신생아 중이염 Otitis media in newborn infants(Neonatal otitis media)
신생아 중이염의 원인
-
병원체 감염이나 다른 원인으로 신생아 중이 강에 생긴 염증을 신생아 중이염이라고 한다.
-
신생아 중이염이 있으면 중이강 속이 곪고 고름이 잡힐 수 있다.
-
신생아의 중이염은 감기, 모세기관지염, 또는 폐렴 등의 상· 하기도 감염을 앓을 때 이차 박테리아 감염 등으로 생길 수 있다.
-
신생아 중이염의 주원인은 바이러스 감염이나 박테리아 감염이다.
-
신생아 중이염을 일으키는 박테리아의 종류는 신생아기 이후 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들의 중이염을 일으키는 박테리아의 종류와 다를 수 있다.
-
드물게 출생하기 전 태아가 중이염에 걸린 후 태어나기도 한다.
-
패혈증이나 폐렴 등을 앓을 때도 중이염이 합병증으로 생길 수 있다.
-
중이강 속에
- 대장균,
- 황색 포도상구균,
- B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균이나
- 비 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균,
- A군 용혈성 연쇄상구군 감염이나
- B군 용혈성 연쇄상구균 감염으로 신생아 중이염이 생길 수 있다.
신생아 중이염의 징상 징후
- 신생아 중이염의 증상징후는 다양하다.
- 주 증상징후는 다음과 같다.
- 감기를 앓을 때나 그 외 다른 바이러스성 상기도 염을 앓는 중 이차 세균 감염으로 급성 박테리아 중이염이 생길 때가 많다.
- 이렇게 생긴 중이염이 있을 때는 감기 등의 증상 징후와 급성 중이염의 증상 징후가 함께 나타날 수 있다.
- 감기 등 바이러스 상기도 감염병을 앓던 신생아에게 중이염이 생기면 감기를 앓는 동안 비교적 잘 먹었었던 모유나 인공영양을 잘 먹지 않고 보통 보다 더 보채고 미열내지 고열이 날 수 있고 잘 자지 않고 때로는 구토 및 설사를 할 수 있다.
- 감기 등으로 코가 막혀 호흡곤란이 생길 수 있다.
- 때로는 중이염에 걸려 있는지 모르고 얼마동안 지날 수 있다.
- 신생아에게 난 어떤 병으로 소아청소년과에 진료 받으러 갔을 때 중이염이 있는 것을 처음 진단받는 경우도 있다.
신생아 중이염의 치료
- 박테리아 감염이 신생아에게 생길 때 신생아들은 그 감염에 대한 저항력이 일반적으로 미약하고 신생아에게 감염된 박테리아는 비교적 짧은 시간 내 전신으로 퍼져 신체 여러 계통의 여러 기관이나 조직으로 감염될 수 있다.
- 중이염이 신생아에게 생길 때도 중이염을 일으킨 박테리아가 중이강 속 이 외 신체 다른 부위로 감염되어 박테리아 감염병을 신체 다른 부위에도 생길 수 있다.
- 이런 이유로 신생아에게 중이염이 있고 열나고 아픈 것 같으면 입원 치료받기도 한다.
- 특히 신생아가 중이염을 앓으면서 열이 나거나 잘 먹지 않고 보채면 입원 치료를 하는 것이 보통이다.
- 합병증이 없고 잘 먹고, 열도 나지 않고, 기분이 좋고 신생아가 전체적으로 건강한 것 같으면 의사의 처방에 따라 경구용 항생제로 중이염을 가정 치료해도 된다.
- 중이염이 완치될 때까지, 보통 소아청소년과 의사의 지시에 따라 중이염이 잘 치료되는지 확인하고 처방받은 약으로 적절한 기간 동안 치료한 후 중이염이 완치되었는지 꼭 추적 진료를 받고 재 진단받아야 한다.[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호백과]-제 18권 소아 이비인후과 질환 참조
Otitis media in newborn infants (Neonatal otitis media) 신생아 중이염
Causes of otitis media in newborns
• Inflammation of the middle ear cavity in newborns due to pathogen infection or other causes is called neonatal otitis media.
• If a newborn has otitis media, the middle ear cavity may become stuffy and collect pus.
• Otitis media in newborns can be caused by secondary bacterial infection when suffering from upper and lower respiratory tract infections such as colds, bronchiolitis, or pneumonia.
• The main cause of otitis media in newborns is viral or bacterial infection.
• The type of bacteria that causes otitis media in newborns may be different from the bacteria that cause otitis media in infants and school-age children after the neonatal period.
• Rarely, a fetus is born with otitis media before birth.
• Otitis media can occur as a complication even when you suffer from sepsis or pneumonia.
In the middle ear
o E. coli,
o Staphylococcus aureus,
o Haemophilus influenzae type B or
o Non-type B Haemophilus influenzae,
o Group A hemolytic streptococcal infection or
o Group B hemolytic streptococcal infection can cause otitis media in newborns.

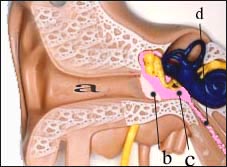
Picture 152. The part marked in purple has a strong middle ear Inflammation of the middle ear is called otitis media. a – external auditory canal, b – tympanic membrane, c – otitis media, d – ear canal Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Signs, Symptoms of otitis media in newborns
• Symptoms and signs of otitis media in newborns vary.
• The main symptoms are as follows.
• Acute bacterial otitis media often occurs as a result of a secondary bacterial infection during a cold or other viral upper respiratory tract infections.
• When you have this type of otitis media, symptoms such as a cold and symptoms of acute otitis media may appear together.
• If a newborn baby who has had a viral upper respiratory tract infection such as a cold develops otitis media, he or she does not eat breast milk or artificial nutrition that he ate relatively well during the cold, and he/she may feel more nauseous than usual, have a low or high fever, may not sleep well and sometimes have vomiting and diarrhea. can
• A cold or other stuffy nose can make breathing difficult.
• Sometimes you may have otitis media for some time without knowing it.
• Otitis media is sometimes diagnosed for the first time when a newborn baby goes to the pediatrician for some disease.
Treatment of neonatal otitis media
• When a bacterial infection occurs in newborns, the resistance to the infection is generally weak, and the bacteria infected with the newborn can spread throughout the body within a relatively short period of time and infect various organs and tissues of various body systems.
• Even when otitis media occurs in newborns, the bacteria that cause otitis media can infect other parts of the body other than the middle ear cavity, causing bacterial infections to occur in other parts of the body.
• For this reason, if a newborn baby has otitis media and has a fever and appears to be sick, hospitalization is sometimes required.
• In particular, if a newborn has otitis media and has a fever or does not eat well, hospitalization is usually required.
• Otitis media can be treated at home with oral antibiotics according to the doctor’s prescription if there are no complications, eat well, no fever, feel good and the newborn is generally healthy.
• Until the otitis media is cured, usually follow the instructions of the pediatrician to see if the otitis media is well treated, and after treatment with the prescribed medication for an appropriate period, follow up and re-diagnose whether the otitis media is completely cured. [Parents] You must also become a doctor – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing] – Refer to Volume 18 Pediatric Otolaryngology Diseases
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
- “The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”