익사(익수사고)와 익사 직전 상태, Drowning and near drowning
-
아무 사고도 나지 않고 구출될 수 있고,
-
익사될 뻔 했지만 구출되어 생명을 구할 수 있고,
-
익사 사고로 죽을 수 있다.
-
물에 빠지면 스스로 살아나든지, 구출되어 살아나든지, 또는 생존 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치로 살아날 수 있다.
-
물에 빠진 아이 자신이 물에서 스스로 나와 응급처치나 생명유지 기본 심폐 소생술 등의 처치를 받지 않고 살아 날 수 있는 익수사고
-
주위에 있는 사람의 도움으로 물속에서 구조된 후 응급처치나 생명유지 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치법 등의 처치를 받지 않고 살아 날 수 있는 익수사고
-
사망 직전 질식 상태에 있고 의식을 잃었으나 호흡과 심장박동은 아직 정지되지 않은 상태에 있는 아이를 물속에서 건져 기본 생명 유지 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치법 등 응급처치로 생명을 구조할 수 있는 익수사고
-
완전히 질식 상태에 있고 호흡도 정지되고 심장도 정지된 직후 익수사고
-
생명을 건질 수 없는 상태로 완전히 질식되어 있고 호흡도 정지되고 심장박동도 정지된 상태의 익수사고로 나눌 수 있다.
| 물에 빠져 물속에 잠기면 바로 죽든지, 바로 죽지는 않았지만 질식 상태에 빠지고 뇌가 손상되어 물에 빠진 후 24시간 내에 죽는 사고를 익사 또는 드라우닝(Drowning)이라고 하며, 물속에 잠겨 질식되었으나 생명을 유지하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치법 등 적절한 처치를 요하는 사고를 익사 직전 상태(니어 드라우닝/Near-drowning)라 한다. |
- 금방 물에 빠져 의식을 거의 잃고 어느 정도 질식되었지만 물속에서 건져 낸 후 생명 유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술 등으로 생명을 구할 수 있는 익수사고를 ‘니어 드라우닝 익사 직전 상태 또는 거의 익사할 뻔했다고 한다.
-
통계에 의하면, 모든 종류의 안전사고로 죽은 아이들 중 10%는 물에 빠져 죽었다(또는 익사했다고 한다).
-
물에 빠져 죽은 아이들의 50%는 5세 이전 영유아들이었다고 한다.
-
흔히 익사 사고는 수영장, 연못, 호수, 집안 목욕탕 등에서 가장 잘 생긴다.
-
-
물이 비강, 인두, 후두, 기관, 기관지, 폐 속으로 들어가 기도가 완전히 막히고 질식되든지,
-
물이 기관 속, 기관지 속, 폐 속으로 들어가지는 않았지만 후두 경련이 생겨 질식되든지,
-
또는 물로 인두 부분 기도, 후두 부분 기도, 기관 부분 기도 등의 기도가 차단되고 그와 동시에 후두경련이 생겨 질식 사망하게 된다고 한다.
-
담수에 빠져 담수가 인두, 기관, 기관지 속, 폐 속으로 흡입되어 무기폐가 생길 수 있고, 폐가 부어 산소가 섭취되지 못해 질식 사망하는 경우가 보통이다.
-
해수에 빠졌을 때는 폐포에 물이 차고 폐가 부어서 질식 사망하는 것이 보통이다.
-
따뜻한 물에 빠졌을 때보다 찬물에 빠져 생긴 익사 직전 상태의 경우 생명을 구할 수 있는 확률이 더 높다.
-
물속에 빠지면서, 두개골이나 목뼈 등이 다칠 수도 있고, 저온증(低溫症)에 빠질 수 있고 전신 경련을 할 수 있다.
-
물속에 들어가기 전에 음주하거나 신경안정제나 다른 종류의 약물을 복용했을 때, 극히 피로할 때, 수영을 전혀 할 줄 모르거나 잘 할 수 없는 경우, 타고 가던 배가 전복되어 물에 빠질 때, 또는 다른 경우에는 익사 직전 상태가 생길 수 있고 때로는 익사사고가 생길 수 있다.
-
-
물속에 빠져 완전히 죽을 때까지 다음과 같은 경로를 거쳐 죽는다.
