신생아 생리적 황달, Physiological jaundice in the newborn infants
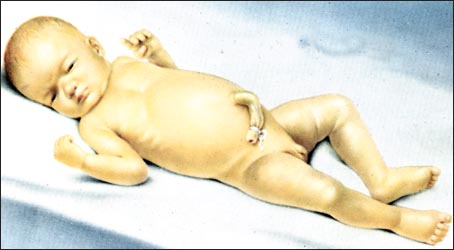
그림 2-363. 아주 심한 신생아 황달로 신생아의 피부가 노랗다.
출처- Clinical Educational Aid, Ross Labotories, Columbus, Ohio, USA 및 소아가정간호백과
- 거의 모든 신생아들이 아무 병이 없이생후 1주 내 황달에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 혈중 빌리루빈 농도가 증가돼서 생후 2~3일 경에 피부가 정상적으로 더 노랗게 변하기 시작하다가 생후 4~7일경 노란 피부색이 자연적으로 정상 피부색으로 돌아가는 것이 보통이다. 이런 황달을 생리적 황달이라고 한다.
- 모든 신생아들에게 생기는 생리적 황달로 피부색이 노란 것을 육안으로 볼 수 있을 정도로 심하게 생기지는 않는다.
- 그렇지만, 정도에 차이는 있지만, 거의 모든 신생아들에게 생리적 황달이 정상적으로 생기는 것이 보통이다.
- 생리적 황달의 정도가 더 심하면 신생아의 피부는 더 노랗게 된다.
- 생리적 황달의 정도가 경미할 때는 신생아의 피부는 거의 정상적이다.
- 신생아 생리적 황달이 생기는 원인은 확실히 모르나 다음과 같은 기전으로 생긴다고 믿고 있다.
- 출생하기 전 태아의 피 속에 있던 태아 적혈구의 수명은 약 80일 정도이고 출생 이후 신생아의 적혈구의 수명보다 훨씬 짧다.
- 출생 후 짧은 시간 내 태아적 적혈구가 정상적으로 쉽게 파괴되고 용혈 된다. 간장이 이런 용혈된 적혈구에서 생성되는 간접형 빌리루빈을 주로 처리한다. 그런데 갓 태어난 신생아의 간장의 기능도 정상적으로 미숙해서 정상적으로 파괴된 적혈구에서 나온 간접형 빌리루빈을 원활하게 처리할 수 없다. 또 갓 태어난 신생아가 생리적으로 탈수될 수 있다. 이상 설명한 여러 조건들과 그 외 다른 여러 조건들이 복합적으로 작용해서 생리적 황달이 신생아에게 생긴다고 한다.
- 정도에 차이는 있지만, 모든 신생아들에게 신생아 생리적 황달이 생긴다.
- 신생아 생리적 황달이 있을 때는 Rh혈액형 부적합 등으로 생긴 병적 황달과 같이 간접형 빌리루빈 혈중 농도가 많이 높아지지 않는 것이 보통이다. 생리적 황달이 심하지 않을 때는 눈에 띌 정도로 피부색이 노랗게 변화 되지 않지만 심할 때는 눈 흰자위와 피부색이 노랗게 된다.
- 신생아에게 생리적 황달도 생길 수 있고, 또는 병적 황달이 따로 생길 수 있다.
- 생리적 황달에다 병적 황달이 동시 생길 수 있다.
- 황달에 걸린 신생아들을 검진만 해서 그 황달이 생리적 황달인지 병적 황달인지 금방 쉽게 가려낼 수 없는 때도 많다.
- 이런저런 이유로 신생아에게 황달이 있으면 어떤 원인으로 생긴 황달인지 생리적으로 생긴 황달인지 꼭 알아봐야 한다.
- 즉 생리적으로 생긴 신생아 생리적 황달인지, 또는 어떤 병으로 생긴 병적 신생아 황달인지를 감별 진단해야 한다.
- 신생아 황달을 감별 진단하기 위해 여러 가지 피검사(혈액검사)를 해야 할 때도 있다. 때로는 반복해서 여러 번 피검사를 해야 할 때도 있다[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질병- 신생아 황달, 선천성 담도 폐쇄증으로 생기는 신생아 황달 참조).
