종기(농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창 Abscess, Furuncles, Folliculitis, Carbuncles
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Chapter 7, Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or 제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
종기(농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창의 개요
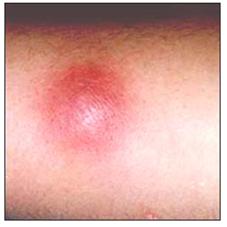
사진 2-51. 팔에 난 황색 포도상구균 종기
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
세균이 모낭에 감염되면 모낭이 곪으면 모낭염(Folliculitis)이라고 한다.
-
세균이 모낭에 감염되고 그 부위 피부층에 염증이 생기고 거기에 고름이 잡히고 피하 연 조직이 괴사되는 염증을 종기(Boils), 농양(Abscess)이라고 한다.
-
여러 개의 종기가 모여 생긴 큰 종기를 종창(Carbuncles)이라고 한다.
-
종기는 황색 포도상구균(Staphylococcus aureus), A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균(A군 연구균), 대장균, 곰팡이(진균), 임질균, 에르시니아균, 머락셀라균, 결핵균, 백트로이드균, 묘소병을 일으키는 Bartonella henselae 세균 등의 감염으로 생길 수 있다.
-
종기의 주 원인이 되는 세균(박테리아)은 황색 포도상구균이다.
-
황색 포도상 구균이 피부층의 진피, 모낭과 피하 연 조직에 감염되어 생긴 국소적 피부층과 피하 연조직 감염병을 프룽클(Furuncles/뾰루지/깊은 농포/종기)라고도 한다.
-
프릉클의 경계는 명확하고 압통이 있는 피부 감염병이다.
-
이물이 신체의 국소에 있으면 박테리아가 거기에 감염되고 고름이 잡히며 고름 주머니 니가 형성된다.
-
고름 주머니 니 속 세균이 그 주위 다른 조직으로 더 이상 퍼져 나가지 못하게 고름 주머니 니에 방어벽이 형성된다. 이런 감염병을 농양(Abscess)이라 한다.
-
이상 설명한 종기, 큰 종기, 농양, 프릉클 등을 임상적으로 이렇게 구분할 수 있지만 그것들을 통틀어 그냥 종기라고 부르기도 한다. 여서도 같은 의미로 쓴다.
종기(농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창의 원인
-
황색 포도상구균이 정상 피부 층에 감염되면 종기가 날 수 있다.
-
그러나 긁히거나 베이거나 찔리거나 불결하거나, 또는 모기 등 곤충에 물린 피부 상처를 통해 황색 포도상구균이 피부 층과 피하 연 조직 깊숙이 감염될 때 종기가 날 수 있다.
-
과거에는 종기가 아주 흔한 감염성 피부질환 중 하나 이였다. 요즘은 위생관리를 잘 하기 때문에 종기가 잘 나지 않는다.
-
또 종기가 나더라도 조기 항생제 치료로 심한 종기는 드물다.
-
찰과상, 곤충 물림, 못 찔림 상처, 가려움 피부 상처, 체부 면도,, 남의 면도기 사용, 남이 쓴 불결한 타월 등으로 황색 포도상구균이 피부 층에 감염되어 종기가 날 수 있다.
-
아토피성 피부염이 있는 아이들의 피부 층에 황색 포도상구균 감염이 더 잘 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 종기나 봉소염, 농가진이 더 생길 수 있다(p.65 참조).
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제17권 소아청소년 피부질환–습진, 아토피성 피부염 참조.
-
그렇지만 아직도 위생시설이 미비한 후진국 아이들에게 종기는 흔한 박테리아 감염성피부질환의 하나로 남아 있다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 및 질환–신생아 농가진, 농가진 참조.
-
커뮤니티 관련 메티실린(Methcillin) 내성 포도상구균(CA-MRSA) 감염으로 생긴 직경 5cm 이하 되는 종기는 항생제로 치료하는 것보다 외과적 절개 배농 치료를 권장한다. 출처-Pediatric News, March 2004.
종기(농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창의 증상 징후
-
종기가 난 신체의 부위와 종기의 크기 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
종기는 깨알만큼 작은 것부터 달걀 크기만 한 것도 있다.
-
종기가 날 때 가렵고 따끔거리고 욱신욱신 아플 수 있고,
-
손으로 누르면 몹시 아플 수 있다.
