천식(기관지 천식)의 분류, 진단, 치료 Classification, diagnosis, treatments of Asthma(Bronchial asthma
2007년도 미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 천식 분류
1. 간헐 천식
2. 지속 천식으로 크게 이분한다. 그리고 지속 천식을
-
경증 지속 천식,
-
중등도 지속 천식,
-
중증 지속 천식으로 분류하고,
3. 천식 환자의 나이에 따른 천식 분류다.
-
소아 천식(소아 기관지 천식)
-
성인 천식(성인 기관지 천식)으로 분류한다.
4. 천식 발작 유발 인자에 따른 천식 분류
-
육체적 운동유발천식(운동유발 천식),
-
바이러스 감염병 유발성 천식,
-
찬 공기 유발성 천식(한랭 유발 천식),
-
수면 유발성 천식,
-
임신 유발성 천식으로 분류한다.
5. 천식의 증상 징후가 얼마나 오랫동안 지속되는지에 따른 천식 분류.
1) 만성 천식
- 천식이 3주 이상 계속 되는 천식
2) 급성 천식
- 천식발작이 갑자기 유발된 이후 3주 이상 계속 되는 천식
3) 천식 발작
- 천식 발작이 갑자기 유발되어 천식 증상 징후가 갑자기 나타나는 천식
4) 천식 지속상태
- 급성으로 유발된 심한 중증 천식 발작을 베타 2 작용제(베타 2 아고니스트제) 분무제(에어로졸) 등 기관지 확장제 치료,
- 전신 코르티코스테로이드제 치료,
- 산소호흡치료,
- 포도당 전질용액 정맥주사 재 수화 치료 등으로 치료해도
- 천식 발작 증상 징후가 쉽게 완화되지 않고
- 그 심한 증상 징후가 수 시간 내지 하루 이틀 동안 계속 되기도 하고,
- 때로는 호흡기 부전증이 생겨 사망 할 수 있는 급성 천식을 천식 지속상태라고 한다.
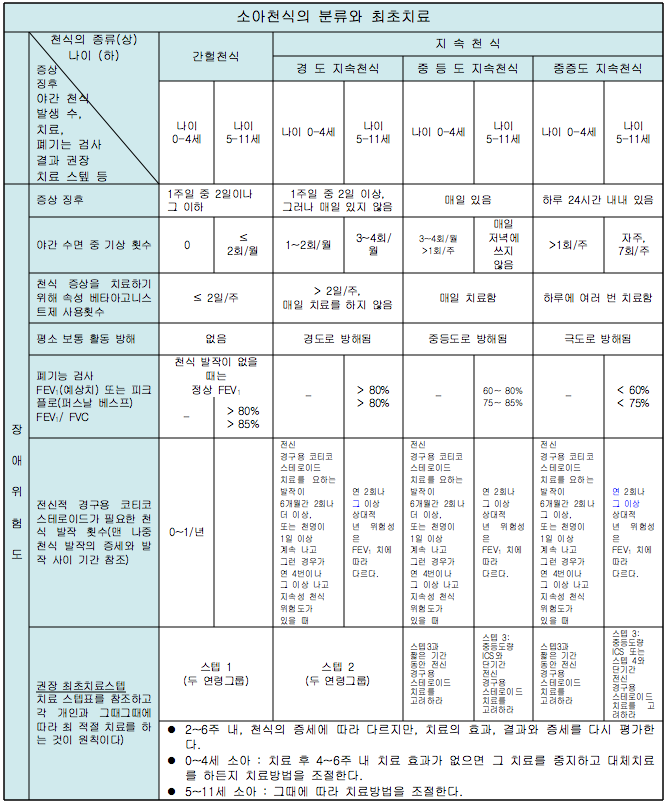
표 8. 2007년 미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 소아 천식의 증상, 분류와 치료
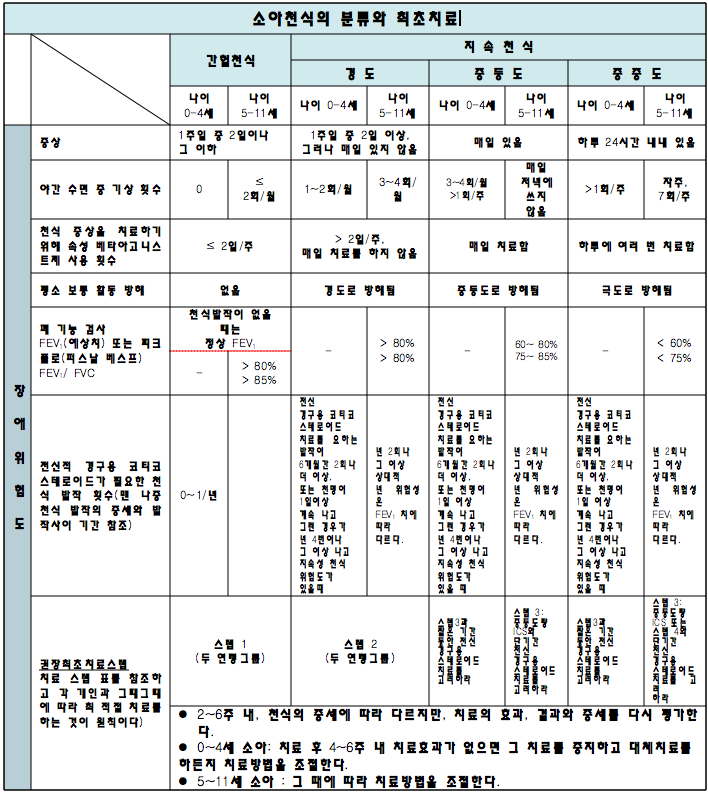
2007년 미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램에 의한 소아 천식의 증상, 분류, 치료 도표
FEV1: 1초간 강제 최대 호기 량
ICS: 흡입용 코르티코스테로이드제
출처; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. 2007년
천식에 관한 웹사이트와 참조문헌
-
www.aaaai.org
-
www.cdc.gov/asthma
-
www.lungusa.org
-
www.aafa.org
-
www.pedasthma-cme.com
-
www.allergyasthmatech.com
-
www.acaai.org
-
www.allergy.mcg.edu
-
www.foodallergy.org
-
Infectious Diseases In Children, Feb. 2004.Vol.17.#2 www.focusonallergies.com
기관지 천식(천식) 증상 징후
-
천식 발작이 유발 될 때의 증상 징후에 관해 구체적으로 설명한다.
-
천식 발작이 유발되면 천식의 증상 징후가 생긴다. 천식의 종류에 따라 증상 징후가 다르며 천식의 중증도(Severity), 환아의 나이, 유발 인자, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 천식의 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
천식 발작이 유발되면 숨이 가쁘고, 기침 하고, 천명이 나는 증상 징후가 꼭 있어야 한다고 믿는 사람들이 많으나 사실은 그와 정반대이다.
-
천식 발작이 경도로 유발되면 숨이 가쁘지도 않고 천명도 나지 않고 기침만 조금하면서 천식을 앓는 경우가 많다.
-
즉, 숨이 가쁘지도 않고, 천명이 나지도 않고, 다만 조금 피로하다든지, 기침만 약간 하는 증상 징후가 나타나는 경미한 간헐 천식을 앓는 아이들이 더 많다.
-
간헐 천식 발작이 유발되면 기침만 간간이 조금 하는 것 이외 다른 증상 징후가 전혀 없는 때도 있다. 이때 피크 플로 미터(Peak flowmeter/최대 유량계)로 최대 호기 유출 속도를 측정해 보면 최대 호기 유출 속도치가 비정상적으로 낮은 것이 발견되고 기관지 천식을 앓고 있다고 처음으로 진단받을 때도 있다(표 9, 10, 11).
