에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병), Human immunodeficiency virus infection(HIV infection Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, AIDS)
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)의 원인
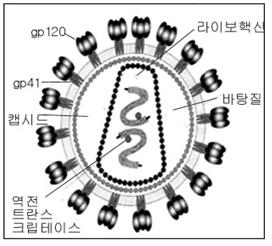
그림 4-14. 사람 면역결핍 바이러스의 구조
출처: Informed Connecticut Physician Update 2006-20008, p.21
-
사람 면역결핍 바이러스(Human Immunodeficiency Virus/ HIV) 감염으로 생기는 감염병을 에이즈, 사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병, 후천성 면역결핍 증후군, 또는 인간 면역결핍 바이러스 감염병이라고 한다.
-
사람 면역결핍 바이러스, 또는 HIV라고 한다. HIV는 레트로바이러스(Retrovirus)의 일종이다.
-
레트로바이러스는 사람에게서만 발견되고 다른 수유동물에서는 발견되지 않는다.
-
HIV(사람 면역결핍 바이러스)에 감염되어 사람 면역체계기능장애가 생긴다.
-
그로 인해 후천성 면역결핍증이 생기고 각종 전신 감염병의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 감염병을 후천성 면역결핍 증후군(Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)이라 한다.
-
HIV 감염병을 앓는 환자를 HIV 감염병 환자라고도 한다.
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)의 역학
-
HIV는 레트로바이러스의 일종이고 감염력이 아주 강한 바이러스이다.
-
HIV에 감염되면
-
대부분에게는 HIV 감염병이 생길 수 있고
-
일부에게는 무증상 HIV 감염병이 생길 수 있고
-
일부에게는 조기 HIV 감염병이 생길 수 있고
-
아주 드물게는 아무 증상 징후도 없고 에이즈도 생기지 않는다.
-
HIV에 감염돼도 전부가 HIV 감염병에 걸리지도 않고 또 앓지도 않는다.
-
-
1996년 한국에서 24명의 소아 HIV 감염병 환자들과 623명의 성인 HIV 감염병을 앓는 환자들이 있었다고 보고했다.
-
2004년 10월 21일 동아일보 기사에 의하면 한국 총 HIV 감염병 환자수는 2,944명이었고 그 중 11명은 10대 아이들이었다.
-
약 백만 명의 미국 사람들이 HIV에 감염되어 있고 그 중 25만~30만 명이 HIV에 감염되어 있는지도 자신이 모르고 있다고 미 CDC는 보고했다.
-
1999년에 미국 소아 HIV 감염병 환자의 수는 8600명이 있고 HIV 감염병은 4세 이전 소아 사망 원인의 8번째이었고, 15∼24세 사망 원인의 6번째 이었다.
-
연구에 의하면, 13세 이하 소아 HIV 감염병 환자들의 84%는 모체로부터 HIV가 수직 감염되었다.
-
13%는 HIV 감염병에 감염된 피를 수혈 받았거나 감염된 피로 만든 약품에서 HIV병에 감염되었고, 3%는 어떻게 해서 HIV에 감염병에 감염되었는지 확실히 알 수 없다.
사진 4-15. 혈액검사를 하기 위해 피를 뺄 때 쓴 주사바늘이나 남의 피를 통해 HIV, B형 간염바이러스나 C형간염바이러스 등에 감염될 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)의 감염 경로
-
HIV는 피, 뇌척수액, 늑막액(흉막액), 모유, 정액, 질액, 침, 소변, 눈물 등 체액에서 발견될 수 있다.
-
즉 인체에서 나온 피, 점액 등을 포함한 모든 종류의 체액에 접촉될 때 HIV에 감염될 수 있다.
-
특히 다음과 같은 경우에 HIV에 더 잘 감염될 수 있다.
- HIV를 보균한 사람이나 HIV 감염으로 에이즈에 걸린 사람과 질 성교를 하거나 항문 성교, 또는 구강 성교를 할 때,
- 특히 매매춘을 하거나 난잡한 동성애를 하는 사람들에게 HIV 감염률이 높다.
- HIV에 오염된 주사바늘이나 의료기구 등을 적절히 멸균처리를 하지 않고 그 의료기구로 또다시 치료하는데 쓸 때 감염될 수 있다.
- HIV에 감염된 임신부에 태어난 태아에게 HIV 감염이 생길 수 있고,
- 또 출산 후 모유수유 중 HIV에 감염될 수 있다.