-
처음 시작할 때는 피부 층의 표면 레벨과 거의 같게 납작하게 나고 색이 붉지만, 불과 몇 시간 사이에 피부 층의 표면 위로 솟아날 수 있고 그 후 점점 더 커지는 것이 보통이다.
-
하루 이틀 지나면 종기의 중앙 부위가 종기의 다른 부위보다 더 빨갛고 뾰족하게 부어 솟아나고 종기 속에 노란 고름이 잡힌다.
-
종기가 다 곪은 후 종기가 자연히 터지면서 거기서 피고름이 흘러나올 수 있고 어떤 때는 그러다가 자연히 나을 수 있다.
-
고름 주머니 속에 있는 황색 포도상구균이 그 근처 정상 피부 층과 피하 조직으로 점차로 감염되어 원래 난 종기 주위에 여러 개의 새 종기들이 더 날 수 있다.
-
그래서 큰 종기가 될 수 있다. 이런 큰 종기를 종창이라고 한다.
-
종기는 신체의 어느 부위에 있는 피부 층에 날 수 있으나 목·겨드랑이·유방·팔다리·얼굴·귀 등의 피부에 더 잘 난다.
-
조그마한 종기가 외이도 속이나, 콧등이나 콧구멍 근처, 또는 얼굴의 중앙 부위에 났을 때 좀 더 욱신욱신 쑤시고 더 아플 수 있다.
-
황색 포도상구균에 의해서 종기가 날 때 종기를 일으킨 포도상구균이 신체 다른 부위로 더 이상 퍼지지 않도록 종기 고름 주머니의 전체를 국소적으로 둘러싸는 종기 고름 주머니 니에 방어벽이 정상적으로 형성된다.
-
종기 고름 주머니를 손으로 눌러 짜면 종기 고름 주머니 니를 둘러싼 방어벽이 무너지면서 종기 고름 주머니 속에 있던 포도상구균과 고름이 주위 조직으로 퍼질 수 있고 혈류를 따라 신체의 다른 부위로 퍼질 수 있다.
-
그래서 포도상구균이 피부·폐·뼈·뇌 등 신체의 여러 계통의 다른 기관과 조직으로 퍼져나갈 수 있고 거기서 뇌막염·패혈증·골수염 등 포도상구균 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 이유로 종기를 손으로 눌러 짜서는 안 된다.
종기(농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창의 진단
-
병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 진단할 수 있다.
-
종기에서 고름이나 피고름 또는 그 외 피검물을 채취해서 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균 배양검사를 하면 어떤 종류의 황색 포도상구균이 종기를 일으켰는지 알 수 있다.
-
그리고 황색 포도상구균이 “D 테스트“로 메티실린(Methcillin) 내성이 있는지 알아본다.
종기(농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창의 치료 및 예방
-
종기의 크기와 중증도, 종기가 난 신체의 부위 등에 따라 치료 방법이 다르다.
-
아주 작은 종기는 인체 면역 방어 체계에 의해 자연적으로 치유될 수 있다.
-
고름이 잡힌 농양은 다음과 같은 방법으로 치료한다.
-
농양을 절개하고 농을 빼주는 치료를 하든지
-
농양을 절개하고 농을 빼주고 Dicloxacillin이나 Cephalexin 등 항 황색 포도상 구구균 항생제 치료를 하든지
-
농양을 절개하고 농을 빼주고 Methicillin 내성 황색 포도상구균에 대한 Clindamycin 이나 Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 항생제로 치료한다.
-
출처; NEJM Sep 2008 p.1063
-
적기에 적절히 치료해 주지 않으면 종기 고름 주머니 속에 있는 황색 포도상구균이 주위에 있는 다른 피부 층과 피하 연 조직으로 계속 감염되어 새 종기가 날 수 있다.
-
어떤 종기는 자연히 낫지 않고 점점 더 커질 수 있다.
-
아프고 빨갛게 붓고 더 심하게 곪아서 종창(腫瘡/Carbuncle)이 된다.
-
평소에 몸을 청결히 하고 위생관리를 잘 해서 종기가 나지 않도록 예방하는 데 힘써야 한다.
-
모기 등 곤충에 물리지 않도록 주의 한다.
-
곤충에 물렸을 때는 곤충에 물린 피부를 베타다인 액 살균제로 예방 치료를 한다.
