용혈성 빈혈 Hemolytic anemia
용혈성 빈혈의 원인
-
적혈구가 혈관 속에서 비정상적으로 파괴되어 생기는 빈혈을 용혈성 빈혈이라고 한다.
-
철분을 음식물에서 충분히 섭취하지 못할 때 골수가 정상적으로 적혈구를 충분히 만들어 낼 수 없다. 이때 철분결핍성 빈혈이 생긴다.
-
그러나 골수에서 피를 만드는데 필요로 하는 철분을 음식물에서 충분히 섭취할 수 있고 골수 조혈 기능이 정상이고 적혈구를 정상으로 충분히 만들어 낼 수 있고,
-
또 골수에서 정상적으로 만들어진 적혈구가 혈관 속에 정상적으로 들어갈 수 있지만,
-
적혈구가 혈관 속에서 비정상적으로 과다 용혈되어 파괴될 때 용혈성 빈혈이 생긴다.
-
용혈성 빈혈은 신생아 Rh 부적합이나 ABO 부적합, 유전성 구상 적혈구증, 유전성 타원형 적혈구증 등으로 적혈구가 파괴되고 용혈 될 때도 생길 수 있다.
-
Rh 부적합이나 ABO 부적합으로 생기는 용혈성 빈혈은 태아나 갓 태어난 신생아들에게 주로 생기고, 유전성 구상 적혈구증으로 생기는 용혈성 빈혈과 타원형 적혈구증으로 생기는 용혈성 빈혈은 한인들에게는 잘 생기지 않기 때문에 여기서는 설명을 생략한다.
-
요즘 자가면역 질환, 각종 약물 중독, 병원체 감염병, 음식물 섭취, 독뱀 물림 등으로 생긴 용혈성 빈혈을 가끔 볼 수 있다.
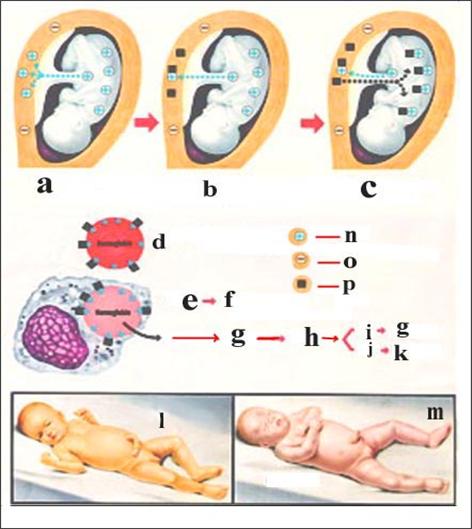
그림 1-22.
태아 적아구증이 생기는 기전과 Rh 부적합으로 태아와 신생아에게 생기는 용혈성 빈혈 및 황달의 기전
a-태아의 Rh 양성 혈액이 Rh(-) 음성 혈액을 가진 임신부의 핏속으로 들어간다.
b-임산부의 핏속에 있는 적혈구가 감작되고 Rh 항체가 형성된다.
c-다음 태어나는 태아의 Rh가 양성인 경우– 모체 내에서 생긴 Rh 항체들이 태아의 핏속으로 들어가서 태아의 Rh 양성인 적혈구와 반응한다.
d-태아의 적혈구에 Rh 항체가 부착된다.
e-적혈구가 파괴된다.
f- 용혈이 생긴다.
g-헤모글로빈이 파괴된다.
h-간접형 빌리루빈이 비정상적으로 과다히 생기고 빈혈이 생긴다.
i-피부가 노래지고,
j-황달이 생긴다.
k-뇌에 간접형 빌리루빈이 착색될 수 있다.
l-핵황달이 생길 수 있다.
m-태아 수종, n-Rh 양성, o-Rh 음성(항원), p-Rh 항체
출처: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA 및 소아가정간호백과
용혈성 빈혈의 종류
1. 자가면역으로 생긴 용혈성 빈혈(자가 면역성 빈혈)
-
자신의 적혈구 항원에 대한 항체가 자기 몸에서 만들어질 수 있다. 몸속의 적혈구 항체가 자신의 적혈구(항원)에 붙어서 적혈구가 파괴되고 용혈 될 때 생기는 빈혈을 자가 면역성 용혈성 빈혈이라고 한다.
-
자가 면역성 용혈성 빈혈은 흔한 빈혈은 아니다.
-
그러나 암이나 파종상 홍반 낭창 등이 있을 때 자가 면역성 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
2. 약물이나 화학약품 중독에 의한 용혈성 빈혈
-
약물이나 화학 약품 중독으로 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
페니실린, 설파제, 클로프로마진, 비타민 K 등 약물 치료를 받을 때 약물 동독으로 적혈구가 용혈되고 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
디티피 백신이나 그 외 예방접종 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 때 백신으로 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
거의 모든 종류의 약물이 용혈성 빈혈을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
약물에 의한 용혈성 빈혈에 걸리지 않도록 가능한 한 처방 없이 어떠한 약물도 함부로 써서는 안 된다.
-
그 밖에 유기성 화학 물질, 무기 화학 물질 등으로 적혈구가 용혈되어 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다. 화학 물질 등을 취급할 때는 항상 조심해야 한다.