-
어떤 부모는 천식이 있는 자녀를 소아청소년과로 데리고 와서 “이 애는 감기만 걸리면 금방 낫지 않고 2~3주 동안, 또는 일 년 내내 기침하면서 감기를 달고 산다.”고 걱정하기도 한다. 또 “이 아이는 기관지가 약해서 그런지 일 년 내내 기관지염을 앓고 밤에 잘 때 기침을 몇 주 동안 계속한다.”고 호소한다. 이런 종류의 경도 지속 천식을 앓는 아이들이 많다.
-
이 때 그 아이의 과거, 현재와 가족의 병력을 자세히 들어보면, 감기를 자주 앓는 것도 아니고 기관지염에 자주 걸린 것도 아니고 그 아이는 천식을 앓고 있기 때문에 기침을 계속 했다는 것을 알 수 있다.
-
이와 같이 많은 부모들은 자녀들이 천식으로 기침을 하고 있는 사실 조차도 모르고 지내는 경우가 많다. 이 예와 같이 천명도 없고 숨을 가쁘게 쉬지도 않고, 기침만 조금씩 자주 하는 경증 지속 천식을 앓는 아이들이 많다.
-
간헐 천식을 앓는 환아들에게 자주 나타나는 천식의 증상 징후, 환아들의 과거, 현재, 가족 병력 등을 잘 들어보지 않으면 단골 소아청소년과 의사들도 그 환아가 천식을 앓고 있는지 확실히 진단할 수 없는 때도 많다. 의사는 이런 간헐 천식을 진단하는데 많은 시간이 필요하다. 때로는 30분 이상 또는 그 이상 더 많은 진료시간이 걸린다. 부모는 의사로 하여금 진단을 옳게 붙일 수 있도록 자녀의 증상 징후, 병력을 사실 있는 그대로 설명해야 정확하게 천식을 진단할 수 있다. 용한 의사는 없다.
-
천식 발작은 흔히 감기나 그 외 다른 바이러스성 호흡기 감염병으로 인해 유발된다.
-
과거에 천식을 한 번 앓았던 과거 병력이 있는 아이들이 감기나 다른 종류의 바이러스성 호흡기 감염병을 또 다시 앓을 때 그 때 마다 바이러스성 호흡기 감염병으로 천식 발작이 유발되는 것이 일반적이다.
-
중증 지속 천식으로 일 년 내내 기침을 조금씩 하기도 하고 천식 치료약으로 일 년 내내 치료 받아야 할 때도 있다. 감기나 바이러스성 호흡기 감염병에 걸릴 때마다 감기 등 바이러스성 감염병으로 기관지 천식 발작이 유발되어 또다시 중증 지속 천식발작이 유발되어 앓을 수 있다.
-
간헐 천식이 경미하게 간헐적으로 발작될 때는 기침을 조금하거나, 또는 기침을 심하게 할 수 있고, 호흡곤란이 생기기도 하고 생기지 않을 수 있고, 천명이 날 때도 있고 나지 않을 때도 있다.
-
앞서 설명한 것과 같이 천식발작의 증상 징후는 그때그때에 따라 다르고 다양하여 천식을 변이성 기도병이라고 한다.
-
감기 등 바이러스성 상·하기도 가염병으로 중등도 지속 천식이나 중증도 지속 천식이 유발되어 응급치료를 받아야 할 때도 있다.
-
연령에 관계없이 신생아, 영유아, 학령기전 유아, 학령기 아이, 사춘기 아이, 성인 모두가 천식에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
천식 발작이 유발될 때 천식 그 자체 때문에 열이 나지 않는다. 그렇지만 감기, 독감, 폐렴 등 감염병으로 천식 발작이 유발되어 천식을 앓을 때 그 감염병으로 열이 날 수 있고 천식을 앓는 중 이차 박테리아 감염병이 있을 때는 그 이차 박테리아 감염병으로 열이 날 수 있다.
-
이때 천식으로 생기는 증상 징후와 감염병으로 생기는 증상 징후가 함께 나타나는 것이다.
| 1997년 천식 분류와 2007년 천식 분류 | |
| 1997 년도 천식 분류 | 2007 년도 천식 분류 |
| 1. 경증(輕症) 천식 | 1. 간헐 천식 |
| 2. 중등도 천식 | 2. 지속 천식 |
| 3. 중증(重症)도 천식 |
|
| 4. 천식 지속 상태 |
|
|
|
미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램은 2007 년도부터 천식 분류
1. 간헐 천식,
2. 지속 천식
1) 경도 지속 천식,
2) 중등도 지속 천식,
3) 중증 지속 천식
으로 3분했다.
- 천식 분류에 따른 증상 징후는 “2007년 미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램에서 권장하는 소아천식 치료(도표 2)”를 참조
기관지 천식의 진단
-
병력, 증상, 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 천식을 진단한다.
-
가슴 X선 사진, 폐 기능검사, 혈액검사 등은 천식을 진단하는 데 도움이 되나 때로는 별로 도움이 안 된다.
-
열이 나지 않고 하는 기침, 가슴이 답답하고 조이는 증상, 호흡곤란, 운동할 때 숨이 차고 호흡하기가 곤란한 증상이 재발될 때 천식이 있는지 의심해야 한다.
-
알레르기 비염이나 아토피 피부염을 과거에 앓았거나 현재 앓고 있는 과거나 현재의 알레르기 질환 병력이 있으면 천식이 있다고 진단하는 데 도움이 된다.
-
5세 이상 아이들은 피크 플로 미터(최대 유량계)로 최대 호기 유출량(최대 날숨 유량)을 측정하면 비정상적인 결과가 나올 수 있다. 최대 호기 유출량을 잴 수 있는 여러 종류의 피크 플로 미터가 있다(사진 186, 187 참조).
-
최대 유량계(최대 호기 유출량 측정계/Peak flow meter)로 최대 호기 유출량을 집에서 부모가 쉽게 측정할 수 있다.
-
천식이 발작될 때 최대 유량계로 최대 호기 유출량을 측정하면 최대 호기 유출량이 정상인지 비정상인지 알 수 있고 천식 치료제로 천식이 나아가는 정도를 알아볼 수 있다.
-
폐활량계로 폐활량을 측정해서 천식을 진단하는 데 도움을 얻을 수 있으나 소아들에게서는 나이와 능력 차이에 따라 폐활량 측정에 한계가 있다.
- 그 환아에게 적어도 1일 이상 지속되는 천명이 있는 증상이 3번 이상 있거나
- 그 환아에게 아토피 피부염이 있거나
- 그 환아의 부모에게 과거나 현재의 가족 천식 병력이 있거나
- 그 환아의 부모에게 상기도염이 아닌 어떤 원인으로 천명이 있거나
- 그 환아의 부모의 혈액 검사에서 호산구 수가 정상 이상으로 증가되거나
- 그 환아의 부모가 알레르기 비염이 있다는 의사의 진단을 받았을 경우에는
- 그 환아에게 천식이 있다고 진단할 수 있다.

사진 186. 천식으로 기관지와 세기관지가 수축된 정도와 천식 치료를 받을 때 치료의 효과를
알아볼 때 사용할 수 있는 천식 치료 의료기구. 이 의료 기구를 피크 플로 메터(Peak Flow meter)라고 한다. 이 기구로 최대 호기 유출량을 쉽게 측정할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
사진 187. 피크 플로 미터(최대 호기 유출량 측정계 또는 최대 유량계)로 최대 호기 유출량을 측정할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
최대 호기 유출 유량계는 값도 싸고 쓰기도 간편하고 쉬우며 최대 호기 유출량을 집에서 수시로 자유롭게 측정할 수 있는 장점이 있다. 그러나 모든 아이들이 이 기구를 이용해서 최대 호기 유출량을 측정할 수 없는 단점도 있다.
