일산화탄소 중독, Carbon monoxide poisoning
일산화탄소 중독의 개요
일산화탄소의 농도가 높은 일산화탄소(CO) 공기를 장시간 동안 또는 짧은 시간 동안 호흡하면 일산화탄소에 중독 될 수 있다.
일산화탄소 중독의 종류
-
고 농도 일산화탄소가 있는 공기를 짧은 시간 동안 호흡해 생긴 일산화탄소 중독을 급성 일산화탄소 중독이라고 한다.
-
고 농도 일산화탄소가 있는 공기를 여러 날 동안 호흡해서 생긴 일산화탄소 중독을 만성 일산화탄소 중독이라 한다.
-
일산화탄소 중독을
-
경도 일산화탄소 중독,
-
중등도 일산화탄소 중독,
-
중증도 일산화탄소 중독으로 분류할 수 있다.
-
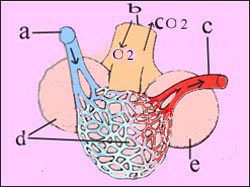
▴ 그림 1-10. 폐포, 폐 모세정맥, 폐 모세동맥, 폐포의 구조
a-폐 세동맥, b-말단 세기관지, c-폐 세정맥, d 와 e-폐포 , CO₂(이산화탄소)와 O₂(산소)가 폐포에서 교환된다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
헤모글로빈은 정상적으로 적혈구 내에 들어 있다.
-
호흡할 때 폐포 속으로 들어온 산소는 헤모글로빈에 부착된다.
-
헤모글로빈은 전신의 모든 기관의 모든 조직의 세포들에 산소를 날라다 주는 역할을 한다.
-
일산화탄소와 산소가 폐포 속이나 혈액 속에 동시 있을 때 산소가 헤모글로빈에 부착하는 친화력보다 일산화탄소가 헤모글로빈에 부착하는 친화력이 200배 더 강하다.
-
어떤 이유로 고 농도 일산화탄소 공기를 정상 이상으로 더 많이 호흡할 때는 헤모글로빈이 산소를 전신의 모든 기관의 조직 세포들에 날라다 주는 대신 일산화탄소를 전신 모든 조직 세포들에 더 많이 날라다 준다. 이때 일산화탄소에 중독 될 수 있다.
-
일산화탄소 중독의 중증도(Severity)에 따라 전신의 모든 조직 세포들에 산소결핍증이 생기고 심하면 조직의 세포들이 질식 상태에 빠진다.
-
다시 설명하면 일산화탄소의 농도가 높은 공기를 호흡할 때는 적혈구 속에 있는 헤모글로빈에 산소가 부착되어 산소 헤모글로빈이 되는 대신 일산화탄소가 헤모글로빈에 부착돼서 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈(일산화탄소 혈색소, Carboxyhemoglobin/CoHgb)이 된다. 그 때문에 헤모글로빈이 신체 각 조직 세포들이 필요한 만큼 산소를 충분히 나를 수 없게 된다.
-
이런 경우, 혈액 헤모글로빈의 양은 정상이나 신체 내 산소결핍증이 생기고 결국에는 일산화탄소 중독에 걸린다. 즉 혈중 헤모글로빈의 농도가 정상이지만 심한 빈혈 상태의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
일산화탄소 중독의 원인
-
잘못 설치한 난방장치,
-
불안전하게 설치한 환기장치,
-
환기가 잘 되지 않는 밀폐된 장소에서 석유, 석탄, 또는 숯 등을 태울 때,
-
밀폐된 자동차 내에서 오랫동안 자동차 엔진을 끄지 않은 상태로 있을 때,
-
자동차 엔진을 오랫동안 끄지 않은 상태에서 주차시킨 밀폐된 차고 내에 오랫동안 있을 때,
-
화재로 생긴 높은 농도의 일산화탄소를 호흡할 때,
-
그 외로 일산화탄소의 농도가 높은 공기를 호흡할 때 일산화탄소 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
화재가 난 장소에서 화상은 입지 않아도 일산화탄소나 그 외 다른 종류의 유독 가스에 중독 될 수 있고
-
환기 시설이 잘 되지 않은 장소에서 연탄을 땔 때 일산화탄소에 중독 될 수 있다.
