심실 중격 결손 Ventricular septal defect(VSD)
please see 심실 중격 결손 Ventricular septal defect(VSD) above.
심실 중격 결손 Ventricular septal defect(VSD)
- 우심실과 좌심실을 나누는 두 심실사이에 있는 칸막이를 심실 중격이라고 한다.
- 태어날 때부터 심실 중격에 비정상적으로 구멍이 뚫려 있는 선천성 심장 기형을 심실 중격 결손이라고 한다.
-
선천성 심장혈관 질환을 비청색증 형 선천성 심장혈관 질환과 전신 청색증형 선천성 심장혈관 질환으로 분류하고
-
심장이나 혈관의 어느 부분에 선천성 심장혈관 기형이 있느냐에 따라 선천성 심장혈관 기형의 종류를 분류 할 수 있다고 전술했다.
-
심실 중격 결손의 크기에 따라
-
작은 심실 중격 결손,
-
중등도 심실 중격 결손,
-
큰 심실 중격 결손으로 3분 할 수 있다.
-
- 심실 중격 결손의 형태와 위치에 따라
-
막양부 심실 중격 결손,
-
근성부 심실 중격 결손,
-
-
대혈관 막 심실 중격 결손으로 심실 중격 결손을 분류하기도 한다.
-
그 원인은 아직 확실히 밝혀지지 않았다.
-
심실 중격 결손의 크기, 환아의 나이, 그 외 함께 있는 다른 종류의 선천성 심장혈관 질환의 공존 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
여기서는 아주 작은 심실 중격 결손, 중등도 심실 중격 결손, 상당히 큰 심실 중격 결손 등 세 가지로 나누어 설명한다.
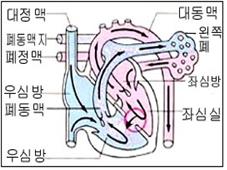
그림 23. 심실 중격 결손. 화살표(→)는 피 흐름방향
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
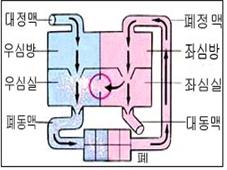
그림 22. 심실 중격 결손. 화살표(→)는 피 흐름방향
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
아주 작은 심실 중격 결손(경도 심실 중격 결손)
아주 작은 심실 중격 결손(경도 심실 중격 결손)의 증상 징후
-
아주 작은 심실 중격 결손이 있는 심장을 진찰할 때 비정상적이고 독특한 비정상 심잡음을 들을 수 있는 것 이외 다른 특이한 증상 징후는 없다.
-
아주 작은 심실 중격 결손이 있는 아이들은 영유아기 때나 학령기 또는 사춘기 때나 그 이후 성인기 동안 육체적 활동을 정상적으로 할 수 있고
-
일상생활을 하는 데도 아무런 지장이 없고
-
평균 수명도 이 기형이 없는 건강한 아이들이나 성인들과 별 차이가 없다.
아주 작은 심실 중격 결손(경도 심실 중격 결손)의 진단
-
증상 징후, 병력, 신체검사, 심장 진찰을 해서 심장혈관 기형이 있다고 의심이 가면 가슴 X-선 검사 등으로 진단한다.
-
심실 중격 결손이 있는 심장 진찰을 할 때 특이한 비정상 심잡음(Holosystolic murmur)이 나타낸다.
-
의사가 아주 작은 심실 중격 결손을 가진 아이의 심장을 진찰할 때 심실 중격 결손을 통해 좌심실 속 혈액이 우심실 속으로 흐를 때 나는 비정상적 심잡음을 청진기로 듣고서 진단을 하는 것이 보통이다.
-
가슴 X-선 사진 검사, 심전도 검사, 심 초음파 검사 등의 검사로 심실 중격 결손을 진단할 수 있다.
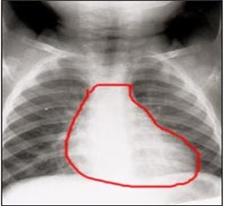
사진 24. 가슴 x-선 사진 검사는 선천성 심장 기형을 진단하는데 도움이 될 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
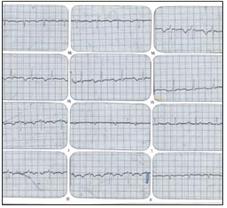
그림 25. 심전도 검사는 선천성 심장혈관 질환을 진단하는데 도움이 될 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
작은 심실 중격 결손에 있을 때의 가슴 X-선 사진 검사, 심전도 검사, 심 초음파 검사의 결과가 모두 정상일 수 있다.