-
최대 유량계(최대 호기 유출량 측정계)로 최대 호기 유출량을 측정하면 최대 호기 유출량이 비정상적으로 낮은 것을 발견할 수 있다. 천식이 발작되어 기관지가 어느 정도로 수축되어 있는지를 측정계로 검사해 간단히 알 수도 있다.
-
천식을 앓는 사람들은 최대 유량계를 집에 가지고 있다가 필요에 따라 최대 호기 유출량을 측정해서 기관지 천식이 발작 여부를 간접적으로 알아볼 수 있다.
-
폐렴, 기관지 내 이물, 기관지 확장증, 폐결핵 등 호흡기 질환과 천식을 감별 진단할 때 측정계를 쓸 수 있다(사진 186, 187 참조).
-
천식의 증상의 정도에 따라 천식을 간헐 천식, 지속 천식으로 크게 분류하고 지속 천식을 경도 지속 천식, 중등도 지속 천식, 중증 지속 천식으로 분류하기도 하고, 천식 발작을 유발시키는 인자에 따라 천식을 분류할 수 있다.
-
심한 육체적 운동으로 천식 발작이 유발될 수 있으며 이를 운동 유발성 천식이라 한다.
표 9. 남성들의 키에 따른 최대 호기 유출량
| 신장 | 연령 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 |
| 인치 | cm | |||||||||||
| 48 | 121.92 | 459 | 510 | 540 | 554 | 555 | 547 | 534 | 520 | 509 | 505 | 512 |
| 50 | 127 | 487 | 517 | 548 | 561 | 562 | 554 | 541 | 528 | 517 | 513 | 519 |
| 52 | 132.08 | 474 | 525 | 555 | 569 | 569 | 561 | 549 | 535 | 524 | 520 | 527 |
| 54 | 137.16 | 481 | 532 | 562 | 576 | 577 | 569 | 556 | 542 | 531 | 527 | 534 |
| 56 | 142.24 | 489 | 539 | 570 | 583 | 584 | 576 | 563 | 550 | 539 | 535 | 541 |
| 58 | 147.32 | 496 | 547 | 577 | 590 | 591 | 583 | 571 | 557 | 546 | 542 | 549 |
| 60 | 152.4 | 503 | 554 | 584 | 598 | 599 | 591 | 578 | 564 | 553 | 549 | 556 |
| 62 | 157.48 | 511 | 561 | 591 | 605 | 606 | 598 | 585 | 571 | 561 | 557 | 563 |
| 64 | 162.56 | 518 | 569 | 599 | 612 | 613 | 605 | 592 | 579 | 568 | 564 | 571 |
| 66 | 167.64 | 525 | 576 | 606 | 620 | 621 | 613 | 600 | 586 | 575 | 571 | 578 |
| 68 | 172.72 | 532 | 583 | 613 | 627 | 628 | 620 | 607 | 593 | 582 | 578 | 585 |
| 70 | 177.8 | 540 | 590 | 621 | 634 | 635 | 627 | 614 | 601 | 590 | 586 | 592 |
| 72 | 182.88 | 547 | 598 | 628 | 642 | 642 | 634 | 622 | 608 | 597 | 593 | 600 |
| 74 | 187.96 | 554 | 605 | 635 | 649 | 650 | 642 | 629 | 615 | 604 | 600 | 607 |
| 76 | 193.04 | 562 | 612 | 643 | 656 | 657 | 649 | 636 | 623 | 612 | 608 | 614 |
표 10. 여성들의 키에 따른 최대 호기 유출량
| 신장 | 연령 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 |
| 인치 | cm | |||||||||||
| 48 | 121.92 | 404 | 411 | 415 | 416 | 417 | 415 | 410 | 403 | 393 | 381 | 366 |
| 50 | 127 | 411 | 418 | 423 | 425 | 425 | 422 | 417 | 410 | 400 | 388 | 374 |
| 52 | 132.08 | 418 | 425 | 430 | 432 | 432 | 429 | 424 | 417 | 407 | 396 | 381 |
| 54 | 137.16 | 425 | 432 | 437 | 439 | 439 | 436 | 431 | 424 | 414 | 402 | 388 |
| 56 | 142.24 | 432 | 439 | 444 | 446 | 446 | 443 | 438 | 431 | 421 | 409 | 395 |
| 58 | 147.32 | 439 | 446 | 451 | 453 | 453 | 450 | 446 | 438 | 429 | 416 | 402 |
| 60 | 152.4 | 446 | 453 | 458 | 460 | 460 | 458 | 453 | 445 | 436 | 424 | 409 |
| 62 | 157.48 | 453 | 460 | 465 | 467 | 467 | 465 | 460 | 452 | 443 | 431 | 416 |
| 64 | 162.56 | 461 | 468 | 472 | 474 | 474 | 472 | 467 | 460 | 450 | 438 | 423 |
| 66 | 167.64 | 468 | 475 | 479 | 482 | 481 | 479 | 474 | 467 | 457 | 445 | 430 |
| 68 | 172.72 | 475 | 482 | 486 | 489 | 488 | 486 | 481 | 474 | 464 | 452 | 437 |
| 70 | 177.8 | 482 | 489 | 494 | 496 | 496 | 493 | 488 | 481 | 471 | 459 | 445 |
| 72 | 182.88 | 489 | 496 | 501 | 503 | 503 | 500 | 495 | 488 | 478 | 466 | 452 |
| 74 | 187.96 | 496 | 503 | 508 | 510 | 510 | 507 | 502 | 495 | 485 | 473 | 459 |
| 76 | 193.04 | 503 | 510 | 515 | 517 | 517 | 514 | 509 | 502 | 492 | 480 | 466 |
출처 : Gregg I. and Nunn A. J. BMJ 1973, 3, 282-284
표 11. 소아들의 신장에 따른 최대 호기 유출량표 11. 소아들의 신장에 따른 최대 호기 유출량
| 신장 | PEFR | |
| 인치 | cm | |
| 40 | 101.6 | 106 |
| 42 | 106.68 | 132 |
| 44 | 111.76 | 159 |
| 46 | 116.84 | 185 |
| 48 | 121.92 | 212 |
| 50 | 127.0 | 238 |
| 52 | 132.08 | 265 |
| 54 | 137.16 | 291 |
| 58 | 147.32 | 344 |
| 60 | 152.4 | 370 |
| 62 | 157.48 | 397 |
| 64 | 162.56 | 423 |
| 66 | 167.64 | 450 |
| 68 | 172.72 | 476 |
| 70 | 177.8 | 503 |
| 72 | 182.88 | 529 |
출처: Godfrey ET AL,Brit. J. Dis. Chest 64, 15, 1970
-
한랭 기온으로 천식 발작이 유발될 수 있는데 이를 한랭 유발성 천식이라고 하며 임신으로 천식 발작이 유발될 때 임신 유발성 천식이라고 한다.
-
운동 유발 천식 병력을 가진 아이들이 육체적 운동을 하지 않을 때는 천식의 증상이 나타나지도 않을 수 있다.
-
운동을 하지 않는 상태에서 진찰을 받을 때 천명이 들리지도 않고 진찰의 결과 거의가 정상일 때가 많다.

사진 188. 달리기 등 육체적 운동으로 천식 발작이 유발될 수 있다. 이런 천식을 육체운동 유발 천식 이라고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD. FAAP
-
중등도 지속 천식이나 중증 지속 천식의 병력이 있는 아이들의 일부는 천명도 나지 않고, 숨을 가쁘게 쉬지도 않고, 기침도 하지 않을 수 있다. 그러나 육체적 운동을 시작하면 육체 운동 유발성 천식 발작이 유발되고 천명, 숨 가쁨 등의 천식 증상이 나타날 수 있다.
