심방 중격 결손의 분류 Classification of atrial septal defect
심방 중격 결손의 분류 Classification of atrial septal defect
1. 난원공 개존 Patent foramen ovale
-
출생 전 태아의 심방 중격에 정상적으로 구멍이 하나 나 있는 데 그것을 난원공이라고 한다. 그 난원공은 출생 후 완전히 막히는 것이 일반적이다.
-
그러나 난원공이 출생 이후에도 완전히 막히지 않는 경우가 가끔 있다.
-
그것을 난원공 개존이라고 한다.
2. 2차공 심방 중격 결손 Ostium secundum defect
-
심방 중격의 중앙 부분에 심방 중격 결손 구멍이 하나 나 하나 이상 여러 개가 선천적으로 나 있을 수 있다. 그 기형을 심방 중격 2차공 심방 중격 결손이라고 한다.
-
결손의 크기는 여러 가지이다.
-
2차공(이차공) 심방 중격 결손이 있어도 대부분의 경우 별 증상이 없다.
-
크기와 증상에 따라 심장 카테터 치료나 심장 수술 치료를 하든지 2차공 심방 중격 결손이 적은 경우 관찰적 치료를 한다.
3. 심내막 융기 결손(심장막 완충재 결손) Endocardial cushion defect
-
심방 중격과 심실 중격이 융합하는 부위에 선천적으로 결손이 생기고 승모판 이상과 삼첨판 이상이 동시 생기는 선천성 심방 중격 결손이다.
-
이 심방 중격 결손증은 심한 선천성 심장 기형의 일종이다.
-
삼첨판 이상과 승모판 이상이 함께 생길 수 있다.
-
심내막 융기 결손에는 1차공 결손과 공동 심방 심실 판구 2 종류가 있다.
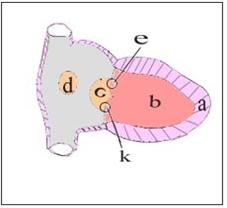
그림 29. 심장 횡면도와 심방 중격 결손증 그림
a-심실벽, b-심실, c-승모판, d-2차공 심방 중격 결손, e-1차공 심방 중격 결손, k-삼첨판
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
1). 1차공 결손(제 1공 결손) Ostium primum defect
2). 공동 심방 심실관 결손 Common atrioventricular canal defect
다음은“심방 중격 결손증”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다.
Q&A. 심방 중격 결손증에 관한 질문
Q.
- 안녕하세요?
- 전 생후 30일된 남아를 둔 초보 왕초보 엄마입니다. 임신 전 아이의 심장이 이상하다 해서 태어나자마자 아이 심장 초음파를 보았는데 심장에 구멍이 안 닫혔다 합니다. 그래서 6개월 후 다시 초음파를 봐서 결정을 내린다고 했는데 이런 경우 자연 완치가 가능한가요? 80%라고 하던데 나머지 20%로 때문에 조금 무섭습니다. 어린 아가가 수술을 하게 된다면 엄마 맘이 얼마나 아픈지…. 이런 경우 어떤지 속 시원히 좀 얘기해 주세요. 병원에서는 두고만 보자고 해서.. 그리고 예방 접종을 해야 하는데 심장과 아무 이상이 없는지.. 병원은 예방 접종비가 만만치 않아 보건소에 가서 하려고 하는데 심장 때문에.. 심장과 예방 접종은 아무 상관없는지 궁금하네요. 빠른 답변 바랍니다.
A.
- 안녕하세요. 좋은 질문을 해주셔 감사합니다. 아이의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등 자세한 정보가 있을수록 보다 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있지만 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변하겠습니다.
- 좌심실과 우심실 사이에 있는 벽을 심실중격이라 하고 좌심방과 우심방 사이에 있는 벽을 심방 중격이라 합니다.
- 선천적으로 이 두 중격 중 한 중격에 비정상적으로 구멍이 나 있는 경우가 있습니다.
- 우심방과 좌심방 사이에 있는 심방 중격에 결손 구멍이 나 있으면 심방 중격 결손이라 하고 우심실과 좌심실의 사이에 중격 결손으로 구멍이 나있으면 그 구멍을 심실 중격 결손이라고 합니다.
- 심방 중격에는 출생 전까지 정상적으로 계속 뚫려있는 난원공 개존도 있습니다.
- 드물게는 출생 후 몇 주까지 정상적으로 뚫려있는 난원공 개존도 있습니다.