-
종기가 처음 시작할 때는 의사의 처방에 따라 파이소헥스(pHisoHex) 액 살균제나 베타다인 액 살균제, 또는 박트로반 항생제 연고를 1일 2∼4회 3, 4일간 발라 치료하면 잘 낫는다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과] 제21권 소아청소년 가정간호 및 학교 건강 참조).
-
종기가 난지 얼마 되지 않았을 때나 거의 다 곪았을 때는 더운물 찜질을 1회 5∼10분 동안 하루에 3, 4회 정도 하면 종기가 더 빨리 더 잘 곪고, 곪은 종기를 수술 칼로 째고 고름을 빼어 치료할 수 있다.
-
파이소헥스 액 살균제로 치료하거나 박트로반 항생제 연고 등을 1일 2~3회 10일 동안 종기에 발라 치료할 수 있다.
-
종기가 난 주위의 피부로 계속 번져 여러 개의 종기가 동시 났을 때나 종기가 나면서 열이 날 때, 비교적 큰 종기가 얼굴이나 콧등, 또는 콧구멍 근처에 났을 때는 의사의 처방에 따라 경구용 옥사실린이나 다른 적절한 항생제로 치료 할 수 있다.
-
더운물찜질을 하고 박트로반 항생제 연고나 파이소헥스 액 살균제를 발라 치료한다. 고름 주머니 니가 완전히 잡힌 종기는 수술 칼로 째서 고름을 빼준다.
-
종기를 일으킨 황색 포도상구균은 감염성이 매우 강하다.
-
따라서 환자 자신은 물론 다른 사람들에게 황색 포도상구균이 더 이상 감염되지 않도록 주의해야 한다.
-
특히 짠 피고름이나 흘러나온 고름을 닦은 거즈나 치료할 때 쓴 의료 기구 등을 맨손으로 만져서도 안 된다.
-
그 때 사용한 거즈는 태우거나 잘 싸서 버려야 한다.
-
의사의 처방에 따라 적절한 항생제로 치료한다.
-
메티실린에 내성 있는 황색 포도상구균(Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus) 감염으로 생긴 종기는 Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, Minocyclin, 또는 Clindamycin 등으로 치료하기도 한다.
-
수건, 면도, 비누, 화장도구 등을 같이 쓰지 않는다.
-
피부에 상처가 생기면 물과 비누로 깨끗이 닦고 적절히 예방 후 치료 한다.
-
Chlohexdine이나 황색 포도상구균을 죽일 수 있는 비누를 적절히 사용한다.
-
Mupirocin 연고(박트로반 연고)를 콧구멍 속과 그 주위에 바른다.
-
손을 깨끗이 씻는다.
-
예방접종 백신은 없다.
종기(농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창의 합병증
-
포도상구균이 신체 다른 부위로 자가 감염될 수 있다.
-
균혈증이나 패혈증.
-
폐, 신장, 간장, 내장 등에 농양.
-
골수염이 .
-
심내막염이 .
-
뇌 농양.
-
척수 농양.
-
그 외.
-
합병증 참조
|
다음은 “종기가 심해요..”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 종기가 심해요..
Q.
메일을 보내긴 했는데 도착이 됐는지 몰라서 다시 내용을 올립니다.
저희 애기는 16개월 된 여아인데 벌써 3번째 사타구니에 종기가 났어요.
보통종기가 아니라 엄청 크고 또 고름도 엄청 많이 나왔습니다.
여긴 모스크바인 관계로 병원을 가도 명쾌한 해답을 얻을 수가 없어요. 그리고 병원에 갔을 때는 단순한 기저귀에서 온 감염이라고 했어요.
양쪽 사타구니에 번갈아서 3번이나 종기가 나고 있는데 어떤 원인이고, 어떻게 처방해야 하는지 알려주세요. 사실 염려 되는 건 다음에 종기가 또 재발하지는 않을지 입니다.
답변 부탁드립니다.
A.
원희님
안녕하십니까. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이와 성별, 과거 현재 가족의 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견, 적절한 임상검사 등의 결과를 종합해서 진단 치료하는 것이 이상적이지만 주신 정보를 참작해서 답변을 드립니다.