- HIV에 오염된 피로 수혈치료를 받을 때
- HIV에 오염된 혈액으로 만든 혈액응고인자제로 치료받는 혈우병 환자들
- HIV에 오염된 피를 취급하는 의료계 종사자들
- HIV에 오염된 피로 만든 약으로 치료 받을 때
- 콩팥 이식이나 다른 기관 이식을 받은 사람들에게 HIV 감염병이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 마약중독자나 죄수들에게 HIV 감염률이 더 높다.
- 아동 학대를 받는 아이들이 HIV에 감염될 수 있다.
- 그 외
- HIV는 곤충·음식물·수영장·의복·전화기 등을 통해 감염되지 않는다.
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)의 잠복기
- HIV에 감염된 후 HIV 감염병의 증상 징후가 나타나는 평균 잠복기는 12~18개월이다.
- HIV에 감염된 후 5년 동안 아무 증상 징후가 없다가 HIV 감염병의 증상 징후가 나타났다는 예도 있다.
- HIV 감염 후 6~12주에 HIV 항체가 성인들이나 아이들에게서 생길 수 있다.
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)의 증상 징후
-
HIV 감염병이 있는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아가 HIV에 감염이 되어도 신생아에게 HIV 감염병의 증상 징후가 곧 나타나는 경우는 아주 드물고 생후 8개월경에 50%가, 2세경에 80%가 나타난다고 한다.
-
나이, 감염의 진행 경과, 기회 감염의 유무와 정도, 치료의 효과, 증세와 중증도 등에 따라 HIV 감염병을 카테고리 N, A, B, C로 나눈다.
다시 설명하면
1. 무증상 HIV 감염병 카테고리 N
2. 경도 증상 HIV 감염병 카테고리 A
3. 중등도 증상 HIV 감염병 카테고리 B
4. 중증 HIV 감염병 카테고리 C로 나눈다.
-
HIV 감염병의 증상 징후는 각 HIV 감염병의 카테고리에 의해서 다르다.
-
그러나 다음 증상들은 HIV 감염병의 카테고리 A에서부터 HIV 감염병 카테고리 C에서 흔히 나타나는 HIV 감염병의 증상 징후들이다.
-
림프절 비대, 간비대, 비장 비대, 재발성 설사, 이하선염과 이하선 부종, 간염, 신장병, 재발성 박테리아 감염병, 아구창, 성장 지연 등 건강한 소아청소년들에게는 잘 나타나지 않는 증상, 징후,
-
또 동반 병들이 나타날 수 있다. 인두통, 열, 체중감소, 설사, 기침, 두통, 출혈, 식욕감퇴, 숨 가쁨, 근육통, 피로 등의 증상 징후들이 나타날 수 있다.
-
입안 점막이나 식도 점막 또는 질강 진균 감염이 생길 수 있고
-
그 부위가 아프고, 음식물을 삼킬 때 인두통 등 여러 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
에이즈 (후천성 면역 결핍 증후군) 환아에게 다음과 같은 기회 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
살모넬라균성 패혈증, 폐렴연쇄구균성 감염, B형 히브균 감염, 결핵 등의 박테리아 감염
-
사이토메갈로바이러스 감염, 헤르페스바이러스 감염 등의 각종 바이러스 감염
-
크립토스포리듐, 톡소풀라스마, 또는 뉴모시스티스 카리니 등의 원충 감염
-
옴 등의 기생충 감염
-
칸디다 곰팡이, 콕시디오즈 진균 등 진균 감염과 히스토플라스마증
-
다른 종류의 반복성 세균성 감염 및, 또는 반복성 세균성 패혈증 등이 생길 수 있고
-
카포시 육종, 단핵구증양 질환과 악성 림프종 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
HIV 감염병으로 사망할 수 있다.
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병) 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견, HIV 배양, HIV 효소면역 검정법, HIV ELISA 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
-
선별 검사를 할 때는 HIV ELISA 검사를 한다.
-
HIV ELISA 검사 결과가 양성으로 나타나면 웨스톤 블롯(Western blot) 분석 검사로 진단을 재확인 한다.
-
최근에는 손가락 등에서 채취한 피 몇 방울로 Oral Quick Rapid HIV-1 Antibody Test 해서 이 병을 20분 내 진단하기도 한다.
-
분만부도 이 검사로 이 병이 있나 없나 쉽게 검사받을 수 있다.
-
이 검사는 99.6%의 진단 특이성 가치가 있다.
-
이상 설명한 검사의 결과가 음성으로 나타나면 HIV에 감염되지 않았다고 볼 수 있으나 HIV 감염 초기에 검사한 이런 종류의 검사 결과가 허위 음성으로 나타날 수 있다.
-
만일 HIV 감염병을 의심하면 재차 검사해서 진단하는 것이 보통이다.