- 태어나기 전에는 정상적으로 우심방 속 혈액이 우심실 속으로 흘러가기도 하고 난원공 공존을 통해 정상적으로 좌심방 속으로 흘러가게 됩니다. 이런 심장 내 혈액 흐름을 출생 전에는 정상적입니다.
- 심장이 정상인 경우는, 출생 이후에는 우심방 속의 전체 혈액이 우심실 속으로 흘러가는 것이 정상적입니다.
- 질문하신 거와 같이 심장의 어느 부위에 결손 구멍이 있는지 확실히 말씀하시지 않아서 확실한 답변을 드릴 수가 없습니다.
- 혹시 난원공이 열려있다는 말씀인지요?
- 또는 심실 중격에 구멍이 뚫려있다는 말씀인지 알 수 없습니다.
- 하여튼 아주 작은 심실중격 결손이나 생후 그대로 계속 열려 있는 난원공 개존은 대개 아무 치료 없이 자연히 막힐 수 있고, 또 아무 치료가 요하지 않은 때도 있습니다.
- 병명을 더 확실히 아시고 단골 소아청소년과 의사선생님께 다시 문의하시기 바랍니다.
- 심장에 생긴 기형에 관계없이 기본예방접종은 권장한 대로 해주시면 됩니다.
- 심실 중격 결손과 심방 중격 결손증을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
다음은“심방 중격 결손증”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다.
Q&A. 심방 중격 결손증에 관한 질문입니다.
Q.
- 답변을 구합니다
- 선생님 안녕하세요. 저희 아기 11월 3일이면 6개월입니다. 3개월 때 심장에 잡음이 들린다고 하여 병원에 갔더니 심방 중격 결손증(이차공 0.2cm)이라고 하더군요. 3개월 후에 다시 검사 해보자고 하더군요. 구멍이 작다고 하면서요. 이제 3개월이 지났습니다. 병원에 가려니 겁도 나고 해서 상담을 요청합니다. 질문 1) 꼭 3개월 후에 가보아야 하는지요. 만약 구멍이 있다고 해도 돌 전에는 수술도 하지 않는다고 하더라구요. 질문 2) 꼭 처음 검사 받은 곳에서 다시 검사 받지 않아도 되겠지요? 의사선생님이 너무 불친절 하셔서,,,,,, 질문 3) 아기가 자꾸 잘 때 뒤집어서 자려고 해요. 왜 자꾸 뒤집어서 자려고 하죠? 그리고 뒤집어서 자니깐 눈이 조금 부어서요. 건강하시구요. 답변 부탁드립니다.
- 안녕하세요. 좋은 질문을 해주셔서 감사합니다. 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등 자세한 정보가 더 많이 있을수록 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있지만 주신 정보를 토대로 답변을 드리겠습니다.
- 심방 중격 결손증에 대해서 심방 중격 결손증에 관한 정보를 읽어보시기 바랍니다.
- 아기의 경우에는 난원공 개존이나 작은 2차공 결손이 있는 것 같습니다.
Q.
꼭 3개월 후에 가보아야 하는지요.
만약 구멍이 있다고 해도 돌 전에는 수술도 하지 않는다고 하더라구요.
A.
아무 증상이 없으니 그 때까지 기다려 보시는 것도 좋을 것 같습니다.
Q. 꼭 처음 검사 받은 곳에서 다시 검사 받지 않아도 되겠지요? 의사선생님이 너무 불친절하셔서,,,,,,
A.
- 의사들에게도 개인적 문제나 가정적 문제 등이 생길 수 있습니다. 그로 인해 기분이 좋지 않은 날도 있을 수 있습니다. 잘 치료되지 않는 환자, 가정, 사회 문제 등으로 마음이 퍽 아프고 괴로운 때가 있습니다.
- 불행하게도 그런 문제로 인해 생긴 아픈 마음 때문에 환자들에게 무의식적으로 편안한 마음을 보이지 못해 환자들의 마음에 불편을 끼칠 수 있습니다. 히브크라테스는 “DO No Harm” 했지만>
- 환아 자녀를 가진 부모들 모두가 FAGS 증후군이 있는 것도 모르고 지나 갈 수 있습니다.
- 불편했던 점을 그 의사에게 편지로 말씀해보시고 용서해 주세요.
- 과거에 한 번이라도 진찰 진단 치료를 받았던 의사한테 또다시 추척 진찰 진단 치료를 받으러 가는 것이 여러모로 좋을 듯합니다.
- 왜냐하면 그 의사가 아기 자녀의 심장 문제에 관해서 더 많은 정보를 가지고 있고 그 의사는 전 번 진찰 진단의 결과와 다음 번 추적 진찰 진단의 결과를 서로 비교할 수 있기 때문에 자녀의 병을 치료 하는데 더 좋은 입장에 있을 수 있습니다.
