약물 아나필락시스(약물 과민증)의 예방, Prevention of anaphylaxis caused by drugs
-
약물 아나필락시스를 약물 과민증이라고도 한다.
- 아나필락시스는 항원 항체 이상 반응으로 생기는 급성 알레르기성 질환 중 하나이다.
- 아나필락시스를 즉시 적절히 치료하지 않으면 사망할 수 있다.
- 아나필락시스를 과민증 또는 과민이라고도 한다.
약물 아나필락시스의 원인
- 페니실린·코티손 등 코르티고스테로이드·인슐린·예방접종 백신·그외 어떤 종류의 약물로 치료받을 때 그 약물로 인해 아나필락시스가 생길 수 있다.
- 약물을 경구로 섭취하거나, 피부나 점막에 바르거나 접촉하거나 비강 속을 통해 기도 속으로 흡입하거나 하 기도 속에 뿜거나, 입으로 먹거나 혈관주사로 맞거나 근육주사로 맞거나, 항문 속이나 질강 속에 좌약을 넣거나, 또는 그외 다른 방법으로 약물로 치료 받을 때 약물 아나필락시스가 유발될 수 있다.
- 약물 아나필락시스는 약물 치료를 받은 후나 약물에 접촉 된후 불과 몇 초 내, 또는 몇 시간 내 생기는 것이 보통이다.
- 아나필락시스는 약물 접촉으로도 유발될 수 있고, 땅콩·견과류·달걀·우유·조개, 또는 새우 등 음식물을 섭취할 때도 유발될 수 있고, 벌이나 곤충에 쏘이거나 물리거나, 접촉되거나 또는 동물에 물렸을 때도 유발 될 수 있다.
- 집 먼지, 집 먼지 진드기, 짐승의 비듬, 털이나 침, 초목의 꽃가루를 흡입해도 그로 인해 아나필락시스가 유발될 수 있다.
- (부모도 반의사가 되어야한다-소아가정간호백과-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료-아나필락시스 참조, 제15권 소아청소년 알레르기 및 면역질환 참조)
약물 아나필락시스의 증상 징후
- 비만 세포(Mast cells)가 뇌하수체와 신체 여러 계통의 기관과 조직에 정상적으로 산재해 있다.
- 히스타민은 신체 각 부위에 산재해 있는 비만세포 내, 뇌하수체의 비만세포 내, 호염기성 세포 내에 과립상태로 있는 것이 보통이다.
- 히스타민은 비만세포 내에서 비만세포 탈 과립과정에 의해 비만 세포막의 밖으로 정상으로 분비된다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제15권 소아청소년 알레르기 및 면역질환-알레르기를 일으키는 기전 그림 참조).
- 항원 항체 이상 반응이 생기면 비만 세포 내 히스타민 과립이 다량으로 갑자기 비만 세포 외로 분비된다.
- 비만세포 내에서 분비되는 히스타민 고립은 신체 내에 있는 다른 세포에서 분비되는 생화학적 활성 물질들-IgE, 사이토카인, 류코트리엔 등과 복합적 작용을 할 수 있다. 이때 아나필락시스가 일어날 수 있다.
- 아나필락시스의 증상 징후는 일률적으로 똑 같이 나타나지 않고 다양하게 나타난다. 그때그때에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다. 생명을 위협할 수 있을 정도로 위중하게 나타날 수도 있고 때로는 피부가 조금 가려운 정도로 경미하게 증상 징후가 나타 날 수 있다.
- 심하게 나타날 때는 전 피부와 점막이 발적되고 붓고 두드러기가 날 수 있다.
- 구토·설사·복통 등을 동반한 소화기계통의 장애도 생길 수 있다.
- 콧물·기침·기관지 천식·천명·청색증·호흡부전증 등의 증상 징후를 동반한 호흡기계통 장애가 생길 수도 있다.
- 혈압이 갑자기 떨어질 수 있고 호흡곤란이 심하게 생길 수 있고 심지어는 쇼크에 빠져 죽을 수도 있다.
약물 아나필락시스의 진단
- 병력·증상·진찰소견 등을 종합해서 진단할 수 있다.
- 환아 자신이나 친 부모 형제자매들 중 누구에게 아토피성 체질이 있거나 알레르기성 질환이 있는 가족병력이 있으면 아나필락시스를 진단하는 데 도움 된다.