-
HIV에 감염되어 에이즈에 걸린 임신부나 HIV를 보균한 임신부로부터 출생됐거나, HIV에 감염된 피를 수혈받았거나, 그런 피로 만든 약품으로 치료를 받았거나, 마약 중독자가 쓴 주사 바늘을 썼거나 또는 매매춘 행위 등을 한 사실 등은 HIV 감염병을 진단하는 데 많이 도움된다.
-
HIV P24 항원검사, 또는 ICD P24 항원검사로 진단할 수 있다. 그러나 검사의 가치가 HIV DNA PCR 검정법으로 진단할 때보다 훨씬 못하다.
-
HIV RNA PCR 검정법으로 진단할 수 있으나 그 검사 결과가 양성으로 나타날 때만 검사 가치가 있다.
-
HIV 배양으로 진단할 수 있으나 경비가 많이 들고 시간이 많이 걸리는 단점이 있다. 그래서 HIV 감염병을 진단할 때 HIV DNA PCR 검정법을 가장 많이 이용한다.
-
HIV에 감염된 모체로부터 출생된 신생아는 출생 후 48시간 내에 HIV 감염병을 확인하기 위해 HIV DNA PCR 검정법으로 진단한다.
-
이 검사의 결과가 음성이면, 생후 1~2개월에 HIV DNA PCR 검정법 검사를 2차로 한다.
-
2차 검사의 결과가 음성이면 생후 2∼4개월에 3차 HIV DNA PCR 검정법으로 검사한다.
-
그 결과가 음성이면 생후 15개월에 4차로 HIV DNA PCR 검정법으로 검사한다.
-
그 검사 결과가 음성이면 생후 18개월에 5차로 검사한다.
-
이때까지 모든 검사의 결과가 음성으로 나타나면 HIV 감염병이 있지 않은 것으로 진단할 수 있다.
-
만일 그 중 어떤 검사의 결과가 양성으로 나타나면 적어도 2번 이상 다른 피검 물 피로 HIV DNA PCR 검정법 검사를 한다. 그 두 결과가 양성으로 나타나면 HIV 감염병이 있다고 진단할 수 있다.
-
HIV 감염에 걸린 임신부에 출생된 모든 아기들은 CD4+ 림프구 수 검사와 CD8+ 림프구 수 검사를 생후 1·2·3·6개월에 반복 검사하고 HIV에 감염되어 있는지 가부를 확실히 진단한다. 그리고 그런 검사를 3개월마다 4번 정도 더 검사할 수 있다.
-
HIV에 감염되면 CD4+ 림프구 수/ CD8+ 림프구 수의 역전이 생길 수 있고 혈중 IgG와 IgA가 증가되고 헤모글로빈 농도가 감소될 수 있다.
-
LDH 혈중 농도증가, 적혈구 침강 속도 상승, 백혈구 수 감소 등이 나타날 수 있다. 이런 검사의 결과는 진단하는 데 보조 가치가 있다.
-
CD4+ 림프구 수 검사치가 정상보다 낮으면 뉴모시스티스 카리니(Pneumocystis Carinii) 원충 감염으로 생기는 폐렴을 예방해 주고 필요에 따라 그 폐렴을 트리메소프림 설파메사돌(박트림/ TMPSMX)이나 펜타미닌 또는 다프손 등으로 치료하기도 한다.
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)의 치료
-
HIV 감염병을 완치할 수 있는 특효약이 아직까지 없다.
-
그러나 에이지티(AZT/Zidovudine·Retrovir), 인디나비(Indinavir), 사쿠인이비어(Saquinivir), PI와 Efavirenza, Didanosine(Videx) 등 항 Retrovirus 약물들 중 한두 가지, 또는 세 가지 약물로 치료하기도 한다.
-
면역글로불린 혈관주사 등으로 치료하기도 한다.
