration, iron binding ability, protein that can bind to iron (Apo-ferritin), hypoglycemic layer red blood cells It can be easily diagnosed by testing blood and iron-binding proteins.
• Fecal occult blood test (FOBT) to see if there is blood in the stool,
• Do a urine test to see if there is blood in the urine or a urinary tract infection.
• Nowadays, studies have shown that hemoglobin levels on the CBC blood test are not abnormally low, which can lead to symptoms of iron deficiency anemia.
• In other words, even if the results of the CBC blood test or the hemoglobin concentration test are normal, iron deficiency may occur.

Photo 1-21. CBC blood test With iron deficiency anemia, it is common to have abnormally smaller red blood cells and abnormally lower levels of hemoglobin in red blood cells. a-red blood cells, b-white blood cells source; Clinical atlas of Blood diseases, 6th edition
• This can lead to signs of iron deficiency anemia.
• The following family and past medical history can be of great help in diagnosing iron deficiency anemia. • Any history of bleeding when the child was born,
• whether the pregnant woman bleeds during pregnancy,
• Have you ever had hemolytic anemia or any type of jaundice, such as Rh incompatibility or ABO incompatibility,
• whether they were born normally at full term,
• Whether you are eating a balanced diet, etc.
• As mentioned above, iron deficiency anemia is less common in healthy children after 4 years of age.
• Therefore, if anemia develops in infants, school-age, or adolescent children after 4 years of age, it is important to first find out if they are bleeding in the stomach, have lead poisoning, or have anemia due to other causes.
• When iron deficiency anemia occurs, in most cases, when a CBC blood test is performed, the red blood cells appear to be empty because the size of the red blood cells is much smaller than the normal size, and the concentration of hemoglobin in the red blood cells is much lower than the normal value.
• It can be diagnosed by doing other blood tests related to the level of iron in the blood and anemia caused by iron deficiency.
• Urinalysis is done to see if you have a urinary tract infection or nephritis.
• Fecal occult blood tests are also done in the stool to check for potential gastrointestinal bleeding.
• Do a stool parasite test to see if there are parasite eggs or adult parasites.
• When you have anemia, it is important to find out what is the root cause of the anemia through these tests.
• For reference, when iron deficiency anemia occurs, bone marrow tests can be diagnosed without routine.
표 1-4. 혈청 철 농도와 철 결합능 Serum iron level and Iron-binding capacity
| age | Serum iron concentration (㎍/100mL) | Iron deficiency ability (㎍/100mL) |
| newborn baby | 90 | 225 |
| 1 day after birth | 50 | 50 |
| 2 weeks after birth | 125 | 230 |
| 3 months old | 50 | 250 |
| 1 year old | 70 | 250 |
| 2 year old | 100 | 250 |
| 10 year old | 110 | 280 |
| Adult woman | 110 | 330 |
| Adult man | 125 | 300 |
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition, p.400
Nelson text book, 15th edition
Treatment depends on the cause of iron deficiency anemia .
• When iron deficiency anemia occurs, the reason for the occurrence of iron deficiency and the cause of the iron deficiency is determined and treated.
• After 6 months of age, when iron deficiency anemia occurs due to only breast milk or whole milk, treatment with oral iron should be given, along with baby food or other types of foods containing a lot of iron.
• Babies who only breastfeed after 6 months of age should be supplemented with iron and vitamins.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia caused by excessive consumption of whole milk.
• After 6 months of age, infants or infants who have passed their first birthday should eat a lot of whole milk and develop iron deficiency anemia, reduce the intake of whole milk to a minimum and feed balanced baby food or meals that are eaten by family members according to age.
• If infants who have passed their first birthday do not eat well-balanced foods and develop iron deficiency anemia due to a long period of only whole milk, they should not feed any whole milk for a while and only give them a balanced diet.
• If you don’t give whole milk to infants or infants who have passed their first birthday, you may be tempted to ask for only whole milk for the first few days without eating any other food.
• Still, if you don’t give the whole milk for 2 to 3 days, you will end up eating new foods.
• From this point on, be patient and give a balanced diet without giving all milk for at least 4 weeks, and treatment with oral iron and multivitamins will cure iron deficiency anemia.
• Of course, after anemia is treated, you can eat a well-balanced diet and reduce the amount of whole milk you consume.