일산화탄소 중독의 증상 징후
-
호흡하고 있는 공기 속에 들어 있는 일산화탄소 농도에 따라, 고 농도 일산화탄소를 얼마나 오랫동안 호흡했는지, 또는 헤모글로빈에 붙어 있는 혈중 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도에 따라 일산화탄소 중독의 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
헤모글로빈에 일산화탄소가 소량 붙어 있는 것은 정상적이다. 일산화탄소가 붙은 헤모글로빈을 CoHgb라 한다. CoHgb의 정상 혈중 농도는 5%나 그 이하이다.
-
CoHgb 혈중 농도가 20% 이상 될 때는 일산화탄소 중독의 증상 징후가 현저하게 나타나기 시작하고, 30% 정도일 때는 일산화탄소에 심하게 중독 될 수 있고, 60% 이상일 때는 사망하는 것이 보통이다(질식 참조).
-
경도 일산화탄소 중독이 급성으로 생길 때는 머리가 무겁고 아플 수 있고 귓속에서 이상한 소리가 나고 정신집중이 잘 안 되며 어지러움, 근육통 등 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
일산화탄소에 심하게 중독 될 때는 혼동되고, 구토하고 오줌똥을 싸고 전신경련을 일으키고 의식을 거의 잃게 된다.
-
일산화탄소에 만성으로 경미하게 중독 될 때는 머리가 뻐근하게 아프면서 어지럽고 속이 메슥거리고 구역질이 나며 기운이 없고 현기증, 기억력 감소, 수면 장애, 신경염, 재발성 감염병, 복통, 적혈구증가증(Polycythemia), 신경정신 이상 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
일산화탄소 농도가 정상 이상으로 높은 공기를 오랫동안 호흡하면 만성 일산화탄소 중독증에 걸릴 수 있다. 이때는 청력이 감소되고 보통 매일 하는 일의 능률이 오르지 않을 수 있다.
-
일산화탄소에 아주 심하게 중독 될 때는 눈동자의 크기가 정상 이상으로 커지고(산동이 생기고), 얼굴이 창백해지며 빨리 호흡하거나 느리게 호흡하고 의식을 잃고 전신경련을 하다가 결국에는 사망한다. Manual of emergency pediatrics 4th edition, Robert M. Reece, M.D. p.224 참조
일산화탄소의 농도가 점점 더 높아지고 일산화탄소를 호흡하는 시간이 점점 더 길어질 때 생길 수 있는 일산화탄소 중독의 증상과 징후를 요약 하면
|
일산화탄소 중독의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해 일산화탄소 중독을 의심되면 헤모글로빈에 붙은 일산화탄소 농도 즉, 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈(일산화탄소 혈색소/Carboxyhemoglobin/ CoHgb)의 혈 중 농도를 측정해서 진단한다.
-
연탄, 숯, 가스 등이 타는 밀폐된 장소에 있었던 사실, 엔진을 끄지 않은 채 놓아두었던 자동차 속이나 그런 자동차를 주차했던 차고 내에 오랫동안 있었던 사실 등을 참고로 해서 일산화탄소 중독을 진단한다(연기를 흡입했을 때, 일산화탄소 중독사고 예방 참조).
표 44. 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈(일산화탄소 혈색소) 농도에 따른 증상 징후
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 1% 이하
When driving on a highway with a carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration of 5% or less |
정상
It is considered normal |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 5% 이하
A carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration of 5% or less, |
고속도로에서 차를 몰 때는 차내에서는 정상으로 본다.
When driving on a highway with |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 10% 이하
The carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration of 10% or less are considered normal |
담배를 피우는 사람의 경우 정상으로 본다. People who smoke cigarettes wi
|
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 15% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is less than 15%, |
육체적 운동을 하는 동안 숨이 조금 가쁘고 앞 머리가 조금 띵하고 얼굴홍조가 생기는 등 증상 징후가 경미하게 나타날 수 있다.
Symptoms may appear mildly during physical exercises, such as shortness of breath, a little thin front head, and facial flushing |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 20% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is 20%, |
육체적 운동을 하지 않는 동안 숨이 가쁘고 앞 머리와 측두에 율동적 두통이 생기는 것이 보통이다.