표 4-2. 만성 사람 면역결핍 바이러스(Human Immunodeficiency Virus/HIV) 감염자 Antiretroviral 치료 적응
| 임상 카테고리 | CD4+T세포 카운트 | 플라스마 HIV 라이보핵산 | 권장 |
| 에이즈 병을 앓는다고 확실히 진단되거나 증상이 심할 때 | 어느 수치든 | 어느 수치든 | 치료한다. |
| 무증상 | CD4+T세포 수 카운트가 200/mm3이하든지 | 어느 수치든 | 치료한다. |
| 무증상 | CD4+T세포 수 카운트가 200/mm3이상이고 350/mm3이든지 그 이하 일 때 | 어느 수치든 | 치료에서 얻는 점과 잃는 점 등을 상의한 후 서로 합의하며 치료한다. |
| 무증상 | CD4+T세포 수 카운트가 350/mm 이상 일 때 | 100,000 이거나 이상일 때 | 대부분의 의사들은 치료를 연기하고 더러는 치료를 시작한다. |
| 무증상 | CD4+T세포 수 카운트가 350/mm3이상 일 때 | 100,000 이하 | 치료하지 않는다. |
출처와 참조문헌 Informed Connecticut Physician Update 2006-20008, p.21
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)의 예방
사진 4-16. 콘돔
콘돔으로 성병과 HIV 감염병 등은 어느 정도 예방될 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
아직도 이 병을 근본적으로 치료하는 특효약도 없고 예방접종 백신도 없다.
-
그러나 의사나 간호사 등이 의료 직업관계로 HIV에 노출되나 비 직업적인 일로 HIV에 노출 될 때 HIV 노출 후 예방적 치료를 Tendfovia, Emtricitabine, Zidovudine, Lambivudine, Ritonavir, Lopinair, Atazanavir, Daurunavir 등의 항 바이러스제 중 두 가지 또는 세 가지 항 바이러스제로 예방적 치료를 하면 예방 효과가 있다고 한다(출처; NEJM, October 29, 2009 p.1768).
사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 HIV에 노출되기 전 예방과 노출후 예방 효과
| 예방 방법 | 예방 효과 |
| 금욕 | 100% |
| 성교 대상자 수를 줄인다. | 일정하지 않다 |
| 콘돔을 옳게잘 이용 한다. | 80% |
| 남성은 포경수술을 받는다. | 효과 없다는 연구도 있고50% 효과도 있다는 연구도 있다 |
| 습관성 약물 주사를 중지한다 | 75% |
| 성교 전 tenofovir disoproxil fumarate /emtricitabine( Truvada) 약을 쓴다 | – |
| 사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 HIV 에 노출된 후 사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 HIV 감염병 치료 약으로 바로 예방적 치료를 시작한다.
|
– |
| 사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 HIV감염에 관한 카운슬링을 닫는다 | – |
소스: AAP News 10/2019
예방 백신이 개발되기 전에 다음과 같이 예방할 수 있다.
-
항상 손을 깨끗이 씻는다.
-
다른 사람의 피를 취급할 때는 고무장갑을 낀다.
-
수혈을 받을 때 HIV에 감염되지 않은 피로 수혈 받는다.
-
피로 만든 어떤 종류의 약물로 치료를 받을 때도 HIV에 감염되지 않은 피로 만든 것만 써야 한다.
-
HIV를 보유한 임신부나, 에이즈를 앓고 있는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아는 에이즈에 걸릴 수 있다. 그러므로 그 엄마에게 태어난 아기는 적절한 진단 치료를 받아야 한다.
-
HIV 감염병으로 앓거나 HIV를 보균한 엄마의 젖을 먹는 신생아는 HIV에 감염될 수 있으므로 그 엄마의 젖을 수유해서는 안 된다.
-
HIV 감염병에 걸린 아이가 건강한 다른 아이들과 같이 놀 수 있고 학교에 갈 수 있다. 그러나 이 병을 앓는 아이의 피나 신체에서 나온 체액에 접촉되지 않도록 주의한다.
-
수혈이 필요할 때 자기 자신의 피를 수혈할 수 있게 자기 피를 미리 빼 혈액은행에 보관할 수 있다. 또 다른 사람들의 피를 수혈 받는 대신 건강한 가족들의 피를 수혈 받을 수 있다.
-
이 병을 앓는 사람과 접촉될 기회가 많아 HIV에 감염될 가능성이 많은 사람들–의사·간호사·임상 검사원·학생·교사 ·경찰관 등은 HIV 감염과 에이즈에 관해서 잘 배우고 HIV 감염병을 예방하는 데 힘써야 한다.
-
성관계를 할 때 콘돔을 쓰면 HIV 감염병을 어느 정도 예방될 수 있지만 완전히 예방될 수 없다.
-
HIV 감염병을 앓는 임신부로부터 태어난 신생아들의 25~35%가 임신 중 자궁 내에서, 분만 중 또는 분만 후, 또는 모유 수유 중 HIV에 감염될 수 있다.
-
그러나 임신 중, 분만 중, 분만 후 6주까지 Zidovudine 항 바이러스제를 경구로 또는 정맥주사로 임신부에게 주면 태어난 아기에게 HIV 감염병 발생률이 현저히 감소된다.