-
전신이 물속에 잠기면 후두경련이 생겨 협착음이 나면서 숨이 가빠지고 기침하고 심장 박동이 빨라지고 정신이 혼미해지고 전신 경련을 하고 저혈압→무호흡(無呼吸)→혼수→심장마비가 생겨 죽는다.
-
물에 빠져 익사 직전 상태에 처해 있는 아이를 물에서 건진 후 즉시 기본 생명 유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술 응급처치법을 사고 현장에서 적절히 잘 하면 생명을 구할 수 있는 경우도 많다.
-
이런 경우에 대비해 가능한 한 누구든지 기본 생명유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 평소에 배우고 연수 재교육 받는다.

▴ 그림 357. 1.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법.
물에 빠진자와 구조자에게 가장 안전한 구조 방법이 무엇인가 생각하는 것이 최우선적이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
물에 빠져 익사하기 직전 상태에 있는 아이를 물속에서 건져내는 처치법으로 생명을 구하는 처치술 구조 방법과 건져낸 후 익사 직전 상태의 아이를 응급처치와 기본 심폐 소생

▴ 그림 358. 2.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 그림 359. 3.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
▴ 그림 360. 4.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 그림 361. 5.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
물에 빠진 아이를 물속에서 건져내는 구조법
-
물에 빠진 사람을 목격하면 누구든지 당황한다.
-
그렇지만 서둘지 말고 침착하게 속히 구출해 주는 것이 중요하다.
-
금방 물속에 빠져 물속에 잠겨 있든지, 물에 빠져 허우적거리면서 의식이 있는 사람을 목격했을 때는 수영을 잘 할 수 있건 잘못 하건 그 당시의 모든 상황을 잘 고려, 참작하고 잘 판단 한 후 물에 빠진 사람을 가장 적절한 방법으로 구조 한다 그림 (357 참조).
-
당황한 나머지 덮어놓고 물속에 서들어 뛰어 들어가지 말아야 한다.
-
수영을 잘 할 수 있든 잘 할 수 없든 그 상황에서 구조 자와 물에 빠진 두 사람의 생명을 가장 안전한 방법으로 구조해야 한다.
▴ 그림 362. 6.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 그림 363. 7.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
▴ 그림 364. 8.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 그림 365. 9.
물에 빠진 사람 구조 방법. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
|
물에 빠진 사람을 처음 목격한 사람이 수영을 잘 할 줄 알건 잘 할 수 없건 그 때의 상황에 따라
|
-
물에 빠졌으나 아직 의식이 있는 학령기 아이나 사춘기 아이의 경우 밧줄 등 안정이 있는 줄을 이용하여 물속에서 구조 할 수 있다.
-
보트 등 배가 있으면 배를 이용해서 구조할 수 있다.
-
큰 플라스틱 병을 이용해서 구조할 수 있다.
-
앞서 설명한 여러 가지 방법으로 구조를 시도해 보고 마지막으로 물에 빠진 사람을 구조하는 법을 전에 교육받았고 그 상황에서 구조할 수 있는 능력 있는 사람이나 그 상황에서 안전하게 구조할 자신이 있으면 물속에 들어가 물에 빠진 아이를 구조해야 한다.
-
그와 동시 주위에 있는 사람에게 도움을 청하고, 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과 의사, 소방서에 연락해서 그들의 도움을 청해야 한다.
물에 빠져 거의 질식 상태에 있는 아이나 거의 사망 직전에 있는 아이를 물속에서 건져낸 후 심폐 소생술 및 응급처치
① 물에 빠져 거의 질식된 상태에 있는 아이나 거의 사망 직전에 있는 아이를 물속에서 건져낸 후 편평한 자리에 눕힌다. 머리와 상체를 하체보다 15도 정도 낮게, 얼굴을 살짝 옆으로 향해 눕힌다.
② 그와 동시에 주위 사람의 도움을 청하고, 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과 의사, 소방서 등에 연락해서 그들에게 도움을 청한다.
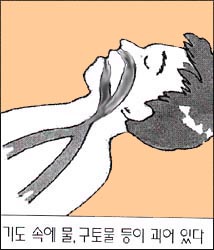
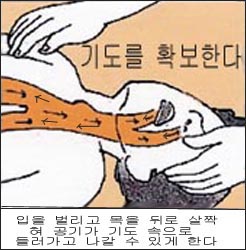
③ 환아의 얼굴과 목을 옆으로 살짝 돌리고 낮게 눕혀 비강, 인두 강, 후두, 기관 속, 기관지 속에 있는 물이나 점액, 구토 물 등이 중력에 의하여 상·하기에서 밖으로 흘러나오게 해 기도(숨통)를 열어 기도 확보를 하고 잘 호흡할 수 있게 도와준다.
