입안의 외상 Trauma of the mouth(Mouth trauma/oral cavity trauma)
입안의 외상의 개요
- 입안의 점막 층, 잇몸, 이(치아), 혀, 인두 등이 외상을 입을 수 있다.
- 외상으로 이(치아)가 빠지고 부러질 수 있고 삘 수 있다.
- 잇몸, 입술, 혀 등이 찢어져 절상이 생길 수 있고 뚫려 자상이 생길 수 있고,
- 입술, 잇몸, 입안의 점막 층에 피가 맺힐 수 있고,
- 외상 입은 입안 상처에서 피가 날 수 있다.
- 때로는 입안의 점막 층의 아래 점막하 조직에 피가 국소적으로 조금 나서 피 꽈리가 입안에 생길 수 있다.
- 피가 조금 맺힌 입안 작은 상처는 그대로 놓고 관찰하면 대개 저절로 낫는다.
- 입술, 잇몸, 혀, 입안 등의 점막 층이 조금 찢어지거나 찔렸을 때는 무균 거즈를 상처에 올려놓고 손가락 끝으로 살짝 눌러 지혈시키고 1, 2분 후에 거즈를 떼고 상처가 얼마나 큰지, 피가 계속 나는지 살펴본다.
- 상처가 크고 피가 멎지 않고 계속 나면 작은 얼음 덩어리나 아이스 바 등을 빨든지 찬 얼음물을 머금고 있으면 대부분의 경우 곧 지혈 된다.
- 그래도 피가 멎지 않고 계속 나든지, 상처가 상당히 크거나, 부모가 집에서 최초 응급치료를 해 줄 자신이 없으면 치과 전문의나 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과, 또는 의료구급대의 지시에 따라 치료한다.
- 입안에 생긴 아주 작은 자상이나 열상에서 나는 출혈은 자연적으로 멎고 낫는 것이 보통이다. 잘 곪지 않고 거의 저절로 낫는 것이 보통이다.
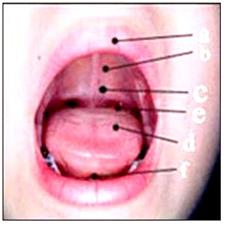
▴ 사진 406. 입안(구강)
a-입술, b-경구개, c-연구개, d-편도, e-혀, f-소대, g-구개수(목젖). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
일반적으로 얇게 째진 혀 열상은 봉합 수술 치료를 받지 않아도 대개 잘 낫는다. 그러나 깊숙이 째진 혀 열상은 흡수되는 봉합실로 봉합 수술 치료를 할 수 있다.
- 입 안에 상처가 생겨서 진찰을 할 때 때로는 혓바닥을 거즈로 싸서 손가락으로 혀를 붙들고 진찰하면 혀가 꼭 잡혀서 진찰하는 데 도움 된다.
- 입안이 찢어지거나 찔렸을 때 파상풍 백신 예방접종 권장에 따라 받는다.
|
다음은 “아기가 혀를 다쳤는데요”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 아기가 혀를 다쳤는데요
Q.
만 18개월 된 아기인데요, 오늘 오후 2시경에 넘어지면서 혀를 깨물었습니다. 병원에 갔더니 한 바늘만 꿰매야겠다고 하더니 아기가 너무 울고 혀를 안으로 자꾸 집어 넣어서 당겨서 꿰매기가 힘들 것 같다며 종합병원 가서 약간 잠들게 하는 마취약으로 꿰매는 방법이 있다고 했습니다.
그런데 제가 그렇게 하지 않고 자연적으로 낳을 수 없겠냐고 했더니 주사 한대와 약을 주시더군요. 그런데 집에 와서 보니까 정말 살이 벌어져 있던데요, 며칠 지나면 약만 먹고도 낳을까요?
꿰매려면 오늘 해야 한다고 했는데 시간은 이미 지나가 버린 것 같은데요. 어떻게 해야 하나요 . 빨대로 우유는 안 먹으려고 하고 죽과 두유는 잘 먹습니다!)
A.
수원님께
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 정보가 많이 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 주신 정보를 참작해 답변을 드립니다.
