질식(가사), Asphyxia (Choking)
질식의 개요
-
여러 가지 원인으로 체내 산소 농도가 정상 이하로 낮고,
-
이산화탄소의 농도가 정상 이상으로 증가되고
-
호흡곤란이 있고,
-
숨을 거의 쉴 수 없고,
-
사망 직전에 이르는 상태를 질식, 또는 가사라고 한다.
-
다시 설명하면, 사망 직전의 호흡곤란 상태를 질식이라 할 수 있다.
-
심한 질식 상태를 즉시 적절히 치료하지 않으면 사망한다.
질식의 원인
-
분만이 하기 전이나 분만 중, 자궁 속에 있던 태아가 여러 가지 원인으로 질식될 수 있고, 또 태어난 후 신생아가 여러 가지 원인으로 질식될 수 있다.
-
질식은 어느 연령층 소아청소년들에게도 생길 수 있다.
-
5세 이전 영유아들에게 질식사고가 더 자주 일어난다.
-
질식 사고는 집 바깥 보다 집안에서 더 잘 일어난다.
-
영유아가 고무풍선을 불고 놀다가 터진 풍선의 조각이 기도 속으로 흡인되어 기도가 폐쇄되어 질식 사망할 수 있다.
-
장난감, 땅콩, 팝콘, 사탕, 그 외 다른 음식물 등이 기도 속으로 잘못 흡인되어 기도가 부분적으로 막히든지 완전히 막힐 때 질식되고 사망할 수 있다.
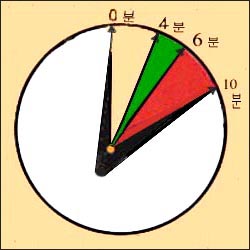
▴ 그림 332. 기도 내 이물로 기도가 막혀 숨을 전혀 쉬지 못할 때는 체내 산소 결핍이 생기고 그로 인해 뇌가 손상되든지 사망할 수 있다. 이물로 막힌 기도(숨통)를 바로 열어 기도 확보를 하고 숨을 정상으로 쉬게 할 수 있는 응급처치를 할 수 있는 시간은 몇 분으로 제한됐다. 기도가 완전히 막혀 숨 쉬지 못하는 상태에 있을 때, 3~4분 이내 뇌가 손상될 수 있지만 4~6분이 지난 후에는 뇌 손상이 생길 수 있고 6~10분이 이후에는 뇌가 완전히 손상된다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
영유아가 밀폐된 냉장고 속이나 자동차 속에 들어가 놀다가 산소결핍으로 질식 사망할 수 있다.
-
심한 선천성 심장혈관 기형, 후천성 심장혈관 질환, 패혈증, 특발성 초자막증(Hyaline Membrane Disease/초자막 질환/ HMD), 자궁 내 태아 산소결핍증, 태변흡입, 익사, 뇌 손상, 뇌출혈, 쇼크, 화재, 자살, 피살 등으로 질식될 수 있다.
-
태아의 목이 탯줄로 꼭 감길 때, 탯줄 매듭, 다른 원인으로 태아가 모체로부터 혈액공급을 충분히 받지 못하거나 산소 공급을 적절히 받지 못할 때 태아가 질식될 수 있다.
-
그 외
이물로 기도 속이 막혀 질식될 때의 증상 징후
-
기도 속이 흡인된 이물로 갑자기 막히면 막힌 기도 이물로 질식될 수 있다.
-
기도 속이 막힌 정도에 따라, 이물의 크기와 종류, 막힌 후 몇 초 내지 몇 분 동안에 생기는 증상 징후, 그 후 몇 시간 내지 몇 년 동안에 생기는 증상 징후, 기도 내 이물로 생긴 염증의 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
기도가 심하게 막힌 후 바로 숨이 가쁘고, 구토하고, 천음(Weezing) 및, 또는 협착음(Stridor)이 생기고, 음성변화, 호흡곤란, 연하곤란 등의 증상 징후가 생기는 것이 보통이다.
-
기도내 이물로 막힌 첫 몇 분 내지 몇 시간 동안, 또는 며칠 내지 몇 달 동안 천식, 기도내 이물을 크루프, 기관지염, 또는 폐렴 등으로 오진할 수 있다.
-
물론, 기도 속이 이물로 심하게 막히면 금방 질식하고 사망할 수 있다.
-
흡입된 기도 내 이물로 질식될 때 증상 징후가 몇 초 내지 몇 분간 지속될 수 있다.
-
기도 내로 이물을 흡인하는 장면을 목격한 사람이 없을 때는 기도 내로 이물이 흡인된지도 모르고 지내다가 늦게서 기도 내 이물을 처음 진단받기도 한다.