④ 그와 동시 구조자의 귀를 아이의 콧구멍과 입 근처에 대든지 앞가슴에 처차자의 손을 얹어 환아가 숨을 쉬고 있나 확인한다.
⑤ 목, 팔목, 팔꿈치, 서혜부 등에 있는 동맥에서 맥박을 짚어 심장이 뛰는지 확인하고 앞가슴이 숨 쉬는 대로 올라갔다 내려갔다 하는지 알아본다.
⑥ 숨을 전혀 쉬지 않지만 아직 살아 있다고 판정하거나 살아 있는지 확실히 모르거나, 숨을 아주 미약하게 쉬거나 아주 어렵게 쉴 때는 처치자의 입을 아이의 입이나 입과 콧구멍에 대고 인공호흡을 시작한다. 맨 처음 공기를 기도 속으로 두 번 불어넣어서 공기가 폐 속으로 들어가는지 확인한다.
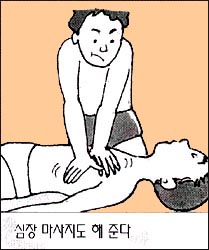
⑦ 그와 동시 심장마사지를 한다.
나이에 따라 5번 심장마사지를 하고 1번 인공호흡을 한다. 즉 생명유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 시작한다.
⑧ 숨을 조금도 쉬지 않거나, 심장이 아주 약하게 박동하거나 아주 느리게 뛰거나, 전혀 뛰지 않아도 아이가 사망했다고 진단이 내릴 때까지 인공호흡과 심장 마사지를 계속해서 기본 심폐 소생술을 한다.
⑨ 처치자 혼자만 있을 때는 인공호흡과 심장 마사지를 처치자 혼자 해야 하고, 두 사람이 있을 때는 한 사람은 심장 마사지를 하고 다른 사람은 인공호흡을 한다.
⑩ 세 사람이나 그 이상 있을 때는 한 사람은 인공호흡을, 그 다음 사람은 심장 마사지를, 그 다음 사람은 젖은 옷을 벗기고 따뜻한 담요 등으로 환자의 몸을 따뜻하게 싸 보온해 주고 그 때 상황에 따라 그 밖에 필요한 다른 응급 처치를 한다.
⑪ 물속에 빠진 아이를 목격하자마자 가능한 한 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과 의사, 소방서 등에 긴급 전화를 해서 그들의 지시에 따라 물속에서 구조한다. 그리고 구조하는 동안도, 또 물속에서 환아를 꺼낸 후 응급처치를 시작하고 필요하면 물속에서 건지는 동안도 인공호흡과 심장 마사지를 한다.
⑫ 물속에서 건졌을 때의 상황에 따라 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치법을 하고 필요한 다른 치료를 받기위해 구급차나 다른 적절한 방법으로 가장 적절한 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 간다. 필요에 따라 병원에 도착하기 전, 또는 의사의 치료를 받기 전까지 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치법을 계속한다.
⑬ 구조자의 입을 아이의 입에, 또는 입과 콧구멍에 대고 인공호흡을 해 줄 때 1분 동안 인공호흡의 횟수는 아이의 나이에 따라 다르다.
⑭ 신생아나 영아에게는 1분 30∼40번 정도, 한 살 이후부터 8세까지 학령기 아이에게는 20∼30번 정도 인공호흡을 한다.
-
신생아나 영아에게 심장 마사지를 할 때는 1분 동안에 90∼100번 정도하고, 돌 지난 유아나 학령기 아이에게 60∼80번 정도 한다( 심폐 소생술(CPR) 참조).
-
영유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들, 성인들에게 기본 심폐 소생술을 할 때 5번 심장 마사지를 하고 한 번(1) 인공호흡을 하는 것이 보통이다.
⑮ 산소가 있으면 물론 산소호흡 치료를 한다.