• Milk is not a food that you must eat every day.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia caused by an unbalanced diet
• When iron deficiency anemia occurs due to an unbalanced diet, take a balanced diet and treat it with oral iron according to the doctor’s prescription.
• In general, iron deficiency anemia is treated with ferrous sulfate oral iron. About 7 days after starting treatment with oral iron, the effect of oral iron treatment begins to appear remarkably.
• During 3-4 weeks of oral iron therapy, the symptoms of anemia gradually disappear one by one, hemoglobin levels return to normal, and iron deficiency anemia can be almost completely cured.
• From this point on, continue with oral iron treatment for 1 to 2 months, and do not follow the doctor’s instructions.
• While treating iron deficiency anemia with iron, you should do a CBC blood test to see if the anemia continues to progress or is cured.
Iron deficiency anemia is treated with iron
• Iron deficiency anemia is mainly treated with oral iron formulations or iron formulations.
• Iron injections can treat iron deficiency anemia, but treatment with iron injections can cause severe side effects.
• It is best not to treat with iron injections as much as possible.
• When treated with an oral iron formulation or iron formulation, the stool and teeth may temporarily darken.
• If oral iron treatment is stopped, black stool or tooth color will soon return to normal.
Iron deficiency anemia is prevented with iron.
• Iron deficiency anemia is more likely to develop in premature or low-weight newborns.
• From 1 to 2 months of age, as prescribed by a doctor, take multivitamins and iron medications to prevent anemia from occurring.
• Very rarely, severe anemia caused by iron deficiency is treated with a blood transfusion.
The following is an example of an Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer for “I have a question about anemia.”
Q&A. I have a question about anemia.
Q.
• The baby is anemic right now.. ㅜㅜ
• I was born as a 2.48 premature baby at 34 weeks and was doing well. When I was first born, I had anemia (I had been in the incubator for 3 weeks and received a blood transfusion once), so I did another antibody test like that, but the child is anemia. A number of 8.1 came out.
• There was no problem with the stool test..
• Now I am feeding Jaehun with iron.
• 1cc each~ (Now it’s 72.5cm and 10 kilos) You told me to test it again after feeding it for a month.. It’s just that, because breastfeeding can lead to anemia, I’m curious about what a mother can do.
• 1. Will it help me to take iron?
• 2. Or would it help if I eat foods that have a lot of iron? (They tell you to boil beef liver around and grind it for baby food..)
• Nowadays, that’s why I feed Jaehun one egg yolk a day. (I’m wondering if it might be helpful~^^) When feeding baby food, I put it on a spoon and feed it for breakfast and lunch..
• It’s been a little over 9 months now…
• Not so long ago, baby food is fed three times a day, but it is very well eaten.. (Sometimes it is fed twice.) It’s mainly rice.. As a snack, I feed it little by little, such as cheese or fruit.
• The teacher tells you what the normal number is and how Jaehun is, but I think the number is too low, so I am worried. • So, as a mother, I want to do some helpful things besides giving me medicine. If Jaehun is simply breastfeeding, or because she is a premature baby, she needs an answer from her teacher on what to do.
• Thank you…!
A.
• Hunnim • Good morning. Thank you for asking.
• If you have a lot of information, such as your child’s age, gender, past and family history, medical examination findings, and clinical test results, we can give you a better answer. We will respond by taking the information you provided into consideration.
• Your baby is already 9 months old.
• Usually, when full-term newborns turn to stone, they usually weigh three times the weight of birth. In the case of a baby, it is 9 months, and it is already four times the weight.
• As you may know, between the 37th and 40th weeks of pregnancy, the baby is born with enough iron from the mother. So, babies born at full term usually do not get iron deficiency anemia, even if they do not consume more iron until the age of 6 months.
• In the case of babies, they seem to have iron deficiency anemia due to iron deficiency because they were born immature newborns and grew quite quickly.
• The normal average hemoglobin concentration for infants and toddlers aged 6 months to 2 years is 12.0 g%. The baby’s hemoglobin concentration is abnormally low, but up to 10.5g% is considered normal.
• Newborns born at full term can develop anemia due to iron deficiency if only breastfeeding is fed until 9 months of age. What’s more, babies born as immature newborns are very likely to develop anemia due to iron deficiency if only breastfeeding.
• Iron deficiency anemia can be prevented when premature newborns are born, by starting to give babies multivitamins and iron drops for preventive treatment at least from 3-4 months of age.
• Iron-added grain meal solid baby food and other types of baby food are fed appropriately for their age and breastfeeding continues to prevent anemia due to iron deficiency.