- 아나필락시스가 유발되기 바로 전 아나필락시스를 일으킬 수 있는 약물(항원) 등을 경구로 섭취했거나 몸에 바르거나 주사를 맞았거나 비강 속이나 기도 속으로 흡인한 사실 등이 있으면 아나필락시스를 진단하는데 큰 도움 된다.
- 약물, 음식물, 또는 그 밖에 다른 것(항원)에 접촉된 사실이 있거나 앞서 설명한 여러 가지 증상 징후가 있을 때 아나필락시스를 비교적 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
- 그렇지만, 약물로 유발된 아나필락시스의 증상과 징후는 항상 일률적으로 뚜렷하게 나타나지 않기 때문에 약물로 유발된 아나필락시스를 금방 확실히 진단하기가 어려운 때도 가끔 있다.
- 드물게, 약물 치료를 받지도 않고 특이한 음식물을 섭취하지도 않고, 또는 곤충에 물리거나 쏘인 사실도 없는데도 아나필락시스가 유발될 수 있다.
- 또 어떤 병의 증상과 징후가 아나필락시스로 생긴 증상과 징후와 거의 비슷하게 나타날 수 있다.
- 그래서 약물로 유발된 아나필락시스의 증상 징후와 다른 병으로 생긴 증상 징후가 비슷할 수 있다.
- 이때 다른 병과 아나필락시스를 감별 진단해야 한다.
약물 아나필락시스의 치료
아나필락시스(아나필락시/아나필락시스 반응/초과민 반응) Anaphylaxis(Anaphylactic reactions)-치료 참조
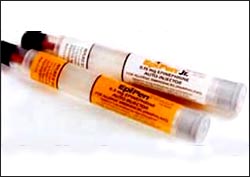
사진 55. 심하게 생긴 아나필락시스 반응을 응급으로 치료할 때 쓸 수 있는 에피네프린 성분이 든 에피펜 자가주사기 주사약 사진.
에피펜의 주성분은 에피네프린이다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP

그림 56. 벌 알레르기가 생기면 환아 자신이나 주위 사람이 에피펜 자가주사기 주사약으로 응급치료를 할 수 있다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
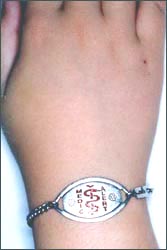
사진 57. 어떤 종류의 약물이나 그 외 것으로 인해 심한 알레르기 반응이 있었으면 그런 심한 알레르기 반응이 있다는 병력을 남에게 알려줄 수 있는 글 표식 팔찌를 끼고 다닌다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP

사진 58. 심한 약물 알레르기나 무엇에 알레르기 반응이 있었다는 글 표식 목걸이를 걸고 다닌다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.FAAP
- 아나필락시스의 중증도에 따라 치료가 다르다.
- 아나필락시스가 심하게 유발되면 몇 초 내지 몇 분 내 생명을 잃을 수 있다.
- 심한 경우, 그 현장에서 적절히 즉시 치료를 시작해야 생명을 건질 수 있다.
- 때로는, 의사의 도움을 청할 겨를도 없이 현장에서 즉시 치료를 시작해야만 생명을 구할 수 있다.
- 그래서 과거에 아나필락시스가 심하게 유발됐던 과거 병력이 있는 소아청소년들에게 아나필락시스가 생기면 본인이나 주위 사람이 그 현장에서 즉시 응급 치료를 시작할 수 있도록 에피네프린 주사약, 아나키트, 또는 에피펜을 평소 항상 지참해야한다.
- 그래서 아나필락시스가 유발되면 그 현장에서 즉시 에피네프린 주사로 응급치료를 시작해야한다. 에피네프린 주사약이 없을 때는 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 긴급 연락을 해 그의 지시에 따라 응급 치료를 그 현장에서 시작하고 가장 가까운 병원이나 응급실로 급히 이송 한다.
- ([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제21권 소아청소년 가정간호-쇼크나 아나필락시스 치료에 쓸 수 있는 에피네프린 주사약 참조)
- 아나필락시스의 중증도와 증상 징후에 따라 아나필락시스를 산소호흡치료, 기본 생명유지 심폐소생술처치나 진보적 심폐소생술 등으로 치료해야 한다.
- 예를 들면, 의사가 현장에 직접 와서 응급처치를 하는 방법이 그 상황에서 가장 적절하고 가능하면 우선 의사가 응급처치를 현장에서 시작하는 것이 가장 이상적이다.