종기는 황색 포도상구균, A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균, 대장균, 곰팡이, 임질균, 에르시니아균, 머락셀라균, 결핵균, 백트로이드균, 묘소병을 일으키는 세균, 또는 그 외 세균 중 한 종류나 몇 종류에 의한 피부 층 및 피부 층 바로 아래에 있는 피하 조직(연조직)에 생긴 박테리아 국소적 감염병입니다.
이상 설명한 세균들이 감염되는 경로는 세균의 종류에 따라 다소 다릅니다.
여기서 주로 황색 포도상구균에 의한 종기에 관해서 설명을 드리겠습니다.
황색 포도상구균은 감염성이 상당히 강해서 한 부위에 생긴 종기 고름주머니에 있는 황색 포도상구균이 신체의 다른 부위로 쉽게 감염될 수 있습니다.
황색 포도상구균은 손, 호흡기계통 등을 통해서 본인이 자신에게 자가 감염을 시킬 수도 있고 다른 사람이 다른 사람에게 감염시킬 수 있습니다.
황색 포도상구균은 건강한 소아청소년들이나 성인들의 피부, 인두 점막, 콧구멍, 비강, 회음부 등에 상존할 수 있습니다.
피부상처, 불결한 피부, 기저귀 피부염, 곤충 물림, 긁힌 피부상처 등 피부 손상을 통해서 감염되는 경우가 흔합니다.
종기의 치료는 종기가 난 부위, 종기가 곪은 정도, 종기의 수 등에 따라 다르고, 종기가 난 환아들의 나이에 따라 달리 치료합니다.
종기가 곪지 않은 상태에 있을 때는 온 습포 찜질은 10~15분간 1일 3~4회, 3~4일간 하면 자연히 나을 수 있습니다.
또는 필요에 따라 옥사실린(Oxacillin), 나프실린(Nafcillin), 세파졸린(Clindamycin) 등의 항생제 중 한 종류를 선택해서 경구 복용치료를 하거나 주사치료를 합니다.
요즘 세계적으로 황색 포도상구균이 항생제에 내성이 생겨 항생제로 잘 치료되지 않는 경향이 있습니다.
그러므로 가능한 한 항생제 치료를 시작하기 전 환부에서 채취한 피검물로 세균 배양 검사를 하고 세균 감수성 검사를 하면서 적절한 항생제로 치료를 시작하는 것이 이상적입니다.
위에 말씀드린 항생제 이 외 다른 종류의 항생제 중 2~3가지 항생제를 동시 써서 치료할 수도 있습니다.
종기가 곪았을 때는 종기를 수술로 고름 주머니 속 고름을 빼고 경구 항생제나 주사 항생제로 5~10일 동안 치료할 수 있습니다.
환부를 맨손으로 만져서는 안 됩니다.
꼭 장갑을 끼고 만져야 합니다.
한번 쓴 장갑이나 거즈 등은 태우든지 다른 사람들에게 감염되지 않도록 버려야 합니다.
이런 복잡한 치료는 어디까지나 의사에게 맡겨야 합니다.
황색 포도상구균은 종기 이 외 골수염, 관절염, 폐렴 등을 일으킬 수 있습니다.
자녀의 경우 왜 세균감염이 사타구니에 생기었는지 이유도 알아야 합니다.
가령 그 부위에 물리적 손상을 입힐 수 있는 타는 놀이를 하는지, 아토피성 피부염이 있는지, 당뇨병이 있는지 등을 알아야 합니다.
종기 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
다음은 “종기, 습진 때문..”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 2 입니다. |
Q&A. 종기, 습진 때문에….
Q.
캐나다에 살고 있는 6살짜리(한국나이로는 7살) 아이 엄마입니다.
5살 무렵부터 아토피가 심하게 드러나서 1년간 고생을 하다가, 지금은 조금 좋아졌습니다.
그런데, 종기가 참 많이 납니다. 어릴 적부터 간혹 나기는 하였지만, 너무도 심해요.
병원에서 처방해준 피부약 때문인지, 요즘은 종기를 달고 다니는 것 같습니다. 왜 그렇죠?
A.
민영님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다. 답이 휴가로 늦어 죄송합니다.
아이의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
종기는 황색 포도상구균이나 A군 연구균, 또는 황색 포도상구균과 A군 연구균 등 두 세균 감염으로 피부층과 피하 조직에 생기는 일종의 박테리아 감염병입니다.
