전염성 심장내막염 (감염성 심내막염) Infectious endocarditis
- 박테리아나 곰팡이, 또는 그밖에 다른 종류의 병원체가 심장 내막에 감염되어 생긴 심장 내막(그림 74)전염병(감염병)을 전염성 심장내막염(감염 심내막염) 또는 감염성 심장내막염이라고 한다.
- 급성으로 생긴 심장 내막염을 급성 심장 내막염, 아급성으로 생긴 심장 내막염을 아급성 심장내막염이라 한다.
전염성 심장내막염의 원인
-
심장에 붙은(심장에서 바로 나온) 한 개의 혈관과 다른 혈관 사이에 치료 목적으로 만든 측도나 선천성 기형 측도가 있는 아이
-
심장 카테터 삽입수술을 받았던 아이
-
심실중격 결손, 대동맥 협착, 팔로 4징, 그 외 다른 종류의 선천성 심장혈관 기형을 가진 아이
-
심장 수술치료를 받았던 아이
-
인공 심장 판막 장치 치료를 받았던 아이
-
류마티스 심장염을 앓고 있거나 그 병을 앓고 다 나은 후 심장판막 손상이 있는 아이
-
코티코스테로이드제나 어떤 종류의 항생제로 장기간 치료 받는 아이
-
선천성 심장혈관 기형이나 후천성 심장혈관 질환이 있는 아이가
-
이를 빼거나, 잇몸수술 치료를 받거나 비뇨기계나 편도 또는 그밖에 상기도나 위장관 등을 수술 받을 때
-
그 외 경우
-
박테리아나 곰팡이 또는 다른 병원체가 심장내막에 감염되어 전염성(감염성) 심장내막염을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
심장 내막염에 걸린 소아청소년들의 80%는 심장에 이미 어떤 이상이 있는 것이 발견되고 20%는 심장에 아무 이상이 없는 것이 발견되었다고 한다.
-
그렇지만 심장, 심장에 붙어 있는 큰 혈관이 정상이고 신체 다른 부위에도 아무런 이상이 없고 코티코스테로이드제 등 어떤 종류의 약물치료도 받지 않고 또 심장 수술이나 구강 수술이나 잇몸 수술치료도 받지 않은 소아청소년에게도 전염성 심장내막염이 드물게 생길 수 있다.
-
저체중 신생아나 체중이 아주 작은 조숙 신생아도 전염성 심장내막염에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
앞에서 설명한 여러 종류의 선천성 심장혈관 기형, 또는 후천성 심장혈관 질환 등을 가진 소아청소년들에게 심장내막염이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다.
-
여러 종류의 박테리아나 곰팡이 등 병원체들의 감염에 의해서 감염성 심장내막염이 생길 수 있으나 그 중 녹색 연쇄상구균 감염이나 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 전염성 심장내막염이 주로 생길 수 있다.
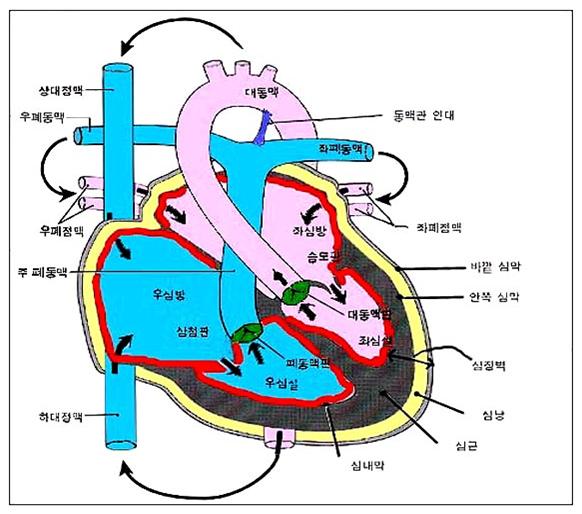
그림 74. 심장과 심장벽
빨간 색으로 표시된 부위가 심장 내막이다.
소스; 소아가정간호백과와
Used with permission from Ross Laboratories Columbus, OH, USA
전염성 심장내막염의 증상 징후
-
전염성 심장 내막염은 급성으로 생길 수도 있고 아급성으로 서서히 생길 수 있다.
