안면신경 마비 Bell’s palsy
안면신경 마비의 개요
-
12쌍의 뇌신경들이 뇌에서 기시되어 두개골에 뚫려 있는 뇌신경 구멍을 통과 해 두개골 밖으로 나온 후 해당 신체 부위에 분포된다.
-
12쌍 뇌신경 중 7번째 뇌신경이 안면신경이다.
-
이 안면신경을 7번째 뇌신경이라고 한다.
-
두피의 전면의 일부, 이마, 눈꺼풀, 안면표정 근육, 뺨, 턱, 혀 등에 분포된다.
-
7 뇌신경은 뇌 속에서 기시되어(그림 1-6 또는 1-12 참조) 두개골 밖으로 나온 후 얼굴의 좌우 양쪽에 하나씩 분포된다.
-
좌우 안면신경 중 좌 안면신경이나 또는 우 안면신경의 전체나 일부가 선천성으로 마비되어 선천성 안면신경마비가 생길 수 있고,
-
후천성으로 마비되어 후천성 안면신경마비가 생길 수 있다(안면신경마비 참조).
-
후천성 안면신경마비는 라임 병, 중이염, 대상포진, 외상 등으로 생길 수 있다.
-
원인을 확실히 알 수 없고, 뇌에도 어떤 이상이 없이 생긴 후천성 안면신경 마비를 벨 마비(Bell’s palsy) 또는 그냥 안면신경마비라고 한다.
안면신경 마비의 증상 징후
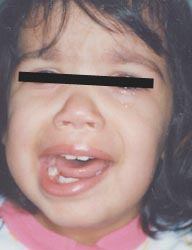
사진1-217. 3세 유아의 좌측 안면신경의 말초부분이 라임 병으로 마비됐다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
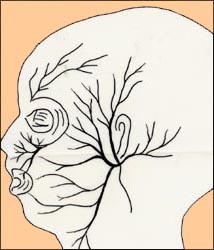
그림1-216. 좌측 안면신경의 분포도
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
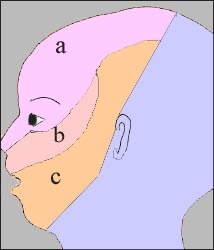
그림1-218. 제 7 뇌신경(안면신경)의 분포도
a,b,c는 안면 신경 분지 분포도.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다.-소아가정간호백과]-제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환 참조.
-
안면신경 마비의 원인과 얼굴의 각 부위에 분포된 안면신경 분지들 중 어느 분지가, 어떤 원인으로 어느 정도로 마비되었는지에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
양쪽 안면신경은 뇌교(그림 1-99 참고)의 기저 속에서 기시되어 두개골에 있는 안면신경 구멍을 통과하여 두개강 밖으로 나온 후, 6개의 안면신경 가지(분지)로 나누어져 두피, 이마, 눈꺼풀, 안면표정 근육, 뺨, 턱으로 분포된다(그림 1-12, 1-216, 1-218).
-
6개의 안면신경 분지 중 한 분지만 마비될 수 있다.
-
마비된 안면신경 분지에 의해 지배받는 얼굴 부분에 있는 안면 표정 근육과 감각이 마비될 수 있고, 거기에 안면 신경 마비 현상이 생길 수 있고, 거기에 있는 근육의 힘이 약해질 수 있다.
-
안면신경이 마비된 쪽의 귀 속 아플 수 있다.
-
마비된 안면신경이 있는 쪽의 얼굴 근육이 마비가 되지 않은 쪽의 안면신경이 있는 얼굴 쪽으로 당겨진다.
-
안면신경이 마비된 쪽 비순 주름살이 뚜렷하게 나타나지 않을 수 있다.
-
그와 반대로 마비되어 있지 않은 쪽 비순 주름살은 마비된 쪽 비순에 비해 더 뚜렷하게 깊게 나타날 수 있다(사진 1-217, 1-219 참조).
-
안면신경 마비의 정도에 따라, 안면신경이 마비된 쪽 눈을 꼭 감을 수 없고, 그 눈에서 눈물이 잘 나오지도 않고 각막건조 현상이 생길 수 있다.
-
혀 앞 부위의 감각이 상실되고 침이 잘 분비되지 않을 수 있다.
안면신경 마비의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해 안면신경 마비를 진단한다.
안면신경 마비의 치료
-
안면신경 마비의 원인, 양쪽 안면 신경 중 어느 쪽 안면신경이 마비됐느냐에 따라, 한쪽 안면신경의 전부가 마비됐느냐, 또는 한쪽 안면신경의 여러 분지 중 어느 분지가 마비되었는지에 따라 치료가 다르다.