Shortness of breath and rhythmic headaches in the forehead and temporal region are common during non-physical exercise |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 30% 일 때
When the concentration of carbon monoxide hemoglobin is 30%, |
신경이 예민해지고 두통, 피로, 판단력 이상, 시야장애, 어지럼 등의 증상이 생긴다. \
nNerves become sensitive and symptoms such as headache, fatigue, abnormal judgment, visual disturbance, and dizziness occur. |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 40~50% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is 40-50%, |
두통, 혼동, 육체적 운동 실조, 기절 등의 증상이 생긴다. Symptoms such as headache, confusion, physical ataxia, and fainting occur |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 60~70% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is between 60 and 70%, |
의식 천명도가 상당히 감소된다. 경련, 호흡부전증 등이 생긴다.
Wheezing is significantly reduced. Convulsions, respiratory failure, etc. occur. |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 80% 이하
Carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is 80%.
|
짧은 시간 내 사망한다.
Death occurs in a short time. |
Sources and references Manual of emergengy pediatrics 4th edition, Robert. M. Reece, M.D.
일산화탄소 중독의 치료
-
일산화탄소 중독을 의심하면 현장에서 안전한 장소로 환아를 바로 옮기는 처치를 우선 한다.
-
일산화탄소 중독의 정도에 따라 의료구급대, 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과에 긴급전화로 그들의 지시에 따라 구급차나 다른 적절한 방법으로 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 간다.
-
경미하게 중독 됐을 때는 신선한 공기를 호흡하게 하는 것이 치료의 전부이다.
-
그렇지만 심하게 중독 됐을 때는 헤모글로빈에 붙어 있는 일산화탄소를 헤모글로빈에서 빨리 분리시키는 치료를 하기 위해 기준기압 100% 산소 호흡 치료나 고압 100% 산소호흡 치료를 한다. 이런 산소치료를 헤모글로빈에 붙은 일산화탄소(Carboxyhemoglobin/CoHgb)의 농도가 5% 이하로 내려올 때 까지 치료한다.
-
중증도 일산화탄소 중독으로 혼수상태에 빠졌을 때는 산소결핍증으로 뇌 손상이 이미 생겨 있을 수 있고, 또 뇌가 많이 부어있을 수 있다. 이런 때는 이미 생긴 뇌부종을 적절히 치료해야 한다.
-
같은 장소에서 일산화탄소의 농도가 높은 공기를 호흡했던 다른 사람들도 일산화탄소에 중독 될 수 있다.
-
때문에 같이 있던 사람들도 적절한 치료를 받아야 한다. 그리고 일산화탄소에 또 다시 중독되지 않도록 예방한다.
-
일산화탄소의 농도가 정상 이상으로 높으면 경종이 울리는 일산화탄소 경보기를 집안에 설치해 일산화탄소 중독을 예방할 수 있다.

▴ 사진 1-37. 일산화탄소 중독을 예방하는 데 쓸 수 있는 일산화탄소 경보기.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Carbon monoxide poisoning 일산화탄소 중독
Overview of carbon monoxide poisoning
- Breathing carbon monoxide (CO) air with a high concentration of carbon monoxide for long or short periods of time can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning.
Types of carbon monoxide poisoning
- Carbon monoxide poisoning caused by breathing air with high concentrations of carbon monoxide for a short period of time is called acute carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning caused by breathing air with high concentrations of carbon monoxide for several days is called chronic carbon monoxide poisoning.
Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Mild carbon monoxide poisoning,
- Moderate carbon monoxide poisoning,
- Severe can be classified as carbon monoxide poisoning.

▴ Figure 1-10.
Structure of alveoli, pulmonary capillary vein, pulmonary capillary artery, alveoli.
The a-pulmonary arterioles, b-terminal bronchioles, c-pulmonary venules, d and e-alveoli, CO₂ (carbon dioxide) and O₂ (oxygen) are exchanged in the alveoli. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- Hemoglobin is normally contained in red blood cells.
- When breathing, oxygen that enters the alveoli attaches to hemoglobin.