⑯ 병원에서 그때그때의 상황과 환아의 상태에 따라 기관 내관 삽입 호흡 치료를 할 수 있고 그 내관을 통과해서 숨을 쉬게 하고
⑰ 산소호흡 치료도 할 수 있고 위 속에 있는 위 내용물을 비위관이나 구위관으로 빼기도 하고 쇼크가 됐으면 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사 등으로 적절히 재수화 치료를 한다.
⑱ 필요에 따라 기관지를 확장시키는 약물로 치료도 하고, 그 외 강심제, 항생제 등으로 치료 한다.
⑲ 혈중 전해질 농도 검사, CBC 혈액 검사, 동맥혈 가스 검사 등 여러 가지의 피 검사, 가슴 X선 사진 검사, 머리와 목의 X선 사진 검사 등을 하고 그 결과에 따라 그때그때 적절히 계속 치료한다.
⑳ 물에 빠져 거의 죽을 뻔했던 익사 직전 상태에 갔던 아이나 물에 빠져 죽은 아이들 중 일부는 수영을 하다가 두개골이나 목뼈, 또는 척추 뼈 등이 다칠 수 있다.
㉑ 물에 빠져 거의 죽을 뻔했던 아이를 소생시키는 중이나 소생시킨 후에 이런 종류의 외상이 있는지도 알아봐야 한다.
㉒ 물에 빠져서 거의 죽을 뻔 했다가 소생된 경우나 혼수상태에서 의식을 완전히 회복된 후 2∼3일 동안 병원 입원 치료를 받으면서 합병증이 발생되나 관찰 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
물에 빠졌을 때 다음과 같은 경우 생명을 구조하기가 어렵다
-
물속에 잠긴 이후 5분 이상이 경과됐을 때
-
3세 이전 영유아가 물속에 잠겨 익사 직전 상태에 이르렀을 때
-
물속에서 꺼낸 이후 10분 이상 기본 심폐 소생술로 응급처지를 받지 않은 경우
-
전신 경련을 하거나 동공이 비정상으로 확장되고 동공 대광 반사가 없을 때
-
혼수상태가 심할 때
-
동맥혈 산도(Ph)가 7.10이거나 그 이하일 때
물에 빠지는 사고와 익사사고 예방
-
잘 예방하면 익사사고는 발생되지 않는다. 따라서 물에 빠지지 않게 전력을 다해 예방해야 한다.
-
학교 체육시간 등을 이용해 모든 학생들에게 수영하는 법, 인공호흡법과 심장 마사지를 통해 기본 심폐 소생술, 물에 빠진 아이를 물속에서 구조하는 법 등을 배워야 한다.
-
공공 수영장에서 수용하다 물에 빠지면 구조할 수 있는 성인 구조대가 있는 때만 아이들이 수영을 할 수 있는 규칙을 만들고 실행해야 한다.
-
영유아 학령기 아이 혼자서 수영장, 가정 풀장, 또는 다른 물속에서 수영하다 익사되지 않게 예방해야 한다.
-
쉽게 전복될 수 있는 카누나 작은 배를 탈 때 익사사고를 예방한다. 특히 물에 빠지지 않도록 될 수 있는 한 서 있지 말고 앉아 있는다.
-
탄 배에 불이 나지 않도록 조심하고
-
배를 탈 때는 구조재킷을 입고, 구명쿠션을 가지고 있어야 한다.
-
배가 전복될 때는 상황에 따라 가능한 한 전복된 배를 꼭 붙들고 있어야 더 쉽게 구조될 수 있다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병과 안전사고의 예방–익사사고 예방 참조).
물에 빠졌을 때와 물에서 구조하는 동안 주의사항
-
물에 빠진 아이를 구조할 때는 그 때의 상황에 따라 구조하는 방법이 다르다.
-
수영을 해서 구조할 수 있는 사람이 물에 급히 뛰어 들어가서 물에 빠진 아이를 구조 시도를 하기 전에 밧줄이나, 빈병, 배 등으로 최초 구조를 시도하든지 그 외 다른 안전 구조방법으로 구조하는 방법을 생각해야 한다.
물에 빠진 아이를 구조할 때 주의 사항을 요약하면
|
Drowning and near-drowning 익사(익수사고)와 익사 직전 상태
Drowning in the water
- Can be rescued without any accident, I was almost drowned, but I was rescued and could save my life,
- You can die in a drowning accident.
- If you fall into the water, you can survive by yourself, rescue and survive, or survive with basic CPR first aid.