질식의 치료
-
질식의 정도, 질식의 원인 등에 따라 다르게 치료 한다.
-
경미하게 질식됐을 때는 질식하게 된 원인을 찾아 원인을 즉시 제거하거나 적절히 치료하고 산소 호흡치료를 하거나 신선한 공기 호흡치료를 한다.
-
그와 동시 질식한 원인과 질식의 정도에 따라 사고 현장에서 응급치료를 한다.
-
누구든지 2∼4분 동안 숨을 쉬지 못하면 질식될 수 있다. 산소 공급 치료를 받지 못하고 계속 질식되면 얼굴이 창백해지고 의식을 잃고 뇌가 손상되고 전신 경련이 유발되고 결국 사망한다.
-
안전사고로 숨을 통 쉬지 못해서 질식되고 의식을 잃을 때는 질식 원인에 따라 응급치료를 바로 시작하고 사고 현장에서 기본 생명유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 하면서 다른 사람의 도움을 청하고, 의료구급대, 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 지시에 따라 사고 현장에서 치료를 시작한다.
-
필요에 따라, 신생아들이나 영아들의 경우, 처치자의 입을 환아의 입과 콧구멍 두 부위에 대고, 유아들이나 학령기 아이들의 경우는, 처치자의 입을 환아의 입에 대고 인공호흡을 하고 심장 마사지를 한다. 즉 기본 생명유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 한다.
-
상황에 따라 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 도움을 받는다.
-
사고 현장에 산소가 있으면 물론 산소 호흡치료를 한다(기도 내 이물, 유아들이나 학령기 아이들이 연기를 흡입했을 때, [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병과 안전사고의 예방–익사사고 예방, 화상사고 예방 참조.)
질식의 예방

▴ 그림 333. 기도 내 이물로 질식되지 않게 예방한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
유아들에게 장난감을 사 줄 때는 장난감이 영유아들이 가지고 놀다가 기도 속으로 흡인되 기도 내로 들어가 질식될 수 있으므로 기도 속으로 흡인될 수 없는 장난감을 사 준다.
-
기도 속으로 흡인될 수 있는 작은 장난감을 영유아가 입에 물고 놀거나, 기도로 흡인될 수 있는 땅콩의 크기의 음식물을 입안에 넣고 먹으면서 뛰어 놀거나, 음식물을 성급하게 먹을 때 음식물이 기도 속으로 흡인해 들어가서 기도 속이 막히면 질식되거나 사망할 수 있다.
-
영유아가 안전사고로 질식되지 않게 예방해야 한다.
-
동전이 기도 속에 들어가 질식될 수 있다.
-
태아나 신생아가 질식되지 않게 산전 임신 건강검진을 잘 받고 의사의 지시에 따라 병원에서 안정하게 분만한다.
Asphyxia (Choking) 질식(가사)
Overview of suffocation
- The oxygen concentration in the body is low below normal due to various reasons,
- The concentration of carbon dioxide increases beyond normal,
- Have trouble breathing,
- They can hardly breathe,
- The condition that reaches just before death is called suffocation or choking.
- In other words, the state of breathing difficulties just before death can be referred to as suffocation.
- Severe choking conditions die if not treated promptly and properly.
Causes of suffocation
- Before or during delivery, the fetus in the womb can be suffocated for various causes, and after birth, the newborn can be suffocated for various reasons.
- Choking can occur in children and adolescents of any age.
- Choking accidents are more common among infants and younger children before the age of five. Choking accidents are more common inside the house than outside the house.
- Infants and toddlers play with a hot air balloon, and a fragment of the balloon that bursts is sucked into the airways, closing the airways, causing suffocation and death.
- Toys, peanuts, popcorn, candy, and other foods are erroneously aspirated into the airways, which can cause suffocation and death when the airways are partially or completely blocked.

▴ Figure 332. When the airway is blocked by a foreign body in the airway and you cannot breathe at all, oxygen starvation occurs in the body, resulting in brain damage or death.
The time for first aid to open airways blocked by foreign bodies, secure airways, and breathe normally, was limited to a few minutes.
When the airway is completely blocked and unable to breathe, the brain may be damaged within 3 to 4 minutes, but after 4 to 6 minutes, brain damage may occur, and after 6 to 10 minutes, the brain is completely damaged. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- Infants and toddlers can die of suffocation from oxygen starvation while playing in a closed refrigerator or car.
