자상, Puncture wounds
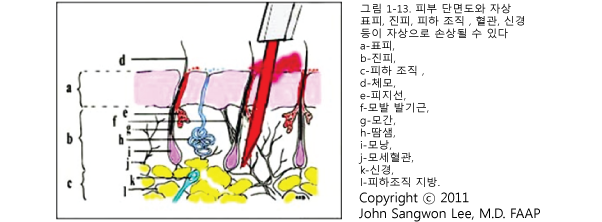
자상의 원인
☞ 미국에서는 2005년,
|
-
칼, 못, 나무 가지, 스플린터(소편/Splinter) 등 날카로운 물체로 찔린 상처 또는 총상 등으로 신체의 일부가 관통되어 생긴 관통상 등을 자상(Puncture wound)이라 한다.
-
녹슬고 불결한 못이나 예리한 칼, 뾰족한 나뭇조각이나 유리조각 등으로 손발이나 그 외 신체 부위가 찔릴 수 있다.
-
대부분의 자상은 안전사고로 생기지만 타인에 의한 상해나 본인에 의한 자해로도 생길 수 있다.
자상의 종류
-
자상에는 몸을 찌른 물체의 전체가 신체 외로 빠져 나온 자상,
-
총알로 뚫린 관통상 자상과 같이 자상의 입구가 있고 자상의 관통 로가 있고 자상의 출구가 있는 자상도 있다.
-
찌른 물체의 일부는 몸속에 남아있고 다른 일부는 빠져 나온 자상,
-
찌른 물체의 전체가 몸속에 그대로 남아 있는 자상.
-
얕게 찔린 자상,
-
깊게 찔린 자상,
-
몸통 한쪽 면에서 다른 쪽 몸통 면까지 뚫린 관통상 자상 등이 있다.
자상의 증상 징후
-
찌른 물체의 크기와 종류, 자상의 크기, 자상의 종류, 자상의 원인, 신체의 어느 부위에 자상이 생겼느냐에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
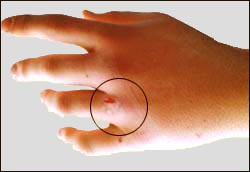
▴ 사진 1-42. 박테리아 감염으로 곪은 손가락.
자상을 입은 부분이 곪고 붓고 아프고 붉어졌다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
가시, 못, 바늘 등 끝이 날카로운 물체로 찔린 작은 자상도 있고, 총상으로 입은 관통상이나 교통사고 등으로 생긴 상당히 큰 자상도 있다.
-
가시, 바늘, 아주 작은 물체로 찔려서 생긴 자상에서 피가 조금 나든지 피가 조금도 나지 않을 수 있고 자상을 입은 신체 부위가 붓지도 않고 아프지도 않을 수 있다.
-
가시가 박혔을 때는 족집게로 가시를 뽑아낼 수 있다.
-
일반적으로, 작은 자상에서 나는 외출혈은 많이 나지 않고 건강에 별 문제가 생기지 않는다. 자상으로 생긴 흉곽강 속이나 복강 속 내출혈은 심할 수 있고 내 출혈로 쇼크 내지 사망도 할 수 있다.
-
못이나 날카로운 나뭇가지 등에 손발이 찔렸을 때는 피가 조금 나고 아프고 자상 상처가 붓을 수 있다.
-
못으로 찔려 생긴 발바닥 자상(족저 자상)에 박테리아가 감염되면 봉소염이 생길 수 있다(족저 자상 참조).
-
운동화를 신은 채 못에 찔려 생긴 발바닥 자상으로 인해 발 골수염도 생길 수 있다.
-
이물질이 자상 상처 속에 들어 있을 때는 그로 인해서 2~3일 내에 감염병이 국소적으로 생길 수 있고 붓고 아플 수 있다.
자상의 치료
1. 작은 자상의 치료
-
찌른 작은 물체의 일부가 자상 상처 속에 그대로 박혀있을 때는 가능한 한 박혀있는 물체를 조심스럽게 뽑아내고
-
자상을 비눗물로 깨끗이 씻어준 후 베타다인액 살균제로 살균 치료한다.
-
그 다음, 자상을 일회용 밴드에이드로 덮고 관찰 한다.
-
또는 멸균 거즈로 자상 상처를 덮고 거즈를 반창고로 고정시키든지, 붕대로 감는다.
-
대부분의 경우, 이런 1차 응급 치료는 부모가 사고 현장에서 한다.
-
부모가 이상 설명한대로 가정에서 자상을 치료할 자신이 없거나, 집에서 응급처치를 한 후 다음 단계 추적 자상 치료가 필요하면 단골 소아청소년과나 병원 응급실에서 치료를 받는다.
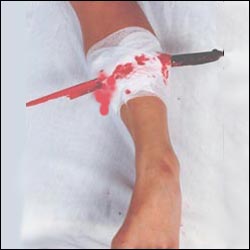
▴ 사진 1-43. 나뭇가지나 예리한 물체 등으로 팔다리나 신체
다른 부위가 깊이 찔렸을 때 찌른 물체가 찔린 상체에
그대로 박혀 있을 때는 의사의 지시 없이 찌른 물체를 자상
상체에서 함부로 잡아 빼내어서는 안 된다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
2. 큰 자상의 치료
-
큰 나뭇가지(사진 63참조)나 다른 종류의 큰 물체로 팔이나 다리, 신체 다른 부위가 깊숙이 찔렸을 때는 가능한 한 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과의 전화 지시에 따라 사고 현장에서 부모가 1차 최초 응급치료를 시작한다.
-
병원 응급실로 이송하기 전에는 의사의 지시가 없이 신체를 찔으고 박혀있는 나뭇가지나 물체 등을 함부로 잡아 빼지 말고 찔려있는 상태 그대로 관찰 치료를 한다.
-
위의 사진 53에서 보는 것과 비슷한 자상 상처가 있을 때 찔려 박혀 있는 물체를 뽑아낼 때 찔린 상처 부위에 있는 말초 신경, 혈관 등이 손상될 수 있다.
-
찌른 큰 물체 전체가 다 빠져 나왔을 때 자상 상처의 정도에 따라 응급 치료를 한다.
-
자상 상처가 클 때도 가능한 한 무균 거즈로 덮고, 자상 상처에서 피가 많이 나면 손가락이나 손바닥으로 출혈 상처를 직접 눌러 지혈시키거나 지혈대로 지혈시키면서 의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 전화 지시에 따라 병원 응급실로 빨리 이송한다.
-
겉으로는 자상이 얼마나 크고 깊은지 확실히 알 수 없는 때가 많다.
-
찌른 나무나 유리조각 등이 전부 다 빠져 나왔는지, 그 일부가 피부층이나 피하 조직 속에 남아 있는지 확실히 알 수 없는 때도 있다. X선 사진 검사나 초음파 검사 등으로 찔린 부위 속에 이물이 남아있는지 알아볼 수 있다.
Puncture wounds 자상
Cause of Puncture wounds
자상의 원인
☞ In the US in 2005,
|
- A piercing wound caused by piercing a part of the body with a sharp object such as a knife, nail, tree branch, splinter (small piece/splinter) or a gunshot wound is called a puncture wound.
- Rusty and unclean nails, sharp knives, sharp pieces of wood or glass can pierce hands and feet or other parts of the body.
- Most cuts are caused by safety accidents, but they can also be caused by injuries by others or by self-injury.