사진 2-364. 황달의 정도, 원인 등을 알기위해 피 검사를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
신생아 황달(신생아 빌리루빈 과잉혈(증)/신생아 과빌리루빈 혈증)의 증상 징후
Neonatal jaundice (Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia)

그림 2-365. 심한 신생아 황달
출처: Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA
- 신생아에게 생기는 황달을 통틀어 신생아 황달(Neonatal jaundice)이라고도 하고 빌리루빈 과잉혈(증)
- 또는 신생아 과빌리루빈혈증(Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia)이라고도 한다. 빌리루빈의 혈중 농도가 정상 이상으로 많이 증가돼서 피부와 눈 흰자위 등이 노랗게 될 수 있다. 황달은 어떤 병의 징후이지 병명은 아니다.
- 정상 신생아들의 60%가 생후부터 7일 이내에 신생아 생리적 황달에 걸린다.
- 혈액 속 적혈구에서 나온 빌리루빈을 간에서 글루코닐 트랜스퍼라제 효소(UDPGA)에 의해 빌리루빈 글루쿠로니데이스(Bilirubin Glucuronides)가 되고 그 것이 바로 직접형 빌리루빈이다. 그 직접형 빌리루빈이 답즙의 성분 중 하나이다.
- 그러나 신생아 경우, 혈액 속 적혈구에서 나온 간접형 빌리루빈을 간에서 적절히 처리해서 직접형 빌리루빈으로 변화시켜 담관을 통해 십이지장으로 분비시키지 못해 혈 중 간접형 빌리루빈(Unconjugate bilirubin)이 때에 따라 증가된다.
- 이때 눈 흰자위가 노랗게 되고 피부가 노랗게 되고 신생아 생리적 황달이 생기게 된다.
- 미국 만삭 신생아들과 거의 만삭에 가까이 태어난 미숙아들 1,000명 중 5~40명이 빌리 광선요법치료를 받는다(출처; NEJM Febuary 2008 p.920).
- 신생아 황달의 원인, 증상 징후, 치료, 예후 등이 신생아기 이후 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들, 성인들에게 생기는 황달의 원인, 증상, 치료와 예후가 다른 점이 많다.
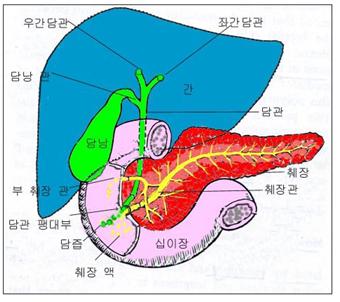
그림 2-366. 간, 췌장과 담즙분비 해부도.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
신생아 황달과 신생아기 이후의 아이들에게 생기는 황달로 다음과 같이 분류한다.
- 모유와 신생아 황달
- 용혈성 빈혈
- 미숙 신생아 황달 참조
- 생리적 신생아 황달
- Rh 부적합으로 인한 신생아 황달
- A B O 혈액형 부적합으로 생기는 신생아 황달
- 모유를 먹는 신생아에게 생기는 모유수유 신생아 황달
- 간염으로 인한 신생아 황달
- 선천성 담도 폐쇄로 생기는 신생아 황달
- G-6-인산 포도당 탈수소효소 결핍으로 인한 신생아 황달
- 그 외 다른 원인으로 인한 신생아 황달
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Physiological jaundice in the newborn infants 신생아 생리적 황달

Figure 2-363. Very severe neonatal jaundice and the newborn’s skin is yellow. Source-Clinical Educational Aid, Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio, USA and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia
• Almost all newborns can develop jaundice within the first week of life without any disease.
• It is common for the skin to turn yellow normally around 2-3 days after birth due to an increase in blood bilirubin concentration, and then return to normal skin color naturally around 4-7 days after birth.
This jaundice is called physiological jaundice.
• Physiological jaundice in all newborns is not so severe that the yellow skin color can be seen with the naked eye.
• However, with varying degrees of severity, it is common for almost all newborns to develop physiological jaundice.
• The more severe physiological jaundice, the more yellow the newborn’s skin.
• When the degree of physiological jaundice is mild, the newborn’s skin is almost normal.
• The cause of physiological jaundice in newborns is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by the following mechanisms.