• If you have anemia, it is a rule to determine the cause of anemia and treat it according to the cause by at least a CBC blood test.
• If you do a CBC blood test one to two weeks after starting treatment with an appropriate iron dose, you can see that the effect of iron treatment appears immediately.
• It is also important to do blood tests and urinalysis as needed.
• For breastfeeding mothers, it is important to eat foods that contain enough iron and vitamins for their own health, and of course, it is good for breastfeeding babies.
• It is not necessary to feed egg yolks because they are particularly good for anemia.
• For babies with many allergies, feeding egg yolks as well as egg whites at a young age may be more likely to result in an allergic reaction.
• However, if you eat the yolk and there is nothing wrong, you can continue to feed.
• Nowadays, grain solid baby food contains a lot of iron, and sometimes it is made by adding iron, so it is not necessary to feed egg yolks to babies who eat grain solid baby food.
• Continue to seek medical examination and treatment at the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents and consult about the problem.
• If you have more questions, please visit again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won . MD
Next, “Tell me about food rejection and childhood anemia.
This is an example of an internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answers about anemia, a child who does not eat well.
Q&A
. Please tell me about food rejection and childhood anemia. Anemia, a child who does not eat well.
Q.
• Hello sir?
• This is a 30 month old male baby. Originally, I don’t eat a lot of milk or food, but I eat mostly milk up to two months ago, and nowadays I feed three meals and feed milk and fruits (juice, cheese, etc.). ) If you do not eat it, and you put a spoonful of rice, you will feel disgusting.
• I’m worried because I have constipation because I don’t eat, and my mother’s point of view is that she doesn’t gain weight and is dry (10.5kg).
• I am worried about any serious problems with my nutritional status. I am worried and curious about how my child will eat well and gain weight like other children. Please help!
A.
• Support • Good morning. Thanks for the great question.
• The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer. We will respond based on the information you provided.
• Infants this age are required to eat the meals the parents eat.
• The child must be trained to eat with a spoon, cup or hand, and must be encouraged to eat.
• Make sure your child eats himself with a spoon. Parents should not spoon-feed children of that age.
• A child is an independent human being, and her parents can love, care for, and raise the child, but not possess it. www.drleepediatrics.com,-Vol. 22 Raise your sons and daughters like this-Refer to possession of love.
• They continue to seek independence from their parents at that age. It is very important to train you to pursue independence little by little and gradually.
• It is easy for all of our parents to make a property love for their children by mistake. You shouldn’t have possessive love. • Milk is not a balanced food, nor is it a must-eat.
• Because of this, you can give them at least 3 meals a day and other snacks.
• It is recommended not to give more than 1 to 2 cups of milk per day. Milk foods are not essential foods that must be eaten.
• If you eat a lot of milk, you can’t afford to eat anything other than milk because the milk you eat every day can get your child most of the nutrients they need each day, such as protein, fat, and carbohydrates.
• Therefore, you naturally avoid eating anything other than milk. Drinking a lot of milk can lead to anemia because milk doesn’t contain enough iron. Sometimes, you may suffer from milk allergies and lactose intolerance.
• When your child is hungry, have them eat breakfast, dinner, and lunch with their family members, and give them regular snacks twice a day.
• According to the growth chart, your child’s weight is 5 percentile. Find out how many percentiles you’ve been growing up along the growth chart from birth until now.
• If your child is growing up along the same percentage of the growth chart in the past and now, you can think that his or her current weight is normal. Each child’s growth rate is determined by nature.
• It is almost impossible to dramatically change the rate of growth, and neither parents nor their children themselves. In other words, the child must grow at the rate of growth at which the child was born.
• When conducting regular health check-ups at the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents, urine tests and anemia tests are also required, and please consult with us about these problems.
• www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 2 Prevention of Child and Adolescent Disease Safety Accidents-Refer to Regular Health Checkups.
• Volume 3 Newborns, Infants, School Age Hunger, Adolescent Hunger, Growth, Development and Development-Applicable Age Growth and Development. anemia. Volume 13 Children and Adolescents Blood, Lymphatic, and Tumor Diseases
• Children who don’t eat well, constitution, and growth chart. Please refer to Book 22, Sons and Daughters, Love and Raise Like This-Yoo-Sik Lee
• Please consult with the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents after receiving medical examination and treatment. • If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won . MD
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”