신생아 감염성 설사(신생아 전염성 설사) Infectious diarrhea in newborn infants

사진 166. 설사.
대변의 형태가 없고 소화되지 않은 음식물이 나오고 물갈이 짙은 변을 설사라고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 164. 감염병 위장염으로 생긴 혈변.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
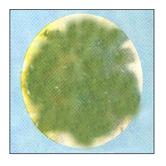
사진 165. 감염병 위장염으로 생긴 푸른 설사 변.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
신생아 감염성 설사(신생아 감염성 설사)의 개요
-
만삭으로 태어난 건강한 신생아들의 대부분은 거의 물과 비슷하게 또는 질게 물똥을 정상적으로 눈다.
-
이런 신생아들의 대변을 설사라고 하지는 않는다.
-
신생아들은 박테리아 감염이나 바이러스 감염 등에 대항할 수 있는 저항력이 원래 미약하다.
-
그래서 신생아기 이후 영유아들이나 그 이후 학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들, 또는 성인들에게는 잘 감염되지 않는 세균(박테리아)나 바이러스 등에 잘 감염되어 신생아들에게 심한 감염병 위장염이 생길 수 있다.
-
신생아에게 박테리아 감염이나 바이러스 감염에 의해서 위장염이 생기면 짧은 시간 내에 설사를 심하게 할 수 있고 또 심하게 탈수될 수 있다.
-
신생아가 우유 단백질 알레르기로 인해서도 설사를 할 수 있다.
-
위장염을 일으킨 박테리아나 바이러스는 일반적으로 감염성이 강력해서 같은 신생아실에 있는 다른 신생아들에게도 쉽게 감염될 수 있다.
-
특히 대장균 위장염을 일으킨 병원성 대장균은 감염성이 강력해서 때로는 같은 신생아실에 입원한 다른 신생아들이 동시 감염성 대장균 위장염에 걸리고 그로 인해서 설사를 할 수 있다[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료–설사 참조, 제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환–대장균 설사
-
특히 대장균, 살모넬라균, 파라티프스균, 이질균과, 황색 포도상구균 등의 병원체는 박테리아 신생아 설사의 주원인이 된다.
-
바이러스 상·하기도 감염병을 일으켰던 같은 바이러스로 인해 신생아 위장염이 생길 수 있고 각종 장 바이러스 감염으로 인해서도 신생아 위장염이 생겨 그로 인해 신생아가 설사를 하기도 한다.
신생아 감염성 설사(신생아 감염성 설사)의 증상 징후
-
신생아 위장염을 일으킨 원인과 정도에 따라 설사와 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
여기서 대장균 위장염으로 생긴 신생아 설사에 대해 주로 설명한다.
-
신생아에게 대장균 위장염이 생기면 잘 먹던 모유나 인공영양을 통 먹지 않는다.
-
초기엔 어딘가가 아픈 것같이 보이고 보채면서 미열 내지 고열이 난다.
-
위장에 가스가 많이 차서 배가 팽만해지고 묽고 푸른 설사 변을 하루에 여러 번 볼 수 있고 때로는 설사 변에 점액과 피가 섞여 있다.
-
심할 때는 불과 몇 시간 내에 심하게 탈수될 수 있고 탈수가 되면 비정상적으로 잠만 계속 자고, 힘이 없어서 전신이 축 늘어질 수 있다.
-
이 병이 곧 적절히 치료되지 않으면 심히 탈수가 되고 쇼크에 빠지고 사망할 수 있다.
신생아 감염성 설사(신생아 감염성 설사)의 진단
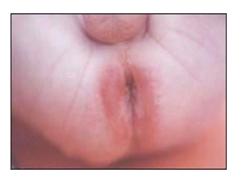
사진 167.신생아 설사로 인한 항문 주위염.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 168. 특히 감염성 설사를 예방하기 위해 손을 자주 씻어야 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 피, 소변, 설사 변, 척수액 등을 채취하여 그 피검 물로 세균배양검사 등을 해 설사의 원인균을 찾아 진단한다.
신생아 감염성 설사(신생아 전염성 설사)의 치료
-
적절히 속히 치료해 주지 않으면 사망할 수 있다.
-
이 병이 의심될 때는 즉시 병원 집중 치료를 받아야 한다.
-
병원 대장균은 주위에 있는 다른 신생아들에게도 쉽게 감염될 수 있다.
-
이 병을 일으킨 병원성 대장균이 다른 신생아들에게 감염되지 않게 이 병을 앓는 신생아를 다른 신생아들로부터 즉시 격리시켜야 한다.
-
포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 탈수를 예방 치료하고 적절한 항생제로 치료한다.
-
이 균이 신생아에게 어디서 감염되었는지 조사한다.
-
병원성 대장균은 비위생적이고 밀집한 신생아실에 있는 신생아나 불결한 집에서 양육 받는 신생아에게 더 잘 감염된다.
-
이런 이유로 특히 신생아를 양호 할 때는 신생아를 돌보기 전, 및 도중에 손을 항시 깨끗이 씻어 이 병을 예방해야 한다.
Infectious diarrhea in newborn infants 신생아 감염성 설사(신생아 전염성 설사)