- Severe congenital cardiovascular anomaly, acquired cardiovascular disease, sepsis, idiopathic hypersubtitles (Hyaline Membrane Disease/hyaline membrane disease/HMD), fetal oxygen deficiency in the uterus, meconium inhalation, drowning, brain injury, cerebral hemorrhage, shock, fire, suicide,
- You may be suffocated by murder, etc.
- When the fetus’s neck is tightly wrapped with the umbilical cord, umbilical cord knots, or other causes, the fetus may suffocate when the fetus does not receive sufficient blood supply from the mother or does not receive adequate oxygen supply. etc
Symptoms, signs of choking due to a foreign body blockage in the airways
- If the airway is suddenly blocked by a foreign body that is aspirated, it can lead to suffocation with the blocked airway foreign body.
- Depending on the degree of blockage in the airways, the size and type of the foreign body, symptoms that occur several seconds to several minutes after the blockage, symptoms that occur several hours to years thereafter, and the degree of inflammation caused by the foreign body in the airways different.
- Shortly after the airway is severely blocked, symptoms such as shortness of breath, vomiting, wheezing, or stridor occur, and symptoms such as voice change, difficulty breathing, and swallowing are common.
- During the first few minutes to several hours, or days to several months of clogging with a foreign body in the airways, asthma, a foreign body in the airways may be misdiagnosed as croup, bronchitis, or pneumonia.
- Of course, if the inside of the airway is severely blocked with a foreign object, it can quickly suffocate and die.
- Symptoms, signs may last from a few seconds to several minutes when suffocated by a foreign body in the inhaled airway.
- When no one has witnessed a scene where a foreign body is aspirated into the airways, the foreign body inside the airways may be diagnosed for the first time, after not knowing that the foreign body has been aspirated into the airways.
Treatment of suffocation
- Treat differently depending on the degree of suffocation and the cause of suffocation. In the case of mild suffocation, find the cause of suffocation and remove the cause immediately or treat it appropriately, oxygen breathing therapy or fresh air-breathing therapy.
- At the same time, emergency treatment is provided at the accident site depending on the cause of the suffocation and the degree of suffocation.
- Anyone who cannot breathe for 2 to 4 minutes can result in suffocation. If you child continues to suffocate without receiving oxygen therapy, your child’s face becomes pale, loses consciousness, damages the brain, causes systemic cramps, and eventually dies.
- When suffocation and consciousness are lost due to a safety accident, emergency treatment is immediately started according to the cause of the suffocation, and basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed to maintain basic life at the site of the accident.
- In accordance with the instructions of a regular pediatrician or a regular pediatrician, treatment begins at the accident site.
- If necessary, in the case of newborns or infants, place your’s mouth on both the mouth and nostrils of the patient, and in the case of infants or school-age children, put your mouth on the patient’s mouth, perform artificial respiration, and perform heart massage. In other words, basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed to maintain basic life.
- Depending on the situation, seek help from a hospital emergency room or a regular pediatrician.
- If there is oxygen at the accident site, of course, oxygen breathing treatment is provided (when foreign bodies in the airways, infants or school-age children inhale smoke,
- [parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Department of Pediatrics and Family Nursing)]-Volume 2 Children and Adolescent Diseases and Safety Prevention of accidents-Refer to Prevention of Drowning Accidents,
Prevention of suffocation

▴ Figure 333. Prevent suffocation from foreign objects in the airways. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- When buying toys for infants, buy toys that cannot be sucked into the airways because the toys are sucked into the airways and suffocated when they play with them.
- Infants and toddlers play with small toys that can be sucked into the airways in their mouths, play while eating peanuts-sized food in their mouths that can be sucked into the airways, or when food is hastily eaten, food is sucked into the airways.
- If It enters and blocks your airways, your child may suffocate or die. Infants and toddlers should be prevented from suffocating in safety accidents.
- Coins can get into the airways and suffocate.
- To prevent suffocation of the fetus or newborn, receive a good prenatal pregnancy health checkup and deliver a stable delivery in the hospital according to the doctor’s instructions.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- 심폐 소생술(CPR)–www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 신생아 심폐 소생술--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 호흡곤란--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 콧구멍 속 이물, 비강 속 이물, 외비공의 이물--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 기도 속에 이물이 들어갔을 때와 질식--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 하임리크 처치법--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 생선가시가 목구멍 속에 걸렸을 때--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 소화기 속 이물, 소화관내 이물, 위장관 내 이물--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- 신생아 질식, 신생아 가사--www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.94, 269
- Nelson textbook, 14 edition, p.458-459
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Red book 29th-31st edition 2012
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
소아과학 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”