아무런 상처가 없는 피부에도 종기가 날 수 있지만 특히 긁어서 생긴 피부 외상이나 다른 원인으로 생긴 피부 외상 등을 통해서 포도상구균 등의 세균 감염이 생기면 종기가 날 수 있습니다.
콧구멍의 언저리에 황색 포도상구균이 상존합니다.
세균 감염으로 콧구멍 언저리에 종기가 잘 생길 수 있고 몸 다른 부위에도 황색 포도상구균 종기 등이 생길 수 있습니다.
따님의 경우, 아토피성 피부염으로 가려우면 긁고, 긁으면 상처가 생기고, 그 상처를 통해 피부층 세균 감염으로 종기가 생길 수 있습니다.
피부 펩티드(Peptide)는 피부 층에 정상적으로 있으면서 화농성 세균성 피부염이 생기지 않게 예방해주는 역할을 합니다.
아토피성 피부염 병력이 있는 아이들의 피부에는 피부 펩티드의 농도가 비정상적으로 낮기 때문에 그로 인해 화농성 세균성 피부염이 더 잘 생길 수 있습니다.
또 아토피성 피부염으로 자주 긁기 때문에 피부가 더 자주 손상되어 화농성 피부염이 더 잘 생깁니다.
아토피성 피부염을 적절히 잘 치료하고 아토피성 피부염이 있는 피부가 곪았다고 의심이 되면 적절한 항생제 등으로 곧 치료하고 평소에 손을 깨끗이 씻고 손톱을 짧게 깎아 피부에 상처를 내지 않게 하는 것이 종기를 예방하는 방법의 일부입니다.
종기의 초기에 박트로반 연고로 치료하면 종기가 잘 치료됩니다.
파이소헥소 액(헥사클로로펜) 살균제로 치료해도 잘 치료됩니다.
저 자신도 아토피성 피부염을 가지고 있는데 화농성 피부감염이 시작될 때 파이소헥스 액 살균제를 한두 번 바르면 더 이상 진행되지 않습니다. 이 약은 의사의 처방에 따라 사용해야합니다. 참고로 말씀드립니다.
아직도 증상 징후가 계속되면 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단을 받으시고 이 문제에 대해서 상담하시기 바랍니다.
종기.
제17권 소아청소년 피부질환–아토피성 피부염,
제21권 소아청소년 가정간호 및 학교 간호–헥사클로로펜(파이소헥소액) 살균제 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Abscess, Furuncles, Folliculitis, Carbuncles (농양), 프릉클(뾰루지/깊은 농포), 모낭염, 종창
Overview of boils (abscesses), Furuncles (rashes/deep pustules), folliculitis, swelling

Photo 2-51. Staphylococcus aureus boil on the arm Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• When bacteria infect the hair follicle, it is called folliculitis when the follicle festers.
• Inflammation in which bacteria infect hair follicles, inflammation of the skin layer in the area, pus is trapped there, and necrosis of the subcutaneous soft tissue are called boils and abscesses.
• Large boils formed by multiple boils are called carbuncles.
• Boils include Staphylococcus aureus, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (group A research bacteria), E. coli, fungi (fungi), gonorrhea, Erysinia, Moraxella, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Bactoloid, Cattle disease It can be caused by infections such as the bacterium Bartonella henselae, which causes the disease.
• The main cause of boils (bacteria) is Staphylococcus aureus.
• Localized skin layer and subcutaneous soft tissue infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus infects the dermis, hair follicles and subcutaneous soft tissues of the skin layer, also known as Furuncles/Pustules/Deep Pustules/Boils.
• Prunkle’s boundary is a clear, tender skin infection.
• If a foreign body is local to the body, bacteria can infect it, catch pus, and form pus pockets.
• A barrier is formed in the pus sac to prevent the further spread of bacteria in the pus sac to other tissues around it. This infectious disease is called an abscess.
• The above-described boils, large boils, abscesses, and Furuncles can be clinically classified in this way, but they are also referred to as boils collectively. Yeoseo also uses the same meaning. Causes of boils (abscesses), Furuncles (rashes/deep pustules), folliculitis, swelling
• Staphylococcus aureus can cause boils when infected with normal skin layers.
• However, boils can occur when Staphylococcus aureus is injected deep into the skin layer and subcutaneous soft tissue, through scratched, cut, stabbed, dirty, or insect-bite skin wounds such as mosquitoes.