아주 작은 심실 중격 결손(경도 심실 중격 결손)의 치료
-
선천성 심실 중격 구멍이 아주 작으면 심실 중격 결손이 자연적으로 막힐 수 도 있고 막히지 않고 일생동안 그대로 있을 수 있다.
-
막히지 않은 상태로 있어도 거의 증상 징후가 없기 때문에 수술치료나 약물 치료를 할 것이 없다.
-
그러나 심실 중격 결손을 가진 아이가 치아 뽑는 치료를 받을 때나, 신체의 어떤 장기에 있는 병을 수술로 치료받을 때는 선천성 심장 기형이 없는 아이들보다 전염성 심내막염에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다. 의사의 처방에 따라 페니실린이나 그 외 다른 적절한 항생제로 전염성 심내막염을 예방적 치료를 해야 한다.
-
때로는 이런 예방적 치료도 할 필요가 없다는 주장도 있다.
-
아주 작은 심실 중격 결손이 있고 아무 증상이 없어도 조기에 정확한 진단을 받아 전염성 심내막염 예방적 치료를 해 주는 것이 대단히 중요하다. 전염성 심장내막염 참조.
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) 심실 중격 결손
• The partition between the two ventricles that divides the right and left ventricles is called the ventricular septum.
• A congenital heart malformation that has an abnormally punctured ventricular septum from birth is called a ventricular septal defect.
• Congenital cardiovascular disease is classified into non-cyanosis type congenital cardiovascular disease and systemic cyanosis type congenital cardiovascular disease.
• It has been mentioned that the type of congenital cardiovascular anomaly can be classified according to which part of the heart or blood vessel has a congenital cardiovascular anomaly.
• Depending on the size of the ventricular septal defect
o small ventricular septal defect,
o Moderate ventricular septal defect,
o Large ventricular septal defect can be done in 3 minutes.
• Depending on the type and location of the ventricular septal defect o Membranous ventricular septal defect, o Muscular ventricular septal defect,
• Ventricular septal defects are sometimes classified as large vascular membrane ventricular septal defects.
• The cause is not yet clear.
• Symptoms differ depending on the size of the ventricular septal defect, the child’s age, and the presence or absence of other types of congenital cardiovascular disease.
• The explanation is divided into three categories: very small ventricular septal defects, moderate ventricular septal defects, and very large ventricular septal defects.

Figure 23. Ventricular septal defect. Arrow (→) is the direction of blood flow Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 22. Ventricular septal defect. Arrow (→) is the direction of blood flow Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Very small ventricular septal defect (mild ventricular septal defect)
Signs and symptoms of very small ventricular septal defects (mild ventricular septal defects)
• When examining a heart with a very small ventricular septal defect, there are no other specific signs of symptoms other than being able to hear an abnormal, peculiar abnormal heart murmur.
• Children with very small ventricular septal defects are capable of normal physical activity during infancy, school age, or puberty or later adulthood.
• There is no obstacle in doing everyday life
• Life expectancy is no different from healthy children or adults who do not have this anomaly.
Diagnosis of very small ventricular septal defects (mild ventricular septal defects)
• If you suspect that you have a cardiovascular malformation due to symptoms, medical history, physical examination, and cardiac examination, you should diagnose it with a chest X-ray.
• When examining a heart with a ventricular septal defect, a peculiar abnormal heart murmur (Holosystolic murmur) appears.
• When a doctor examines the heart of a child with a very small ventricular septal defect, it is common to diagnose abnormal heart murmurs with a stethoscope when blood from the left ventricle flows into the right ventricle through the ventricular septal defect.
• Ventricular septal defects can be diagnosed with tests such as chest X-ray examination, electrocardiogram, and echocardiography.

Picture 24. Chest x-ray examination can be helpful in diagnosing congenital heart anomalies. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 25. An electrocardiogram can be helpful in diagnosing congenital cardiovascular disease. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Results of chest x-ray, electrocardiogram, and echocardiography when in small ventricular septal defects may all be normal.
Treatment of very small ventricular septal defects (mild ventricular septal defects)
• If the congenital ventricular septal orifice is very small, the ventricular septal defect may be blocked spontaneously or may remain unblocked for life.
• Even if it is unblocked, there are few signs of symptoms, so there is no need for surgical treatment or medication.
• However, children with ventricular septal defects may be more prone to infectious endocarditis than children without congenital heart malformations when undergoing tooth extraction treatment or surgically treating diseases in certain organs of the body. Infectious endocarditis should be treated prophylactically with penicillin or other appropriate antibiotics as prescribed by a doctor.
• Sometimes it is argued that even this preventive treatment is not necessary.
• Even if you have a very small ventricular septal defect and no symptoms, it is very important to get an early and accurate diagnosis and provide preventive treatment for infectious endocarditis. See infectious endocarditis.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”