-
이때 육체적 운동으로 천식 발작이 유발됐는지 이미 있던 천식의 증상이 육체적 운동과 함께 더 심해졌는지는 감별 진단하기가 어렵다.
-
한랭 기온에 노출될 때만 천식 발작이 유발되는 아이들도 있다. 찬 공기를 쐬지 않을 때는 천식 증상이 나타나지도 않아서 진찰을 해 보아도 천식 증상이 발견되지 않을 수 있다.
-
운동 유발성 천식이나 한랭 유발성 천식이 있는 아이를 검진할 때 한랭 기온에 노출될 때나 운동을 할 때 천식 증상 징후와 병력을 들어보지 않으면 천식이 있다고 진단하기가 어렵다.
-
환아가 경험했던 증상 징후, 과거 병력, 알레르기 질환의 유무, 아토피 체질의 유무 등을 총 종합해서 여러 종류의 기관지 천식을 진단한다.
-
때로는 천식 발작이 유발될 때 천식을 적절한 천식 치료 약물로 치료해 보고 그 치료 효과에 따라 기관지 천식을 진단할 때도 있다.
-
천식 발작을 천식 치료 치료제로 치료하기 전에 최대 호기 유출량 측정계나 다른 종류의 기구로 최대 호기 유출량을 측정한다. 그 다음 적절한 천식치료 약물로 치료한 후, 예를 들면 흡입입용 알부테롤 HFA 분무 흡입치료를 한 5∼10분 후, 최대 호기 유출량을 또다시 측정한다. 이 때 천식치료 약물로 치료하기 전과 후의 최대 호기 유출량 치의 차이를 보고 천식이 있는지 없는지 진단할 수 있다.
-
천식을 진단하는 데 알레르기 피부 시험은 일반적으로 잘 쓰지 않는다. 그렇지만 어떤 종류의 항원이 아이에게 알레르기 질환을 일으키는지 알아보기 위해서 알레르기 피부 시험을 해볼 수 있다.
-
과거에 친 부모 형제자매들 중 누구에게 천식이 있었거나 현재 앓고 있는 병력이 있을 때는 그 친 형제자매들에게 천식이 생길 가능성이 아주 많다.
-
본인이나 친 부모 형제자매들 중 누구에게 아토피 체질, 아토피 피부염, 옻나무 접촉성 피부염, 음식물(식품) 알레르기, 약물 알레르기, 그 외 알레르기 질환이 있을 때는 그 친 형제자매들 중 다른 친 형제자매들에게도 천식이 생길 가능성이 대단히 많다. 이런 가족 병력은 천식을 진단하는데 큰 도움이 된다.
-
YKL-40(“Mammalian chitinase–like proteins) 검사치가 천식환자의 15%에서 증가되고 기관 과반응의 10%에서 증가될 수 있다. 이 검사가 천식을 진단하는데 큰 도움이 될 수도 있다.
사진 189. 가슴, 폐, 심장 X선 사진
필요에 따라 가슴, 폐, 심장 X선 사진검사를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
출처 및 참조문헌
-
The New England Journal of Medicine April 17, 2008
기관지 천식(천식)의 치료
① 그림으로 보는 천식 발작의 유발 인자, 항원과 치료
그림 190. 그림으로 본 천식 발작, 천식 발작 유발 항원과 인자와 치료
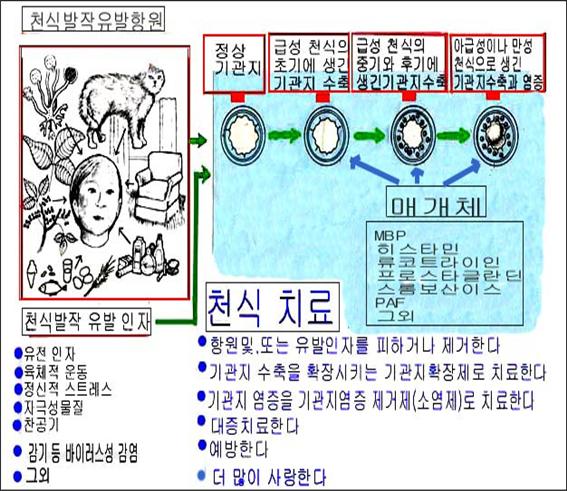
참조문헌-Journal of respiratory diseases. Vol.13, #10 소아가정간호백과
- MBP; 주요 호염기구 세포독성 효소(호염기구 (Major basophilic protein)가 분비되고
- PAF:혈소판활성화 인자(Platelet activating factor, PAF)
- Leukotriene:류코트리엔
표 2. 소아천식 장기간 컨트롤 치료약물과 보통 치료용량 (0~11세)
(2007년 미 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 권장)
| 천식치료 약 이름과 용량 (상품명) | 0 – 4 세 | 5 – 11 세 |
| Inhaled corticosteroid (흡입용 코티코스테로이드) | 표 4 참조 | 표 4 참조 |
| 장시간 β2-아드레날린작동성 아고니스트 Salmeterol DPI 50 ㎍/blister(Severent Diskus) |
4세 이하 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 매 12시간마다 한 blister |
| Formoterol DPI 12 ㎍/1회용 캪슬(Foradil Aerolizer) | 5세 이하 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 매 12시간마다 한 캡슬 |
| 종합 천식 치료약 Fluticasone/Salmeterol DPI 100 ㎍/50 ㎍(Advair Diskus) |
4세 이하 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 한번 흡입치료를 하루에 2번 |
| Fluticasone/Salmeterol HFA 45 ㎍/21 ㎍, 115㎍/21㎍, 230㎍/21㎍ (Advair HFA) | 4세 이하 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 12세 이하 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 |
| Budesonide/formoterol HFA MDI 80 ㎍/4.5 ㎍(Symbicort) |
소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 2 puff 를 하루 2번 |
| Cromolyn/Nedocromil Cromolyn MDI 제 0.8 mg/puff (Intol inhaler) |
소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 2 puff 를 하루 4번 |
| Cromolyn Sodium 흡입 용액 20 mg/ample | 1 ample을 하루 4번. 2세 이하 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 1 ample을 하루 4번 |
| Nedocromil MDI 제 1.75 mg/puff (Tilade inhaler) | 6세 이하 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 2 puff 를 하루 4번 |
| Leukotrience 수용체 안타고니스트 Montelukast 4~5mg 추어불 정; 4mg 미립 패케트(Singulair) |
취침전 4mg (1~5세 소아) | 취침전 5mg (6~14세 소아) |
| Zarfirlukst 10mg 정 (Accolate) | 소아 천식치료에 관한 안정성과 효력에 대한 연구 결과가 없다 | 10mg 하루 2번 (7~11세 소아) |
| Methylxanthines Theophylline 용액, 지속성 방출 정, 캡슬(여려 종류 상품) |
최초 치료 용량은 체중 Kg당 10mg을 1일 총용량으로 계산한다. 보통 최대 용량은 참조문헌에 따른다. | 최초 치료 용량은 체중 Kg당 10mg을 1일 총 용량으로 계산한다. 보통 최대 용량은 1일 매 체중 Kg당 16mg이다. |
|
DPI; Dry powder inhaler (건말 흡입기) HFA; hydrofluroalkane |
||
출처-Update on the 2007 National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
표 3. 소아 천식 컨트롤과 치료약물의 조절
(2007년 미 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 권장)
- FEV1: 1초 간 강제 호기량
- FVC: Forced Vital Capacity(강제 폐활량, 노력성 폐활량)
- 출처-Update on the 2007, National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
표 4. 소아 천식 치료용 흡입용 코르티코스테로이드제 1일 추정 용량 비교표 (2007년 미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 권장)
| 최소 1일 용량 | 중간 1일 용량 | 최대 1일 용량 | |
| 약명 (상품명) | 0~4세 5~11세 | 0~4세 5~11세 | 0~4세 5~11세 |
| Beclomethasone HFA 40㎍/Puff 또는 80㎍(Qvar) |
80~160ug | >160~320ug | >320㎍ |
| Budesonide DPI 90㎍ 또는 180㎍/흡입 (Pulmicort Flehaler) 200㎍/흡입(Pulmicort Turbuhaler) |
