신생아 두혈종 Cephalohematoma of newborn infants(cephalohematomas in newborn infants/neonatal cephalohematomas)
- 신생아의 두개골 (두골)의 바깥 표면과 그 두개골 바깥 표면을 둘러싸고 있는 두개골 골막 안쪽 면 사이에 있는 공간에 피가 괸 것을 신생아 두혈종이라고 한다.(그림 7~9 참조)
- 두개골은 8개의 두개골 뼈 조각으로 구성되어 있다. 즉 한 개의 전두개골, 후두개골, 접형골, 사골과 2개의 두정골, 2개의 측두개골 총 8개의 두개골 조각뼈로 구성된다.
- 두혈종은 여러 개의 두개골 조각뼈들 중 한 개의 두개골 뼈 조각 부분에 국한되어 생긴다.
- 신생아 두혈종은 머리의 한쪽에 하나 생길 수 있고 머리의 양쪽에 각각 하나씩 두 개가 동시 생길 수 있다.
- 신생아 두혈종이 생긴 머리 부분이 큰 혹이 난 것처럼 부어오를 수 있다. 신생아 두혈종의 크기는 여러 가지다.
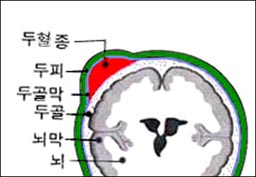
그림 8. 두개골의 바깥 표면과 두개골의 골막의 사이에 괸 피를 신생아 두혈종이라고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
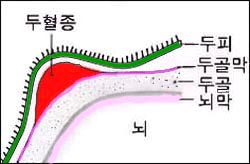
그림 9. 두개골의 맨 바깥 표면과 두개골 골막의 사이에 괸 피를 신생아 두혈종이라고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
신생아 두혈종의 원인
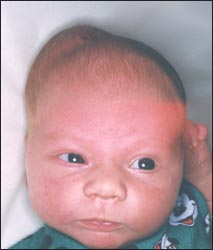
사진 10. 우측 머리에 생긴 신생아 두혈종.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
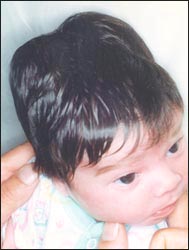
사진 11. 양측 머리에 생긴 신생아 두혈종.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 분만 중 산도에 가장 먼저 나온 태아의 머리의 일부가 산도에 눌릴 때 두개골의 맨 바깥 표면과 그 부분의 두개골을 둘러싸고 있는 두개골 골막(두개골막) 사이에 있는 작은 혈관이 파열되고 그 사이에 피가 괴어 신생아 두혈종이 생긴다.
- 자연분만, 난산, 또는 겸자 분만으로 태어난 신생아에게도 두혈종이 간혹 생길 수 있다.
- 분만 중 태아의 머리가 산도의 압력으로 심하게 압박되지 않아도 신생아 두혈종이 생길 수 있다.
- 피를 쉽게 흘릴 수 있는 전신 출혈성 질환이 있는 아기에게 두혈종이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 아주 작은 미숙 신생아로 태어날 때 아기의 머리가 산도에 심하게 압박되지 않아도 갓 태어난 미숙아의 머리에 두혈종이 생길 수 있다.
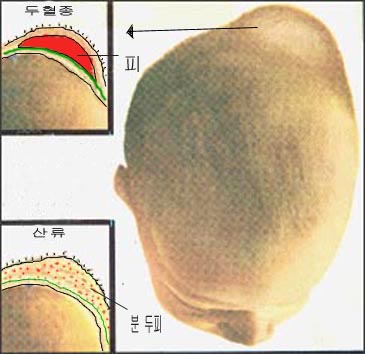
그림 7.신생아의 산류와 두혈종의 감별진단.
아기의 머리가 분만 중 산도에 눌려 갓 태어난 신생아의 두피에 피가 맺혀 생긴 산류와 두개골과 두개골 골막사이에 난 피로 생긴 두혈종
출처: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA와 소아가정간호백과
신생아 두혈종의 증상 징후
- 신생아 두혈종은 출생 후 24시간 이내 나타날 수 있으나, 생후 2~3일 경 더 현저하게 나타난다.
- 신생아 두혈종은 머리의 가장 윗부분, 즉 오른쪽 두정골 부위나 왼쪽 두정골 부위, 또는 양쪽의 두정골 부위에 나타 날 수 있다.
- 피가 조금 괴어 있는 신생아 두혈종은 밤알 크기만 하고 피가 많이 괴어 있는 신생아 두혈종은 달걀 크기만 하다.
- 신생아 두혈종의 바로 위에 있는 두피는 정상 두피의 색깔과 같은 것이 보통이다. 신생아 두혈종을 손으로 살살 만지면 말랑말랑한 촉감이 있지만 아프지는 않다.
- 신생아 두혈종이 상당히 크면 갓 태어난 신생아의 전체 혈 양 중 상당한 양이 신생아 두혈종 속으로 출혈될 수 있고 그로 인해 신생아에게는 출혈성 빈혈이 생길 수 있다. 신생아 두혈종 속에 괸 혈액 속의 적혈구가 파괴되면서 빌리루빈이 비정상적으로 다량 생성될 수 있다.
- 빌리루빈이 혈액 속으로 흡수되면 신생아에게 황달이 생길 수 있다.
- 신생아 두혈종의 25% 정도는 경미한 두개골 골절을 동반할 수 있다.
- 신생아 두혈종과 함께 생긴 경미한 두개골 골절은 대개 선상 두개골 골절이다.
- 두개골 골절도 아무런 치료 없이 저절로 낫는 것이 보통이다.

