윌리암스 증후군 Williams syndrome
- 윌리암스 증후군은 유전병이다.
- 윌리암스 증후군이 있는 아이의 상악의 너비는 보통보다 더 넓고
- 하악이 좁고
- 윗 입술이 길고
- 이마가 넓고 크고
- 코가 위로 추켜져 있어 마치 꼬마 요정의 얼굴 형태와 비슷한 얼굴 형태를 나타낸다.
-
그리고 성장과 지능의 발육이 지연될 수 있고 영아기에 혈중 칼슘 농도가 비정상으로 높을 수 있다. (p.00 대동맥 협착 참조)
-
이 병이 있는 아이에게 대동맥판 상부 협착증이 있을 수 있고 폐동맥 협착증도 있을 수 있다3, 4, 그 외.
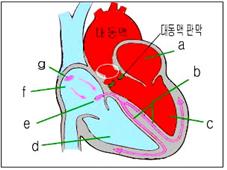
그림 41. 대동맥판 상부 협착(흰색◯내)
a-좌 심방, b-심장자극 전도, c-좌 심실,
d-우 심실, e-방실 결절, f-우 심방, g-동방결절
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Q&A. 윌리엄스 증후군과 대동맥 판막 상부 협착
Q.
- 1달 20일된 남아입니다. 출생 후 심장에서 소리가난다고 큰 병원에 갔는데 심장 초음파 촬영 후 동맥이 좁다는 소견과 윌리엄스증후군이 의심된다는 소리를 들었습니다. 아직 넘 어려 더 지켜봐야한다고요 근데 오늘은 고환이 이상해서 병원에 갔는데 탈장이라고 합니다.
- 수술은 쉬운 것인지 어떻게 돌봐줘야 하는지요. 정상아를 대하듯이 해야 하는지 조심스럽습니다.
- 또 윌리엄스 증후군이란 것은 그 증상을 보니 지능이 낮고 발육이 느리며 얼굴 모양이 정상인과 다르다 등등이 있는데 이 병을 가진 사람은 모두 다 나타나는 건지요? 넘 답답한 마음에 여쭤봅니다
A.
- 정옥님
- 안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다. 걱정이 많이 되시겠습니다.
- 이미 고명하신 소아 심장내과 전문의의 진단을 받으시고 윌리암스 증후군과 탈장에 관해서 많은 정보를 이미 얻었으리라고 믿습니다.
- 제가 더 도움을 드릴 수 있을지 우선 걱정이 생깁니다.
- 다음 글은 문헌에서 얻은 정보 글입니다.
- 1961년 윌리암스(Williams)가 대동 판막 상부 협착이 있고 지능이 낮고 꼬마 요정(Elfin) 얼굴의 형태를 한 환아의 예를 의학계에 발표하고 그 증상 징후로 가진 선천성 병을 윌리암스 증후군이라고 병명을 부쳤습니다.
- 그 후 거의 비슷한 얼굴의 형태를 가진 영아들 중 일부에게 특발성 고 칼슘혈증이 있는 케이스가 의학계에 또 보고 됐습니다.
- 또 Dr. Garcia가 꼬마 요정형 얼굴 형태를 가진 아이에게 대동맥판막 상부 협착과 특발성 고 칼슘혈이 있는 환자의 케이스를 의학계에 보고했습니다.
- 이상 설명한 3가지의 주 증상들은 항시 함께 나타나지 않고 어떤 환아에게 3가지 주 증상들 중 한 가지 주 증상만 생길 수 있다는 것도 보고됐습니다.
- 또 3가지의 주 증상들 중 한 가지 주 증상만 있으면서 비정상적 치아, 목소리 이상, 성장지연 등 다른 증상 징후도 있을 수 있다는 것도 보고됐습니다.
- 다시 설명하면 윌리암스 증후군이 있는 아이에게 반드시 지능 저하가 생기지는 않습니다.