180~400㎍ | >400~800㎍ | >800㎍ |
| Budesonide Inhalation Suspension 소아천식분무요법 용량 0.25mg, 0.5mg, 0.5mg/2ml(Pulmicort Respules) |
0.25~0.5mg 0.5mg | >0.5~1mg 1mg | >1.0mg 2.0mg |
| Flunisolide 250㎍/puff(AeroBid) |
500~750㎍ | 1000~1250㎍ | 1250㎍ |
| Flunisolide HFA 80㎍/puff(AeroBid-M) |
160㎍ | 320㎍ | 640㎍이나 그 이상 |
| Fluticasone HFA/MDI 44㎍, 110㎍, 또는 250㎍/흡입(Flovent HFA) |
176㎍ 88~176㎍ | >176~352㎍ >176~352㎍ | >352㎍ >352㎍ |
| Fluticasone DPI 50㎍, 100㎍, 또는 250㎍/흡입(Flovent Diskus) |
100~200㎍ | >200~400㎍ | >400㎍ |
| Mometasone DPI 200㎍/흡입(Flovent Diskus) (Asmanex Twisthaler) |
– – | – – | – – |
| Triamcinolone acetonide 75㎍/puff (Azmacort Inhalation Aerosol) |
300~600㎍ | >600~900㎍ | >900㎍ |
|
HFA- hydrofluoroalkane(건말 흡입기) DPA-dry poder inhaler |
|||
출처-Update on the 2007, National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
소아 천식 스텦 치료 (2007년 미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 에서 권장하는)
표 15. 소아 천식 스텝치료
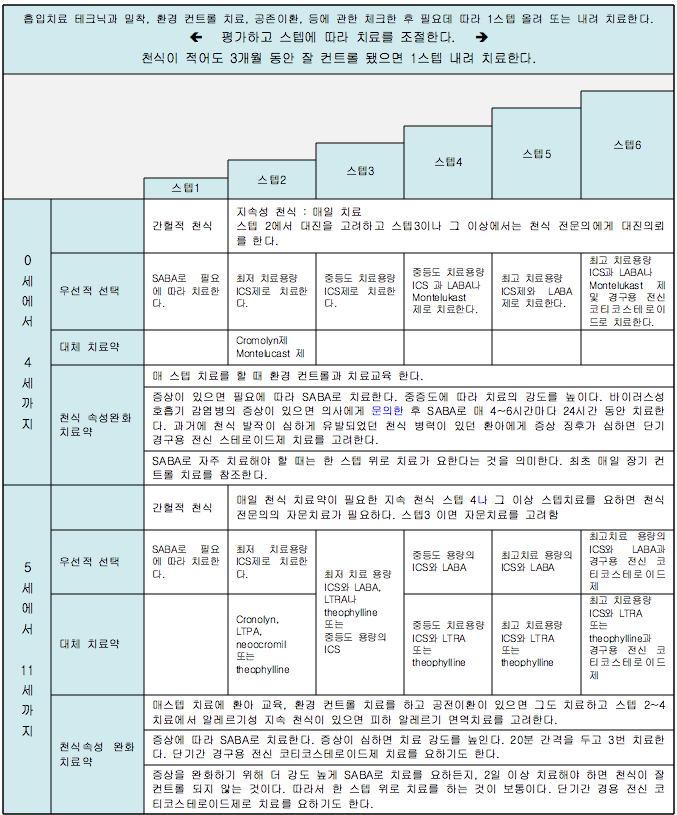
-
ICS : Inhaled corticosteroid(흡입 코티코스테로이드제)
- SABA : Short acting beta 2 – adrenergic agonist – 단기 작용 베타 2 – 아드레날린성 작용제
- LABA : Long acting beta 2 – adrenergic agonist – 단기 작용 베타 2 – 아드레날린성 작용제
- LTRA : Leukotrine receptor antagonist – 류코트리엔 수용체 길항제
- 출처-Update on the 2007, National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
- 어떤 병을 앓든 병을 효과적으로 치료하기 위해서 의사, 환아, 보호자가 삼위일체가 되어 서로 잘 협조해야 한다.
-
특히 소아 천식을 효과적으로 치료하려면 환아와 부모가 천식 치료에 책임성 있게 협조해야 하고, 특히 담당 의사가 옳게 진단하고 옳은 천식 치료를 해야 한다.
-
부모가 소아 천식에 관한 의학 지식을 많이 배우고 알아야 한다.
-
천식 발작을 유발시킬 수 있는 항원, 인자들에 관한 환경 컨트롤에 관해 1차적 책임은 부모와 환아에게 주로 있다.
-
천식을 올바르게 치료하기 위해서는 부모와 환아와 의사가 일개 소아 천식 치료 팀의 멤버가 되어야 소아 천식을 성공적으로 치료할 수 있다.
-
급성 천식을 적절히 치료하지 않으면 만성 천식으로 진행될 수 있다. 만성 천식으로 많이 고생도 할 수 있고 심하면 사명할 수 있다.
-
급성 천식이 만성 천식으로 진행되지 않도록 적절히 치료해야 한다.
-
일생 생활을 정상적으로 하기 위해 천식발작을 적절히 치료하고 천식 발작이 유발되지 예방하여야한다.
-
천식 발작이 유발될 때 생긴 증상 징후를 제때에 치료하고, 그 증상을 가진 천식이 더 이상 생기지 않게 예방하고, 폐 기능을 정상적으로 유지하고, 천식 발작이 다시 유발되지 않게 예방하고, 천식 치료약으로 생긴 부작용을 예방하는 데 특히 힘써야 한다.
Classification, diagnosis, treatments of Asthma (Bronchial asthma) 천식(기관지 천식)의 분류, 진단, 치료
2007 American Asthma Education and Prevention Program Asthma Classification
1. Intermittent Asthma
2. It is largely divided into persistent asthma. and persistent asthma
• mild persistent asthma;
• moderate persistent asthma;
• Classified as severe persistent asthma;
3. Asthma classification according to the age of asthma patients.
• Asthma in children (bronchial asthma in children)
• Classified as adult asthma (adult bronchial asthma).
4. Classification of asthma according to trigger factors for asthma attacks
• Physical exercise-induced asthma (exercise-induced asthma);
• Asthma induced by viral infections;
• Cold Air Induced Asthma (Cold Induced Asthma);
• sleep-induced asthma;
• Classified as pregnancy-induced asthma.
5. Classification of asthma based on how long the symptoms of asthma persist.
1) Chronic asthma
• Asthma that lasts more than 3 weeks
2) acute asthma
• Asthma that continues for more than 3 weeks after the onset of an asthma attack 3) asthma attack
• Asthma with sudden onset of asthma attacks and sudden onset of asthma symptoms
4) Asthma persistence
• Treatment of severe acute asthma attacks with bronchodilators, such as beta 2 agonists (beta 2 agonists) sprays (aerosols);
• treatment with systemic corticosteroids;
• oxygen breathing therapy;
• Even if treated with glucose pre-solution, intravenous rehydration, etc
. • If the symptoms of an asthma attack are not easily relieved,
• The severe symptoms may last for hours or even a day or two;
• Acute asthma, which can sometimes lead to respiratory failure and death, is called persistent asthma.
Table 8. 2007 US Asthma Education and Prevention Program Symptoms, Classification, and Treatment of Childhood Asthma Symptoms, Classification, and Treatment

Chart of Children’s Asthma by the American Asthma Education and Prevention Program, 2007 FEV1: Forced maximum expiratory volume in 1 second ICS: Inhaled corticosteroids source; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Asthma Education and Prevention Program.
