요도구 폐쇄, 요도 중간 부위 폐쇄, 방광-목 폐쇄(방광 경부폐쇄) Urethral meatal stenosis, Midurethral obstruction, Bladder neck obstruction
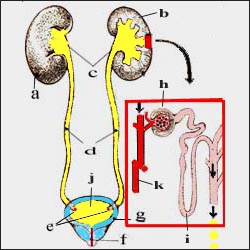
그림 1-1. 신장, 비뇨계 구조
a-우 신장, b-좌 신장, c-신우, d-요관, e-요관구, f-요도, g-방광, h-사구체, i-헨레계제, j-소변, k-혈관.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
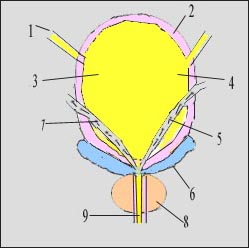
그림 1-2. 남성 내부 생식기(남성 내 생식기관)와 방광, 요관
1-요관, 2-방광 벽, 3.4-방광 내 소변, 5.7-정관, 6-정액 낭(정낭), 8-전립선(섭호선), 9-요도.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
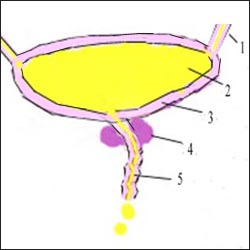
그림 1-3. 남성 생식기관과 방광, 요관
1-요관, 2-방광 내 소변, 3-방광 벽, 4-전립선, 5-요도.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
요도구 폐쇄, 요도 중간 부위 폐쇄, 방광-목 폐쇄(방광 경부폐쇄)의 원인
- 신장의 신우에서 요관·방광·요도·외 요도구까지 신장 비뇨기계 부분을 통틀어 요로라고 한다.
- 요로의 일부 또는 대부분이 선천성 기형으로 막힐 수 있고, 후천성 원인으로도 막힐(폐쇄될) 수도 있다.
- 요로 감염에 의해 요로가 막힐 수도 있다.
- 전체 요로 중 외 요도구(Extermal urethral meatus)가 막히면 요도 구멍 폐쇄(요도 입구 폐쇄, Urethral meatal stenosis)가 생길 수 있고,
- 요도의 중간 부위가 폐쇄되면 요도 중간 부위 폐쇄(Midurethral obstruction)가 생기고,
- 방광-목(방광 경부/Bladder neck)이 폐쇄되면 방광-목 폐쇄(방광 경부폐쇄/Bladder neck obstruction)가 생길 수 있다.
- 이런 요로 폐쇄는, 앞에서 설명한 것과 같이, 선천적 또는 후천적으로 생길 수 있다.
- 때로는 요로 감염에 의해 생기기도 한다.
- 또 방광 요관 밸브 부분이 폐쇄될 수 있고, 그로 인해 요로 감염이 생길 수 있고, 방광 요관 역류도 생길 수 있다.
- 요로 감염은 재발할 수 있다.
- 방광 경부 폐쇄의 24-40%에서 방광 요관 역류가 생긴다.
- 여성의 요로 하부 감염의 주원인은 방광 이하 요로 부분의 폐쇄라고 믿는다.
요도구 폐쇄, 요도 중간 부위 폐쇄, 방광-목 폐쇄(방광 경부폐쇄)의 증상 징후
- 요로의 어느 부위가 폐쇄되어 있느냐, 폐쇄의 정도가 얼마나 되나, 폐쇄의 원인이 무엇인가, 폐쇄로 인해 생긴 합병증이나 요로 폐쇄 및 그때그때의 공존 이환 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
요도구 폐쇄, 요도 중간 부위 폐쇄, 방광-목 폐쇄(방광 경부폐쇄)의 진단
- 요로 폐쇄의 종류·정도·원인 등에 따라 진단한다.
- 병력, 증상 징후, 검진, 배뇨 방광 요도 조영술 검사, 구두부우지 측정검사, 방광 내시경 검사 등으로 진단한다.
요도구 폐쇄, 요도 중간 부위 폐쇄, 방광-목 폐쇄(방광 경부폐쇄)의 치료
- 요도구 절개술, 요도 절개술, 방광-목 폐쇄 수술적 조형 수술, 요도 확장 치료 등의 수술로 치료하고, 적절한 항생제로 치료한다.
- 원인과 정도 등에 따라 완치 내지 호전될 수 있다.
Urethral meatal stenosis, Midurethral obstruction, Bladder neck obstruction 요도구 폐쇄, 요도 중간 부위 폐쇄, 방광-목 폐쇄(방광 경부폐쇄)

Figure 1-1. Structure of the kidneys and urinary system a-right kidney, b-left kidney, c-renal right, d-ureter, e-ureter, f-urethra, g-bladder, h-glomera, i-Henre system, j-urine, k-vessel. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-2. Male internal genitalia (male reproductive system), bladder, and ureter 1-ureter, 2-bladder wall, 3.4-urinary in the bladder, 5.7-vas deferens, 6-seminal vesicles (seminal vesicles), 8-prostate (subsurface), 9-urethra. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-3. Male reproductive system, bladder and ureter 1-ureter, 2-urine in the bladder, 3-bladder wall, 4-prostate, 5-urethra. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Causes of urethral obstruction, middle urethra obstruction, bladder-neck obstruction (bladder neck obstruction)
• From the kidney of the kidney to the ureter, bladder, urethra, and external urethra, the entire part of the kidney and urinary system is called the urinary tract.
• Some or most of the urinary tract may be blocked with congenital malformations, and may also be blocked (obstructed) from acquired causes.
• The urinary tract may be blocked by a urinary tract infection.
• Obstruction of the external urethral meatus of the entire urinary tract can lead to urethral orifice obstruction (urethral meatal stenosis)
• When the middle part of the urethra is obstructed, a middle part of the urethra (Midurethral obstruction) occurs,
• Bladder-neck obstruction (bladder neck obstruction) can occur when the bladder-neck (bladder neck) is obstructed.
• These urinary tract obstructions can be congenital or acquired, as described above.
• Sometimes caused by a urinary tract infection.
• In addition, the ureter valve of the bladder may be closed, resulting in a urinary tract infection, and bladder ureteral reflux.
• Urinary tract infections can recur.
• Bladder ureter reflux occurs in 24-40% of bladder neck obstructions.
• We believe that the main cause of lower urinary tract infections in women is an obstruction of the urinary tract below the bladder.
Symptoms of urethral obstruction, middle urethra obstruction, bladder-neck obstruction (bladder neck obstruction)
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on which part of the urinary tract is obstructed, how much is the degree of obstruction, what is the cause of the obstruction, complications caused by obstruction, urinary tract obstruction, and coexistence at that time.
Diagnosis of urethral obstruction, middle urethra obstruction, bladder-neck obstruction (bladder neck obstruction)
• Diagnosis is based on the type, degree, and cause of urinary tract obstruction.
• Diagnosis is based on medical history, symptom signs, examination, urination cystourethrography, oral swelling test, and bladder endoscopy.
Treatment of urethral obstruction, middle urethra obstruction, bladder-neck obstruction (bladder neck obstruction)
• Treatment with urethral incision, urethral incision, bladder-neck closure surgical plastic surgery, urethral dilatation treatment, etc., and treatment with appropriate antibiotics.
• Depending on the cause and severity, it can be cured or improved.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Diagnosis and treatment, A critical evaluation of urethral obstruction in female children, Dixon Walke, M.D. and George A. Richard, M.D., Pediatrics, Vol 15, 51, #2 Feb. 1973. p.272-277.
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”