• In the past, boils were one of the most common infectious skin diseases. These days, because the hygiene is well maintained, the boil does not come out well.
• Even if you have a boil, severe boils are rare with early antibiotic treatment.
• Staphylococcus aureus can infect the skin layer and cause boils, such as abrasions, insect bites, nail puncture wounds, itchy skin wounds, shaving on the body, using someone else’s razor, or a dirty towel worn by others.
• Staphylococcus aureus infection is more likely to develop on the skin layers of children with atopic dermatitis, which can lead to more boils, cellulitis, and impetigo (see p.65).
• [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Pediatric and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 17 Child and Adolescent Skin Diseases-Refer to eczema, atopic dermatitis.
• Nevertheless, boils remain a common bacterial infectious skin disease in children in underdeveloped countries with poor hygiene facilities.
• [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 6 Newborn growth and development and disease-Newborn impetigo, refer to impetigo.
• For community-related methicillin-resistant staphylococcal aureus (CA-MRSA) infection, boils less than 5 cm in diameter are recommended for surgical incisional drainage rather than antibiotic treatment. Source-Pediatric News, March 2004. Symptoms of a boil (abscess), Furuncles (rash/deep pustules), folliculitis, swelling
• Symptoms differ depending on the area of the body where the boil is and the size of the boil.
• Some boils are small enough to be sesame seeds to the size of an egg.
• It can be itchy, tingling and sore when a boil occurs,
• It can be very painful when pressed with your hand.
• At first start it is flattened and reddish in color, about the same as the surface level of the skin layer, but can rise above the surface of the skin layer in just a few hours, and then it usually gets bigger and bigger.
• After a day or two, the central part of the boil is redder and sharper than the other parts of the boil, swelling, and yellow pus is caught in the boil.
• After the boil is fully festered, the boil spontaneously bursts, and blood pus may ooze from there, and sometimes it can heal naturally.
• Staphylococcus aureus in the pus pouch can gradually infect the nearby normal skin layer and subcutaneous tissue, causing several more new boils to grow around the original boil.
• So it can be a big boil. Such a large boil is called swelling.
• Boils can spread to any part of the body’s skin layers, but they are more common on the skin such as the neck, armpits, breasts, limbs, face, and ears.
• Small boils in the ear canal, near the nostrils or nostrils, or in the center of the face may make it more sore and more painful.
• When a boil is caused by Staphylococcus aureus, a protective wall is normally formed on the boil pus sac, which locally surrounds the entire boil sac so that the staphylococcus aureus that caused the boil does not spread to other parts of the body.
• Hand pressing the boil pus pouch breaks down the barrier surrounding the boil pus pouch, allowing staphylococcus and pus in the boil pus pouch to spread to surrounding tissues and to other parts of the body along the bloodstream.
• So, staphylococcus can spread to other organs and tissues in various systems of the body, such as skin, lungs, bones, brain, and staphylococcal infections such as meningitis, sepsis, and osteomyelitis.
• For this reason, the boil should not be squeezed by hand. Diagnosis of boils (abscesses), Furuncles (rashes/deep pustules), folliculitis, swelling
• You can diagnose this disease by combining your medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
• Collecting pus, blood pus, or other specimens from the boil and performing a gram-staining microscopic bacteriological examination or bacterial culture test will reveal which type of Staphylococcus aureus caused the boil.
• Then check if Staphylococcus aureus is resistant to methicillin with the “D test”. Treatment and prevention of boils (abscesses), Furuncles (rashes/deep pustules), folliculitis, swelling
• The treatment method differs depending on the size and severity of the boil and the part of the body where the boil has occurred.
• Very small boils can be healed naturally by the body’s immune defense system. • An abscess in which pus is caught is treated in the following ways.
• whether to incise the abscess and remove the abscess.
• The abscess is incised, the abscess is removed, and anti-S. aureus antibiotics such as Dicloxacillin or Cephalexin are given.
• The abscess is incised, the pus is removed and treated with Clindamycin or Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole antibiotics against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. • source; NEJM Sep 2008 p.1063
• If not properly treated in a timely manner, Staphylococcus aureus in the boil pus bag can continue to infect other layers of skin and subcutaneous soft tissue around it, resulting in a new boil. • Some boils don’t heal naturally and can get bigger and bigger.
