유리 수은 구강 체온계나 유리 수은 항문 체온계로 체온 재는 법 How to take oral temperature or rectal temperature by glass mercury thermometer
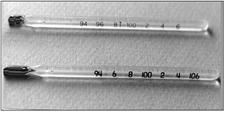
사진 26. 위 수은 유리 체온계는 주로 항문 체온을 잴 때 쓰고 아래 수은 유리 체온계는 주로 구강 체온을 잴 때 쓴다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 27. 위 수은 유리 체온계는 주로 항문 체온을 잴 때 쓰고 아래 수은 유리 체온계는 주로 구강 체온을 잴 때 쓴다. 원 내 체온계 모양에 좀 차이가 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
참고로, 미국에서 수은 유리 체온계를 사용을 권장하지 않지만 수은 유리 체온계의 값이 싸고, 보관하기 쉽고 가지고 다니기가 간편하고 쉽게 쓸 수 있기 때문에 아직 버리지 않고 계속 쓰는 가정이 많다. 그래서 여기서 수은 유리 체온계에 관해 더 설명 한다.
-
유리로 만든 수은 체온계로 체온을 가장 정확하게 재기 위해 체온계의 끝 부분을 입안이나 겨드랑 속 또는 항문 속에 얼마 오랫동안 넣고 있다가 꺼내야 옳게 재는 체온인지에 관해 이론이 많다.
-
연구에 의하면 수은 유리 체온계를 입안에 7분 동안, 겨드랑에 5분 동안, 항문 속에 4분 동안 넣었다 꺼내야 가장 정확히 측정한 체온이라고 한다.
-
실제로는 이렇게 4-7분 동안 체온을 재지 않고 유리로 만든 수은체온계를 3~5분 정도 입안이나 항문 속에 넣었다 빼서 체온을 재는 것이 보통이다. (전자 체온계로 체온을 재는 데는 불과 몇 초 내지 1분 내에 잴 수 있고 체온 재는 인건비도 절약할 수 있다.)
-
4~6세 이전 대부분의 영유아들은 입안에서 수은 유리 구강 체온계를 3~5분 동안 입안에 계속 넣고 있을 수 없고, 또 수은 유리 구강 체온계를 입안에 넣고 있는 동안 체온계를 깨물어 부술 수 있다.
-
4~6세 이전 영유아들의 체온을 잴 때는 입안에서 구강 체온을 재는 대신 항문 속이나 겨드랑 이에서 체온을 재야한다.
-
아이들의 체온을 잴 때 재기 전에 체온을 재는 이유와 방법에 대해 간단히 설명해야 한다.
-
4~6세 이상 아이들의 체온을 잴 때는 수은 유리 구강 체온계로 입안에서 잴 수 있다.
-
겨드랑 체온을 잴 때는 수은 항문 유리 체온계나 수은 유리 구강 체온계 중 어느 것을 써도 된다.
-
심한 운동을 한 후 바로 잰 체온은 가만히 앉아 휴식을 취한 후 바로 잰 체온보다 정상적으로 조금 더 높다.
-
응급한 경우를 제외하고 정신적으로 육체적으로 잠시 동안 쉬었다가 체온을 재는 것이 좋다.
-
열나면서 심하게 아플 때는 어느 때든지 어디서든지 체온을 재도 된다.
-
이 수은 유리 체온계로 체온을 재는 법에 대하여 다음에 더 구체적으로 설명한다.
How to take oral temperature or rectal temperature by glass mercury thermometer

Picture 26. The upper mercury glass thermometer is mainly used to measure anal temperature, and the lower mercury glass thermometer is mainly used to measure oral temperature. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 27. The upper mercury glass thermometer is mainly used to measure anal temperature, and the lower mercury glass thermometer is mainly used to measure oral temperature. You can see that the shape of the thermometer in the circle is slightly different. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• For reference, although the use of mercury glass thermometers is not recommended in the United States, many households continue to use mercury glass thermometers because they are cheap, easy to store, easy to carry, and easy to use. So here we explain more about the mercury glass thermometer.
• For the most accurate measurement of body temperature with a mercury thermometer made of glass, there are many theories as to whether the tip of the thermometer must be placed in the mouth, armpit, or anus for a long time before taking it out to measure correctly. • Studies have shown that the most accurate body temperature is measured when a mercury glass thermometer is placed in the mouth for 7 minutes, in the armpit for 5 minutes, and in the anus for 4 minutes.
• In practice, it is common to take a mercury thermometer made of glass in the mouth or anus for 3 to 5 minutes without taking the temperature for 4-7 minutes and then take it out and take it out. (It can take only a few seconds to a minute to take body temperature with an electronic thermometer, and labor costs for measuring body temperature can also be saved.)
• Most infants and toddlers before 4-6 years of age cannot hold a mercury glass oral thermometer in their mouth for 3 to 5 minutes, and can bite the thermometer while holding the mercury glass oral thermometer in their mouth.
• When taking the temperature of infants and young children before the age of 4 to 6 years, the body temperature should be taken in the anus or in the armpit instead of taking the oral temperature in the mouth.
• When taking children’s temperatures, briefly explain why and how to take their temperature before taking them.
• When taking the temperature of children aged 4 to 6 years old, the temperature can be taken in the mouth with a mercury glass oral thermometer.
• For axillary temperature, either a mercury anal glass thermometer or a mercury glass oral thermometer may be used.
• The body temperature taken right after intense exercise is normally slightly higher than the body temperature taken right after sitting still and resting.
• Except in case of emergency, it is recommended to take a body temperature after resting for a while mentally and physically.
• If you have a fever and are seriously ill, you may take your body temperature anytime, anywhere.
• How to take body temperature with this mercury glass thermometer is explained in more detail below.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제 6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제 20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-본 사이트의 내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine