자궁 내막증 Endometriosis
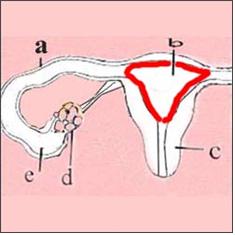
그림 2-5. 자궁의 내막 (붉은 선으로 표시된 부분).
a-난관, b-자궁강, c-자궁 경부, d-난소, e-난자.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.,FAAP
-
자궁의 내막 조직에는 자궁 내막 선(샘)과 자궁 간질 조직이 있다.
-
자궁의 내벽 조직이 골반강 내에 있는 복막 또는 난소 등 여러 부위에 이소성으로 있을 수 있고,
-
자궁의 내막 조직에 에스트로겐 의존성 염증이 생기는 병을 자궁 내막증이라고 한다(출처: NEJM January, 2009, p.268).
-
자궁 내막증은 22세 이하의 젊은 여성들과 사춘기 여아들에게서 흔히 볼 수 있는 병이다.
-
출산을 할 수 있는 연령층 여성들의 5~10%에게 자궁 내막증이 있다.
-
월경 곤란증을 수반하는 사춘기 아이들의 30~67%에서 자궁 내막증이 발견된다.
-
자궁 내막증의 주 증상은 골반 내 통증, 골반 내 덩어리, 불임증, 성교 중 통증 및, 또는 월경 곤란증 등이다.
자궁 내막증의 진단
-
병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합해서 자궁 내막증이 의심되면, 자궁 강 내시경 검사와 자궁내막 생체 조직검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
-
척추 디스크탈 등과 감별 진단해야 한다.
자궁 내막증의 치료
-
통증은 대증 치료하고, 이 병이 더 진행되지 않게 예방적 치료를 하며, 임신될 수 있도록 치료한다.
-
정도에 따라 관찰적 치료를 하거나, 타이레놀이나 아이브프로펜(모트린) 등 진통제로 대증 치료하고, 수술 치료, 피임약 치료, Leuprolide과 Nafarelin 등으로 치료하기도 한다.
-
최근 12~24세 사춘기 여아들과 젊은 여성들을 대상으로 연구한 결과에 의하면, 주기적인 호르몬 치료와 비 스테로이드 항염증제 치료, 내시경 검사와 자궁 내막증 환부제거 치료를 겸하면 치료 효과가 좋다.
-
또 내시경 검사와 자궁 내막증 환부 제거 치료를 하고, 계속 피임제 치료, 계속 프로제스론제 치료 또는 계속 GnRH 길항제로 치료한 결과 치료 효과가 좋았다(Pediatric News, Sep 2008, p.39).
-
외과적 수술 치료를 받은 후 약 20%가 재발된다.
-
그 외 치료.
Vaginal discharge and external genitalia discharge 질 분비물(대하/냉)과 외음 분비물

Figure 2-5. The endometrium of the uterus (indicated by the red line). a-fallopian tubes, b-uterine cavity, c-cervix, d-ovary, e-egg. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• The endometrial tissue of the uterus contains the endometrial gland (gland) and uterine interstitial tissue.
• The tissue of the inner wall of the uterus may be ectopic in several areas, such as the peritoneum or the ovary, in the pelvic cavity,
• A disease in which estrogen-dependent inflammation occurs in the endometrial tissue of the uterus is called endometriosis (Source: NEJM January, 2009, p.268).
• Endometriosis is a common disease in young women under the age of 22 and in adolescent girls.
• Endometriosis is present in 5 to 10% of women in the age group who can give birth.
• Endometriosis is found in 30% to 67% of adolescent children with dysmenorrhea.
• The main symptoms of endometriosis are pain in the pelvis, lumps in the pelvis, infertility, pain during intercourse, and/or dysmenorrhea.
Diagnosis of endometriosis
• If endometriosis is suspected by combining medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, it can be diagnosed by endoscopy and endometrial biopsy.
• Differential diagnosis with spinal disc prolapse is required.
Treatment of endometriosis
• Pain is treated as a symptom, preventive treatment to prevent further progression of the disease, and treatment so that pregnancy can occur.
• Depending on the degree, observational treatment, symptomatic treatment with pain relievers such as Tylenol or Ibprofen (Motrin), surgery treatment, contraceptive treatment, Leuprolide and Nafarelin, etc. may be used.
• According to the results of a recent study of 12 to 24 years old adolescent girls and young women, periodic hormonal therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory therapy, endoscopy and endometriosis lesion removal therapy are both effective in treatment.
• In addition, after endoscopy and endometriosis treatment, continued contraceptive treatment, continued progesterone treatment, or continued treatment with GnRH antagonists, the treatment effect was good (Pediatric News, Sep 2008, p.39).
• About 20% relapse after undergoing surgical treatment.
• Other treatment.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”