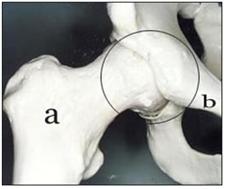
사진 156. 고관절
a-대퇴골, b-좌골, ○으로 표시한 부위에 고관절이 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
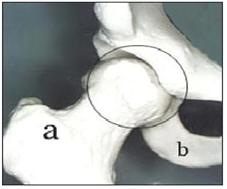
사진 157. 고관절
a-대퇴골, b-좌골, ○으로 표시한 부위에 고관절이 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
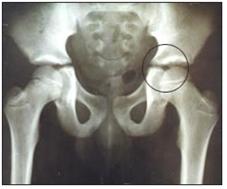
사진 158. 양쪽 전후면 고관절 X선 사진
◯으로 표시된 부위에 좌 고관절이 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
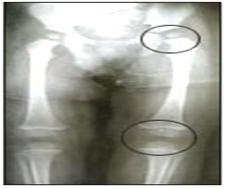
사진 159. 양쪽 전후면 고관절 X선사진
◯으로 표시된 부위(상)에 좌 고관절이 있다. 좌 무릎관절(슬관절)(하)이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 관절을 둘러싸고 있는 막을 관절막이라고 한다.
- 관절낭 막은 두 겹으로 되어 있다. 두 겹의 관절낭 막 중 안쪽 관절막을 활막 또 윤활막이라고 한다(그림 160 참조).
- 이 활막에 생긴 염증을 활막염이라 한다.
- 활막에 일시적으로 염증이 생겼다가 거의 완전히 회복되는 병을 일과성 활막염이라고 한다.
- 여러 종류의 염증이 신체 모든 관절의 활막에 일시적으로 생겼다가 나을 수 있다.
- 여기서는 염증이 고관절의 활막에 일시적으로 생겼다가 나은 일과성 고관절 활막염에 대해서 주로 설명하기로 한다(선천성 고관절 탈구, 후천성 고관절 탈구, 탈구 참조).
일과성 활막염의 원인
-
원인은 아직도 확실히 모른다.
-
바이러스가 고관절의 활막에 감염되어 이 병이 생긴다는 설도 있고, 고관절에 생긴 사소한 외상으로 인해 생긴다는 설도 있다.
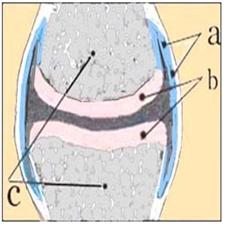
그림 161. 무릎 관절과 활막의 구조
a-활막(윤활막), b-관절 연골, c-경골(하)과 대퇴골(상)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP
일과성 활막염의 증상
-
고관절에 생긴 일과성 활막염의 증상 징후는 다양하다.
-
이 병이 나타나기 약 2주 전 경 감기나 다른 종류의 바이러스성 상기도 감염병이나 바이러스성 하기도 감염병 등을 앓았던 병력이 있는 경우가 많다.
-
3~7세 남 유아들이나 학령기 아이들에게 더 잘 발생된다.
-
고관절의 활막에 염증이 생기면, 고관절이 아프고 그쪽 다리를 절름거리면서 걷는다.
-
겉에서 육안으로 볼 수 있을 정도 고관절이 붓지 않고 전신 열이 거의 나지 않는다.
-
어떤 때는 고관절 활막염이 생긴 다리의 무릎 관절만 조금 아플 수 있고 그쪽 고관절과 무릎 관절이 동시 아플 수 있다(p.000에 있는 Q&A 참조)
-
허벅다리도 아플 수 있다.
-
박테리아성 감염으로 고관절염이 생겼을 때는 고열이 나고 고관절에 심한 관절통이 생기지만, 일과성 활막염이 있을 때는 고관절이 그렇게 많이 아프지 않은 것이 보통이다.
-
미열이 날수 있다.
-
일과성 활막염이 고관절에 있을 때 고관절에 생긴 통증은 박테리아성 관절염·바이러스성 관절염·결핵성 관절염·라임 병성 고관절염, 류마티스 고관절염, 연소성 류마토이드 고관절염, 대퇴골 골절, 백혈병, 고관절 탈구 등으로 생긴 고관절 통증과 비슷할 때가 있다. 따라서 그런 병들과 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
이 병이 심할 때는 일과성 활막염이 있는 고관절이 아파서 잘 걷지 못한다.
-
고관절에 통증은 밤이나 아침에는 더 심할 수 있다.
-
이 병은 대증치료를 하고 1~2주 지나면 낫는 것이 보통이다.
일과성 활막염의 진단 치료
-
병력·증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 추정 진단한다.
-
고관절의 X선 사진 검사· CT 스캔 검사·투베르쿨린결핵 피부 반응 검사· CBC 피 검사(전 혈구 계산 검사) 등으로 다른 고관절염과 감별 진단할 수 있다.
-
위에서 설명한 것같이 이 병과 다른 여러 종류의 병에 의해서 생긴 고관절염을 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
확실한 진단이 나올 때까지 의사의 처방 없이 타이레놀, 아스피린, 또는 모트린 등 해열, 진통, 항염증제로 치료해서는 안 된다. 병을 확진하는 데 지장을 주기 때문이다.
-
이 병은 특별히 치료하지 않아도 저절로 낫는 것이 보통이다.