- A drowning accident in which a drowning child himself can come out of the water and survive without first aid or basic CPR for life support.
- A drowning accident that can survive without receiving treatment such as first aid, basic CPR, first aid, etc. after being rescued from the water with the help of a nearby person
- A drowning accident in which a child who is in a state of suffocation immediately before death and unconscious,
- but whose breathing and heartbeat are not yet stopped, is rescued from the water to maintain basic life, and can save lives through first aid measures such as basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation and first aid measures.
Drowning immediately after being completely suffocated, breathing and heart stopped It can be divided into a drowning accident in which life is not saved, completely suffocated, breathing is stopped, and heartbeat is stopped.
An accident that dies immediately after being drowned in water or submerged in water dies within 24 hours after falling into the water due to a suffocation state and brain injury, although it is submerged in water and suffocated but sustains life.
An accident that requires appropriate treatment, such as basic CPR first aid, is called a state on the verge of drowning (near-drowning).
- He fell into the water, almost lost consciousness, and was suffocated to some extent, but after being rescued from the water, he suffered a drowning accident that could save his life through basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation to sustain life.
- According to statistics, 10% of children who died in all kinds of safety accidents drowned. It is said that 50% of the children who died drowning were infants and toddlers before the age of five.
- Often, drowning accidents occur most commonly in swimming pools, ponds, lakes, and in-house baths.
When a child falls into the water
- Whether water enters the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, the airways are completely blocked and suffocates,
- Water did not enter the trachea, bronchi, or lungs, if the laryngeal spasm and suffocation occurred,
- Or, it is said that airways such as the pharyngeal partial airway, laryngeal airway, and tracheal airways are blocked with water, and at the same time, laryngeal spasm occurs, resulting in suffocation.
- Inhalation of freshwater into the pharynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs due to falling into freshwater can lead to atelectasis, and it is common to die asphyxia because the lungs are swollen and oxygen cannot be ingested.
- When drowning in seawater, it is common to die of asphyxiation due to the alveoli being filled with water and the lungs swollen.
- There is a higher chance of saving lives if your child is drowning in cold water than if your child was drowning in warm water.
- While falling in the water, your child may injure his skull or neck, he may fall into hypothermia, and he may have systemic convulsions.
- When your child drinks before entering the water, take a tranquilizer or other type of medication, when he may be extremely tired, when he does not know how to swim at all or when he is unable to swim well, when the boat he were going to roll over and fall into the water, or in other cases
- There can be conditions on the verge of drowning, and sometimes drowning can occur.
- They die through the following path until they are completely submerged in the water. When the whole body is submerged in the water, a laryngeal spasm occurs and a stridor sound occurs, shortness of breath, coughing, heartbeat accelerates confusion, systemic convulsions, hypotension → apnea → coma → heart attack and death.
- In many cases, life can be saved if the basic CPR first aid method to maintain basic life immediately after drowning a child who is drowning drowned out of the water is properly done at the accident site.
- In preparation for such a case, anyone learns basic CPR to maintain basic life as much as possible and receives training retraining.

▴ Figure 357. 1. How to rescue a drowned person. Thinking about what is the safest way to rescue drowners and rescuers is a top priority. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
A treatment that saves a child’s life from drowning after being drowned in water,
A rescue method, and first aid and basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation for a child who is on the verge of drowning after the rescue.

▴ Figure 358. 2. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 359. 3. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 360. 4. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 361. 5. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
A rescue method to rescue a drowned child out of the water
- Anyone who sees a drowning person is confused.
- However, it is important not to rush, calmly and quickly rescue. Whether you are drowning in the water right away, or if you see a conscious person struggling while drowning, consider carefully all the circumstances at that time, whether you can swim well or do something wrong, and then fall into the water.
- Rescue people in the most appropriate way Figure (see 357).
- You shouldn’t jump into the water after covering it up in a panic.
- Whether you can swim well or not, you must rescue the life of the rescuer and the two drowned in the safest way in that situation.

▴ Figure 362. 6. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 363. 7. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 364. 8. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 365. 9. How to rescue a drowned person. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Whether the first person to see a drowning person knows how to swim well or not, depending on the situation at that time
1. Objects such as empty plastic bottles that can float well in water,
2. Tubes with air that float well in water and do not explode, etc.
3 . A long rope that does not break, First of all, you need to use a boat, such as a boat, to rescue the drowned person by using the means to rescue the drowned person.