Picture 166. Diarrhea. A stool that has no form of stool, undigested food comes out, and watery stool is called diarrhea. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 164. Bloody stool resulting from infectious gastroenteritis Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 165. Blue diarrhea caused by infectious gastroenteritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Overview of neonatal infectious diarrhea (neonatal infectious diarrhea)
• The majority of healthy newborns born full-term will normally gaze on water almost like or hardly. • These newborn stool is not called diarrhea.
• Newborns are inherently poorly resistant to bacterial or viral infections.
• So, infants and toddlers after newborn periods, school-age children, adolescents, or adults are susceptible to infection with bacteria (bacteria) or viruses that are not well-infected, resulting in severe infectious gastroenteritis in newborns.
• Gastroenteritis caused by a bacterial or viral infection in a newborn can cause severe diarrhea within a short period of time and can lead to severe dehydration.
• Newborns may have diarrhea due to milk protein allergy.
• The bacteria or viruses that cause gastroenteritis are generally highly infectious and can easily infect other newborns in the same neonatal room. • In particular, the pathogenic E. coli, which caused E. coli gastroenteritis, is highly infectious, so sometimes other newborns admitted to the same neonatal room may develop concurrent infectious E. coli gastroenteritis and diarrhea. Refer to Vol. 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents-Diarrhea, Vol. 9 Children and Adolescent Digestive Diseases-E.coli Diarrhea
• In particular, pathogens such as E. coli, Salmonella, Paratyphoscopy, Shigella and Staphylococcus aureus are the main causes of bacterial diarrhea.
• Newborn gastroenteritis may occur due to the same virus that caused the upper and lower respiratory tract infectious diseases, and newborn gastroenteritis may occur due to various intestinal viral infections, resulting in diarrhea in newborns.
Symptoms signs of infectious diarrhea in newborns (infectious diarrhea in newborns)
• Diarrhea and symptom signs differ depending on the cause and severity of newborn gastroenteritis.
• Here, we mainly describe neonatal diarrhea caused by E. coli gastroenteritis.
• If a newborn baby develops E. coli gastroenteritis, do not eat whole breast milk or artificial nutrition, which was well eaten.
• In the beginning, it looks like something is sick, and you have a mild or high fever while looking at it. • The stomach is full of gas, and the stomach is full, and you can see watery, blue diarrhea several times a day, sometimes with mucus and blood in the stool.
• In severe cases, you may become severely dehydrated within a few hours. If you are dehydrated, you may continue to sleep abnormally, and your whole body may be drooping due to lack of strength.
• If the disease is not treated properly soon, it can be severely dehydrated, shock, and die.
Diagnosis of infectious diarrhea in newborns (infectious diarrhea in newborns)

Picture 167. Peranalitis due to diarrhea in newborns. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 168. Wash your hands frequently, especially to prevent infectious diarrhea. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• If this disease is suspected by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, symptoms, and examination findings, blood, urine, diarrhea, spinal fluid, etc. are collected, and bacterial culture tests are conducted with the specimen to find and diagnose the causative agent of diarrhea.
Treatment of infectious diarrhea in newborns (infectious diarrhea in newborns)
• If not treated properly and promptly, it can lead to death.
• If you suspect this disease, you should seek immediate hospital intensive care.
• Escherichia coli can easily infect other newborn babies in the vicinity.
• Newborns with this disease should be immediately isolated from other newborns so that the pathogenic E. coli that caused the disease does not infect other newborns.
• Intravenous injection of glucose electrolyte solution prevents and treats dehydration and treats with appropriate antibiotics.
• Investigate where the fungus was infected in newborns.
• Pathogenic E. coli is more susceptible to newborns in unsanitary and dense neonatal rooms, or to newborns who are kept in dirty homes.
• For this reason, you should always wash your hands thoroughly before and during care of the newborn, especially when the newborn is in good condition to prevent this disease.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권. 신생아의 성장 발육 양육 질환
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 20th edition
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”