-
이 병이 발병되기 전에도 있었던 원래 질환 등 선천성 심장혈관 기형이나 후천성 심장혈관 질환으로 생긴 증상 징후와 전염성 심장 내막염을 일으킨 박테리아의 종류 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다를 수 있다.
-
미열 내지 고열이 나다 안 나다 하면서 몹시 피곤해 보이고 어딘가가 아픈 것같이 보이지만 아픈 국소와 원인을 확실히 쉽게 가늠하기 어려운 때가 많다.
-
두통, 근육통, 복통, 한전 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
심장 내막뿐만 아니라 심장에 있는 여러 종류의 판막에도 감염될 수 있고 거기에 염증이 생기며 심장이 극도로 쇠약해질 수 있다.
-
심장 쇠약의 중증도에 따라 다른 여러 가지 증상 징후가 나타난다.
-
전염성 심장 내막염에 있던 고름 덩어리가 혈관 속으로 흘러 들어가서 신체 전 혈류를 따라 눈, 뇌 등 전신으로 퍼져 나갈 수 있다.
-
또 그 고름 덩어리가 전에 퍼져 있는 혈관을 막을 수 있고 특히 뇌 속으로 흘러가서 박테리아 뇌 농양이나 뇌 출혈, 또는 뇌막염을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
심장 내막에 생긴 감염병이 심장 내막에만 국한되지 않고 심장의 전 근육층으로 퍼져 심장벽이 뚫릴 수 있다.
-
전염성 심장 내막염을 일으킨 박테리아가 피부에 감염될 때는 빨간 피부 반점이 손발 등의 피부에도 생길 수 있다.
-
간과 비장이 비정상적으로 커질 수 있고 비정상 병적 심잡음이 날 수 있다.
그림 75. 선천성 심장 기형이 있는 아이들이 치아 치료를 받을 때나 어떤 수술을 받을 때는 적절한 항생제로 심내막염을 예방적 치료도 받아야 한다
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
전염성 심장 내막염의 진단
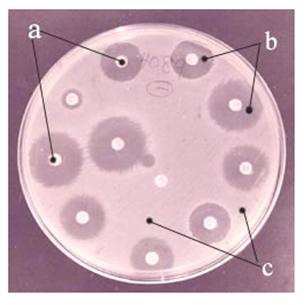
사진 76. 피(혈액) 세균배양검사(Blood culture)를 해서 진단할 수 있다. 그 전염성 심장내막염의 치료에 가장 적절한 항생제의 종류가 무엇인지 알아보기 위해 세균 항생제 감수성 검사도 한다.
a-각 종 항생제 디스크, b-항생제 디스크 속에 있는 항생제성분으로 인해 그 주위에 세균이 자라지 않은 배지,
c-세균이 자란 배지
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
병력, 손톱 밑에 생긴 출혈 반점 등 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 병원에 입원 진단 치료를 받는다.
-
전염성 심장 내막염을 일으킨 세균이 신체 전 혈액 속에도 들어가 있기 때문에 피를 여러 번 채취하여 혈액 세균배양검사를 한다.
-
혈액 세균배양검사의 1~2%는 아무런 세균이 배양되지 않을 수 있다.
-
그밖에 피 검사와 소변 검사, 심장 X-선 검사, 심초음파 검사, 그 외 다른 여러 가지 검사로 진단한다.
전염성 심장내막염의 치료
-
혈액 세균배양검사의 결과에서 찾아낸 박테리아를 가장 잘 죽일 수 있는 항생제를 선택해 항생제 혈관주사로 4~6주간 치료한다.
-
적절한 항생제로 적절히 치료해도 전염성 심장 내막염에 걸린 환자들의 25%는 사망한다고 한다.
Infectious endocarditis 전염성 심장내막염 (감염성 심내막염)
• Infectious disease (infectious disease) caused by infection of the lining of the heart by bacteria, fungi, or other types of pathogens (Figure 74) is called infectious endocarditis (infectious endocarditis) or infectious endocarditis.
• Acute endocarditis is called acute endocarditis, and subacute endocarditis is called subacute endocarditis.
Causes of infectious endocarditis
• A child with a therapeutic or congenital anomaly measure between one blood vessel attached to the heart (directly from the heart) and another blood vessel.