2007 Websites and References on Asthma
• www.aaaai.org
• www.cdc.gov/asthma
• www.lungusa.org
• www.aafa.org
• www.pedasthma-cme.com
• www.allergyasthmatech.com
• www.acaai.org
• www.allergy.mcg.edu
• www.foodallergy.org
• www.aanma.org
• Infectious Diseases In Children, Feb. 2004.Vol.17.#2 www.focusonallergies.com
Bronchial Asthma (Asthma) Symptoms, Signs
• Be specific about the symptoms and signs of an asthma attack.
• When an asthma attack is triggered, symptoms of asthma occur. Symptoms and signs differ depending on the type of asthma, and symptoms of asthma differ depending on the severity of asthma, the age of the child, triggering factors, and the presence or absence of complications.
• Many people believe that the symptoms of shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing are essential when an asthma attack is triggered, but the opposite is true.
• When asthma attacks are mildly induced, there are many cases of people with asthma with no shortness of breath and no wheezing and only a slight cough.
• More children have mild intermittent asthma, which shows signs of not being short of breath, not wheezing, just feeling a little tired or coughing.
• When an intermittent asthma attack is triggered, there are times when there are no signs of symptoms other than an occasional cough. At this time, when the maximum expiratory flow rate is measured with a peak flowmeter (peak flowmeter), it is found that the maximum expiratory rate is abnormally low, and in some cases, the patient is diagnosed with bronchial asthma for the first time (Tables 9, 10, 11).
• Some parents bring their asthmatic child to the pediatric department and worry, “This child doesn’t get better if he catches a cold, and he coughs for two to three weeks or all year round.” He also complains, “This child has bronchitis all year round, probably because his bronchial tubes are weak, and he coughs at night for several weeks.” Many children have this type of mild persistent asthma.
At this time, if you listen closely to the child’s past, present and her family’s medical history, it is clear that she did not have frequent colds or bronchitis, and that the child continued coughing because she had asthma.
• Many parents do not even know that their child is coughing with asthma. As in this example, there are many children with mild persistent asthma who have no wheezing, no shortness of breath, and only small and frequent coughing.
• Frequently, even regular pediatricians cannot diagnose with certainty whether the child has asthma unless they listen carefully to the symptoms of asthma, the child’s past, present, and family history, which are common in children with intermittent asthma.
Doctors spend a lot of time diagnosing this type of intermittent asthma. Sometimes it takes more than 30 minutes or more. In order to accurately diagnose asthma, parents must describe their child’s symptoms, signs, and medical history as they are, so that the doctor can correctly attach the diagnosis. There is no compassionate doctor.
• Asthma attacks are often caused by a cold or other viral respiratory infections.
• It is common for children with a previous history of asthma to have an asthma attack whenever they have a cold or another viral respiratory infection again.
• With severe persistent asthma, you may cough a little all year round, and you may need to be treated year-round with asthma medications. Whenever you catch a cold or a viral respiratory infection, a viral infection such as a cold triggers a bronchial asthma attack, which can cause another severe and persistent asthma attack.
• Intermittent asthma, in mild, intermittent attacks, may have a slight or severe cough, may or may not cause shortness of breath, and may or may not cause wheezing.
• As described above, the symptoms of asthma attacks vary and vary from time to time, so asthma is called mutant airway disease.
• Viral upper and lower respiratory tract infections such as colds can sometimes cause moderate or persistent asthma and require emergency treatment.
• Newborns, infants, preschoolers, school-age children, adolescents, and adults can all get asthma, regardless of age.
• Asthma itself does not cause fever when triggering an asthma attack. However, when an asthma attack is triggered by an infectious disease such as a cold, flu, or pneumonia and you have asthma, you can develop a fever from the infectious disease, and if you have a secondary bacterial infection while you have asthma, you can develop a fever from the secondary bacterial infection.
• At this time, symptoms of asthma and symptoms of infectious diseases appear together.
| Asthma Classification 1997 and Asthma Classification 2007 | |
| 1997 Asthma Classification | 2007 Asthma Classification |
| 1. Mild Asthma (輕症) | 1. intermittent asthma |
| 2. Moderate asthma | 2. Persistence asthma |
| 3. Severe Asthma (heavy degree) | 1) Mild persistent asthma |
| 4. Asthma persistent state | 1) Mild persistent asthma |
| 3) Severe persistent asthma | |
Since 2007, the American Asthma Education and Prevention Program has
1. Intermittent asthma,
2. Persistent Asthma
1) mild persistent asthma;
2) moderate persistent asthma;
3) severe persistent asthma was made for 3 minutes.
• For symptoms and signs according to asthma classification, see “Childhood Asthma Treatment Recommended by the American Asthma Education and Prevention Program, 2007 (Figure 2)”
Diagnosis of bronchial asthma
• Diagnose asthma by combining medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
• Chest X-rays, lung function tests, and blood tests can help diagnose asthma, but sometimes they are not very helpful.
• When symptoms such as cough without fever, chest tightness, shortness of breath, shortness of breath and difficulty breathing during exercise recur, you should suspect that you have asthma.
• Past or present history of allergic rhinitis or atopic dermatitis is helpful in diagnosing asthma.
• Children over 5 years old may have abnormal results when measuring peak expiratory flow (maximum expiratory flow) with a peak flow meter (maximum flow meter). There are several types of peak flow meters that can measure peak expiratory flow (see photos 186 and 187).
• Peak flow meter (peak flow meter) allows parents to easily measure peak expiratory flow at home.
• Measuring peak expiratory output with a peak flow meter during an asthma attack can determine whether peak expiratory output is normal or abnormal, as well as the progression of asthma with asthma medications.
• Measuring spirometry with a spirometer can help in diagnosing asthma, but there is a limit to measuring spirometry in children due to age and ability differences.
• The child has 3 or more symptoms of wheezing lasting at least 1 day, or
• If the child has atopic dermatitis or
• the child’s parent has a past or present family history of asthma;
• If the child’s parent has wheezing due to any cause other than upper respiratory tract infection, or
• The child’s parent’s blood test shows an abnormally high eosinophil count or
• If the child’s parent is diagnosed with allergic rhinitis by a doctor,
• It can be diagnosed that the child has asthma.

Picture 186. The degree of constriction of bronchi and bronchioles due to asthma and the effectiveness of treatment Asthma treatment medical device that can be used to check. This medical device is called a Peak Flow meter. With this instrument, the maximum expiratory flow can be easily measured. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Photo 187. A peak flow meter (maximum expiratory flow meter or peak flow meter) can measure peak expiratory flow. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• The maximum expiratory flow meter is inexpensive, easy to use, and has the advantage of being able to freely measure the maximum expiratory flow at home. However, there is a disadvantage that not all children can measure the maximum expiratory output using this instrument.
• Measuring peak expiratory flow with a peak flow meter (maximum expiratory flow meter) may reveal an unusually low peak expiratory flow. It is possible to find out simply by examining how much the bronchi are contracted due to an asthma attack.
• People with asthma can indirectly check for attacks of bronchial asthma by keeping a peak flow meter at home and measuring peak expiratory flow as needed. • The meter can be used to differentially diagnose asthma and respiratory diseases such as pneumonia, endobronchial foreign body, bronchiectasis, and pulmonary tuberculosis (see photos 186 and 187).
• Asthma can be broadly classified into intermittent asthma and persistent asthma according to the severity of asthma symptoms, persistent asthma into mild persistent asthma, moderate persistent asthma, and severe persistent asthma. can • Excessive physical exercise can trigger asthma attacks, which is called exercise-induced asthma.