• Fetal red blood cells in the fetal blood before birth have a lifespan of about 80 days, much shorter than that of newborns after birth.
• Fetal red blood cells are normally easily destroyed and hemolyzed within a short time after birth. The liver mainly processes the indirect bilirubin produced by these hemolytic red blood cells. However, the function of the liver of newborn newborns is also normally immature, so indirect bilirubin from normally destroyed red blood cells cannot be processed smoothly. In addition, newborn babies can be physiologically dehydrated. It is said that physiological jaundice occurs in newborns due to a combination of conditions described above and other conditions.
• Neonatal physiological jaundice develops in all newborns, although varying in severity.
• When neonatal physiological jaundice is present, it is common that the blood level of indirect bilirubin is not very high, such as morbid jaundice caused by Rh blood type incompatibility. When physiological jaundice is not severe, the skin color does not change noticeably to yellow, but the whites of the eyes and skin color become yellow when it is severe.
• Physiological jaundice may occur in newborns, or pathological jaundice may develop separately.
• Both physiological jaundice and morbid jaundice can occur at the same time.
• There are many times when newborns with jaundice can not be easily screened for physiological or pathological jaundice.
• If a newborn has jaundice for one or the other reasons, it is important to find out what causes jaundice or physiological jaundice.
• In other words, whether it is physiological jaundice in newborns or pathological jaundice in newborns caused by any disease, a differential diagnosis should be made.
• There are times when you need to do several blood tests (blood tests) to differentially diagnose neonatal jaundice. Sometimes it is necessary to perform blood tests several times repeatedly [Parents must also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing]-Volume 6 Newborn growth and development and disease-Newborn jaundice and newborn jaundice caused by congenital biliary atresia)

Photo 2-364. Blood tests are done to determine the degree and cause of jaundice. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Signs, symptoms of neonatal jaundice (hyperbilirubin in newborns/hyperbilirubinemia in newborns) Neonatal jaundice (Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia) Figure 2-365. Severe neonatal jaundice Source: Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA
• Neonatal jaundice is also known as neonatal jaundice in newborns. Excessive blood in bilirubin (symptoms).
• Also known as neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.
The blood levels of bilirubin increase more than normal, and the skin and whites of the eyes may turn yellow. Jaundice is a sign of a disease, not a disease name.
• 60% of normal newborns develop neonatal physiological jaundice within 7 days of birth.
• Bilirubin from red blood cells in the blood is converted into bilirubin glucuronides in the liver by the gluconyl transferase enzyme (UDPGA), which is the direct bilirubin. The direct form of bilirubin is one of the ingredients of bile.
• In newborns, however, indirect bilirubin from red blood cells in the blood is properly processed by the liver to convert it into direct bilirubin, which is not secreted to the duodenum through the bile duct, and thus the amount of indirect bilirubin in the blood is sometimes increased.
• At this time, the whites of the eyes become yellow, the skin becomes yellow, and physiological jaundice of the newborn occurs.
• Five to 40 of 1,000 full-term newborns and nearly full-term infants in the United States receive Billy phototherapy (source; NEJM Febuary 2008 p.920).
• The causes, symptoms, treatment, and prognosis of neonatal jaundice are different in the causes, symptoms, treatment and prognosis of jaundice in infants, school-age children, adolescent children, and adults after the neonatal period.

Figure 2-366. Liver, pancreas and bile secretion anatomy diagram. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Neonatal jaundice and jaundice occurring in children after the neonatal period are classified as follows.
1. Breast milk and neonatal jaundice
2. Hemolytic anemia
3. See jaundice in immature neonates
4. Physiological neonatal jaundice
5. Neonatal jaundice due to Rh incompatibility
6. A B O Neonatal jaundice caused by blood type incompatibility
7. Breastfeeding newborn jaundice in breastfed newborns
8. Newborn jaundice due to hepatitis
9. Neonatal jaundice due to congenital biliary obstruction
10. Neonatal jaundice due to G-6-phosphate glucose dehydrogenase deficiency
11. Neonatal jaundice due to other causes
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
“Parents should also be at least the half -doctors”-the content is not a substitute for information and treatment obtained from your doctor.
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”