- 또는 가장 안전하고 빠른 교통수단을 이용해 가장 가까운 동네 병원이나 큰 병원 응급실로 환자를 데리고 가든지, 또는 가장 빠르고 적절한 다른 방법으로 치료해야 한다.
- 아나필락시스의 중증도에 따라 치료를 다르게 할 수 있다.
- 심한 아나필락시스는 에피네프린, 코르티코스테로이드, 산소호흡, 혈압 상승제, 기관지 확장제·항히스타민제·전해질용액 주사·인공호흡·심폐 소생술 등으로 병원 응급실 치료를 하는 것이 기본이다.
- 경우에 따라, 기관내관 삽입으로 산소 호흡 치료를 한다.
약물 아나필락시스의 예방
- 아나필락시스를 유발시켰던 약물, 음식물, 또는 그 외 항원을 또다시 먹거나, 마시거나, 흡입하거나, 뿌리거나, 바르거나, 접촉하거나 주사로 맞지 말아야 한다.
- 거의 모든 종류의 약물로 인해 아나필락시스가 유발될 수 있는 가능성이 있다.
- 약물로 치료를 받을 때는 될 수 있는 한 의사의 처방이나 지시에 따라서 약물 선택를 해서 치료 받아야 한다.
- 특히, 아토피성 체질이 있는 소아 청소년 자녀들이 약물로 치료 받을 때는 약물로 아나필락시스가 유발될 가능성이 더 있을 수 있고, 또 약물 알레르기나 약물 부작용이 생길 가능성이 더 많다.
- 그런 사실을 항상 염두에 두고 약물 치료에 임해야한다.
- 아나필락시스가 유발됐을 때 응급 치료를 할 수 있는 에피펜, 아나키트, 또는 에피네프린 성분이 든 응급처치 주사약을 항상 준비하고 평소에도 지참해야 한다.
- 약물로 꼭 치료를 받아야 할 경우에는 될 수 있는 한 여러 종류의 약 성분이 섞여 있는 종합 약물제로 치료하지 말고 가능한 한 단 한 종류의 약물 성분이 든 단가 약물로 치료받는다.
- 과거에 어떤 약물이나 그 외 어떤 음식물 등으로 아나필락시스가 생겼을 때는 아나필락시스를 유발시켰던 약물의 이름이 쓰인 표식 목걸이나 표식 팔찌를 항상 걸고 다녀야 한다(사진 57, 58 참조).
- 과거에 아나필락시스를 유발시켰던 약물이나 그 물질을 절대로 또다시 쓰지 말아야 한다.
- 어떤 약물로 치료할 때, 목걸이 표식이나 팔찌 표식에 쓰여 있는 약물 이름과 같은 약물이나 같은 성분이 든 약물을 그 아이에게 절대로 또 주어서는 안 된다.
- 페니실린으로 아나필락시스가 유발됐던 사람들에게 페니실린이나 페니실린 성분이 든 다른 종류의약이나 페니실린의 화학적 구조와 비슷한 화학적 구조를 가진 페니실린 이외 약물에 의해서도 아나필락시스가 유발 될 수 있다.
- 어떤 종류의 항생제나 다른 종류의 약물로 치료할 때는 의사의 지시에 따라서 쓴다. 아토피 체질이 있는 아이들과 과거에 아나필락시스가 생겼던 아이들은 가능한 한 처방해 준 약물만 써야 한다.
- 과거에 어떤 약물이나 벌 알레르기 등으로 아나필락시스가 유발됐던 아이들은 에피네프린 주사약이나 에피펜 자가 주사기 약, 또는 아나키트 자가 주사기 약을 평소에 지참하고, 그 아이가 사는 집, 다니는 학교, 타고 다니는 가정용 승용차 등에 항상 보관했다가 아나필락시스가 유발될 때 환아 본인이나 주위 사람이 에피네프린 주사약으로 현장에서 아나필락시스를 응급 치료해야 한다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제21권 소아청소년 가정간호- 쇼크나 아나필락시스의 치료에 쓸 수 있는 에피네프린 주사약 참조.
- 기관지 천식·알레르기성 비염·아토피성 피부염 등 알레르기성 질환이 있는 병력이 있는 소아청소년 자녀들에게는 벌 알레르기, 약물 아나필락시스가 생길 가능성이 더 많다.