- 필요하면 그 의사가 가장 좋은 소아심장과 전문의에게 진료 의뢰서를 써줄 수 있을 것입니다. 그 의사 선생님이 자녀의 심장문제를 계속 치료하는 게 더 좋지 않을까요.
- 그러나 아기자녀의 병을 아기 아빠와 단골 소아청소년과 의사와 아기 엄마가 상의해서 최후 결정을 내리시기 바랍니다.
Q.
- 아기가 자꾸 잘 때 뒤집어서 자려고 해요 왜 자꾸 뒤집어서 자려고 하죠? 그리고 뒤집어서 자니깐 눈이 조금 부어서요.
A.
- 어떤 신생아나 영아이든 등을 바닥에 대고 얼굴이 천장을 향해 자는 것을 소아청소년과에서 권장합니다.
- 생후4~ 6개월 이후 대부분의 영아들의 등을 바닥에 대고 재울수가 없습니다.
- 그래서 그렇게 등을 대고 재우기가 아주 어렵습니다.
- 그렇게 재우도록 노력해 보시지요. 뒤집어 자면 눈이 조금 붓는 현상은 정상입니다. 더러는 심장 이상이나 신장 이상 등으로 눈이 부을 수 있지만 그런 이유로 눈이 붓지 않는 것 같습니다.심방 중격 결손증을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 또 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주시기 바랍니다.
- 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Classification of atrial septal defect심방 중격 결손의 분류
Classification of atrial septal defect
1. Patent foramen ovale
• Before birth, the fetus normally has a hole in the atrial septum, which is called an oval hole. It is common for the oval hole to be completely blocked after birth.
• However, sometimes the ovarian cavity is not completely blocked after birth.
• It is called ovarian cavities.
2. Ostium secundum defect
• One or more than one atrial septal defect hole may be congenital in the central part of the atrial septum.
- The malformation is called atrial septal secondary hole atrial septal defect.
• The size of the defect varies.
• Secondary hole (secondary hole) Even with atrial septal defect, in most cases there are no symptoms.
• Depending on the size and symptoms, cardiac catheter treatment or cardiac surgery treatment, or observational treatment if the secondary cavity atrial septal defect is small.
3. Endocardial cushion defect
• It is a congenital atrial septal defect in which a defect occurs in the area where the atrial septum and the ventricular septum converge, and the mitral and tricuspid valve abnormalities occur at the same time.
• This atrial septal defect is a type of severe congenital heart malformation.
• Tricuspid and mitral valve abnormalities can occur together.
• There are two types of endocardial ridge defects: a primary cavity defect and a common atrial ventricular valve.
Figure 29. Illustration of transverse heart and atrial septal defect a-ventricular wall, b-ventricle, c-mitral valve, d-2 primary atrial septal defect, e-1 primary atrial septal defect, k-tricuspid valve Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
1). Ostium primum defect
• Atrial septal defects are common over the mitral and tricuspid valves, and abnormalities of the mitral and tricuspid valves are common.
• Primary cavity defect is a type of severe congenital heart malformation.
• Treated with heart surgery.
2). Common atrioventricular canal defect
• A type of severe atrial septal defect with atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, mitral valve defect, and tricuspid valve defect.
• It is more prevalent in children with Down syndrome and is often accompanied by other types of heart anomalies, such as stenosis of the pulmonary arteries.
• Treated with heart surgery.
The following is an example of questions and answers for online child and adolescent health counseling on “atrial septal defect”.
Q&A.
Questions about atrial septal defect
Q.
• Good morning?
• I am a novice mother with a boy who is 30 days old. The child’s heart was abnormal before pregnancy, so as soon as I was born, I saw the child’s echocardiogram, and the hole in her heart was not closed. She said that so she made a decision after 6 months and she looked at the ultrasound again, but is it possible for her to heal spontaneously in this case? They say 80%, but the remaining 20% is a bit scary. If a young baby has surgery, how painful her mother’s heart will be…. Please tell me about how it would be like this. The hospital told me to see you alone.. And I have to get vaccinations, but if there is anything wrong with the heart.. The hospital is going to go to the public health center because the vaccination fee is not too high. Please reply soon.
A.
• Good morning. Thank you for asking a good question. The more detailed information, such as the child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the better we can give you, but we will respond based on the information you provided.
• The wall between the left and right ventricles is called the ventricular septum, and the wall between the left and right atrium is called the atrial septum.