- 그 원인은 아직도 확실히 모릅니다.
- 더 자세한 것은 대동맥 판 상부 협착에 관한 그림과 윌리암스 증후군을 참고하시기 바랍니다. 그리고 탈장에 관해서는 어떤 종류의 탈장을 말씀하시는지 확실히 모르지만 서혜부 탈장을 말씀하시는 줄로 압니다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환–서혜부 탈장에 관한 정보를 읽어보시기 바랍니다.
- 참고적으로 서혜부 탈장의 수술은 날짜를 정해서 선택적 수술로 소아 외과 전문의가 조기에 수술해 주는 것이 보통입니다.
- 더 자세한 것은 단골소아청소년과 의사와 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- 더 필요한 정보를 질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요.
- 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Williams syndrome 윌리암스 증후군
• Williams syndrome is an inherited disease.
• The width of the maxilla in a child with Williams syndrome is wider than usual and
• The mandible is narrow
• The upper lip is long
• Forehead is wide and large
• The nose is squeezed up, giving it a face shape similar to that of an elf.
• And growth and development of intelligence may be delayed, and blood calcium levels may be abnormally high during infancy. (See p.00 Aortic Stenosis)
• Children with this disease may have supaortic valve stenosis and pulmonary artery stenosis3, 4, etc.

Figure 41. Upper aortic valve stenosis (in white◯) a-left atrium, b-cardiac stimulation conduction, c-left ventricle, d-right ventricle, e-atrioventricular nodule, f-right atrium, g-sinus nodule Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Q&A. Williams syndrome and upper aortic valve stenosis
Q.
• A boy who is 1 month and 20 days old. After birth, I went to a big hospital because my heart was making a sound, and after an echocardiography, I was told that my artery was narrow and that Williams syndrome was suspected. I’m still too young to watch more, but today I went to the hospital because my testicles were weird, and it’s called a hernia.
• Is the surgery easy and how do I take care of it? I am careful whether I should do it like I would treat a normal child.
• Also, the symptoms of Williams syndrome include low intelligence, slow development, different face shape from normal people, etc. Does all of the people with this disease appear? I ask for my frustration A.
• Jeong Ok-nim
• Good morning. Thank you for asking. You will be worried a lot.
• I believe you have already been diagnosed with a renowned pediatric cardiologist and have already learned a lot about Williams syndrome and hernias.
• First of all I am worried about whether I can help more.
• The following text is an informational text obtained from the literature.
• In 1961, Williams presented to the medical community an example of a child with an upper valve stenosis, low intelligence, and an Elfin face.
• Since then, a case of idiopathic hypercalcemia in some of the infants with almost similar facial morphology has been reported to the medical community again.
• Another Dr. Garcia reported to the medical community a case of a child with an elf-shaped face with supra-aortic stenosis and idiopathic hypercalcemia. • It has also been reported that the three main symptoms described above do not appear together at all times, and that a child may develop only one of the three main symptoms.
• It has also been reported that there may be other signs of symptoms, such as abnormal teeth, voice problems, and delayed growth, with only one of the three main symptoms.
• In other words, impaired intelligence does not necessarily occur in children with Williams syndrome.
• The cause is still unknown.
• For more details, please refer to the picture of upper aortic valve stenosis and Williams syndrome. And when it comes to hernias, I’m not sure what kind of hernia you’re referring to, but I know you’re referring to a groin hernia. [Parents should also be antidoctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 9 Children and Adolescents Digestive Diseases-Please read the information on inguinal hernia.
• For reference, surgery for an inguinal hernia is an optional operation on a fixed date, and it is common for a pediatric surgeon to perform the operation early.
• For more information, please consult with your regular pediatrician.
• If you have more questions, please visit again for more information.
• Thank you. Lee Sang-won dream
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
The michael J. Bresnan Child Neurology course. Continuing Medical Education, Boston Children’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School. September 2014
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”