-
안면신경 마비는 안과 전문의, 이비인후과 전문의, 소아청소년과 전문의, 소아 신경내과 전문의, 그 외 다른 특수과 전문의가 한 치료 팀의 멤버가 되어서 서로 협력해서 치료해야 할 때가 많다.
-
눈을 정상적으로 감지 못할 때는 안면신경 마비가 생긴 쪽 눈을 안대로 가려 안구 손상이 생기지 않도록 예방 치료 한다.
-
눈물이 정상적으로 분비되지 않아 각막, 결막 등이 건조될 수 있다.
-
인공눈물로 치료하기도 한다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병–라임 병 참조)
-
벨 마비는 코르티코스테로이드제로 치료하기도 한다. 안면신경 마비가 라임 병으로 생겼을 때는 항생제로 치료한다.
-
안면신경 마비를 적절히 잘 치료해도 약 5%는 완치 되지 않는다고 한다.
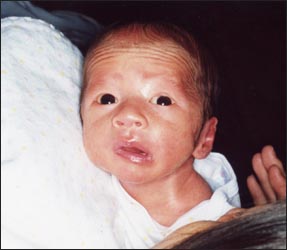
사진1-219. 갓 태어난 신생아에게 생긴 왼 쪽 제 7 뇌신경 마비(안면신경 마비).
쌍태아 임신 중 자궁 내 한 쌍태아가 다른 쌍태로부터 눌려 생긴 선천성 안면신경 마비(사진 1-219). 그냥 관찰치료를 한 결과 생후 3개월 내 자연 회복이 됐다.(사진 00참조)
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD.,FAAP
|
다음은“4개월된 남자아이 이마에 주름이 잡혀요”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강 상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 4개월 된 남자아이 이마에 주름이 잡혀요
Q.
- 만 4개월 된 남아입니다. 동네 소아청소년과에서 예방접종을 할 때 애가 많이 울었거든요. 입술 모양을 보시고는 7번 신경 마비인 것 같다고 하셨어요. 오른쪽 입술이 쳐집니다. 특이한 것은 위쪽으로 쳐다볼 때 이마에 3줄 주름이 잡힙니다. 선천적으로 근육이 안 생긴 건가요? 분만 중 손상인가요? 후자의 경우는 수주 내지 4개월 정도면 돌아온다고 하던데… 몇 분께 여쭤보니..이마에 주름이 잡히는 것은 안면 신경마비는 아니라고…선천적으로 근육이 안 생겨서 그렇다고 하던데.. 선생님이 생각하시기에 원인은요? 치료방법은 없나요? 이런 아이가 제법 있나요? 이마에 주름은 영원히 안 없어지나요? 너무 걱정됩니다. 그러고 보니 태어날 때도 입모양이 이상해요.
A.
- 안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다.
- 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 많은 정보가 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 답변을 드립니다.
- 그간 고명한 의사 선생님들의 진찰 진단을 받으시고 고견을 들으셔서 많이 아시고 계신 선생님께 제가 인터넷으로 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있을까 두렵습니다.
- 이마의 주름살 문제에 관해 답변을 드리려면 진찰이 꼭 필요하다는 것을 말씀드리고 싶습니다.
- 이마에만 주름살이 그런 식으로 생긴 예는 아직까지 한 번도 보지 못했습니다.
■ 이마에 주름살이 비정상적으로 생기면
- 다음과 같은 경우를 생각해 볼 수 있습니다.
- 정상적으로 이마에 주름살이 더 굵게 잘 생기는 아이들도 있고 성인들도 있습니다.
- 그 외 이마 근육이 선천성으로 존재하지 않으면 그렇게 주름살이 생길 수 있고,
- 이마근육은 정상이지만 이마 피부가 비정상적으로 더 크고 더 넓으면 주름살이 생길 수 있고,
- 이마 피하조직에 어떤 이상이 생겨 피하조직 발육부진이 있거나
- 이마 피하지방이 정상적으로 축적되지 안 해도 주름살이 크게 비정상적으로 생길 수 있습니다.
- 그 외로 “엘로스–단로스 증후군‘(표4-40참조) 등 어떤 유전병으로도 주름살이 크게 생길 수 있습니다.
- 그러나 무엇 때문에 아기 이마에게 주름살이 크게 생겨 있는지 확실히 답변을 드릴 수 없습니다.
■ 오른쪽 입술이 쳐지는 증상도 여러 가지 이유로 생길 수 있습니다.
- 가령 근무력증,
- 입술, 안면근육문제,
- 말초신경문제 등의 원인으로 생길 수 있습니다.