• There is a congenital abnormal hole in one of these two septa.
• If there is a defect hole in the atrial septum between the right and left atrium, it is called an atrial septal defect. If there is a hole between the right and left ventricle as a septal defect, the hole is called a ventricular septal defect.
• In the atrial septum, there are also openings of the ovary that remain open normally until birth.
• Rarely, there are open ovarian cavities that are normally open up to several weeks after birth.
• Before birth, blood in the right atrium normally flows into the right ventricle, and normally flows into the left atrium through the coexistence of the ovarian cavity. This blood flow in the heart is normal before birth.
• If the heart is normal, after birth, it is normal for all blood from the right atrium to flow into the right ventricle.
• As you asked, I couldn’t give you a definite answer because you weren’t sure which part of the heart there is a missing hole.
• Are you saying that the oval hole is open?
• Or, you don’t know if it’s a hole in the ventricular septum.
• Anyway, very small ventricular septal defects or ovarian openings that remain open after birth can usually block spontaneously without any treatment, and sometimes no treatment is required.
• Know the name of the disease more clearly, and ask your regular pediatrician again.
• Regardless of heart abnormalities, basic vaccination should be done as recommended.
• See Ventricular Septal Defects and Atrial Septal Defects.
• If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won.MD
The following is an example of questions and answers for online child and adolescent health counseling on “atrial septal defect”.
Q&A.
This is a question about atrial septal defect.
Q.
• seek answers
• Hello sir. My baby is 6 months on November 3rd. When I went to the hospital because I heard a murmur in my heart at 3 months, it was said that it was an atrial septal defect (secondary hole 0.2cm).
They told me to test again in 3 months. They say the hole is small. Now 3 months have passed. I was afraid to go to the hospital, so I asked for a consultation.
Question 1) Should I go there after 3 months? Even if there is a hole, they say that they don’t even have surgery before the stone.
Question 2) It is not necessary to have to be tested again at the place where it was first tested. The doctor is so unkind,,,,,,
Question 3)
When the baby keeps sleeping, I try to turn over and sleep. Why do you keep turning upside down to sleep? And since I sleep upside down, my eyes are a little swollen. You are healthy. please answer about my question.
• Good morning. Thanks for asking a good question. The more detailed information we have, such as the child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the better we can give you a better answer, but we will respond based on the information you provided.
• About Atrial Septal Defects Read information about atrial septal defects.
• In the case of a baby, it seems that there is an open ovarian cavity or a small secondary cavity defect.
Q.
Should I go there after 3 months? Even if there is a hole, they say that they don’t even have surgery before the stone.
A. There are no symptoms, so it would be nice to wait until then.
Q.
I don’t have to have to do it again at the place where it was first tested. The doctor is so unkind,,,,,,
A.
• Doctors can also have personal or family problems. There may be days when you feel bad because of that. There are times when the heart hurts and suffers from poorly treated patients, family, and social problems.
• Unfortunately, the soreness caused by such problems can cause unconsciousness of unconsciousness to the patients, causing discomfort to the patients’ minds. Hypocrates says “DO No Harm”
• All parents with children with children may pass by without knowing they have FAGS syndrome.
• Please write to the doctor about any discomfort and forgive it.
• In many ways, it would be nice to go back to the doctor who had received medical checkup treatment at least once in the past to receive follow-up diagnosis treatment.
• Because the doctor has more information about the baby’s heart problems and the doctor can compare the results of the previous and next follow-up diagnosis, he is in a better position to treat the child’s illness. Can be on
• If necessary, the doctor will be able to write a referral to the best pediatric cardiologist. Wouldn’t it be better for the doctor to continue treating his child’s heart problems?
• However, please consult with your baby’s father, your regular pediatrician, and your baby’s mother to make a final decision about your child’s illness.
Q.
• When my baby keeps sleeping, I try to sleep upside down. Why do I keep trying to sleep upside down? And since I sleep upside down, my eyes are a little swollen.
A.
• The Department of Pediatrics recommends that any newborn or infant sleep with their back on the floor and face to the ceiling.
• After 4-6 months of age, most infants cannot sleep on their backs.
• So it’s very difficult to sleep on your back like that.
• Try to sleep like that. When sleeping upside down, it is normal for the eyes to swell a little. In some cases, the eyes may be swollen due to an abnormality in the heart or kidneys, but for that reason, the eyes do not seem to be swollen, see Atrial Septal Defect.
• If you have any further questions, please contact us again.
• Thank you. Lee Sang-won dream
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
- Red book 29th edition 2012
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”