요도하열 Hypospadias
-
남아의 자지의 외 요도구가 정상 위치에 뚫려 있지 않고 자지의 아래 부위 엉뚱한 부위에 뚫려 있는 선천성 자지 기형을 요도하열이라고 한다.
-
요도하열은 자지 뿌리가 시작되는 사타구니 부위에서부터 정상 외 요도구가 뚫려 있는 귀두의 끝 부위의 사이의 어디에 생길 수 있다.
-
갓 태어난 125명의 남아 신생아들 중 1명에게 요도하열이 생긴다.
요도하열의 원인, 증상 징후
-
요도하열의 종류·정도 등에 따라 증상 징후가 많이 다르다.
-
요도하열의 85%는 정상적으로 뚫려 있어야 할 외 요도구의 위치에서 사타구니 쪽으로 약간 떨어진 귀두의 하부에 생긴다.
-
이렇게 경미한 요도하열의 대부분은 아무런 증상 징후가 없으며, 치료가 필요 없다.
-
그러나 사타구니 부위에 있는 자지 뿌리의 하부에 생긴 요도하열이 있는 남아는 서서 정상적으로 소변을 볼 수 없다.
-
자지 뿌리의 바로 아래 부위에 심한 요도하열(그림 2-38의 3 참조)이 있을 때에는, 자지가 비정상적으로 작을 수 있고, 조금 구부러져 있을 수 있다.
-
고환이 음낭 속에 들어 있지 않고 서혜관 속이나 복강 속에 잠재되어 있을 수 있다.
-
자지의 뿌리 부위의 바로 아래에 생긴 요도하열이 있는 아이는 또래 남아들처럼 오줌을 서서 볼 수 없기 때문에 고민할 수 있다.
요도하열의 진단
-
병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 진단한다.
-
소변검사와 소변 세균 배양 검사로 요로 감염 등이 있는지 알아본다.
-
또 요도하열이 있는 아이의 경우, 다른 종류의 선천성 기형이 비뇨기계에 있는지 알아보아야 한다.
요도하열의 치료
-
요도하열의 대부분은 경미하고 별 지장이 없기 때문에 치료가 전혀 필요치 않다.
-
그러나 자지의 뿌리가 있는 부위의 아래에 생긴 심한 요도하열은 적어도 4~5세가 될 때까지 소아 비뇨기과 전문의로부터 수술 치료를 받아야 한다.
-
수술로 잘 치료되면 정상적으로 성생활을 할 수 있다.
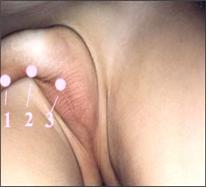
사진 2-38. 1. 2. 3은 요도하열이 생길 수 있는 자지의 부위.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
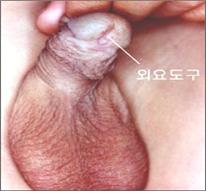
사진 2-37. 경미한 요도하열.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Hypospadias 요도하열
• A congenital penis deformity in which the external ureter of the boy’s cock is not pierced in the normal position and is pierced in the wrong part of the lower part of the cock is called hypospadias
r.
• Hypourethral fever can occur anywhere between the groin area where the penis root begins to the tip of the glans where the extraneous ureter is pierced.
• One in 125 newborn boys develops hypospadias
Causes, symptoms and signs of suburethral fever • Symptoms and signs vary greatly depending on the type and degree of hypospadias.
• 85% of suburethral fever occurs in the lower part of the glans, slightly away from the location of the external urethra, which should normally be pierced, toward the groin.
• Most of these mild suburethral fevers have no symptoms and do not require treatment.
• However, a boy with hypospadias that develops under the root of the cock in the groin cannot stand and urinate normally.
• When there is severe hypospadias (see 3 in Figure 2-38) in the area just below the root of the cock, the cock may be abnormally small and may be slightly bent.
• The testicles may not be in the scrotum and may be latent in the groin or abdominal cavity.
• A child with hypospadias that develops just below the root of the penis may be troubled because he cannot urinate and see like boys his age. Diagnosis of hypospadias
• Comprehensive diagnosis including medical history, symptoms, and examination findings. • Check for urinary tract infections through a urine test and a urine bacterial culture test.
• Also, in children with hypospadias, you should check for other types of congenital malformations in the urinary system. Treatment of hypospadias
• Most of the hypospadias is mild and does not cause any problems, so no treatment is required. • However, severe hypospadias that develops under the root of the penis requires surgical treatment from a pediatric urologist until at least 4-5 years of age. • If treated well with surgery, you can have a normal sex life.

Photo 2-38. 1. 2. 3 is the part of the cock where hypospadias can occur. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-37. Mild hypospadias. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처 및 참조문헌
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”