Table 9. Maximum expiratory flow by height for men Height Age 표 9. 남성들의 키에 따른 최대 호기 유출량
| Hight | Age | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 |
| Inch | cm | |||||||||||
| 48 | 121.92 | 459 | 510 | 540 | 554 | 555 | 547 | 534 | 520 | 509 | 505 | 512 |
| 50 | 127 | 487 | 517 | 548 | 561 | 562 | 554 | 541 | 528 | 517 | 513 | 519 |
| 52 | 132.08 | 474 | 525 | 555 | 569 | 569 | 561 | 549 | 535 | 524 | 520 | 527 |
| 54 | 137.16 | 481 | 532 | 562 | 576 | 577 | 569 | 556 | 542 | 531 | 527 | 534 |
| 56 | 142.24 | 489 | 539 | 570 | 583 | 584 | 576 | 563 | 550 | 539 | 535 | 541 |
| 58 | 147.32 | 496 | 547 | 577 | 590 | 591 | 583 | 571 | 557 | 546 | 542 | 549 |
| 60 | 152.4 | 503 | 554 | 584 | 598 | 599 | 591 | 578 | 564 | 553 | 549 | 556 |
| 62 | 157.48 | 511 | 561 | 591 | 605 | 606 | 598 | 585 | 571 | 561 | 557 | 563 |
| 64 | 162.56 | 518 | 569 | 599 | 612 | 613 | 605 | 592 | 579 | 568 | 564 | 571 |
| 66 | 167.64 | 525 | 576 | 606 | 620 | 621 | 613 | 600 | 586 | 575 | 571 | 578 |
| 68 | 172.72 | 532 | 583 | 613 | 627 | 628 | 620 | 607 | 593 | 582 | 578 | 585 |
| 70 | 177.8 | 540 | 590 | 621 | 634 | 635 | 627 | 614 | 601 | 590 | 586 | 592 |
| 72 | 182.88 | 547 | 598 | 628 | 642 | 642 | 634 | 622 | 608 | 597 | 593 | 600 |
| 74 | 187.96 | 554 | 605 | 635 | 649 | 650 | 642 | 629 | 615 | 604 | 600 | 607 |
| 76 | 193.04 | 562 | 612 | 643 | 656 | 657 | 649 | 636 | 623 | 612 | 608 | 614 |
Table 10. Maximum expiratory flow by height for wome
| hight | age | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 |
| Inch | cm | |||||||||||
| 48 | 121.92 | 404 | 411 | 415 | 416 | 417 | 415 | 410 | 403 | 393 | 381 | 366 |
| 50 | 127 | 411 | 418 | 423 | 425 | 425 | 422 | 417 | 410 | 400 | 388 | 374 |
| 52 | 132.08 | 418 | 425 | 430 | 432 | 432 | 429 | 424 | 417 | 407 | 396 | 381 |
| 54 | 137.16 | 425 | 432 | 437 | 439 | 439 | 436 | 431 | 424 | 414 | 402 | 388 |
| 56 | 142.24 | 432 | 439 | 444 | 446 | 446 | 443 | 438 | 431 | 421 | 409 | 395 |
| 58 | 147.32 | 439 | 446 | 451 | 453 | 453 | 450 | 446 | 438 | 429 | 416 | 402 |
| 60 | 152.4 | 446 | 453 | 458 | 460 | 460 | 458 | 453 | 445 | 436 | 424 | 409 |
| 62 | 157.48 | 453 | 460 | 465 | 467 | 467 | 465 | 460 | 452 | 443 | 431 | 416 |
| 64 | 162.56 | 461 | 468 | 472 | 474 | 474 | 472 | 467 | 460 | 450 | 438 | 423 |
| 66 | 167.64 | 468 | 475 | 479 | 482 | 481 | 479 | 474 | 467 | 457 | 445 | 430 |
| 68 | 172.72 | 475 | 482 | 486 | 489 | 488 | 486 | 481 | 474 | 464 | 452 | 437 |
| 70 | 177.8 | 482 | 489 | 494 | 496 | 496 | 493 | 488 | 481 | 471 | 459 | 445 |
| 72 | 182.88 | 489 | 496 | 501 | 503 | 503 | 500 | 495 | 488 | 478 | 466 | 452 |
| 74 | 187.96 | 496 | 503 | 508 | 510 | 510 | 507 | 502 | 495 | 485 | 473 | 459 |
| 76 | 193.04 | 503 | 510 | 515 | 517 | 517 | 514 | 509 | 502 | 492 | 480 | 466 |
Source : Gregg I. and Nunn A. J. BMJ 1973, 3, 282-284
Table 11. Maximum expiratory output by height in children Table 11. Maximum expiratory outflow by height in children
| Hight | PEFR | |
| Inch | cm | |
| 40 | 101.6 | 106 |
| 42 | 106.68 | 132 |
| 44 | 111.76 | 159 |
| 46 | 116.84 | 185 |
| 48 | 121.92 | 212 |
| 50 | 127.0 | 238 |
| 52 | 132.08 | 265 |
| 54 | 137.16 | 291 |
| 58 | 147.32 | 344 |
| 60 | 152.4 | 370 |
| 62 | 157.48 | 397 |
| 64 | 162.56 | 423 |
| 66 | 167.64 | 450 |
| 68 | 172.72 | 476 |
| 70 | 177.8 | 503 |
| 72 | 182.88 | 529 |
Source: Godfrey ET AL, Brit. J. Dis. Chest 64, 15, 1970
• Cold temperatures can trigger an asthma attack, which is called cold-induced asthma. When an asthma attack is triggered by pregnancy, it is called pregnancy-induced asthma.
• Children with a history of exercise-induced asthma may not show symptoms of asthma when they are not physically active.
• When you go to a medical examination without exercising, you do not hear wheezing, and the results of the examination are often normal.

Picture 188. Physical exercise, such as running, can trigger an asthma attack. This type of asthma is called physical exercise-induced asthma. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD. FAAP
• Some children with a history of moderate or severe persistent asthma may not wheeze, breathe heavily, or cough. However, starting physical exercise can trigger physical exercise-induced asthma attacks, and asthma symptoms such as wheezing and shortness of breath may appear.
• At this time, it is difficult to differentially diagnose whether an asthma attack was induced by physical exercise or whether the symptoms of asthma worsened with physical exercise.
• Some children only have asthma attacks when exposed to cold temperatures. Asthma symptoms do not appear when you do not receive cold air, so you may not find any asthma symptoms even when you examine yourself.
• When screening a child with exercise-induced asthma or cold-induced asthma, it is difficult to diagnose asthma without hearing signs and history of asthma symptoms when exposed to cold temperatures or when exercising.
• Diagnose various types of bronchial asthma by synthesizing the symptoms and signs the child has experienced, past medical history, presence of allergic diseases, and atopic constitution.
• Sometimes, when an asthma attack is triggered, asthma is treated with an appropriate asthma medication, and bronchial asthma is diagnosed according to the treatment effect.
• Measure peak expiratory flow with a peak expiratory flow meter or other type of instrument before treating an asthma attack with asthma medication. Then, after treatment with an appropriate asthma medication, for example, 5 to 10 minutes after inhaled albuterol HFA spray inhalation, the maximum expiratory output is measured again. At this time, the presence or absence of asthma can be diagnosed by looking at the difference in the maximum expiratory output before and after treatment with asthma medication.
• Allergic skin tests are not commonly used to diagnose asthma. However, you can do an allergic skin test to see what kind of antigen is causing the allergy in your child.
• If any of your biological parents’ siblings had or has had asthma in the past, your biological siblings are more likely to develop asthma.
• If you or any of your biological siblings have atopic constitution, atopic dermatitis, poison ivy contact dermatitis, food (food) allergy, drug allergy, or other allergic diseases, you can also There is a very high chance that you will develop asthma. This family history is very helpful in diagnosing asthma.