일반적으로, 혀에 생긴 경미한 열상은 봉합 수술 치료를 하지 않아도 잘 낫습니다. 그러나 깊숙이 째진 큰 혀 열상은 봉합 수술 치료를 해주는 것이 좋습니다.
제가 진찰을 하지 않고 어느 정도로 열상이 혀에 생겼는지 확실히 모르기 때문에 봉합수술로 치료해야 되는지 관찰 치료를 해도 되는지 확실히 말씀을 드릴 수 없습니다.
단골 소아청소년과의 권장에 따라서 치료하시는 것이 좋다고 생각합니다.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호 백과]-제9권 소아청소년 소화기계 질환–입안의 외상 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
The trauma of the mouth (Mouth trauma/oral cavity trauma)
Overview of Trauma in the Mouth
• The mucous membranes of the mouth, gums, teeth (tooth), tongue, and pharynx can be traumatized.
• Trauma can cause your teeth (tooths) to fall out, break, or sprain.
• Torn gums, lips, tongue, etc. may cause cuts, punctures, and cuts;
• The lips, gums, and mucous membranes of the mouth may bleed;
• Traumatic mouth wounds may bleed.
• Occasionally, a small amount of blood may appear in the submucosal tissue below the mucosal layer of the mouth, resulting in an aneurysm in the mouth.
• A small wound in the mouth with a little blood will usually heal on its own if you leave it and observe it.
• When the mucous membrane layer of the lips, gums, tongue, or mouth is slightly torn or punctured, place sterile gauze on the wound and lightly press with your fingertips to stop bleeding.
• If the wound is large and the bleeding does not stop, sucking on a small ice cube or ice bar or holding cold ice water will stop the bleeding in most cases.
• If the bleeding does not stop, the wound is quite large, or the parents are not confident to provide first aid at home, follow the instructions of a dentist, hospital emergency room, regular pediatric department, or medical paramedic.
• Bleeding from very small cuts or lacerations in the mouth usually stops and heals spontaneously. It is usually not stinging well and usually gets better on its own.

▴ Picture 406. Mouth a – lip, b – palate, c – soft palate, d – tonsils, e – tongue, f – frenulum, g – uvula. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• In general, thin tongue lacerations usually heal well without sutures. However, deep-seated tongue lacerations can be treated surgically with resorbable sutures.
• When examining because there is a wound in the mouth, sometimes wrapping the tongue in gauze and holding the tongue with your fingers will help to hold the tongue tightly.
• Follow tetanus vaccination recommendations for mouth rips or punctures.
The following is an example of a Q&A on health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “Baby has injured his tongue.”
Q&A. Baby hurt his tongue
Q.
My 18-month-old baby fell and bit his tongue around 2 pm today. When I went to the hospital, he said that he had to sew only one needle, and he said that the baby was crying too much and that it would be difficult to sew it by sticking his tongue inside and pulling it. But when I asked if I couldn’t give birth naturally without doing that, he gave me an injection and medicine. But when she came home, she looked really fat. After a few days, will she give birth just by taking medicine?
I thought I had to do it today to sew, but time seems to have passed. What should I do . I try not to drink milk with a straw, but eat porridge and soy milk well!)
A.
to Suwon Hello. Thank you for asking a question. We can give you a better answer if you have a lot of information such as the child’s age, gender, past and family history, examination findings, and clinical test results. We will respond based on the information you have provided. In general, minor lacerations on the tongue heal well without sutures. However, for large tongue lacerations that are deeply slit, surgical treatment with sutures is recommended. Since I don’t know for sure to what extent the laceration has occurred on the tongue without an examination, I can’t say for sure whether it should be treated with sutures or observational treatment. I think it is better to treat according to the recommendation of the regular pediatrician.
[Parents should also become at least the half-doctors – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing] – Vol. 9 Children’s and adolescent digestive system diseases – Trauma to the mouth, etc. Please visit again if you have more questions. thank you. Lee Sang-won Dream출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care
응급환자관리 정담미디어
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
소아과학 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”