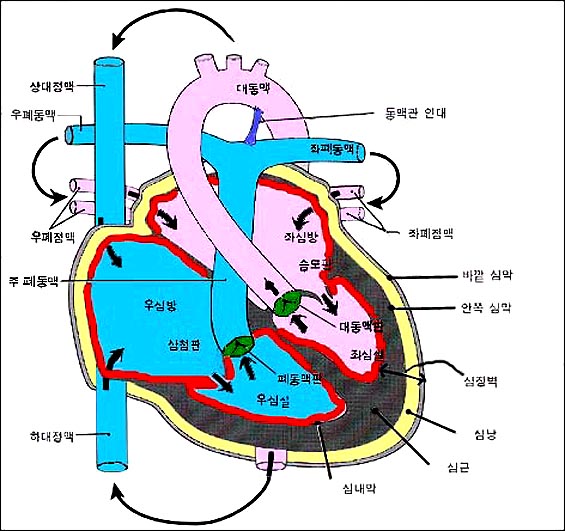
그림 74. 심장 혈관,심장 판막, 심장벽, 심장혈관 혈류의 흐름 방향
빨간 색으로 표시된 부위가 심장 내막이다.
소스; 소아가정간호백과와
Used with permission from Ross Laboratories Columbus, OH, USA
- 전염성(감염성) 심장내막염의 원인 증상 진단 치료에 관해 이미 앞서 설명했다.
- 여기에서는 전염성 심내막염을 항생제 예방적 치료 방법에 관해 주로 설명한다.
- 대부분의 선천성 심장 기형이나 인공 심장판막 등을 가진 아이에게는 전염성 심장내막염이 생길 가능성이 더 많다.
- 따라서 선천성 심장기형을 가지고 있는 아이들의 부모들은 자녀들이 전염성 심장내막염에 걸리지 않도록 예방해 주는 방법에 대해서 잘 알아야 한다.
- 선천성 심장기형 등을 가진 아이가 이를 뽑는 치료를 받거나, 입안, 아데노이드, 편도, 위장관, 비뇨기 등을 수술 치료를 받는 도중 수술 받는 병소 등에 있던 박테리아가 핏속으로 들어가 심내막에 감염되어서 감염성 심장내막염을 일으킬 수 있다.
- 부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가장간호 백과 제2권 소아청소년 질병 및 안전 사고 예방-항생제나 설파제 등으로 전염병을 예방할 때 참조
- 작은 심방중격 결손이나 그 외 몇 종류의 선천성 심장기형을 제외한 거의 모든 선천성 심장기형이 있는 아이들이 앞서 설명한 수술을 받을 때는 의사의 처방에 따라 페니실린, 에리스로마이신, 반코마이신, 스트렙토마이신, 앰피실린, 겐타마이신 등 여러 종류의 항생제들 중 한 가지 또는 두세 가지 항생제로 수술받기 30분~1시간 전과 수술 받은 후 6시간 후 1회 더 주어 전염성 심장내막염을 예방한다.
Prevention of infectious endocarditis 전염성 심장 내막염의 예방 (감염성 심내막염의 예방)

Figure 74. Cardiovascular, heart valve, heart wall, cardiovascular blood flow direction The area marked in red is the endocardium. sauce; Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing Used with permission from Ross Laboratories Columbus, OH, USA
• Diagnosis and treatment of causative symptoms of infectious (infectious) endocarditis have already been described above.
• This section mainly describes antibiotic prophylactic treatment for infectious endocarditis.
• Children with most congenital heart anomalies or prosthetic heart valves are more likely to develop infectious endocarditis.
• Therefore, parents of children with congenital heart anomalies should know how to prevent their children from contracting endocarditis.
• When a child with congenital heart malformation receives tooth extraction treatment, or during surgical treatment of the mouth, adenoids, tonsils, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, etc., bacteria from the surgical lesion enter the bloodstream and infect the endocardium, thereby preventing infectious endocarditis. can cause
• www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 2 Prevention of Diseases and Safety Accidents in Children and Adolescents – When preventing infectious diseases with antibiotics or sulfa drugs
• Children with almost any congenital heart anomaly, except for small atrial septal defects or some other congenital heart anomalies, receive the above-described surgery, as prescribed by their doctor, with penicillin, erythromycin, vancomycin, streptomycin, ampicillin, or gentamycin. Infectious endocarditis is prevented by giving one or two or three antibiotics among various antibiotics such as 30 minutes to 1 hour before and 6 hours after surgery.
출처 및 참조문헌 Sources and Referenes
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제 6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제 20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”