- 또한 그런 문제가 선천성으로 또는 후천성으로 생길 수 있습니다.
- 제 7 뇌신경(안면신경) 중 한쪽의 전체 또는 양쪽의 전체가 마비될 수 있고,
- 한쪽 제 7 뇌신경의 가지(분지) 중 일부의 분지,
- 또는 한쪽 제 7 뇌신경의 전부가 마비될 수 있고, 그 마비가 선천성, 특발성, 후천성으로 손상될 수도 있습니다. 이 때 얼굴의 양쪽, 한쪽, 또는 한쪽 얼굴의 일부분이 마비가 될 수 있습니다.
- 때로는 분만 중 어떤 원인으로 안면신경이 마비될 수 있고
- 출생 후 바이러스성 감염이나 박테리아성 감염병 등으로 제 7 뇌신경이 마비 될 수 있습니다.
- 그 외 제7뇌신경이 마비의 원인이 더 있습니다.
- 하신 질문에 정확한 답변을 드릴 수 없어 죄송스럽습니다. 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단을 또 받으시고 그 문제에 관해 상담하시고 가능하면 소아청소년과 전문의의 소개로 소아 신경내과 전문의의 도움을 받으시고 또 이비인후과 전문의와 안과 전문의의 진찰도 아울러 받으시는 것이 좋다고 생각합니다.
- 안면신경마비를 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다.이상원 드림
Facial nerve palsy (Bell’s palsy) 안면신경 마비
Overview of facial nerve palsy
• Twelve pairs of cranial nerves originate from the brain, pass through a cranial nerve hole in the skull, come out of the skull, and then distribute to the corresponding body part.
• Of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves, the 7th cranial nerve is the facial nerve.
• This facial nerve is called the 7th cranial nerve.
• Distributed in the front part of the scalp, forehead, eyelids, facial expression muscles, cheeks, chin, and tongue.
• 7 cranial nerves originate in the brain (see Figures 1-6 or 1-12), come out of the skull, and are distributed one by one on the left and right sides of the face.
• Among the left and right facial nerves, congenital facial nerve paralysis may occur due to congenital paralysis of the left or right facial nerve,
• Acquired paralysis may result in acquired facial nerve palsy (see Facial nerve palsy). • Acquired facial nerve palsy can be caused by Lyme disease, otitis media, shingles, or trauma.
• Acquired facial nerve palsy, which is caused by unknown causes and without any abnormalities in the brain, is called Bell’s palsy or just facial nerve palsy. Symptoms signs of facial nerve palsy

Photo 1-217. The peripheral part of the left facial nerve in a 3-year-old infant was paralyzed by Lyme disease. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-216. Distribution of the left facial nerve Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-218. Distribution of the 7th cranial nerve (facial nerve) a,b,c are facial nerve branch distribution maps. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• [Parents should also be anti-doctors.-Pediatric and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Refer to Volume 18, Children’s and Adolescent Otolaryngology Diseases.
• Symptoms differ depending on the cause of the facial nerve palsy, which branch of the facial nerve branches distributed in each part of the face, and to what degree the paralysis was caused. • Both facial nerves originate from the base of the pons (refer to Fig. 1-99), pass through the facial nerve hole in the skull and come out of the cranial cavity, and then divided into six facial nerve branches (branches), scalp, forehead, eyelids, and It is distributed in facial expression muscles, cheeks, and jaw (Fig. 1-12, 1-216, 1-218).
• Only one of the six facial nerve branches can be paralyzed.
• Facial expression muscles and sensations in the part of the face dominated by the paralyzed facial nerve branch may be paralyzed, and facial nerve palsy may develop there, and the muscles there may be weakened.
• Pain in the ear on the side where the facial nerve is paralyzed.
• The facial muscles on the side with the paralyzed facial nerve are pulled toward the face with the facial nerve on the non-paralyzed side.
• The nasolabial folds on the side where the facial nerve is paralyzed may not appear clearly.
• Conversely, wrinkles on the nasolabial folds on the non-paralyzed side may appear more pronounced and deeper than the nasolabial folds on the paralyzed side (see photos 1-217, 1-219).
• Depending on the degree of facial nerve paralysis, the eye on the side where the facial nerve is paralyzed cannot be closed tightly, tears may not come out easily from the eye, and corneal dryness may occur.
• Numbness in the front of the tongue may be lost and saliva may be difficult to secrete.
Diagnosis of facial nerve palsy
• Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, and examination findings to diagnose facial nerve palsy.