4. Even a person who can swim well should carefully judge whether it is possible to safely rescue the drowned person by jumping into the water after considering the various situations at that time, or whether there may be a danger to the life of the rescuer himself, and then go to rescue.
5. Confused, the rescuer can rush into the water without considering his own safety and the safety of the drowned person, and the drowned person and the rescuer can drown together.
6. In the case of a school-age child or adolescent child who has fallen into the water but is still conscious, it is possible to rescue in the water using a stable rope such as a rope. If you have a boat, such as a boat, you can use it to rescue.
7. It can be rescued using a large plastic bottle. If you have tried rescue in the various ways described above, and finally, if you had previously been educated on how to rescue a drowned person and have the ability to rescue in that situation, or if you are confident to rescue safely in that situation, you can go into the water and drown.
8. You have to rescue the child. At the same time, you should ask for help from people around you, and contact the medical paramedics, hospital emergency room, regular pediatricians, doctors, and fire departments for their help.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation and first aid after removing a child who is drowning in water and is almost suffocating or is almost on the verge of death from the water
① Rescue a child who is almost suffocated by drowning or who is almost on the verge of death from the water and lay it on a flat surface. Lay your head and upper body about 15 degrees lower than your lower body and your face slightly to the side.
② At the same time, ask for help from people around you, and contact the medical paramedics, hospital emergency room, regular pediatricians, doctors, fire departments, etc. to ask them for help.
③ Turn the patient’s face and neck slightly to the side and lay it down to make the nasal cavity, pharyngeal cavity, larynx, trachea, and water, mucus, vomiting water, etc. in the trachea flow out from the upper and lower airways by gravity. It opens the airway and helps you breathe well.
④ At the same time, place the rescuer’s ears near the child’s nostrils and mouth, or place the child’s hand on the chest to check if the child is breathing.
⑤ Check if the heart is beating by pointing the pulse at the arteries in the neck, wrist, elbow, and groin, and see if the forearm goes up and down as you breathe.
⑥ If your child does not breathe at all, but judge that he is still alive, you are not sure if he is alive, or he breathes very weakly or breathes very hard, start artificial respiration by putting the person’s mouth into the child’s mouth, or mouth and nostrils. The first time you blow air into his airways twice, check to see if the air gets into his lungs.
⑦ Do a heart massage at the same time. Depending on his age, do 5 heart massages and 1 artificial respiration. In other words, basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation is started to maintain life.
⑧ Even if he does not breathe at all, his heart is beating very weakly, beating very slowly, or even if he does not beath at all, continue to perform basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation with artificial respiration and heart massage until a diagnosis is made that the child has died.
⑨ When the person in charge is alone, artificial respiration and cardiac massage should be performed by the person in charge. When there are two persons, one person performs heart massage and the other person performs artificial respiration.
⑩ When there are three or more, one person will receive artificial respiration, the next one will have a heart massage, and the next will take off the wet clothes and wrap the patient’s body warm with a warm blanket, etc. Do any other first aid you need outside.
⑪ As soon as you see a child drowned, make an emergency call to the medical paramedics, hospital emergency room, regular pediatricians, fire department, etc., and rescue them in the water according to their instructions.
Also, during rescue and after removing the child from the water, first aid is initiated, and if necessary, artificial respiration and heart massage are performed while the child is removed from the water.
⑫ According to the situation when you are rescued from the water drowning, perform basic CPR first aid, and take an ambulance or other appropriate method to the most appropriate hospital emergency room to receive other necessary treatment. If necessary, continue with basic CPR first aid before arriving at the hospital or until receiving medical attention.
⑬ When giving artificial respiration with the rescuer’s mouth in the child’s mouth, or in the mouth and nostrils, the number of artificial respirations for one minute varies depending on the child’s age.
⑭ For newborns and infants, give 30-40 times per minute, and 20-30 times for school-age children from one year old to 8 years old. When doing heart massages to newborns or infants,
- do it 90 to 100 times per minute, and 60 to 80 times for older infants or school-age children (refer to CPR).
- When performing basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation to infants, school-age children, adolescent children, and adults, it is common to do five heart massages and one (1) artificial respiration.