- Hemoglobin carries oxygen to the cells of all tissues in all organs of the body.
- When carbon monoxide and oxygen are in the alveoli or blood at the same time, the affinity that carbon monoxide attaches to hemoglobin is 200 times stronger than the affinity that oxygen attaches to hemoglobin.
- For some reason, when you breathe more than normal in high-concentration carbon monoxide air, hemoglobin carries more carbon monoxide to all the tissue cells of the body instead of transporting oxygen to the tissue cells of all organs throughout the body. This can lead to poisoning with carbon monoxide.
- Depending on the severity of carbon monoxide poisoning, oxygen deficiency occurs in all tissue cells throughout the body, and in severe cases, tissue cells fall into a state of asphyxiation.
- In other words, when breathing air with a high concentration of carbon monoxide, oxygen is attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells and becomes oxygen hemoglobin. Instead, carbon monoxide is attached to hemoglobin and becomes carbon monoxide hemoglobin (Carboxyhemoglobin/CoHgb).
- As a result, hemoglobin cannot carry enough oxygen to each tissue cell in the body as needed.
- In this case, the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is normal, but oxygen deficiency occurs in the body and eventually, carbon monoxide poisoning occurs.
- In other words, although the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood is normal, symptoms, signs of severe anemia may occur.
Causes of carbon monoxide poisoning
- Incorrectly installed heating devices,
- Ventilation system installed insecurely,
- When burning petroleum, coal, or charcoal in an enclosed place with poor ventilation,
- When the car engine has not been turned off for a long time in a closed car,
- When your child is in an enclosed garage parked for a long time without turning off the car engine for a long time,
- When breathing high concentrations of carbon monoxide from a fire,
- Other than that, breathing air with high levels of carbon monoxide can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Your child can be poisoned by carbon monoxide or other types of toxic gases without getting burned in a place where there is a fire.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning can occur when briquettes are fired in poorly ventilated areas.
Symptoms signs of carbon monoxide poisoning
- Symptoms, signs of carbon monoxide poisoning differ depending on the concentration of carbon monoxide in the air your child is breathing, how long you child has breathed high concentrations of carbon monoxide or the concentration of carbon monoxide hemoglobin in the blood attached to hemoglobin.
- It is normal for hemoglobin to contain a small amount of carbon monoxide. Hemoglobin with carbon monoxide is called CoHgb.
- The normal blood level of CoHgb is 5% or less.
- When the blood level of CoHgb is above 20%, symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning begin to appear remarkable, when it is about 30%, severe carbon monoxide poisoning can occur, and when the concentration is above 60%, death is common (see suffocation).
- When mild carbon monoxide poisoning occurs acutely, the head may be heavy and painful, there may be strange noises in the ear, difficulty concentrating, and symptoms such as dizziness and muscle pain may occur.
- When you are severely poisoned to carbon monoxide, your child is confused, vomiting, peeing, convulsions, and almost loss of consciousness.
- When chronically mildly poisoned to carbon monoxide, the head is sore, dizzy, nauseous, nauseous, dull, memory loss, sleep disorders, neuritis, recurrent infectious diseases, abdominal pain, polycythemia, neuropsychiatric disorders, etc.
- Symptoms may occur. Long-term breathing of air with a carbon monoxide concentration above normal can lead to chronic carbon monoxide poisoning. At this point, your chil’s hearing may be reduced and the efficiency of your usual daily tasks may not increase.
- When very severely poisoned by carbon monoxide, the size of the eyes becomes larger than normal (mydriasis occurs), the face becomes pale, breathes quickly or slowly, loses consciousness, convulses, and eventually dies.
- Manual of emergency pediatrics 4th edition, Robert M. Reece, M.D. See p.224 Summarizing the symptoms and signs of carbon monoxide poisoning that can occur when the concentration of carbon monoxide increases and the time to breathe carbon monoxide becomes longer and longer.
- At first, it starts with asymptomatic no-signs → then it leads to fatigue, headache, anxiety and depression → neuropsychiatric dysfunction, general fatigue, goosebumps, abdominal pain, confusion, dizziness, etc.→ ataxia, convulsions → myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, loss of consciousness → ends with death.