Treatment of facial nerve palsy
• Depending on the cause of the facial nerve palsy, which of both facial nerves is paralyzed, the treatment depends on whether all of one facial nerve is paralyzed, or which branch of one facial nerve is paralyzed.
• Facial nerve palsy often requires an ophthalmologist, an otorhinolaryngologist, a pediatrician, a pediatric neurologist, and other specialty specialists to become members of a treatment team and cooperatively treat them.
• When the eyes cannot be properly closed, preventive treatment is performed to prevent eye damage by covering the eye on the side where the facial nerve is paralyzed with an eye patch. • Because tears are not secreted normally, the cornea and conjunctiva may become dry. • Sometimes treated with artificial tears ([Parents should also be anti-doctors-Pediatric and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Vol. 7 Pediatric and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-Lime Disease)
• Bell’s palsy is sometimes treated with corticosteroids. When the facial nerve palsy is caused by Lyme disease, it is treated with antibiotics.
• Even if the facial nerve palsy is properly treated, about 5% of them are not cured.

Photo 1-219. Left 7th cranial nerve palsy (facial nerve palsy) in newborn infants. Congenital facial nerve paralysis caused by compression of one twin in the uterus from another twin during twin pregnancy (Pictures 1-219). As a result of just observational treatment, it recovered naturally within 3 months of life. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD.,FAAP
The following is an example of a question-and-answer on the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling on “The forehead of a 4 month old boy is wrinkled”.
Q&A.
A 4 month old boy has wrinkles on his forehead.
Q. • The boy is only 4 months old. The child cried a lot when vaccinating at the local pediatrics and adolescents department. When he looked at the shape of his lips, he said he thought it was a seventh nerve palsy. The right lip is sagging. The peculiar thing is that when looking upwards, there are three lines of wrinkles on the forehead. Are you born with no muscle? Is it impaired during delivery? In the case of the latter, it is said that it will come back in a few weeks to 4 months, but… I asked a few people… that wrinkles on the forehead are not facial nerve palsy… What is the cause? Is there any treatment method? Do you have any children like this? Wrinkles on the forehead never go away? I’m so worried. Come to think of it, the shape of my mouth is strange even when I am born.
A.
• Good morning. Thank you for asking.
• If you have a lot of information, such as your child’s age, gender, past and family history, medical examination findings, and clinical test results, we can give you a better answer. We will respond based on the information you provided.
• I am afraid that I will be able to give a better answer on the Internet to a teacher who knows a lot because I have been diagnosed with the medical examination by famous doctors and teachers. • I would like to tell you that a medical examination is essential to answering the wrinkles on the forehead.
• I haven’t seen any examples of wrinkles like that on the forehead only.
■ If wrinkles appear abnormally on the forehead
• Consider the following scenario.
• Some children and adults usually have thicker wrinkles on their foreheads. • If the other forehead muscles are not congenital, wrinkles may occur.
• Forehead muscles are normal, but if the forehead skin is abnormally larger and wider, wrinkles may appear,
• There is an abnormality in the subcutaneous tissue for the forehead, and the
• Even if the forehead subcutaneous fat does not accumulate normally, wrinkles may appear abnormally large.
• Other genetic diseases such as “Elos-Danross syndrome” (refer to Table 4-40) can cause large wrinkles.
• However, we are unable to answer for sure what is causing the large wrinkles on the baby’s forehead.
■ Symptoms of sagging on the right lip can also occur for a number of reasons. • For example, myasthenia gravis,
• lip and facial muscle problems,
• It can be caused by peripheral nerve problems.
• They can also be congenital or acquired.
• All of one or both of the seventh cranial nerves (facial nerves) may be paralyzed,
• a branch of some of the branches (branches) of one seventh cranial nerve,
• Alternatively, all of one of the seventh cranial nerves may be paralyzed, and the paralysis may be congenital, idiopathic, or acquired. At this time, both sides of the face, one side, or part of one face may become paralyzed.
• Sometimes the facial nerve can be paralyzed for some reason during delivery
• After birth, the 7th cranial nerve may be paralyzed due to viral infections or bacterial infections.
• There are other causes of paralysis of the 7th cranial nerve.
• We are sorry for not being able to provide an accurate answer to your question. I think it is good to have another examination at the Department of Pediatrics and adolescents, consult about the problem, and seek help from a pediatric neurologist by referral to a pediatrician, if possible, and also see an otolaryngologist and an ophthalmologist.
• Please refer to facial nerve palsy.
• If you have more questions, please visit again. Thank you, Lee Sang-won
출처와 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Handbook of Pediatric Neurology, Katherine B. Sims, MD
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”