-
신문·TV·의학 참고서 등을 통해 HIV 감염병 예방법을 배우고 실천에 옮긴다.
에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병) 소아청소년들에게 기본 예방접종을 통상적으로 하는 방법
-
B형 간염 백신을 비롯한 DTaP, IPV, MMR, Hib, 폐렴연쇄상구균 감염 백신, 인플루엔자 백신, A형 간염 백신 등은 HIV 감염병에 걸리지 않은 소아청소년들과 거의 같게 예방접종해 줄 수 있다.
-
생 폴리오(소아마비) 백신과 BCG 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주지 않는다.
-
수두 백신은 의사의 권장에 따라 한다.
표 4-3. 임신 분만 기간 동안, 신생아기 동안 HIV 감염병 발병률을 감소시키는 Ziduvudine 예방적 치료 방법
| 임신, 분만, 출산, 주산기, 출생 후 | Zidovudine 예방적 치료 경로 | Zidovudine 예방적 치료 용량 |
| 임신 14주부터 출산이 끝날 때까지 | 경구 | 200mg, 1일 3회, 또는 300mg, 1일 2회 |
| 진통, 분만 중 | 혈관 주사 | 첫 1시간 동안 체중 매 kg 당 Zidovudine 2mg을 혈관으로 주고, 그 다음부터는1시간에 체중 매 kg 당 Zidovudine을 아기가 태어날 때까지 혈관으로 준다. |
| 태어나자마자 신생아기에게 경구로 투여한다, | 경구 | 체중 매 kg 당 2mg을, 하루 4회, 생후 6주 동안 준다. |
출처: Red book, 27th edition, 2006. P.394
-
갓 태어난 신생아가 분만 시 HIV 감염병이 있는 분만부로 부터 HIV에 감염되지 않게
-
갓 태어난 신생아를
-
zidovudine으로 6주간,
-
zidovudiner 6 주+ nevirapine 8 일간
-
또는 zidovudine 6주+ nelfinavir과lamivudine 2주간 예방적 치료를 한 결과 zidovudine으로 예방 치료를 한 결과 보다 2~3종류의 antiretroviral 제로 예방 치료한 결과가 더 예방 효과가 있었다. 소스: NEJM 2012; 366:2368-2379June 21, 2012
-
-
사람 면역 결핍 바이러스(HIV) 감염 고 위험도 군에 속한 미 고교 9~12학년의 학생들은 기본 HIV 검사를 기본적으로 받으라고 권장한다. 소스: Contemporary Pediatrics eConsult Jan 12, 2012
Human immunodeficiency virus infection (HIV infection Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, AIDS) 에이즈(사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 감염병)
Causes of AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease)

Figure 4-14. Structure of human immunodeficiency virus Source: Informed Connecticut Physician Update 2006-20008, p.21
Cause
Infectious diseases caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are called AIDS, human immunodeficiency virus infectious diseases, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or human immunodeficiency virus infectious diseases.
It is called the human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV. HIV is a type of retrovirus. Retroviruses are found only in humans and not in other lactating animals. Human immune system dysfunction is caused by infection with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus).
As a result, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome may occur and symptoms of various systemic infectious diseases may occur.
This infectious disease is called acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Patients with HIV-infected diseases are also referred to as HIV-infected patients.
Epidemiology of AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease)
HIV is a type of retrovirus and is a highly infectious virus.
If you are infected with HIV, Most people can develop HIV infectious diseases, Some may develop asymptomatic HIV infectious diseases, Some may develop early HIV infection, Very rarely, there are no signs of symptoms and AIDS does not develop.
Even if they are infected with HIV, not all of them suffer from HIV infectious diseases, nor do they suffer from it.
In 1996, it was reported that there were 24 pediatric HIV-infected patients and 623 adult HIV-infected patients in Korea. According to an article in the Dong-A Ilbo on October 21, 2004, the total number of HIV infectious disease patients in Korea was 2,944, of which 11 were teenage children.
The US CDC reported that about 1 million Americans are infected with HIV, and 250,000-300,000 of them are unaware that they are infected with HIV.
In 1999, the number of children with HIV infectious diseases in the United States was 86,000, and HIV infectious disease was the 8th cause of death in children before age 4 and the 6th cause of death in children aged 15 to 24. According to the study, 84% of children under 13 years of age with HIV-infected disease were vertically infected with HIV from their mothers.
Thirteen % received blood transfusions of HIV-infected blood or were infected with HIV from drugs made from infected blood, and 3% were not sure how they were infected with HIV-infected diseases.

