요붕증 Diabetes insipidus
- 소아들에게서 그렇게 흔히 볼 수 있는 병은 아니지만 가끔 볼 수 있는 병이다.
- 요붕증은 수분을 많이 마시고 소변을 많이 보고 목이 몹시 마르는 갈증을 동반하는 병이다.
- 소변 비중이 감소되고 삼투압이 감소된다.
- 연구에 의하면, 1970-1996년 동안 37명의 남아들과 42명의 여아들에게 중추성 요붕증이 있었고 평균 나이는 7세였으며, 7년 6개월 동안 추적 치료를 했다.
- 그 연구 결과를 표 3-3에 요약한다.
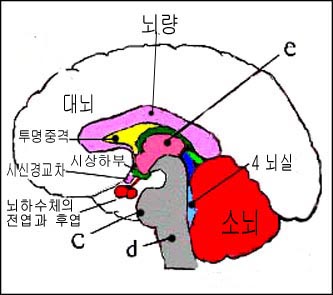
그림 122. 시상하부와 뇌하수체 전엽과 후엽
c-교뇌, d-연수, e-시상
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
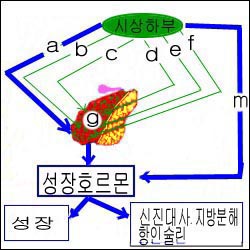
그림 1-4. 뇌하수체와 시상하부.
a-성장 호르몬 자극호르몬,
b-부신피질 자극호르몬,
c-갑상선 자극호르몬분비,
d-성샘 자극호르몬,
e-황체 자극호르몬 유리호르몬,
f-프로랙틴 자극인자와 프로랙틴 분비억제호르몬,
g-뇌하수체 전엽,
m-소마토스타틴(성장호르몬 분비억제 호르몬).
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
표 3-3. 중추성 요붕증
| 연구 년도 | 1970~1996 |
| 평균 나이 | 7세 |
| 총 환자 수 | 79명 |
| 검사와 검진 | 뇌하수체 전엽 기능검사, MRI 검사, 주기적 추적 관찰 치료 |
| 원인 | 랑그한스세포조직구증 – 12명 뇌종양 – 18명 두개골 골절 – 2명 자가 면역 다증 내분비선 질환(특발성)-41명 유전성 질환 – 5명 |
| MRI 검사 | 94% 이상에서 최초는 초강력성이 없었고 그 후 37%에서 뇌하수체 경이 두꺼워 졌다. |
| 호르몬 검사 | 뇌하수체 전엽호르몬의 결핍, 성장호르몬 결핍이 48%에서 있었다. |
| 발병 초기 평균 연령 | 0.6세 |
| 시상하부의 시각으로 위 핵(Supraoptic nucleus)과 뇌실 옆 핵(Paraventricula nucleus)에 손상이 생겨 중추성 요붕증이 생기게 하는 병 | 배세포종, 두개 인두관종, 조작구증, 매독, 결핵 등으로 인한 염증, 자가면역 병, 혈관성 질환, 사고로 인한 외상, 수술로 인한 외상, 유전 등 |
출처와 참조문헌
Mohamad Maghnie, M.D., PhD., and Others, Central diabetes insipidus in children and young adults
The New England Journal of Medicine Oct. 5, 2000, p.998
요붕증의 종류
-
요붕증에는 다음과 같이 여러 종류가 있다.
- 중추성 요붕증(Central diabetes insipidus)-항이뇨호르몬(Vasopressin/ADH) 결핍으로 생기는 요붕증을 중추성 요붕증이라 한다.
- 중추성 요붕증은 가장 흔한 형의 요붕증이고 50%에서 원인을 확실히 모르는 특발성이다. 시상하부에 문제가 있어 뇌하수체 후엽에서 ADH 합성을 할 수 없어 생기는 병이다.
- 신성 요붕증(원발성 요붕증/Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus)-요붕증 중에 2번째로 많이 보는 요붕증이다. 신장 세뇨관이 항이뇨호르몬에 영향을 받지 않아 생기는 요붕증이다.
- 정신성 요붕증(Psychogenic diabetes insipidus)-정신적인 요인으로 생기는 요붕증이다.
- 약물성 요붕증(Drug insipidus)-Lithium carbonate, 전신마취약, Methoxyflurane, 또는 Demeclocycline 등의 약물로 인해 생기는 요붕증이다.
- 임신성 요붕증(Gestational insipidus)-임신으로 생기는 요붕증
-
여기서 주로 중추성 요붕증에 관해 설명한다.
요붕증의 증상 징후
-
극도로 소변을 다량으로 보고 상당히 갈증이 생기기 때문에 찬물이나 얼음이나 얼음물을 많이 섭취한다.
-
당뇨병이 있을 때도 수분을 많이 섭취하고 소변을 많이 보고 소변에 당이 나오고 혈당 농도가 증가되지만 요붕증이 있을 때는 소변에 당이 나오지 않고 혈당 농도도 증가되지 않는다. 탈수도 될 수 있지만 수분을 많이 섭취하기 때문에 탈수가 심하게 생기지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
소아에서는 성장 발육 장애가 생길 수 있다.
요붕증의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 검진을 통해서 요붕증을 의심하면 혈당, 혈 중 전해질, 혈 칼슘 검사와 소변검사 등을 해 진단한다.
