- 골수 기능에 재생불량(Aplasia)성이 생겨 골수가 적절히 빨리 기능할 수 없어 이미 있는 혈액세포를 보충할 수 있는 새 혈액세포를 형성하지 못하는 경우를 재생 불량성 빈혈이라고 한다.
- 재생 불량성 빈혈이 있을 때는 헤모글로빈 농도만 감소되는 것이 아니라 적혈구 수, 백혈구 수, 혈소판 수도 동시 감소된다.
-
그래서 범혈구 감소증이 나타난다.
재생불량성 빈혈의 종류
-
재생불량성 빈혈은 선천성으로 생기는 재생불량성 빈혈과
-
후천성으로 생기는 재생불량성 빈혈이 있고
-
급성 재생불량성 빈혈,
-
아급성 재생불량성 빈혈
-
만성 재생불량성 빈혈로 분류될 수 있다.
재생불량성 빈혈의 원인
1 선천성 재생불량성 빈혈은 유전성으로 생긴다.
-
극히 드물다.
-
여기서 설명은 생략한다.
2 후천성 재생 불량성 빈혈의 원인.
-
클로람페니콜, 설파제, 간질 치료약 등 여러 종류의 약물.
-
유기 물질중독이나 무기 물질중독.
-
방사능에 노출 됐을 때.
-
바이러성 감염병이나 박테리성 감염병.
-
암이나 백혈병 등을 치료할 때 쓰는 항암 치료제 .
-
그 외
재생불량성 빈혈의 증상 징후
-
재생불량성 빈혈의 정도, 원인에 따라 다르고,
-
급성 재생불량성 빈혈이냐 만성 재생불량성 빈혈이냐, 또 재생불량성 빈혈 합병증의 유무에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
재생불량성 빈혈이 있으면 골수에서 적혈구와 그 외 혈구가 조금 만들어지든지 전혀 만들어지지 않을 수 있다.
-
따라서 재생불량성 빈혈이 있을 때 심한 빈혈이 생기는 것이 보통이다.
-
때로는 골수에서 백혈구와 혈소판가 정상적으로 생성되지 않을 수 있다.
-
이때는 혈소판의 수치가 비정상적으로 많이 감소되어 혈소판 감소증이 생길 수 있다.
-
그로 인해 신체 여러 부위에서 출혈이 생길 수 있고 피부 출혈반점, 피 맺힘, 멍이 생길 수 있다.
-
백혈구 수치가 비정상적으로 많이 감소될 수 있다.
-
그래서 박테리아 침입에 정상적으로 저항할 수 없을 수 있다.
-
따라서 각종 박테리아 감염으로 박테리아성 감염병에 걸리기 쉽다.
-
대부분의 재생불량성 빈혈은 골수 이식으로 치료하지 않는 한 예후가 좋지 않은 혈액병이다. 재생불량성 빈혈의 ⅓은 급성으로 진행된다.
-
그로 인해 심한 빈혈이 생기고 짧은 기간 내 사망한다. ⅓은 완전 치유된다. 나머지 ⅓은 아급성이나 만성으로 진행된다.
재생불량성 빈혈의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 CBC 피 검사와 골수흡인 검사 등을 해서 진단한다.
재생불량성 빈혈의 치료
-
재생불량성 빈혈의 정도, 원인, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 치료한다.
-
이 병을 일으킨 원인을 빨리 제거하고 피한다.
-
약물이 원인이면 쓰던 약물을 바로 중지하고,
-
이 병의 원인이 될 것이라고 의심되는 유기 물질이나 무기 물질에 더 이상 노출되어서는 안 된다.
-
가능한 한 방사능에 더 이상 노출되지 않도록 한다.
-
바이러스 감염이나 박테리아 감염병 등으로 재생불량성 빈혈이 생겼을 때는 그 감염병을 속히 치료한다.
-
재생불량성 빈혈의 일부는 안드로겐제와 코티코스테로이드제 등 호르몬제로 치료한다. 그러나 그 치료의 효과는 확실치 않다.
-
그때그때 생긴 증상 징후에 따라 대증치료를 한다.
-
심한 빈혈은 적혈구 수혈로, 혈소판 감소증과 출혈은 혈소판 수혈 등으로 적절히 대증치료 한다.
-
박테리아성 감염병은 적절한 항생제로 치료하고 각종 감염병에 걸리지 않도록 주의 한다. 이 병을 앓는 환아가 감염병을 앓는 사람들과 근접하지 않도록 특히 조심 한다.
-
환자의 골수와 생리적으로 맞는 골수를 가진 사람을 찾아 그 사람의 골수로 골수 이식치료를 할 수 있다.