Photo 4-15. You can get infected with HIV, hepatitis B virus, or hepatitis C virus through an injection needle or someone else’s blood used to drain blood for a blood test. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
The path of infection of AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease)
• HIV can be found in body fluids such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid, pleural fluid (pleural fluid), breast milk, semen, vaginal fluid, saliva, urine, and tears.
• In other words, you can get HIV when you come into contact with all kinds of body fluids, including blood and mucus from the body.
• You are more susceptible to HIV, especially if you:
1. When having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with a person with HIV or with a person who has AIDS due to HIV infection;
2. HIV infection rates are high, especially among those who engage in prostitution or promiscuous homosexuality.
3. When HIV-contaminated needles or medical devices are not properly sterilized and used to treat them again, the infection may occur
. 4. HIV infection can occur in a fetus born to an HIV-infected pregnant woman, 5. You can also become infected with HIV during breastfeeding after childbirth. 6. When receiving blood transfusion treatment with HIV-contaminated blood
7. Hemophilia patients treated with coagulation factors made from HIV-contaminated blood
8. Medical workers dealing with HIV-contaminated blood
9. When receiving treatment with drugs made from HIV-contaminated blood
10. People who have had kidney transplants or other organ transplants are more likely to develop HIV infection.
11. HIV infection rates are higher among drug addicts and prisoners.
12. Children who are abused can become infected with HIV.
13. Others
14. HIV is not transmitted through insects, food, swimming pools, clothing, and telephones.
The incubation period of AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease)
• The average incubation period for symptoms of HIV infection after HIV infection is 12 to 18 months.
• In some cases, there were no symptoms for 5 years after being infected with HIV, and then symptoms of an HIV-infected disease appeared.
• HIV antibodies can develop in adults or children 6 to 12 weeks after HIV infection.
Symptoms Signs of AIDS (Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infectious Disease)
• Even if a newborn born to a pregnant woman with an HIV infection becomes infected with HIV, it is very rare for the newborn to show symptoms of an HIV infection soon, 50% at 8 months of age and 80% at 2 years of age.
• HIV-infected diseases are classified into categories N, A, B, and C according to age, progression of infection, presence and severity of opportunistic infections, effectiveness of treatment, symptoms and severity, etc.
In other words
1. Asymptomatic HIV infection category N
2. Mild symptom HIV infectious disease category A
3. Moderate symptom HIV infectious disease category B
4. Divide into severe HIV infection category C.
• Symptoms and signs of HIV infection are different for each category of HIV infection.
• However, the following symptoms are the symptoms of HIV infectious disease common in HIV infectious disease category A to HIV infectious disease category C.
• Lymph node enlargement, hepatomegaly, spleen enlargement, recurrent diarrhea, mumps and parotid edema, hepatitis, kidney disease, recurrent bacterial infection, thrush, growth retardation, etc. Symptoms, signs, and symptoms that do not appear well in healthy children and adolescents.
• There may also be comorbid illnesses.
- Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, weight loss, diarrhea, cough, headache, bleeding, loss of appetite, shortness of breath, muscle pain, and fatigue.
• Mouth or esophageal mucosa or vaginal fungal infection may develop
• The area is sore, and when swallowing food, there may be a number of symptoms, including a sore throat. Children with AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) may develop opportunistic infectious diseases such as:
• Bacterial infections such as Salmonella sepsis, pneumococcal infection, Heb B infection, and tuberculosis
• Various viral infections such as cytomegalovirus infection and herpes virus infection
• Protozoal infections such as Cryptosporidium, Toxopulasma, or Pneumocystis carini
• Parasitic infections such as scabies
• Histoplasmosis and fungal infections such as Candida fungi and Coccidios fungi • Other types of recurrent bacterial infections and/or recurrent bacterial sepsis may occur.
• Kaposi’s sarcoma, mononucleosis and malignant lymphoma may develop.
• You can die from HIV infection.
AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease) diagnosis
• It can be diagnosed by medical history, symptom signs, examination findings, HIV culture, HIV enzyme immunity assay, and HIV ELISA test.
• When screening, do an HIV ELISA test.
• If the HIV ELISA test results are positive, reconfirm the diagnosis with a Western blot assay.
• Recently, the disease is diagnosed within 20 minutes by performing the Oral Quick Rapid HIV-1 Antibody Test with a few drops of blood collected from the fingers and the like.
• The delivery department can also be easily tested for the presence or absence of this disease through this test.
• This test has a diagnostic specificity value of 99.6%.
• If the above-described test results are negative, it can be considered that you are not infected with HIV, but this kind of test results, which were tested in the early stages of HIV infection, may appear false negative.