-
그러나 일과성 고관절 활막염으로 심하게 아플 때, 또는 진단이 확실히 나지 않았을 때는 병원 입원치료를 받는다.
-
아픈 다리를 잡아당겨 치료하는 다리 견인 장치로 치료하면서 다른 병으로 생긴 관절염과 감별 진단한다.
-
활막염이 있는 고관절이 더 이상 아프지 않을 때까지 걷거나 달리기 등의 육체적 운동을 하면 염증이 있는 고관절에 더 부담이 갈 수 있다. 그래서 특히 다리에 힘을 주는 육체적 운동을 하지 말아야 한다.
-
부득이 걸어야 할 때는 목발을 짚고 걷게 하든지 집에서 안정을 취하도록 한다.
-
대개는 일과성 고관절 활막염은 1~2주 정도 지나면 자연히 낫는다.
-
활막염이라 확실히 진단이 난 후 고관절이 계속 아프면 타이레놀이나 모트린 등으로 대증 치료를 할 수 있다.
Transient Synovitis (Toxic Synovitis) 일과성 활막염

Photo 156. Hip joint A-femur, b-sciatic bone, there is a hip joint in the area marked with ○. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Photo 157. Hip joint A-femur, b-sciatic bone, there is a hip joint in the area marked with ○. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 158. X-ray of both anterior and posterior hip joints There is a left hip joint in the area marked with ◯. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 159. X-ray of both anterior and posterior hip joints There is a left hip joint in the area marked with ◯ (upper). The left knee joint (knee joint) (lower). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
• The membrane surrounding the joint is called the joint membrane.
• The joint capsule membrane has two layers. Among the two layers of the joint capsule membrane, the inner joint membrane is called the synovial membrane or synovial membrane (see Figure 160).
• Inflammation of this synovial membrane is called synovitis.
• Transient synovitis is a disease in which the synovial membrane is temporarily inflamed and almost completely recovered.
• Several types of inflammation can occur temporarily in the synovial membranes of all joints in the body and then heal.
• Transient hip synovitis, in which inflammation occurs temporarily in the synovial membrane of the hip joint, and then heals, will be mainly described (see congenital hip dislocation, acquired hip dislocation, and dislocation).
Causes of transient synovitis
• The cause is still unknown.
• There is a theory that the disease is caused by a virus infecting the synovial membrane of the hip joint.

Figure 161. Structure of the knee joint and synovial membrane a-synovial membrane (synovial membrane), b-articular cartilage, c-tibia (bottom) and femur (top) Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP
Symptoms, signs of transient synovitis
• Symptomatic signs of transient synovitis in the hip joint vary.
• About 2 weeks before the onset of this disease, there are many cases of having a cold or other viral upper respiratory tract infections or viral lower respiratory tract infections.
• It is more common in boys aged 3-7 years or in school-age children.
• When the synovial membrane of the hip joint becomes inflamed, the hip joint hurts and the person walks with a limp in that leg.
• The hip joint is not swollen enough to be seen with the naked eye, and there is hardly any body heat.
• Sometimes, only the knee joint of the leg with hip synovitis may be slightly painful, and both the hip joint and the knee joint may be sore at the same time (see Q&A on p.000).
• Your thighs may also hurt.
• Bacterial infection of the hip joint causes high fever and severe hip joint pain, but with transient synovitis, the hip joint usually does not hurt as much.
• You may have a low fever.
• When transient synovitis is in the hip joint, the pain in the hip joint is similar to the hip pain caused by bacterial arthritis, viral arthritis, tuberculosis arthritis, Lyme disease hip arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, femur fracture, leukemia, and hip dislocation. have. Therefore, it is necessary to differentially diagnose such diseases.
• When this disease is severe, the hip joint with transient synovitis hurts, making it difficult to walk. • Hip pain may be worse at night or in the morning.
• This disease usually gets better after 1 to 2 weeks after symptomatic treatment.
Diagnosis, treatment of transient synovitis
• A presumptive diagnosis is made by synthesizing medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
• Hip joint X-ray examination
• CT scan examination • Tuberculin tuberculosis skin reaction test
• CBC blood test (complete blood count) can be used for differential diagnosis from other hip arthritis.
• As described above, hip arthritis caused by this disease and several other diseases should be differentially diagnosed. • Do not use antipyretic, analgesic, or anti-inflammatory drugs such as Tylenol, Aspirin, or Motrin without a doctor’s prescription until a definitive diagnosis is made. Because it interferes with the diagnosis of the disease.
• This disease usually gets better on its own without any special treatment.
• However, if you are seriously ill from transient hip synovitis, or if the diagnosis is not clear, you should be hospitalized.
• Differential diagnosis from arthritis caused by other diseases while treating with a leg traction device that pulls and treats a sore leg.
• Physical exercise such as walking or running until the hip joint with synovitis is no longer sore can put more strain on the inflamed hip joint. Therefore, you should avoid doing any physical exercise that especially strengthens your legs.
• When walking is unavoidable, have them walk on crutches or rest at home.
• Transient hip synovitis usually resolves spontaneously in 1 to 2 weeks.
• If the hip joint continues to hurt after a definite diagnosis of synovitis, treatment can be symptomatic with Tylenol or Motrin.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 안효섭 외 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other