- 그런 소아청소년 자녀들에게는 다른 종류의 약물에도 알레르기가 생길 가능성이 많다.
- 어떤 종류의 약물로 치료 받을 때 극히 주의해야 한다.
Prevention of anaphylaxis caused by drugs
약물 아나필락시스(약물 과민증)의 예방
- Drug anaphylaxis is also called drug hypersensitivity. Anaphylaxis is one of the acute allergic diseases caused by an antigenic antibody reaction.
- If anaphylaxis is not treated promptly and appropriately, it can lead to death. Anaphylaxis is also referred to as hypersensitivity or irritability.
Causes of drug anaphylaxis
- When treated with corticosteroids such as penicillin and cortisone,
- insulin, vaccination vaccines, or any other drug, anaphylaxis can occur due to the drug.
- Drugs are taken orally, applied to the skin or mucous membranes, inhaled into the airways through the nasal passages, exhaled into the lower airways, eaten by mouth, received by vascular injection, received by intramuscular injection, or suppositories in the anus or vaginal cavity
- Drug anaphylaxis can be triggered when treated with drugs or other methods.
- Drug anaphylaxis usually develops within seconds or hours after treatment with drugs or after contact with drugs.
- Anaphylaxis can also be triggered by drug contact, it can also be triggered by eating foods such as peanuts, nuts, eggs, milk, shellfish, or shrimp, and it can also be triggered by bees or insect stings, bites, contact, or animal bites.
- Inhalation of house dust, house dust mites, animal dander, hair, saliva, and pollen from plants can also cause anaphylaxis.
- (Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Refer to Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing-Vol. 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents-Anaphylaxis, Vol. 15, Children and Adolescent Allergies and Immune Diseases)
Symptoms, signs of drug anaphylaxis
- Mast cells are normally scattered in the pituitary gland and various organs and tissues of the body.
- Histamine is usually in the form of granules within mast cells scattered in each part of the body, within mast cells of the pituitary gland, and within basophilic cells.
- Histamine is normally secreted out of the mast cell membrane by the process of mast cell degranulation within the mast cells ([Parents must also become at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing)-Vol. 15 Child and Adolescent Allergy and Immune Diseases-Mechanisms that cause allergies See picture).
- When an antigenic antibody reaction occurs, a large amount of histamine granules in mast cells are suddenly secreted outside the mast cells.
- Histamine isolation secreted in mast cells can have a complex action with biochemically active substances secreted from other cells in the body -IgE, cytokines, leukotriene, and the like.
- At this time, anaphylaxis may occur.
- Symptoms of anaphylaxis do not appear uniformly and vary.
- Symptoms and signs vary from time to time. Symptoms can be life-threatening, serious, and sometimes mildly itchy skin.
- When severe, the entire skin and mucous membranes may become red, swollen, and hives.
- Disorders of the digestive system may also occur, accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Respiratory system disorders with symptoms such as runny nose, cough, bronchial asthma, wheezing, cyanosis, and respiratory failure may occur.
- Your child’s blood pressure can drop suddenly, he can have severe breathing difficulties, and he can even die from shock.
Diagnosis of drug anaphylaxis
- It can be diagnosed by combining medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
- It is helpful to diagnose anaphylaxis if the patient himself or his parents’ siblings have an atopic constitution or a family history of allergic diseases.
- It is very helpful in diagnosing anaphylaxis if a drug (antigen) that can cause anaphylaxis was taken orally, applied to the body, received an injection, or aspirated into the nasal cavity or airways immediately before anaphylaxis was triggered.
- Anaphylaxis can be diagnosed relatively easily when there is contact with drugs, food, or anything else (antigen), or when there are several symptoms, signs described above. However, since the symptoms and signs of drug-induced anaphylaxis do not always appear uniformly and clearly,
- it is sometimes difficult to diagnose drug-induced anaphylaxis quickly and reliably.
- In rare cases, anaphylaxis can be triggered without medication, no unusual food intake, or no insect bites or stings.
- In addition, the symptoms and signs of some diseases may appear similar to those caused by anaphylaxis.
- So, the symptoms of drug-induced anaphylaxis may be similar to those of other diseases.
- At this time, different diseases and anaphylaxis should be differentially diagnosed.