Type of Puncture wounds
- a stab wound in which the entire body of a stabbed body has fallen out of the body
- There are also stab wounds that have a stab-shaped entrance, a stab-penetrating path, and a stab-shaped exit like a piercing wound by a bullet.
- Some of the stabbed objects remain in the body, others are cut off,
- A stab wound in which the entire stabbed object remains in the body.
- Shallow stab wounds,
- A deep stab wound,
- There are penetrating cuts from one side of the torso to the other.
Symptoms, signs of Puncture wounds
- Symptoms, signs differ depending on the size and type of the stabbed object, the size of the cut, the type of the cut, the cause of the cut, and the part of the body where the cut occurred.

▴Photo 1-42. Fingers infected by a bacterial infection.
The wounded area became festering, swollen, painful, and red.
Copyright ⓒ2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- Some small cuts are stabbed with sharp-end objects such as thorns, nails, and needles, and there are also very large cuts caused by piercing wounds or traffic accidents caused by gunshot wounds.
- A thorn, a needle, or a stab caused by a very small object may bleed a little or may not bleed, and the injured body part may not swell or hurt.
- When thorns are stuck, you can pull them out with tweezers.
- In general, bleeding from small cuts does not occur much, and there is no problem with health.
- Internal bleeding in the thoracic or abdominal cavity caused by a stab can be severe, and internal bleeding can cause shock or death
- If your hands or feet are stabbed by nails or sharp branches, you may bleed a little, hurt, and swell cut wounds.
- Bacterial infections in plantar cuts caused by nails can lead to cellulitis (see Plantar cuts).
- Osteomyelitis of the foot can also occur due to a cut on the sole of the foot caused by a nail piercing while wearing sneakers.
- When a foreign substance is in the cut wound, the infectious disease may develop locally within 2-3 days, and it may cause swelling and pain.
Treatment of puncture wounds
- Treatment of small cuts
- If part of the stabbed small object remains stuck in the cut wound, carefully pull out the stuck object as much as possible.
- After washing the cuts with soapy water, sterilize them with betadine solution disinfectant.
- Then, cover the cut with a disposable band-aid and observe.
- Alternatively, cover the cut wound with sterile gauze and fix the gauze with a band-aid, or wrap it with a bandage.
- In most cases, this first emergency treatment is performed by parents at the accident site.
- If parents are not confident to treat cuts at home as described above, or if they need follow-up cuts at the next step after taking first aid at home, receive treatment at a regular pediatrics department or hospital emergency room.

▴ Photo 1-43. Limb with tree branches.
When the stabbed object has remained in place, You must not pull it out of your child’s body cut without instructions from a doctor. Copyright ⓒ2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP ‘
- Treatment of Puncture wounds
- If an arm, leg, or another part of the body is deeply punctured with a large branch (refer to photo 63) or another large object, the parent will start treatment the first emergency at the accident site as instructed by the hospital emergency room or a regular child and adolescent department as much as possible.
- Before being transported to the hospital emergency room, without the instructions of a doctor, and do not pull the object stabbed.
- When there is a stab wound similar to that shown in the above picture 53 when the stabbed object is pulled out, the peripheral nerves and blood vessels in the stabbed wound may be damaged.
- When the entire stabbed object has come out, emergency treatment is given depending on the severity of the cut.
- Even if the cut wound is large, cover it with sterile gauze as much as possible, and if the cut is bleeding a lot, press the bleeding wound directly with your finger or palm to stop the bleeding or stop the bleeding with a tourniquet and follow the call from a medical paramedic or regular pediatrician to the hospital emergency room
- It is often not clear how large and deep the stab is.
- There are times when it is not clear for sure whether all the stabbed wood or glass pieces have come out, and whether some of them remain in the skin layer or subcutaneous tissue.
- You can check if there is any foreign body in the punctured area by using an X-ray examination or ultrasound examination.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31 edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”