3. 감염병에 의한 용혈성 빈혈
-
박테리아 감염병이나 바이러스 감염병으로 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
특히 말라리아 원충으로 적혈구가 용혈되어 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
감염병으로 6-인산 포도당 탈수소효소 결핍증이 생길 수 있고 용혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 6장 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질환-6-인산 포도당 탈수소효소 결핍증으로 인한 신생아 황달(글루코스-6-포스페이트디하드로 지네이스 결핍증으로 인한 신생아 황달/6-인산 포도당 탈수소효소 결핍증으로 인한 신생아 황달/포도당-6-인산 효소 결핍증으로 인한 빈혈/G6PD의 결핍증(Jaundice caused by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency/ G6PD deficiency jaundice)
용혈성 빈혈의 진단 치료
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰 소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 CBC 피 검사, 소변 검사, 대변 검사, 콤스 검사, 빌리루빈 농도, 항원과 항체 검사 등으로 확진한다.
-
그 원인에 따라 치료한다.
Hemolytic anemia 용혈성 빈혈
Causes of hemolytic anemia
• Anemia caused by abnormal destruction of red blood cells in blood vessels is called hemolytic anemia.
• When you don’t get enough iron from food, your bone marrow cannot normally make enough red blood cells. At this time, iron deficiency anemia occurs.
• However, you can get enough iron from food, which is needed to make blood in the bone marrow, and the bone marrow hematopoiesis is normal and you can make enough red blood cells to be normal,
• Also, red blood cells made normally in the bone marrow can enter the blood vessel normally,
• Hemolytic anemia occurs when red blood cells are destroyed by abnormally excessive hemolysis in blood vessels.
• Hemolytic anemia can also occur when red blood cells are destroyed and hemolytic, such as neonatal Rh incompatibility or ABO incompatibility, hereditary spherocytosis, or hereditary oval erythrocytosis.
• Hemolytic anemia caused by Rh incompatibility or ABO incompatibility occurs mainly in fetuses or newborn infants, and hemolytic anemia caused by hereditary spherocytosis and hemolytic anemia caused by oval erythrocytosis are not common in Koreans, so explanations are omitted here.
• Hemolytic anemia caused by autoimmune diseases, various drug addiction, pathogen infectious diseases, food intake, poison snake bites, etc. can sometimes be seen these days.

Figure 1-22. The mechanism of fetal erythroblastosis and hemolytic anemia and jaundice in the fetus and newborn due to Rh incompatibility Rh-positive blood from a-fetus enters the blood of pregnant women with Rh(-) negative blood. The red blood cells in the blood of b-pregnant women are sensitized and Rh antibodies are formed. c- If the Rh of the next fetus is positive-Rh antibodies generated in the mother enter the fetal blood and react with the fetal Rh-positive red blood cells. The Rh antibody is attached to the red blood cells of the d-fetus. e-red blood cells are destroyed. f- hemolysis occurs. g-hemoglobin is destroyed. An abnormal excess of h-indirect bilirubin occurs and anemia occurs. i-skin becomes yellowish, j-jaundice develops. Indirect bilirubin can be stained in the k-brain. l-nucleus jaundice may develop. m-fetal species, n-Rh positive, o-Rh negative (antigen), p-Rh antibody Source: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA and Pediatric Family Nursing Encyclopedia.
Types of hemolytic anemia
1. Hemolytic anemia caused by autoimmunity (autoimmune anemia)
• Your body may make antibodies to your red blood cell antigen. Anemia that occurs when red blood cells in the body attaches to their own red blood cells (antigens) and destroys red blood cells and causes hemolysis is called autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
• Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is not a common anemia.
• However, autoimmune hemolytic anemia can occur when there is cancer or disseminated lupus erythematosus.
2. Hemolytic anemia caused by drug or chemical poisoning
• Hemolytic anemia can result from drug or chemical poisoning.
• When receiving medications such as penicillin, sulfa drugs, clopromazine, and vitamin K, red blood cells can be hemolyzed and hemolytic anemia can occur due to drug east poisoning.
• When vaccinated with the DTP vaccine or other vaccination vaccines, hemolytic anemia can occur with the vaccine.
• Almost any type of drug can cause hemolytic anemia.
• To avoid drug-induced hemolytic anemia, any medication should not be used without a prescription, as far as practicable.
• In addition, hemolytic anemia may occur due to hemolysis of red blood cells with organic chemicals and inorganic chemicals. Always be careful when handling chemicals.
3. Hemolytic anemia due to infectious disease
• Hemolytic anemia can be caused by bacterial or viral infections.
• Hemolytic anemia can occur due to hemolysis of red blood cells, especially with protozoal malaria.
• Infectious diseases can lead to 6-phosphate glucose dehydrogenase deficiency and hemolytic anemia.
• [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Chapter 6 Neonatal growth and development and disease-6- Neonatal jaundice due to phosphate-glucose dehydrogenase deficiency (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency Neonatal jaundice/6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency neonatal jaundice/Anemia caused by glucose-6-phosphate deficiency/G6PD deficiency (Jaundice caused by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency/ G6PD deficiency jaundice)
Diagnostic treatment of hemolytic anemia
• Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, and examination findings. If this disease is suspected, it is confirmed by CBC blood test, urine test, stool test, Combs test, bilirubin concentration, antigen and antibody test.
• Treat according to the cause.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응
-
급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”