⑮ If you have oxygen, of course, take oxygen-breathing treatment.
⑯ In the hospital, depending on the situation at that time and the patient’s condition, endotracheal tube insertion breathing treatment can be performed, and breathing through the inner tube can be performed.
⑰ Oxygen breathing treatment is also possible, and the contents of the stomach in the stomach may be removed through a nasogastric tube or an oral gastrointestinal tube, and if a shock occurs, appropriate rehydration treatment is performed by intravenous injection of a glucose electrolyte solution.
⑱ If necessary, treat with drugs that expand the bronchi, and treat with other cardiac medications, antibiotics, etc.
⑲ According to the results, various blood tests such as blood electrolyte concentration test, CBC blood test, arterial blood gas test, chest X-ray photo test, head and neck X-ray photo test, etc. are performed, and according to the result, appropriate treatment is continued on time.
⑳ Children who almost died by drowning in water or some of the children who died drowning may injure their skulls, neck bones, or spinal bones while swimming.
㉑ You should also find out if there is any kind of trauma while resuscitating a child who almost died from drowning in water or after resuscitation.
㉒ In the case of resuscitation after almost dying from drowning in water, or after being in a hospital for 2-3 days after fully recovering from consciousness in a coma, complications occur, but observational treatment is usually performed.
When drowning, it is difficult to save a life in the following cases:
- When more than 5 minutes have passed since submerged in water
- When infants and toddlers before the age of 3 are submerged in water and reach a state on the verge of drowning If you have not received first aid by basic CPR for 10 minutes or more after taking out from the water
- Full body convulsions or abnormally dilated pupils and no pupillary reflex
- When the coma is severe
- When arterial blood acidity (Ph) is 7.10 or less
Prevention of drowning and drowning accidents
- If prevented well, drowning accidents do not occur.
- Therefore, you must do all you can to prevent drowning in the water.
- Students should learn how to swim in school physical education classes, etc., basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation through artificial respiration and cardiac massage, and how to rescue a drowned child in the water.
- Make and implement rules that allow children to swim only when there is an adult rescue team available to rescue them from being held in a public swimming pool and drowning. Infants and children of school age must be prevented from drowning while swimming alone in a swimming pool, home pool, or other water.
- when riding a canoe or small boat that can easily overturn.
- In particular, do not stand and sit as far as possible to avoid drowning. Be careful not to catch fire on the ship on board
- When riding a boat, you must wear a rescue jacket and have a life cushion.
- When a boat is overturned, it can be more easily rescued by holding the overturned boat as tightly as possible depending on the situation
- (Parents should also become at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing)-Vol. 2 Prevention of childhood and adolescent diseases and safety accidents-Drowning See Accident Prevention).
Precautions when drowning and while rescued from the water.
When rescuing a drowned child, the rescue method differs depending on the situation at that time.
- Before a person who can rescue by swimming jumps into the water and attempts to rescue a child who has fallen into the water,
- First attempt to rescue with a rope, empty bottle, or boat, or other safe rescue methods should be considered.
- To summarize the precautions when rescuing a drowned child
- Choose the most appropriate rescue method.
- When rescuing a drowned child, try to rescue the face and upper body first if possible. If possible, start artificial respiration underwater as needed.
- When you know that water or vomiting water is in his airways, he can’t breathe and start the treatment to open his airway.
- So, it is very important to open the airway by removing the vomit water from the airway.
- .Opening his mouth slightly, tilting his neck back slightly, and turning his head slightly to the side can open his airways better.
- Among children who have drowned in water, there may be a head injury, a neck bone injury, etc.
- When performing first aid, do not move any part of the body such as the neck carelessly.
- If necessary, artificial respiration is performed by placing your mouth on the child’s mouth and nostrils or mouth. Also do a heart massage.
- When more than one person is present, one person will have artificial respiration and the other will have a heart massage.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Manual of emergency pediatrics 4th edition, Robert M. Reece, M.D., p.133,241-242
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.319-322
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Mose Grossman, M.D., p.303-304
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.317-319
-
Nelson textbook, 14 edition p.230-233
-
신생아 심폐 소생술
-
호흡곤란
-
콧구멍 속 이물, 비강 속 이물, 외비공의 이물
-
기도 속에 이물이 들어갔을 때와 질식
-
하임리크 처치법
-
질식 참조
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
소아과학 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”