Source; The New England Journal of Medicine, March 19, 2009, p.1218.
Diagnosis of carbon monoxide poisoning
- If carbon monoxide poisoning is suspected by combining medical history, symptoms, and medical examination findings, the concentration of carbon monoxide attached to hemoglobin, that is, carbon monoxide hemoglobin /Carboxyhemoglobin/CoHgb), is measured and diagnosed.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning is diagnosed by referring to the fact that it was in an enclosed place where briquettes, charcoal, gas, etc., burned, in a car that was left without turning off the engine, or in the garage where such a car was parked for a long time. See Prevention of carbon monoxide poisoning accidents).
able 44. Symptoms signs according to the concentration of carbon monoxide hemoglobin (carbon monoxide hemoglobin)
표 44. 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈(일산화탄소 혈색소) 농도에 따른 증상 징후
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 1% 이하
When driving on a highway with a carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration of 5% or less |
정상
It is considered normal |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 5% 이하
A carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration of 5% or less, |
고속도로에서 차를 몰 때는 차내에서는 정상으로 본다.
When driving on a highway with |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 10% 이하
The carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration of 10% or less are considered normal |
담배를 피우는 사람의 경우 정상으로 본다.
People who smoke cigarettes wi
|
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 15% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is less than 15%, |
육체적 운동을 하는 동안 숨이 조금 가쁘고 앞 머리가 조금 띵하고 얼굴홍조가 생기는 등 증상 징후가 경미하게 나타날 수 있다.
Symptoms may appear mildly during physical exercise, such as shortness of breath, a little thin front head, and facial flushing |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 20% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is 20%, |
육체적 운동을 하지 않는 동안 숨이 가쁘고 앞 머리와 측두에 율동적 두통이 생기는 것이 보통이다.
Shortness of breath and rhythmic headaches in the forehead and temporal region are common during non-physical exercise |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 30% 일 때
When the concentration of carbon monoxide hemoglobin is 30%, |
신경이 예민해지고 두통, 피로, 판단력 이상, 시야장애, 어지럼 등의 증상이 생긴다.
Nerves become sensitive and symptoms such as headache, fatigue, abnormal judgment, visual disturbance, and dizziness occur. |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 40~50% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is 40-50%, |
두통, 혼동, 육체적 운동 실조, 기절 등의 증상이 생긴다.
Symptoms such as headache, confusion, physical ataxia, and fainting occur |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 60~70% 일 때
When the carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is between 60 and 70%, |
의식 천명도가 상당히 감소된다. 경련, 호흡부전증 등이 생긴다.
Wheezing is significantly reduced. Convulsions, respiratory failure, etc. occur. |
| 일산화탄소 헤모글로빈 농도가 80% 이하
Carbon monoxide hemoglobin concentration is 80%.
|
짧은 시간 내 사망한다.
Death occurs in a short time. |
Treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning
- If you suspect carbon monoxide poisoning, give priority to moving the child from the site to a safe place.
- Depending on the degree of carbon monoxide poisoning, call a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrics by emergency phone call and take them to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means according to their instructions.
- When you are mildly poisoned, the whole treatment is to breathe fresh air.
- However, when severely poisoned, 100% oxygen breathing treatment or high pressure 100% oxygen breathing treatment is performed to quickly separate carbon monoxide from hemoglobin.
- This oxygen therapy is treated until the concentration of carbon monoxide (Carboxyhemoglobin/CoHgb) attached to hemoglobin falls below 5%.
- When your child falls into a coma due to severe carbon monoxide poisoning, your child may already have brain damage due to oxygen deficiency, and the brain may be swollen.
- In this case, the brain edema that has already occurred should be properly treated. Other people who breathe air with high levels of carbon monoxide in the same place can also become addicted to carbon monoxide.
- Because of this, those who were with him should also receive appropriate treatment. It also prevents carbon monoxide from poisoning again.
- If the concentration of carbon monoxide is higher than normal, you can prevent carbon monoxide poisoning by installing a carbon monoxide alarm that sounds an alarm.

▴ Photo 1-37. A carbon monoxide alarm can be used to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”