• It hurts, red, swollen, and festers more severely, resulting in swelling (腫瘡/Carbuncle). • You should try to prevent boils by keeping your body clean and hygienic on a regular basis. • Be careful not to be bitten by insects such as mosquitoes.
• In case of insect bites, preventive treatment of insect bites with betadine liquid disinfectant.
• When the boil first begins, according to the doctor’s prescription, apply pHisoHex solution disinfectant, betadine solution disinfectant, or Bactroban antibiotic ointment 2 to 4 times a day for 3 or 4 days to heal. Also, you must be an anti-doctor-Pediatric Family Nursing Encyclopedia] Refer to Vol. 21, Family Nursing and School Health for Children and Adolescents). • When the boil has not yet come on or is almost completely festered, apply hot water for 5-10 minutes 3 or 4 times a day for 5 to 10 minutes to make the boil fester faster and more quickly, and the festered boil can be treated by slicing it with a surgical knife and removing pus. have.
• Treatment with Phisohex liquid disinfectant or Bactroban antibiotic ointment can be applied to the boil 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
• When multiple boils are simultaneously spreading to the skin around the boil, or when a fever occurs with a boil, or when a relatively large boil is on the face or nose, or near the nostrils, use oral oxacillin or oral oxacillin according to the doctor’s prescription. It can be treated with other suitable antibiotics.
• Treat with hot water and apply Bactroban antibiotic ointment or Phisohex liquid disinfectant. The boil in which the pus pocket teeth are completely caught is removed with a surgical knife.
• Staphylococcus aureus, which causes boils, is highly infectious. • Therefore, care must be taken to prevent further infection of Staphylococcus aureus to others as well as to themselves.
• In particular, don’t touch salty blood pus, gauze to wipe out spilled pus, or medical equipment used for treatment with your bare hands.
• The gauze used at that time should be burnt or well wrapped and discarded.
• Treat with appropriate antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor.
• Boils resulting from methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection may be treated with Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, Minocyclin, or Clindamycin.
• Do not share towels, shaving, soap, and makeup tools.
• If there is a wound on the skin, clean it with water and soap, and properly prevent and treat it.
• Use chlorohexidine or soap that can kill Staphylococcus aureus properly.
• Apply Mupirocin ointment (Bactroban ointment) in and around the nostrils.
• Wash your hands thoroughly.
• There is no vaccination vaccine. Complications of boils (abscesses), pruncles (rashes/deep pustules), folliculitis, swelling
• Staphylococcus can infect itself to other parts of the body.
• Bacteremia or sepsis.
• Abscesses in the lungs, kidneys, liver, and intestines.
• Osteomyelitis.
• Endocarditis.
• Brain abscess.
• Spinal cord abscess.
• etc.
• See complications
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer for “I have severe boils..”
Q&A.
The boil is severe.
Q.
I sent an e-mail, but I do not know if it has arrived, so I will post the content again. My baby is a 16-month-old girl, and she already had a boil in her third groin. It’s not a normal boil, but it’s really big and there’s a lot of pus out there.
Since this is Moscow, I can’t get a clear answer even if I go to the hospital. And when I went to the hospital, he said it was an infection from a simple diaper.
There are three boils in both groins alternately. Please tell me what is the cause and how to prescribe it. In fact, what I worry about is whether the boil will return again next time. please answer my question.
A.
Wonhee Hello. Thanks for asking. Ideally, diagnosis and treatment should be performed by synthesizing the results of the child’s age and gender, past and present family medical history, symptom signs and medical examination findings, and appropriate clinical examinations, but we will respond with the information given in consideration. Boils are Staphylococcus aureus, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, Escherichia coli, fungi, gonorrhea, yersinia, Moraxella, tuberculosis, bacteroid, bacteria that cause cat disease, or one or several types of other bacteria It is a local infectious disease caused by bacteria in the skin layer and the subcutaneous tissue (soft tissue) just below the skin layer.
The path through which the above-described bacteria are infected is somewhat different depending on the type of bacteria.
Here I will explain mainly about boils caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylococcus aureus is highly infectious, so Staphylococcus aureus in a boil pus sac from one area can easily infect other areas of the body.
Staphylococcus aureus can self-infect itself through the hand or respiratory system, or other people can infect other people.