• YKL-40 (“Mammalian chitinase-like proteins) levels can be elevated in 15% of asthmatics and in 10% of organ hyperreactivity. This test can be of great help in diagnosing asthma.

Picture 189. X-ray of chest, lungs, and heart X-rays of the chest, lungs, and heart are performed as needed. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP Sources and references
• The New England Journal of Medicine April 17, 2008
Treatment of bronchial asthma (asthma)
① Asthma attack trigger factors, antigens and treatment

Figure 190. Asthma Attacks, Asthma Attack Inducing Antigens, Factors, and Treatment References – Journal of respiratory diseases. Vol.13, #10 Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing
• MBP; Major basophilic cytotoxic enzymes (Major basophilic protein) are secreted and
• PAF: Platelet activating factor (PAF)
• Leukotriene: Leukotriene
Table 2. Asthma in children long-term control drugs and usual therapeutic doses (0-11 years) (Recommended by the American Asthma Education and Prevention Program, 2007) 표 2. 소아천식 장기간 컨트롤 치료약물과 보통 치료용량 (0~11세)
(2007년 미 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 권장)
| Asthma treatment drug name and dose (brand name) | 0 – 4 years old | 5 – 11 years old |
| Inhaled corticosteroid | See Table 4 | See Table 4 |
| Salmeterol DPI 50 ㎍/blister(Severent Diskus) | There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children under 4 years of age. | One blister every 12 hours |
| Formoterol DPI 12 μg/1 Disposable Foradil Aerolizer | There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children under 5 years of age. | One capsule every 12 hours |
| combined asthma medication Fluticasone/Salmeterol DPI 100 ㎍/50 ㎍(Advair Diskus) |
There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children under 4 years of age. | Inhalation therapy twice a day |
| Fluticasone/Salmeterol HFA 45 ㎍/21 ㎍, 115㎍/21㎍, 230㎍/21㎍ (Advair HFA) | There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children under 4 years of age. | There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children under 12 years of age. |
| Budesonide/formoterol HFA MDI 80 ㎍/4.5 ㎍(Symbicort) |
There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children. | 2 puffs twice a day |
| Cromolyn/Nedocromil Cromolyn MDI 제 0.8 mg/puff (Intol inhaler) |
There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children. | 2 puffs 4 times a day |
| Cromolyn Sodium Inhalation Solution 20 mg/ample | 1 ample 4 times a day. There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children under 2 years of age. | 1 ample 4 times a day |
| Nedocromil MDI 제 1.75 mg/puff (Tilade inhaler) | There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children under 6 years of age. | 2 puffs 4 times a day |
| Leukotriene receptor antagonists Montelukast 4-5mg Chewable Tablets; 4mg particulate packet (Singulair) | 4mg before bedtime (for children 1-5 years old) | 5mg before bedtime (children 6-14 years old) |
| Zarfirlukst 10mg tablet (Accolate) | There are no studies on the safety and efficacy of asthma treatment in children. | 10mg twice a day (children 7-11 years old) |
| Methylxanthines Theophylline Solutions, Long-Release Tablets, Capsules (Multiple Products) |
The initial therapeutic dose is calculated as the total daily dose of 10 mg/kg body weight. Usually, the maximum dose is according to the references. | The initial therapeutic dose is calculated as a total daily dose of 10 mg/kg body weight. Usually, the maximum dose is 16 mg/kg of body weight per day. |
|
DPI; Dry powder inhaler (건말 흡입기) HFA; hydrofluroalkane |
||
Source-Update on the 2007 National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
표 3. 소아 천식 컨트롤과 치료약물의 조절 (2007년 미 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 권장)

- FEV1: Forced expiratory volume in 1 second
- FVC: Forced Vital Capacity
- Source-Update on the 2007, National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
Table 4. Comparison of estimated daily doses of inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of childhood asthma (recommended by the American Asthma Education and Prevention Program, 2007)
표 4. 소아 천식 치료용 흡입용 코르티코스테로이드제 1일 추정 용량 비교표 (2007년 미국 천식 교육 및 예방 프로그램 권장)
| Minimum daily dose | Medium daily dose | The maximum daily dose | |
| brand name | 0-4 years 5-11 years | 0-4 years 5-11 years | 0-4 years 5-11 years |
| Beclomethasone HFA 40㎍/Puff or 80㎍(Qvar) |
80~160ug | >160~320ug | >320㎍ |
| Budesonide DPI 90㎍ or 180㎍/inhahation (Pulmicort Flehaler) 200㎍/inhale(Pulmicort Turbuhaler) |
180~400㎍ | >400~800㎍ | >800㎍ |
| Budesonide Inhalation Suspension Dosage of pediatric asthma spray therapy 0.25mg, 0.5mg, 0.5mg/2ml(Pulmicort Respules) |
0.25~0.5mg 0.5mg | >0.5~1mg 1mg | >1.0mg 2.0mg |
| Flunisolide 250㎍/puff(AeroBid) |
500~750㎍ | 1000~1250㎍ | 1250㎍ |
| Flunisolide HFA 80㎍/puff(AeroBid-M) |
160㎍ | 320㎍ | 640㎍ or more |
| Fluticasone HFA/MDI 44㎍, 110㎍, or 250㎍/inhale(Flovent HFA) |
176㎍ 88~176㎍ | >176~352㎍ >176~352㎍ | >352㎍ >352㎍ |
| Fluticasone DPI 50㎍, 100㎍, or 250㎍/inhale(Flovent Diskus) |
100~200㎍ | >200~400㎍ | >400㎍ |
| Mometasone DPI 200㎍/inhale(Flovent Diskus) (Asmanex Twisthaler) |
– – | – – | – – |
| Triamcinolone acetonide 75㎍/puff (Azmacort Inhalation Aerosol) |
300~600㎍ | >600~900㎍ | >900㎍ |
|
HFA- hydrofluoroalkane((dry inhaler) ) DPA-dry poder inhaler |
|||
Source-Update on the 2007, National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
Treatment of pediatric asthma staff (recommended by the 2007 American Asthma Education and Prevention Program)
Table 15. Pediatric asthma step therapy

• ICS: Inhaled corticosteroid (inhaled corticosteroid)
• SABA : Short acting beta 2 – adrenergic agonist – Short acting beta 2 – adrenergic agonist • LABA : Long acting beta 2 – adrenergic agonist – Short acting beta 2 – adrenergic agonist • LTRA : Leukotrine receptor antagonist – Leukotriene receptor antagonist
• Source-Update on the 2007, National asthma education and prevention program. Guidelines for the treatment of asthma in children
• In order to effectively treat any disease, the doctor, the child, and the caregiver must work together as a Trinity.
• In order to effectively treat asthma in children, children and their parents must cooperate responsibly in the treatment of asthma. In particular, the doctor in charge must correctly diagnose and treat asthma properly.
• Parents need to learn and know a lot of medical knowledge about childhood asthma.
• Parents and children are primarily responsible for environmental control of antigens and factors that can trigger asthma attacks.
• In order to properly treat asthma, parents, children, and doctors must be members of a pediatric asthma treatment team to successfully treat childhood asthma.
• If acute asthma is not properly treated, it can progress to chronic asthma. You may suffer a lot from chronic asthma, and in severe cases, you may be on a mission.
• Appropriate treatment is required to prevent acute asthma from progressing to chronic asthma.
• In order to lead a normal life, it is necessary to properly treat asthma attacks and prevent them from occurring.
• Timely treatment of the symptoms of an asthma attack trigger, prevent further asthma with that symptom, maintain normal lung function, prevent recurrence of asthma attacks, and prevent asthma attacks from occurring again. Particular attention should be paid to preventing side effects.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”