Drug anaphylaxis treatment
- Anaphylaxis (Anaphylactic reactions)-see treatment

Photo 55. Photo of an Epi-Pen auto-injector injection drug-containing epinephrine that can be used to treat severe anaphylaxis reactions as an emergency. The main component of Epipe is epinephrine. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 56. If a bee allergy occurs, the patient himself or the person around him can receive emergency treatment with an Epi-Pen auto-injector. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 57. If you have had a severe allergic reaction due to some kind of drug or something, wear a bracelet with writing markings to inform others about the history of such a severe allergic reaction. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 58. He wears a necklace that says he had a severe drug allergy or an allergic reaction to something. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
- Treatment varies depending on the severity of anaphylaxis.
- If anaphylaxis is severely triggered, it can kill lives within seconds to minutes.
- In severe cases, it can be life-saving if treatment is initiated promptly and appropriately at the site.
- Sometimes, life can be saved only by starting treatment immediately in the field, without even having time to seek medical help.
- So, if anaphylaxis occurs in children and adolescents with a history of severe anaphylaxis in the past, your child should always bring an injection of epinephrine, an Anakit, or Epi-Pen so that you or others around you can begin emergency treatment immediately at the site. So, if anaphylaxis is triggered, emergency treatment should be started immediately with an epinephrine injection at the site.
- When epinephrine injections are not available, an emergency contact is made to a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or a regular pediatrician, and according to his instructions, emergency treatment is initiated at the site and promptly transferred to the nearest hospital or emergency room. (See [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Pediatric Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 21 Child and Adolescent Family Nursing-Refer to Epinephrine Injection, which can be used to treat shock or anaphylaxis) Depending on the severity and symptoms of anaphylaxis, anaphylaxis should be treated with oxygen resuscitation, basic life-sustaining cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or progressive cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- For example, the method of first aid by a doctor who comes directly to the site is most appropriate in the situation and, if possible, it is most ideal for the doctor to initiate first aid at the site.
- Or, take the patient to the nearest local hospital or the emergency room of a large hospital using the safest and fastest means of transportation, or another method that is the fastest and most appropriate for treatment.
- Treatment can be done differently depending on the severity of anaphylaxis. Severe anaphylaxis is basically treated in the hospital emergency room with epinephrine, corticosteroids, oxygen respiration, blood pressure boosters, bronchodilators, antihistamines, electrolyte solution injections, artificial respiration, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- In some cases, oxygen breathing therapy is performed with endotracheal tube insertion.
Prevention of drug anaphylaxis
- Drugs, foods, or other antigens that have caused anaphylaxis should not be eaten, drink, inhaled, sprayed, applied, contacted, or injected again.
- There is a possibility that anaphylaxis can be triggered by almost any type of drug. When receiving treatment with drugs, as much as possible, you should choose the drug and receive treatment according to the doctor’s prescription or instructions.
- In particular, when children and adolescents with atopic constitution are treated with drugs, there is a greater possibility of inducing anaphylaxis with drugs, and also more likely to cause drug allergies or drug side effects.
- With that in mind, your child should always be on medication. When anaphylaxis is triggered, first-aid injections containing EpiPen, Anakit, or epinephrine, which can be used for emergency treatment, should always be prepared and brought with you as usual.
- If your child must be treated with drugs, do not treat them with a comprehensive drug containing as many types of drug ingredients as possible, and receive treatment with a unit price drug containing only one type of drug component as much as possible.
- In the past, when anaphylaxis occurred due to a drug or other food, you should always wear a marker necklace or bracelet with the name of the drug that caused anaphylaxis (see photos 57 and 58).
- Drugs or substances that have triggered anaphylaxis in the past should never be used again.
- When treating with a drug, never give the child another drug with the same drug name or the same ingredient as the drug name on the necklace or bracelet marker.
- Anaphylaxis can also be induced by penicillin or other drugs containing penicillin, or drugs other than penicillin, which have a chemical structure similar to that of penicillin. When treated with certain types of antibiotics or other types of drugs, use as directed by your doctor.
- Children with atopic constitution and children with anaphylaxis in the past should use only prescribed medications as much as possible.
- Children whose anaphylaxis was triggered by certain drugs or bee allergies in the past usually bring epinephrine injections, EpiPen auto-injection drugs, or Anakit self-injection drugs, and the child’s home, school, or car Always keep it, then anaphylaxis
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Red book 29th edition 2012
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 19th Edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
소아과학 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”