사진12.신생아 두혈종이 양쪽 두정골 부분에 생겨있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
신생아 두혈종의 진단
- 병력 증상 징후 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 두부 X선 사진 검사로 확진할 수 있다.
신생아 두혈종의 치료
- 국소 도포용 크림이나 연고를 발라 치료 할 필요가 없다.
- 신생아 두혈종은 생후 6주에서 3개월 정도 지나면 저절로 없어진다.
- 드물게 신생아 두혈종 속에 괸 피가 석회화될 수 있다.
- 그러다가 거기에 혹 같이 단단하고 작은 석회화된 살덩어리가 얼마 동안 만져질 수 있다. 이것도 몇 개월이 지나면 자연히 없어진다.
- 신생아 두혈종 속에 괸 피를 주사바늘로 뽑거나 수술칼로 째고 뺄 필요도 없다.
Cephalohematomas in newborn infants/neonatal cephalohematomas 신생아 두혈종
• Blood in the space between the outer surface of the newborn’s skull (head bone) and the inner surface of the periosteum of the skull that surrounds the outer surface of the skull is called neonatal cephalohematoma (see Figures 7-9).
• The skull is made up of eight cranial bone fragments. In other words, it is composed of a total of eight cranial fragments: one frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid, two parietal, and two temporal bones.
• Cephalohematoma is confined to one of the skeletal bones of the skull.
• Neonatal cephalohematomas can develop on one side of the head and two on each side of the head at the same time.
• The head of the neonatal cephalohematoma may swell as if it were a large lump. Neonatal cephalohematomas vary in size.

Figure 8. The blood that bleeds between the outer surface of the skull and the periosteum of the skull is called a neonatal cephalohematoma. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 9. The blood that bleeds between the outermost surface of the skull and the periosteum of the skull is called a neonatal cephalohematoma. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Causes of neonatal cephalohematoma

Photo 10. Newborn cephalohematoma on the right head. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 11. Neonatal cephalohematoma on both heads. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• When part of the head of the fetus, which first appeared in the birth canal during delivery, is pressed against the birth canal, a small blood vessel between the outermost surface of the skull and the cranial periosteum surrounding the skull (cranial periosteum) ruptures and blood bleeds between Neonatal cephalohematoma develops.
• Newborns born with spontaneous delivery, difficult labor, or forceps delivery can occasionally develop cephalohematomas.
• Neonatal cephalohematomas can develop even if the fetus’s head is not severely compressed by the pressure of the birth canal during delivery.
• Babies with systemic bleeding disorders that can bleed more easily are more likely to develop cephalohematomas.
• When born as a very small, premature infant, cephalohematomas can develop on the head of a newborn premature infant, even if the baby’s head is not heavily pressed against the birth canal.

Fig. 7. Differential diagnosis of parity and cephalohematomas in newborns. Cephalohematoma caused by blood formation on the scalp of a newborn baby due to the baby’s head being pressed against the birth canal during delivery, and blood between the skull and the periosteum of the skull. Source: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA and Pediatric Family Nursing Encyclopedia.
Symptoms signs of neonatal cephalohematoma
• Neonatal cephalohematoma can appear within 24 hours after birth, but it is more pronounced around 2 to 3 days after birth.
• Neonatal cephalohematomas can appear in the uppermost part of the head, ie in the right or left parietal area, or in both parietal areas.
• Newborn cephalohematomas with a little blood clot are the size of a chestnut, while newborn cephalohematomas with a lot of blood are the size of an egg.
• The scalp directly above the neonatal cephalohematoma is usually the same color as the normal scalp. If you gently touch a newborn baby’s head hematoma with your hand, it has a soft touch, but it doesn’t hurt.
• If the neonatal cephalohematoma is very large, a significant amount of the newborn’s total blood volume can bleed into the neonatal cephalohematoma, which can lead to hemorrhagic anemia in the newborn. The destruction of red blood cells in the blood of the neonatal cephalohematoma can cause abnormally large amounts of bilirubin to be produced.
• When bilirubin is absorbed into the blood, it can cause jaundice in newborns
• About 25% of neonatal cephalohematomas can be accompanied by minor skull fractures.
• Minor skull fractures with neonatal cephalohematomas are usually linear skull fractures. • Skull fractures usually heal on their own without any treatment.

Picture 12: Newborn cephalohematomas appear on both parietal bones. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of neonatal cephalohematoma
• If the disease is suspected by taking the medical history, symptoms, signs, examination findings, etc., it can be confirmed by a head x-ray examination.
Treatment of neonatal cephalohematoma
• There is no need to apply topical creams or ointments for treatment.
• Neonatal cephalohematomas disappear on their own after 6 weeks to 3 months. • Rarely, calcification of the blood in the neonatal cephalohematoma can occur.
• Then there may be some hard, small calcified flesh like bumps that can be touched for some time. This also disappears naturally after a few months.
• There is no need to pluck the blood from the neonatal cephalohematoma with a needle or slit with a surgical knife.
출처와 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Handbook of Pediatric Neurology, Katherine B. Sims, MD
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”