Staphylococcus aureus can exist on the skin, pharyngeal mucosa, nostrils, nasal cavity, and perineum of healthy children and adolescents or adults. Infection is common through skin damage, such as skin wounds, unclean skin, diaper dermatitis, insect bites, and scratched skin wounds.
The treatment of boils differs depending on the area where the boil has spread, the degree of festering of the boil, and the number of boils, and is treated differently depending on the age of the children with boils.
When the boil is not festered, warm compresses can be healed naturally by applying warm compresses for 10 to 15 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day, for 3 to 4 days. Or, if necessary, select one of antibiotics such as Oxacillin, Nafcillin, Clindamycin, etc., and receive oral treatment or injection treatment. These days, Staphylococcus aureus has become resistant to antibiotics worldwide and tends to be poorly treated with antibiotics. Therefore, it is ideal to start treatment with appropriate antibiotics while performing a bacterial culture test with the specimen collected from the affected area and performing a bacterial susceptibility test as much as possible before starting antibiotic treatment. In addition to the antibiotics mentioned above, two to three antibiotics may be used at the same time among other types of antibiotics.
When the boil is festered, the boil can be treated with an oral antibiotic or injection antibiotic for 5 to 10 days after removing the pus from the pus bag through surgery. Do not touch the affected area with your bare hands. Be sure to wear gloves and touch them. Once worn, gloves or gauze should be discarded so as not to burn or infect others. This complex treatment should be left to the doctor.
In addition to boils, Staphylococcus aureus can cause osteomyelitis, arthritis, and pneumonia. In the case of children, you should also know why the bacterial infection has occurred in the groin. For example, you need to know if you are playing a ride that can cause physical damage to the area, if you have atopic dermatitis, if you have diabetes. Please see boils, etc. If you have more questions, please visit again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won. MD
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question-and-answer example 2 on “due to boils, eczema..”. \
Q&A. Because of a boil, eczema….
Q.
I am a mother of a 6-year-old (7-year-old in Korean age) living in Canada. Since she was 5 years old, she has been exposed to severe atopy, and she has struggled for a year, and now she is a little better. However, there are a lot of boils. She has been born from time to time since she was a child, but it is too severe. Maybe it’s because of the skin medicine prescribed by the hospital, but these days I seem to have a boil. Why?
A.
Minyoung Good morning. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question. Sorry for the late answer due to vacation. The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer.
We will respond based on the information you provided. Boils are a type of bacterial infection that occurs in the skin layer and subcutaneous tissue due to two bacterial infections: Staphylococcus aureus, group A research bacteria, or Staphylococcus aureus and group A research bacteria.
Boils can also occur on unscathed skin, but if bacterial infections such as staphylococcus aureus occur through skin trauma caused by scratching or other causes, the boil can occur. Staphylococcus aureus resides on the periphery of the nostrils. Bacterial infections can lead to boils around the nostrils and Staphylococcus aureus boils in other parts of the body.
In the case of a daughter, if it is itchy due to atopic dermatitis, it may scratch, and if it is scratched, a wound may occur, and a boil may occur due to bacterial infection of the skin layer through the wound.
Skin peptides are normally in the skin layer and play a role in preventing the development of purulent bacterial dermatitis. Children with a history of atopic dermatitis have abnormally low levels of dermal peptides in the skin, which may make them more likely to develop purulent bacterial dermatitis.
In addition, because of frequent scratching with atopic dermatitis, the skin is damaged more often and purulent dermatitis is more prone.
Atopic dermatitis is treated properly and if you suspect that the skin with atopic dermatitis has festered, immediately treat it with appropriate antibiotics, etc. It is a part of. Treatment with Bactroban ointment in the early stages of the boil will heal the boil well.
Treatment with Phisohex solution (hexachlorophene) disinfectant also cures well.
But no more available.
I myself have atopic dermatitis, but when purulent skin infection begins, I apply Phisohex liquid disinfectant once or twice and it will not proceed anymore. This drug should be used as prescribed by your doctor.
I will tell you for your reference. If symptoms still persist, seek medical advice at the Department of Pediatrics and adolescents, and consult about this problem. boil. Volume 17 Skin Diseases in Children and Adolescents-Atopic Dermatitis, Please refer to Volume 21, Child and Adolescent Home Nursing and School Nursing-Hexachlorophene (Phisohexo), Disinfectant, etc. If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won . MD
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”