• If you suspect an HIV infection, it is common to retest and diagnose.
• Born from an HIV-infected and AIDS pregnant woman, or from a pregnant woman with HIV, who has been transfused with HIV-infected blood, has been treated with drugs made from such blood, uses needles from drug addicts, or is prostitutes. The fact that you have done your back is very helpful in diagnosing HIV-infected diseases.
• It can be diagnosed with the HIV P24 antigen test or the ICD P24 antigen test. However, the value of the test is far less than when diagnosed with the HIV DNA PCR assay.
• It can be diagnosed with the HIV RNA PCR assay, but it is worth testing only if the test results are positive.
• It can be diagnosed with HIV culture, but it is expensive and time-consuming. So, when diagnosing HIV infectious diseases, the HIV DNA PCR assay is most often used.
• Newborns born from an HIV-infected mother are diagnosed with an HIV DNA PCR assay to identify HIV infection within 48 hours after birth.
• If the result of this test is negative, the second HIV DNA PCR test is performed at 1 to 2 months of age.
• If the result of the 2nd test is negative, it is tested by the 3rd HIV DNA PCR assay at 2-4 months of age.
• If the result is negative, it is tested by HIV DNA PCR assay 4 times at 15 months of age.
• If the test result is negative, it is tested 5 times at 18 months of age.
• If the results of all tests up to this point are negative, it can be diagnosed as having no HIV infection.
• If the result of any of the tests is positive, perform the HIV DNA PCR assay with the other specimen at least two times or more. If both results are positive, it can be diagnosed as having an HIV infection.
• All babies born to pregnant women with HIV infection should have a CD4+ lymphocyte count and a CD8+ lymphocyte count repeated at 1, 2, 3 and 6 months of age to make sure they are infected with HIV. And such tests can be done four more times every three months.
• HIV infection can lead to a reversal of CD4+/CD8+ lymphocyte counts, increased blood IgG and IgA, and decreased hemoglobin levels.
• Increased blood levels of LDH, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and decreased white blood cell count may occur.
The results of these tests have a secondary value in diagnosing.
• If the CD4+ lymphocyte count is lower than normal, pneumonia caused by protozoal infection of Pneumocystis Carinii is prevented, and the pneumonia is treated with trimethoprim sulfa meadow (Bactrim/ TMP¬SMX) or pentamidine, if necessary. It can also be treated with dapsone.
Treatment of AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease)
• There are still no special drugs that can cure HIV infectious diseases.
• However, it may be treated with one or two or three of anti-retrovirus drugs such as AZT/Zidovudine Retrovir, Indinavir, Saquinavir, PI and Efavirenza, Didanosine (Videx)
• It is sometimes treated with an immunoglobulin vascular injection.
Table 4-2. Adaptation of antiretroviral therapy to patients infected with chronic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
표 4-2. 만성 사람 면역결핍 바이러스(Human Immunodeficiency Virus/HIV) 감염자 Antiretroviral 치료 적응
| Clinical category | CD4+T cell count | Plasma HIV ribonucleic acid | recommend |
| When you are clearly diagnosed with AIDS or have severe symptoms | Any figures | Any figure | Treat |
| Asymptomatic | Whether the count of CD4+T cells is less than 200/mm3 | Any figure | Treat |
| Asymptomatic | When the count of CD4+T cells is greater than or equal to 200/mm3 and is less than or equal to 350/mm3 | Any figure | After discussing the gains and losses from treatment, they agree with each other to treat them. |
| Asymptomatic | When the count of CD4+T cells is more than 350/mm | 100,000 or more | Most doctors postpone treatment and sometimes start treatment. |
| Asymptomatic | When the count of CD4+T cells is more than 350/mm | 100,000 or lesser | Not Treat |
Sources and references Informed Connecticut Physician Update 2006-20008, p. 21 Prevention of AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease)

Photo 4-16. condom With condoms, sexually transmitted diseases and HIV-infected diseases can be prevented to some extent. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• There are still no special drugs to cure the disease and no vaccines for immunization.
• However, when doctors or nurses are exposed to HIV due to medical professional relations but are exposed to HIV due to non-professional work, antiviral drugs such as Tendfovia, Emtricitabine, Zidovudine, Lamivudine, Ritonavir, Lopinavir, Atazanavir, and Daurunavir should be treated as a prophylactic treatment after exposure to HIV. It is said that prophylactic treatment with two or three antiviral agents has a prophylactic effect (source; NEJM, October 29, 2009 p.1768).