-
뇌하수체 기능검사, 뇌 MRI 검사 등으로 진단한다.
-
소변의 농도가 비정상적으로 낮고 삼투압이 낮다.
요붕증의 치료
-
1차 원인을 치료하면서 다음과 같이 치료한다.
-
중추성 요붕증은 데스모프레신(Desmopressin)으로 치료하고,
-
전신 경련이 있으면 그 경련을 카르바마제핀(Carbamazepine)등 항경련약으로 치료한다.
-
신성 요붕증은 이뇨제 Hydrochlorothiazide (HCT or HCTZ), Indomethacin 등으로 치료한다.
-
때로는 Amiloride로 Hypokalemia을 치료하고 적절히 수분공급을 한다.
-
정신적 요붕증은 적절한 정신요법으로 치료한다.
Diabetes insipidus 요붕증
• It is not a common disease in children, but it is occasionally seen.
• Diabetes insipidus is a disease that accompanies the thirst of drinking a lot of fluids, urinating a lot, and having a very dry throat.
• Urine specific gravity decreases and osmotic pressure decreases.
• According to the study, during 1970-1996, 37 boys and 42 girls had central diabetes insipidus with an average age of 7 years and followed up for 7 years and 6 months.
• The study results are summarized in Table 3-3.

Figure 122. Anterior and posterior lobes of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland c-gyobrain, d-training, e-thalamus Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-4. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. a-growth hormone stimulating hormone, b- adrenocorticotropic hormone, c-secretion of thyroid stimulating hormone, d-sex gland stimulating hormone, e-luteal stimulating hormone-free hormone, f-prolactin stimulating factor and prolactin secretion inhibitory hormone, g-anterior pituitary gland, m-somatostatin (growth hormone inhibiting hormone). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Table 3-3. Central diabetes insipidus 표 3-3. 중추성 요붕증
| Research year 1970~1996 | 1970~1996 |
| Average age | 7 years old |
| Total number of patients | 79 pesons |
| Tests and examinations | Anterior pituitary function test, MRI test, periodic follow-up treatment |
| cause | Langhans cell histiocytosis-12 brain tumors-18 skull fractures-2 autoimmune multidisciplinary endocrine diseases (idiopathic)-41 inherited diseases-5 |
| MRI | Above 94%, there was no superpower at first, and then, in 37%, the pituitary gland became thick. |
| Hormone test | Anterior pituitary hormone deficiency and growth hormone deficiency were found in 48%. |
| Average age at the beginning of onset | 0.6 years |
| A disease that causes central diabetes insipidus due to damage to the supraoptic nucleus and the nucleus next to the ventricle (Paraventricula nucleus) through the hypothalamus vision. | Inflammation due to germ cell tumors, cranial pharyngeal ducts, manipulatory syndrome, syphilis, tuberculosis, etc., autoimmune diseases, vascular diseases, trauma due to accidents, trauma due to surgery, genetics, etc. |
Sources and references Mohamad Maghnie, M.D., PhD., and Others, Central diabetes insipidus in children and young adults The New England Journal of Medicine Oct. 5, 2000, p.998
Types of diabetes insipidus
• There are several types of diabetes insipidus:
1. Central diabetes insipidus-Anti-diuretic hormone (Vasopressin/ADH) deficiency caused by diabetes insipidus is called central diabetes insipidus.
2. Central diabetes insipidus is the most common type of diabetes insipidus and is idiopathic in 50% of which the cause is unknown. It is a disease caused by the inability to synthesize ADH in the posterior pituitary due to a problem in the hypothalamus.
3. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus)-This is the second most common diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus occurs because the renal tubules are not affected by antidiuretic hormones.
4. Psychogenic diabetes insipidus-This is diabetes insipidus caused by mental factors.
5. Drug insipidus-This is diabetes insipidus caused by drugs such as Lithium carbonate, general anesthetic, Methoxyflurane, or Demeclocycline.
6. Gestational insipidus-diabetes insipidus caused by pregnancy
• This is mainly about central diabetes insipidus.
Symptoms, signs of diabetes insipidus
• I drink a lot of cold or ice or ice water because I am extremely thirsty after urinating in extremely large quantities.
• Even when you have diabetes, drink a lot of fluids and urinate a lot, and your urine contains sugar and your blood sugar levels increase. It can also be dehydrated, but it is usually not very dehydrated because you drink a lot of fluids.
• Children may develop impaired growth.
Diagnosis of diabetes insipidus
• If diabetes insipidus is suspected through medical history, symptoms, and examination, it is diagnosed through blood sugar, blood electrolyte, blood calcium and urine tests.
• Diagnose with pituitary gland function test and brain MRI test.
• The concentration of urine is abnormally low and the osmotic pressure is low.
Treatment of diabetes insipidus
• Treating the primary cause as follows.
• Central diabetes insipidus is treated with Desmopressin,
• If you have systemic cramps, treat them with anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine.
• Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is treated with diuretics Hydrochlorothiazide (HCT or HCTZ), Indomethacin, etc.
• Sometimes Amiloride is used to treat hypokalemia and provide adequate hydration.
• Psychiatric diabetes insipidus is treated with appropriate psychotherapy.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drle epediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Mohamad Maghnie, M.D., PhD. and Others, Central diabetes insipidus in children and young adults
-
The New England Journal of Medicine Oct. 5, 2000, p.998
-
Nelson textbook, 16 edition
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”