-
아직도 완치되기가 힘든 병이므로 이 병에 걸리지 않도록 전력을 다해 예방에 힘써야 한다.
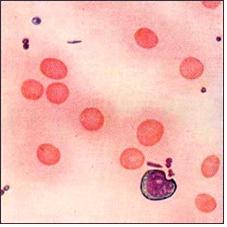
사진 1-23. 재생불량성 빈혈의 CBC 피 검사
출처: Glinigal atlas of blood diseases
A Piney, M.D. and Stanley Wyard
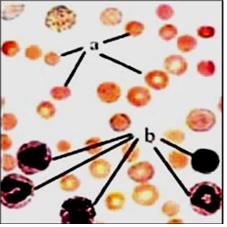
사진 1-24. 정상 CBC 피 검사
a-적혈구, b-백혈구, c-적혈구가 부서진 것같이 보이는 것들이 혈소판
Aplastic anemia 재생불량성 빈혈(재생불량 빈혈)
• Aplastic anemia is a case in which the bone marrow is unable to function properly and quickly due to aplasia in its function to form new blood cells capable of replenishing existing blood cells.
• With aplastic anemia, not only the hemoglobin concentration decreases, but the red blood cell count, white blood cell count, and platelet count simultaneously.
• So, pancytopenia occurs.
Types of aplastic anemia
• Aplastic anemia is a congenital aplastic anemia and
• have acquired aplastic anemia • acute aplastic anemia,
• Subacute aplastic anemia
• Can be classified as chronic aplastic anemia. Causes of aplastic anemia
1. Congenital aplastic anemia is hereditary.
• Extremely rare.
• Description is omitted here.
2. Causes of acquired aplastic anemia.
• Several types of drugs, including chloramphenicol, sulfa drugs, and antiepileptic drugs.
• Organic or inorganic poisoning.
• When exposed to radiation.
• Viral infectious disease or bactericidal infectious disease.
• Anticancer drugs used to treat cancer or leukemia.
• etc
Symptoms signs of aplastic anemia
• Depends on the degree and cause of aplastic anemia,
• Symptoms differ depending on whether you have acute aplastic anemia, chronic aplastic anemia, and aplastic anemia complications. • With aplastic anemia, the bone marrow may make little or no red blood cells and other blood cells.
• Therefore, it is common to develop severe anemia when you have aplastic anemia. • Sometimes the bone marrow may not produce white blood cells and platelets normally.
• At this time, the platelet level is abnormally decreased, which can lead to thrombocytopenia.
• This can lead to bleeding in various parts of the body, resulting in skin bleeding spots, blood clots, and bruising.
• White blood cell counts can be abnormally reduced.
• So you may not be able to normally resist bacterial invasion.
• Therefore, it is easy to get bacterial infectious diseases from various bacterial infections.
• Most aplastic anemia is a blood disease with a poor prognosis unless treated with a bone marrow transplant. ⅓ of aplastic anemia progresses acutely.
• It results in severe anemia and dies within a short period of time. ⅓ is completely healed. The remaining ⅓ is subacute or chronic.
Diagnosis of aplastic anemia
• Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, symptoms and examination findings. If this disease is suspected, CBC blood test and bone marrow aspiration test are performed to diagnose.
Treatment of aplastic anemia
• Treat according to the degree of aplastic anemia, the cause, and the presence or absence of complications. • Eliminate and avoid the cause of the disease quickly.
• If the drug is the cause, stop using the drug immediately,
• No further exposure to organic or inorganic substances suspected of causing this disease.
• As far as possible, avoid further exposure to radiation.
• When aplastic anemia occurs due to a viral infection or bacterial infection, the infectious disease is treated promptly. • Some aplastic anemia is treated with hormones such as androgens and corticosteroids. However, the effectiveness of the treatment is uncertain.
• Treat symptomatic treatment according to the symptoms and symptoms that occurred then.
• Severe anemia is appropriately treated with red blood cell transfusion and thrombocytopenia and bleeding with platelet transfusion.
• Bacterial infectious diseases are treated with appropriate antibiotics, and care should be taken not to get various infectious diseases. Be especially careful not to allow children with this disease to come close to people with infectious diseases.
• You can find a person who has a bone marrow that physiologically matches the patient’s bone marrow and undergo bone marrow transplantation with that person’s bone marrow.
• It is a disease that is still difficult to be cured, so you should do your best to prevent it from getting sick.

Photo 1-23. CBC blood test for aplastic anemia Source: Glinigal atlas of blood diseases A Piney, M.D. and Stanley Wyard

Photo 1-24. Normal CBC blood test a-red blood cells, b-white blood cells, c-red blood cells that appear to be broken are platelets
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 소아과학 안효섭 외 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”