Prevention of human immunodeficiency virus before and after exposure to HIV
사람 면역 결핍 바이러스 HIV에 노출되기 전 예방과 노출후 예방 효과
| Prevention method | Preventive effect |
| Abstinence | 100% |
| Reduce the number of people who have sex | Not constant |
| Use condoms properly and well. | 80% |
| 남성은 포경수술을 받는다. | Some studies show that it is not effective, and others show that it is 50% effective. |
| Stop addictive drug injection | 75% |
| Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate /emtricitabine (Truvada) before sexual intercourse | – |
| After exposure to human immunodeficiency virus HIV, prophylactic treatment is started immediately with drugs to treat human immunodeficiency virus HIV infection.
|
– |
| Closing Counseling About Human Immunodeficiency Virus HIV Infection | – |
Source: AAP News 10/2019
Before a preventive vaccine is developed, it can be prevented by:
• Always wash your hands thoroughly.
• Wear rubber gloves when handling other people’s blood.
• When you receive a blood transfusion, you receive a blood transfusion that is not infected with HIV.
• When receiving treatment with any type of blood-made medication, only use blood made from HIV-free blood.
• Newborns born to pregnant women with HIV or to pregnant women with AIDS can get AIDS. Therefore, babies born to the mother must receive appropriate diagnostic treatment.
• Newborns who are breastfeeding from an HIV-infected or HIV-infected mother may be infected with HIV and should not breastfeed her mother.
• A child with an HIV infection can play with other healthy children and go to school. However, be careful not to come into contact with the blood or body fluids of the child with this disease.
• When a blood transfusion is needed, you can take your own blood and store it in a blood bank so that you can transfuse your own blood. Instead of having another person’s blood transfused, you can get the blood of healthy family members.
• People who are more likely to become infected with HIV due to their increased chances of contact with people with this disease-doctors, nurses, clinical inspectors, students, teachers, police officers, etc. should learn about HIV infection and AIDS well and work hard to prevent HIV infection.
• Using condoms during sexual intercourse can prevent some the HIV infections, but it cannot be completely prevented.
• 25% to 35% of newborns born to pregnant women with HIV-infected diseases can become infected with HIV in the womb during pregnancy, during or after delivery, or during breastfeeding.
• However, if Zidovudine antiviral drugs are given orally or intravenously to pregnant women during pregnancy, delivery, and up to 6 weeks after delivery, the incidence of HIV infection in the newborn baby is significantly reduced.
• Learn how to prevent HIV infection and put it into practice through newspapers, TV, and medical reference books.
How to routinely give basic vaccinations to children and adolescents with AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infectious disease)
• Hepatitis B vaccine, DTaP, IPV, MMR, Hib, pneumococcal infection vaccine, influenza vaccine, hepatitis A vaccine, etc. can be vaccinated almost the same as children and adolescents without HIV infection.
• Do not immunize with live polio (polio) vaccine and BCG vaccine.
• Varicella vaccine should be administered as recommended by a doctor.
Table 4-3. Zidovudine prophylactic treatment method to reduce the incidence of HIV infection during pregnancy, delivery and during the neonatal period
표 4-3. 임신 분만 기간 동안, 신생아기 동안 HIV 감염병 발병률을 감소시키는 Ziduvudine 예방적 치료 방법
| Pregnancy, delivery, childbirth, perinatal period, after birth | Zidovudine prophylactic treatment route | Zidovudine prophylactic treatment dose |
| From the 14th week of pregnancy to the end of childbirth | oral | 200mg, 3 times a day, or 300mg, 2 times a day |
| Labor, during childbirth | Vascular injection | For the first hour, 2mg of Zidovudine per kg of body weight is given to blood vessels, and from then, Zidovudine per kg of body weight is given to blood vessels in 1 hour until the baby is born. |
| It is administered orally to the newborn as soon as birth | oral | Give 2mg per kg of body weight, 4 times a day, for 6 weeks after birth. |
Source: Red book, 27th edition, 2006. P.394
• To prevent newborn infants from becoming infected with HIV from delivery mothers with HIV-infected diseases at delivery.
• newborn baby o 6 weeks with zidovudine,
o zidovudiner 6 weeks + nevirapine 8 days
O or zidovudine 6 weeks + nelfinavir and lamivudine 2 weeks prophylactic treatment result, the result of prophylactic treatment with 2~3 antiretroviral agents was more prophylactic than the result of prophylactic treatment with zidovudine. Source: NEJM 2012; June 21, 2012
• Students in high school grades 9-12 in the high-risk group of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are encouraged to take a basic HIV test. Source: Contemporary Pediatrics eConsult Jan 12, 2012
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th – 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- 소스: AAP News 10/2019
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”