• Children who had undergone cardiac catheterization
• Children with ventricular septal defects, aortic stenosis, palosing, and other types of congenital cardiovascular anomalies • A child who received heart surgery treatment
• A child who was treated with an artificial heart valve device.
• Children who have rheumatoid heart disease or who have had heart valve damage after healed from the disease • Children receiving long-term treatment with corticosteroids or some kind of antibiotic
• Children with congenital cardiovascular malformations or acquired cardiovascular disease
• When removing a tooth, undergoing gum surgery, or undergoing surgery on the urinary system, tonsils, or other upper respiratory tract or gastrointestinal tract
• Other cases
• Bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens can infect the lining of the heart and cause infectious (infectious) endocarditis.
• 80% of children and adolescents with endocarditis reported that they had already found something wrong with their heart, and 20% said that there was nothing wrong with the heart.
• However, the heart and large blood vessels attached to the heart are normal, there is no abnormality in other parts of the body, and are contagious to children and adolescents who have not received any kind of medication, such as corticosteroids, and have not received heart surgery, oral surgery, or gum surgery. In rare cases, endocarditis can develop.
• Infectious endocarditis can also occur in underweight newborns or premature infants of very small weight.
• Endocarditis is more likely to develop in children and adolescents with several types of congenital cardiovascular malformations, or acquired cardiovascular disease, as described above.
• Infectious endocarditis may be caused by infection with pathogens such as various bacteria or fungi, but among them, infectious endocarditis may occur mainly due to green streptococcal infection or Staphylococcus aureus infection.

Figure 74. Heart and heart wall The area marked in red is the endometrium. sauce; Department of Pediatric Home Nursing Used with permission from Ross Laboratories Columbus, OH, USA
Symptoms signs of infectious endocarditis
• Infectious endocarditis can develop acutely or subacutely and slowly.
• Symptoms may differ depending on the type of bacteria that caused infectious endocarditis and congenital cardiovascular anomalies or acquired cardiovascular disease, such as the original disease before the onset of the disease.
• A mild or high fever seems very tired and seems to be painful somewhere, but it is often difficult to determine the painful area and cause clearly and easily.
• Symptoms such as headache, muscle pain, abdominal pain, and KEPCO may occur.
• In addition to the lining of the heart, many types of valves in the heart can be infected and inflamed and the heart can become extremely weak.
• A number of symptoms appear, depending on the severity of the heart failure.
• A mass of pus from infectious endocarditis can flow into the blood vessels and spread throughout the body, including the eyes and brain.
• The pus can also clog blood vessels that have previously spread and can flow especially into the brain, causing a bacterial brain abscess, brain hemorrhage, or meningitis.
• Infectious diseases in the heart lining are not limited to the heart lining, but can spread to the entire muscle layer of the heart and puncture the heart wall.
• When the bacteria that caused infectious endocarditis infect the skin, red skin spots can also develop on the skin, such as the hands and feet. • The liver and spleen may become abnormally enlarged and abnormal pathological heart murmurs may occur.

Figure 75. Children with congenital heart malformations should also receive prophylactic treatment for endocarditis with appropriate antibiotics when undergoing dental treatment or any surgery. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of infectious endocarditis

Picture 76. It can be diagnosed by performing a blood culture test. Bacterial antibiotic susceptibility tests are also done to determine which type of antibiotic is most appropriate for the treatment of the infectious endocarditis. a-antibiotic discs of various types, b-a medium that does not grow bacteria around due to the antibiotic component in the antibiotic disc, c-bacteria grown medium Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• If you suspect this disease, you should be admitted to a hospital for diagnosis and treatment.
• Since the bacteria that caused the infectious endocarditis are also in the blood throughout the body, blood is collected several times and tested for blood bacteriosis.
• 1-2% of blood bacteriological tests may not contain any bacteria.
• In addition, blood and urine tests, X-rays of the heart, echocardiography, and other tests are used to diagnose.
Treatment of infectious endocarditis
• Select the antibiotic that can best kill the bacteria found in the results of the blood bacteriological culture test, and treat it with an antibiotic vascular injection for 4-6 weeks.
• Even with appropriate treatment with appropriate antibiotics, 25% of patients with infectious endocarditis die.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”